Abstract
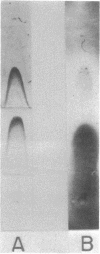
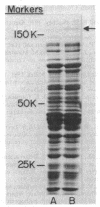
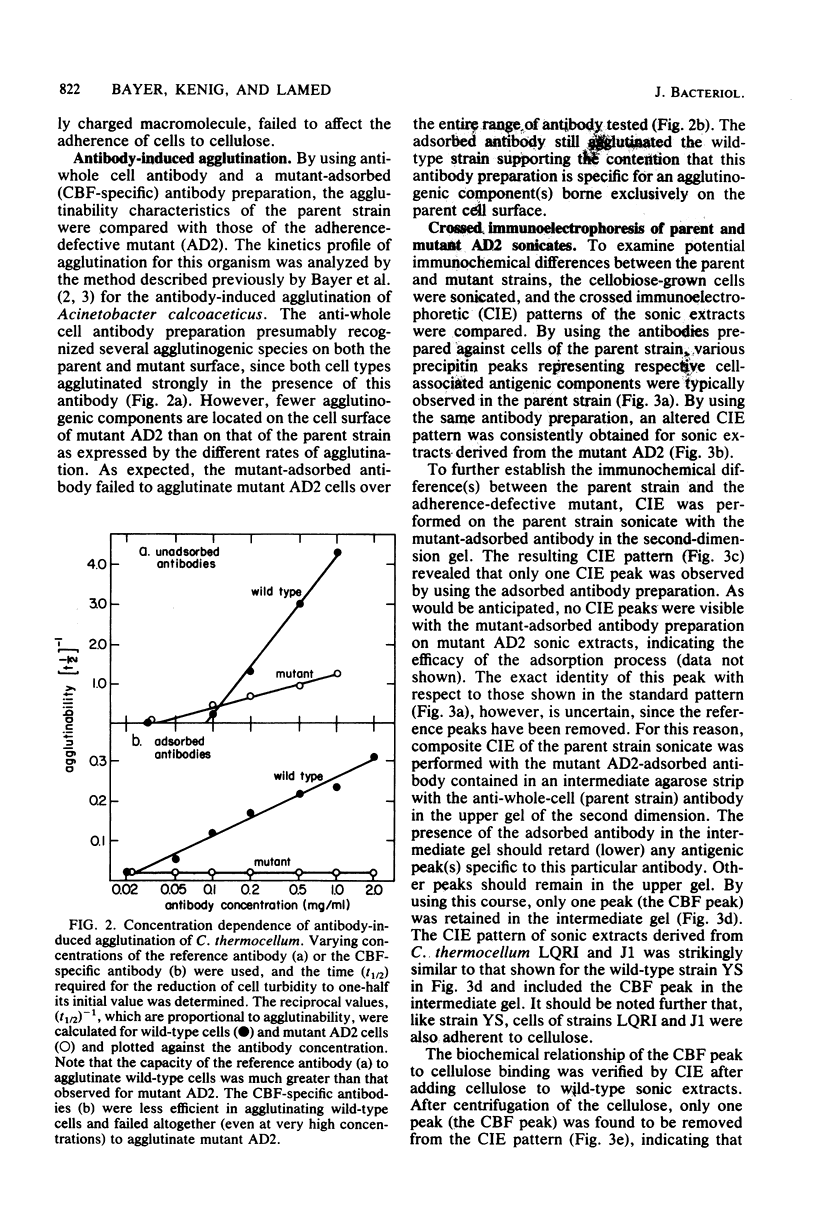
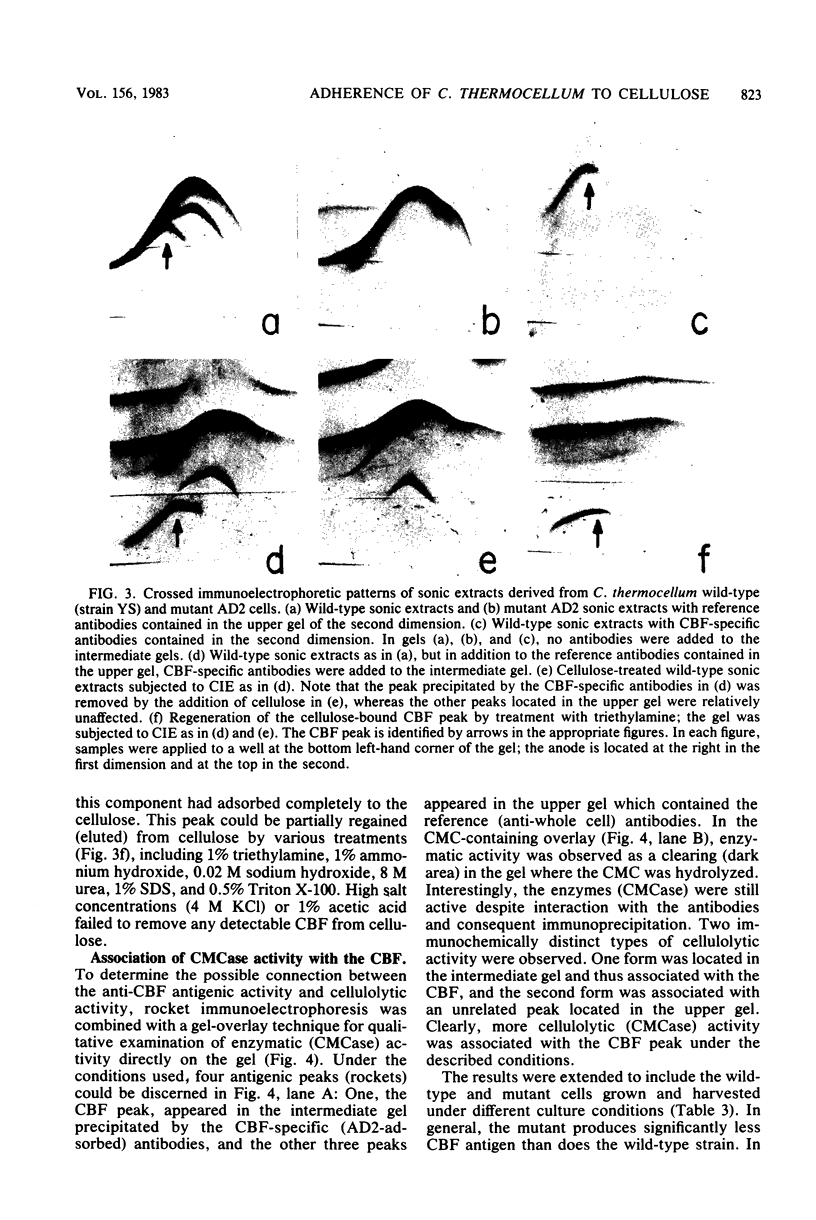
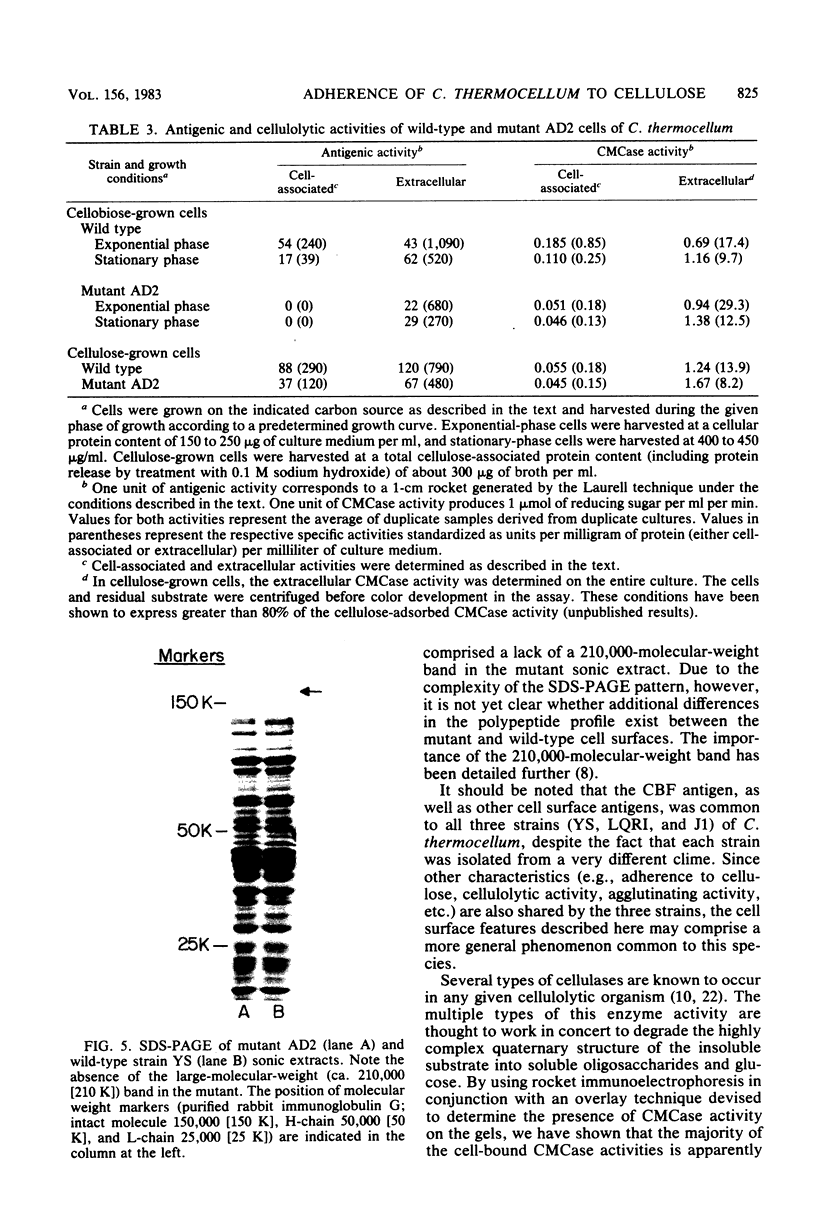
The adherence of Clostridium thermocellum, a cellulolytic, thermophilic anaerobe, to its insoluble substrate (cellulose) was studied. The adherence phenomenon was determined to be selective for cellulose. The observed adherence was not significantly affected by various parameters, including salts, pH, temperature, detergents, or soluble sugars. A spontaneous adherence-defective mutant strain (AD2) was isolated from the wild-type strain YS. Antibodies were prepared against the bacterial cell surface and rendered specific to the cellulose-binding factor (CBF) by adsorption to mutant AD2 cells. By using these CBF-specific antibodies, crossed immunoelectrophoresis of cell extracts revealed a single discrete precipitation peak in the parent strain which was absent in the mutant. This difference was accompanied by an alteration in the polypeptide profile whereby sonicates of strain YS contained a 210,000-molecular-weight band which was missing in strain AD2. The CBF antigen could be removed from cell extracts by adsorption to cellulose. A combined gel-overlay--immunoelectrophoretic technique demonstrated that the cellulose-binding properties of the CBF were accompanied by carboxymethylcellulase activity. During the exponential phase of growth, a large part of the CBF antigen and related carboxymethylcellulase activity was associated with the cells of wild-type strain YS. However, the amounts decreased in stationary-phase cells. Cellobiose-grown mutant AD2 cells lacked the cell-associated CBF, but the latter was detected in the extracellular fluid. Increased levels of CBF were observed when cells were grown on cellulose. In addition, mutant AD2 regained cell-associated CBF together with the property of cellulose adherence. The presence of the CBF antigen and related adherence characteristics appeared to be a phenomenon common to other naturally occurring strains of this species.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Rosenberg E., Gutnick D. The isolation of cell surface mutants of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):295–300. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Skutelsky E., Goldman S., Rosenberg E., Gutnick D. L. Immunochemical identification of the major cell surface agglutinogen of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-92. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):1109–1119. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. Cellulase location in Cellvibrio fulvus. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):51–57. doi: 10.1139/m75-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sakajoh M., Halliwell G., Madia A., Demain A. L. Saccharification of Complex Cellulosic Substrates by the Cellulase System from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1125-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Setter E., Bayer E. A. Characterization of a cellulose-binding, cellulase-containing complex in Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.828-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Zeikus J. G. Ethanol production by thermophilic bacteria: relationship between fermentation product yields of and catabolic enzyme activities in Clostridium thermocellum and Thermoanaerobium brockii. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):569–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.569-578.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBEE R. H. The anaerobic thermophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):51–63. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.51-63.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Weimer T. K., Zeikus J. G. Cellulolytic and physiological properties of Clostridium thermocellum. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00429622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of Extracellular Cellulase Activities of Clostridium thermocellum LQRI and Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):231–240. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.231-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Purification and characterization of an endoglucanase (1,4-beta-D-glucan glucanohydrolase) from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):341–350. doi: 10.1042/bj1990341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitersen N., Medeiros J., Mandels M. Adsorption of Trichoderma cellulase on cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1977 Jul;19(7):1091–1094. doi: 10.1002/bit.260190710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petre J., Longin R., Millet J. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-1,4-glucanase from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochimie. 1981 Jul;63(7):629–639. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines O., Bayer E. A., Gutnick D. L. Localization of emulsan-like polymers associated with the cell surface of acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):893–905. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.893-905.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., SIU R. G. H., LEVINSON H. S. The biological degradation of soluble cellulose derivatives and its relationship to the mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):485–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.485-497.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Bayer E. A., Delarea J., Rosenberg E. Role of Thin Fimbriae in Adherence and Growth of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 on Hexadecane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):929–937. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.929-937.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Eshdat Y., Silverblatt F. J., Ofek I. Bacterial adherence to cell surface sugars. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:119–141. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.289-297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]