Abstract
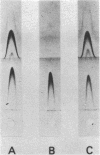
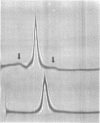
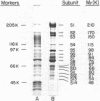
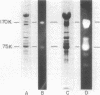
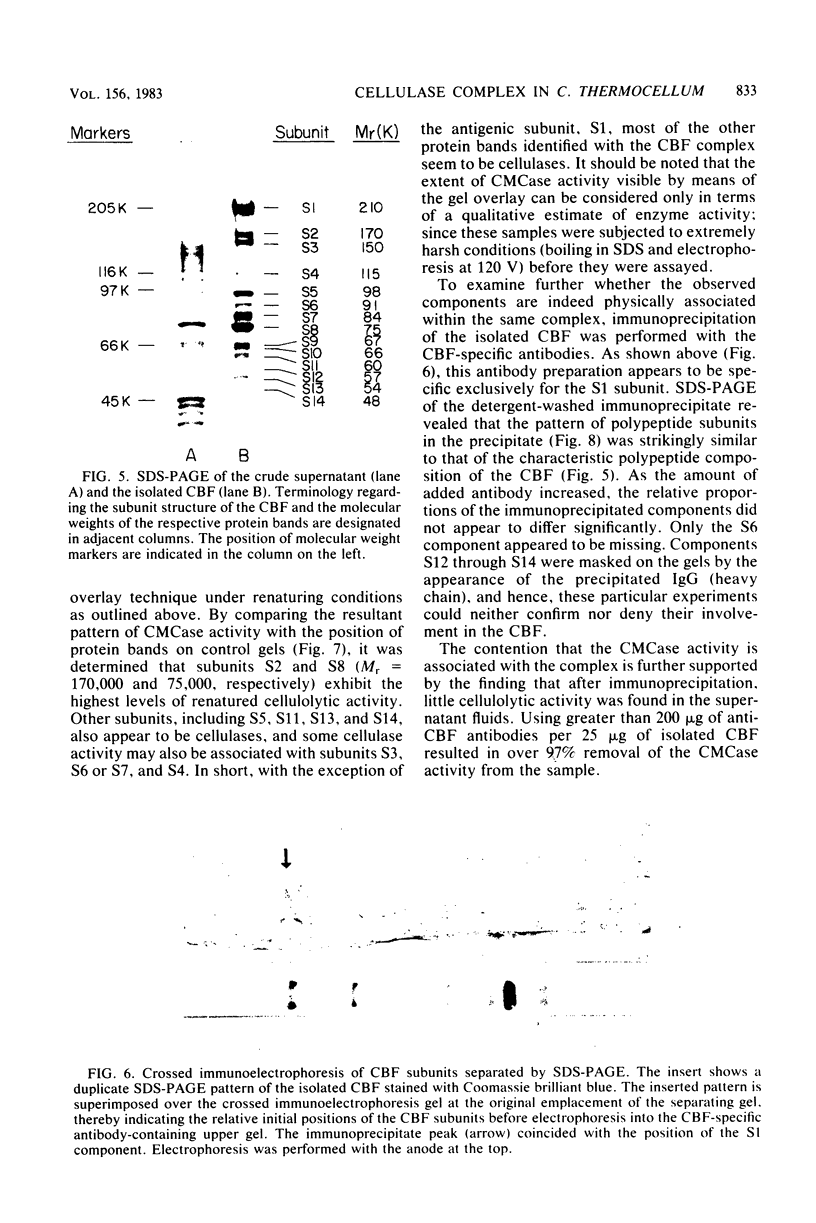
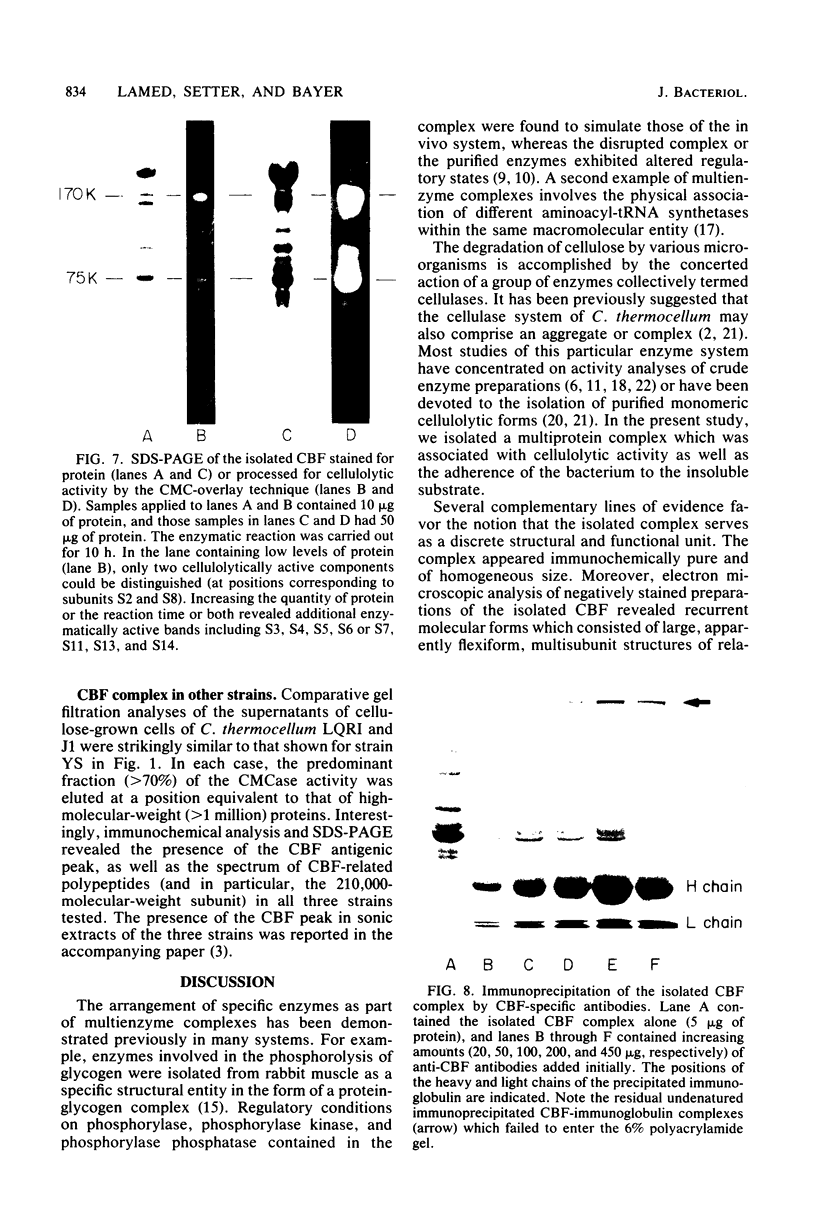
The isolation and biochemical characterization of the extracellular form of a cellulose-binding factor (CBF) from Clostridium thermocellum is described. The CBF was isolated from the culture supernatant by a two-step procedure which included affinity chromatography on cellulose and gel filtration on Sepharose 4B. The isolated CBF was homogeneous as determined by immunoelectrophoresis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, gel filtration, and analytical ultracentrifugation analysis. The CBF was found to form a complex which exhibited a molecular weight estimated at 2.1 million. Electron microscopic analysis of negatively stained preparations of the isolated CBF revealed a particulate, multisubunit entity of complicated quaternary structure. The molecule appeared to be about 18 nm in size. Although urea failed to break the complex into its component parts, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate resolved the CBF complex into 14 polypeptide bands. Immunoprecipitation experiments confirmed that these polypeptides indeed formed part of the same complex. Interestingly, by using the whole-cell immunization procedure described in the accompanying article (Bayer et al., J. Bacteriol., 156:818-827, 1983) only one CBF subunit (Mr = 210,000) was found to be antigenically active. By using a gel-overlay assay technique, at least eight of the remaining CBF-associated polypeptide components were shown to exhibit cellulolytic activity. The results are consistent with the contention that the CBF comprises a discrete, multisubunit complex or group of closely related complexes which exhibit separate antigenic and multiple cellulase activities in addition to the property of cellulose binding.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Jurivich D., Goodenough U. W. Localization of cellular antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):281–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Kenig R., Lamed R. Adherence of Clostridium thermocellum to cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):818–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.818-827.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse C. A., Papermaster D. S. Membrane protein analysis by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Science. 1975 Aug 8;189(4201):469–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1154021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawthorne J. M. Extracellular carbohydrase complex from rumen contents. Ann Rech Vet. 1979;10(2-3):249–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haschke R. H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Meyer F., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. 3. Regulation of phosphorylase phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6657–6663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Meyer F., Haschke R. H., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. II. Activation by calcium. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6649–6656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sakajoh M., Halliwell G., Madia A., Demain A. L. Saccharification of Complex Cellulosic Substrates by the Cellulase System from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1125-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. A., Springhorn S. S. Renaturation of enzymes after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7467–7473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Haschke R. H., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. I. Isolation and characterization of the protein-glycogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6642–6648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirande M., Gache Y., Le Corre D., Waller J. P. Seven mammalian aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases co-purified as high molecular weight entities are associated within the same complex. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):733–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Weimer T. K., Zeikus J. G. Cellulolytic and physiological properties of Clostridium thermocellum. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00429622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of Extracellular Cellulase Activities of Clostridium thermocellum LQRI and Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):231–240. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.231-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Purification and characterization of an endoglucanase (1,4-beta-D-glucan glucanohydrolase) from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):341–350. doi: 10.1042/bj1990341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petre J., Longin R., Millet J. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-1,4-glucanase from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochimie. 1981 Jul;63(7):629–639. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu I., Hungate R. E. The extracellular cellulases of Ruminococcus albus. Ann Rech Vet. 1979;10(2-3):251–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]