Abstract
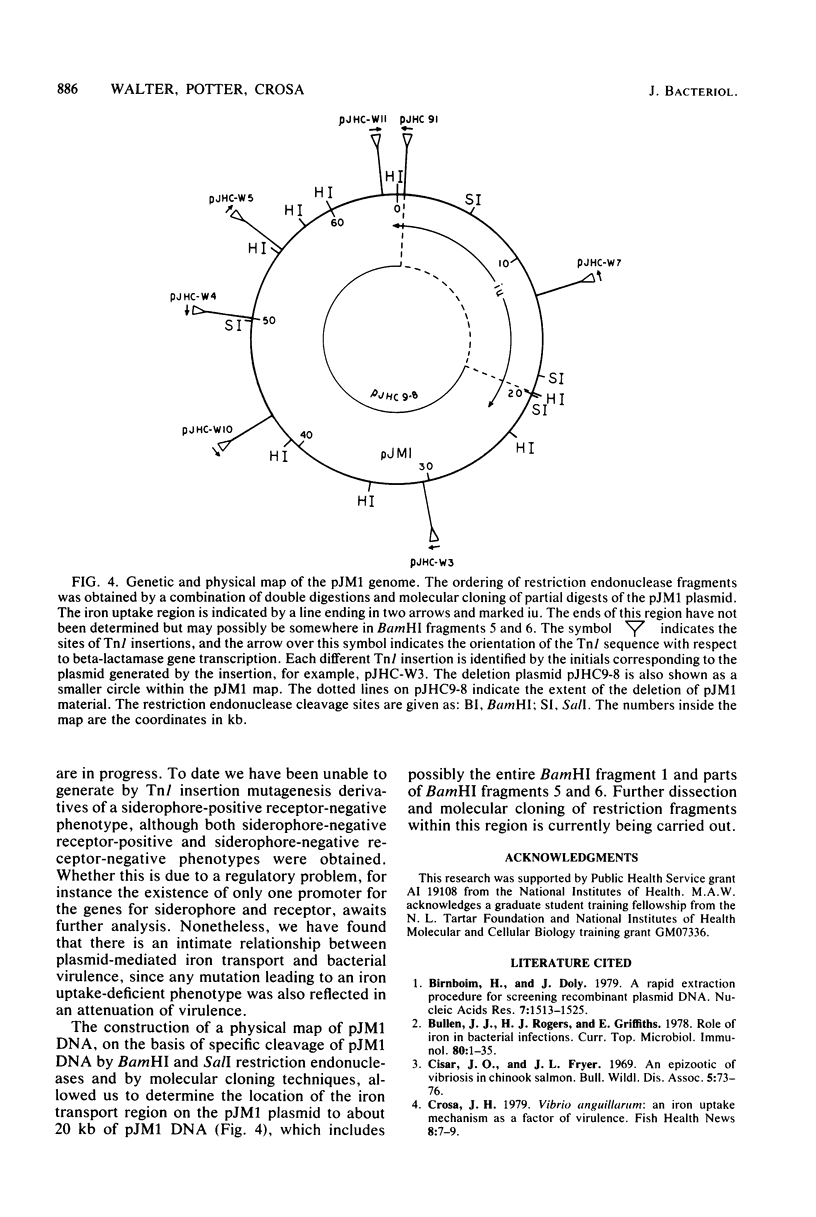
Plasmid pJM1 from an invasive strain of Vibrio anguillarum mediates an iron-sequestering system that is associated with the ability of this bacterium to cause septicemia in marine fishes. This plasmid-mediated iron uptake system was analyzed by using mutations caused by transposon Tnl. Restriction endonuclease analysis of iron uptake-deficient and -proficient derivatives generated by insertion of Tnl and molecular cloning experiments permitted us to localize the plasmid regions involved in the process of iron sequestration to a stretch of about 20 kilobase pairs. In addition, the existence of two plasmid-mediated components involved in the process of iron uptake in V. anguillarum was defined: a diffusible substance which functions as a siderophore and a nondiffusible receptor for complexes of iron-siderophore, which we have tentatively identified as the pJM1 plasmid-mediated outer membrane protein OM2 of V. anguillarum.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Fryer J. L. An epizootic of vibriosis in chinook salmon. Wildl Dis. 1969 Apr;5(2):73–76. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-5.2.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):566–568. doi: 10.1038/284566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
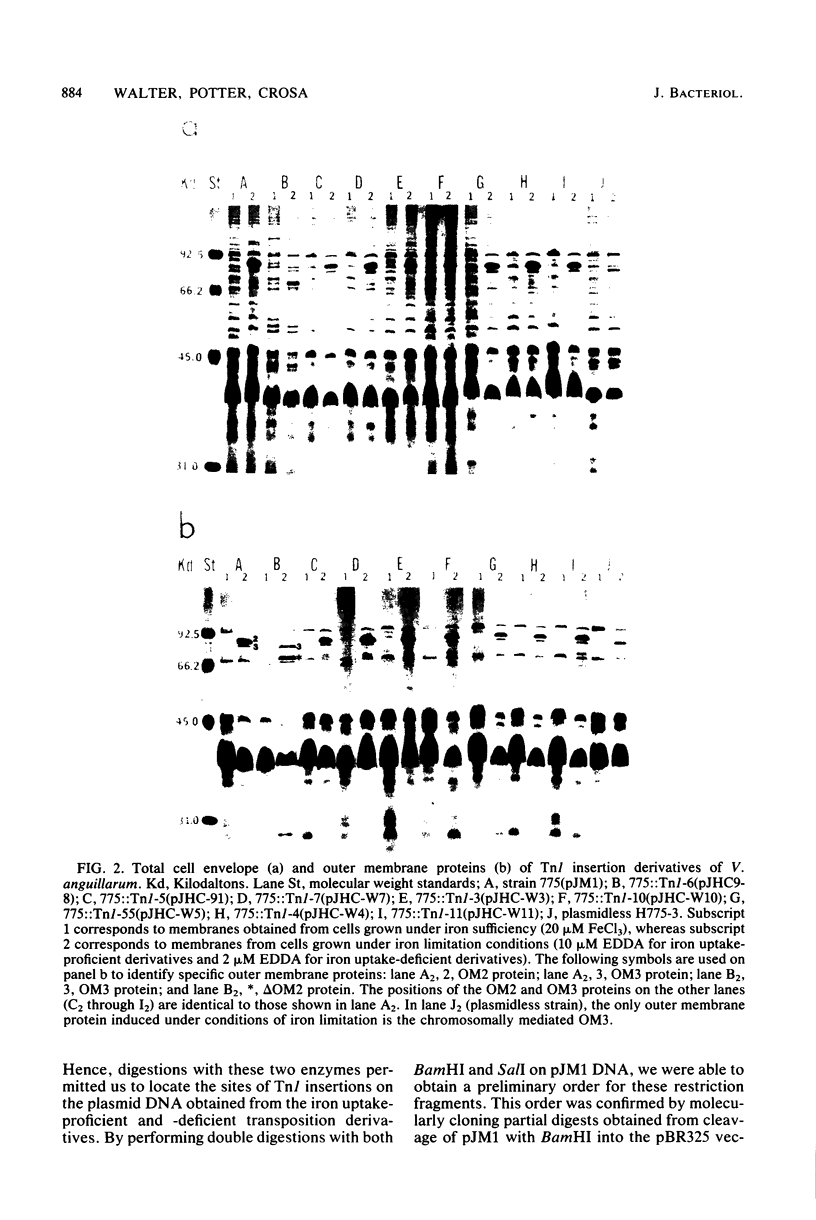
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L. Outer membrane proteins induced under conditions of iron limitation in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum 775. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):223–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.223-227.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L., Schiewe M. H. Curing of a plasmid is correlated with an attenuation of virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.897-902.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Luttropp L. K., Falkow S. Molecular cloning of replication and incompatibility regions from the R-plasmid R6K. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):443–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Schiewe M. H., Falkow S. Evidence for plasmid contribution to the virulence of fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):509–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.509-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Ingram L. C., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of a R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1822. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.529-537.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E. Transposition of ampicillin resistance from RP4 to other replicons. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00268228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. The critical role of iron in host-bacterial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1428–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H. Novel iron uptake system specified by ColV plasmids: an important component in the virulence of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):925–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.925-932.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Warner P. J. ColV plasmid-mediated, colicin V-independent iron uptake system of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):411–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.411-416.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]