Abstract
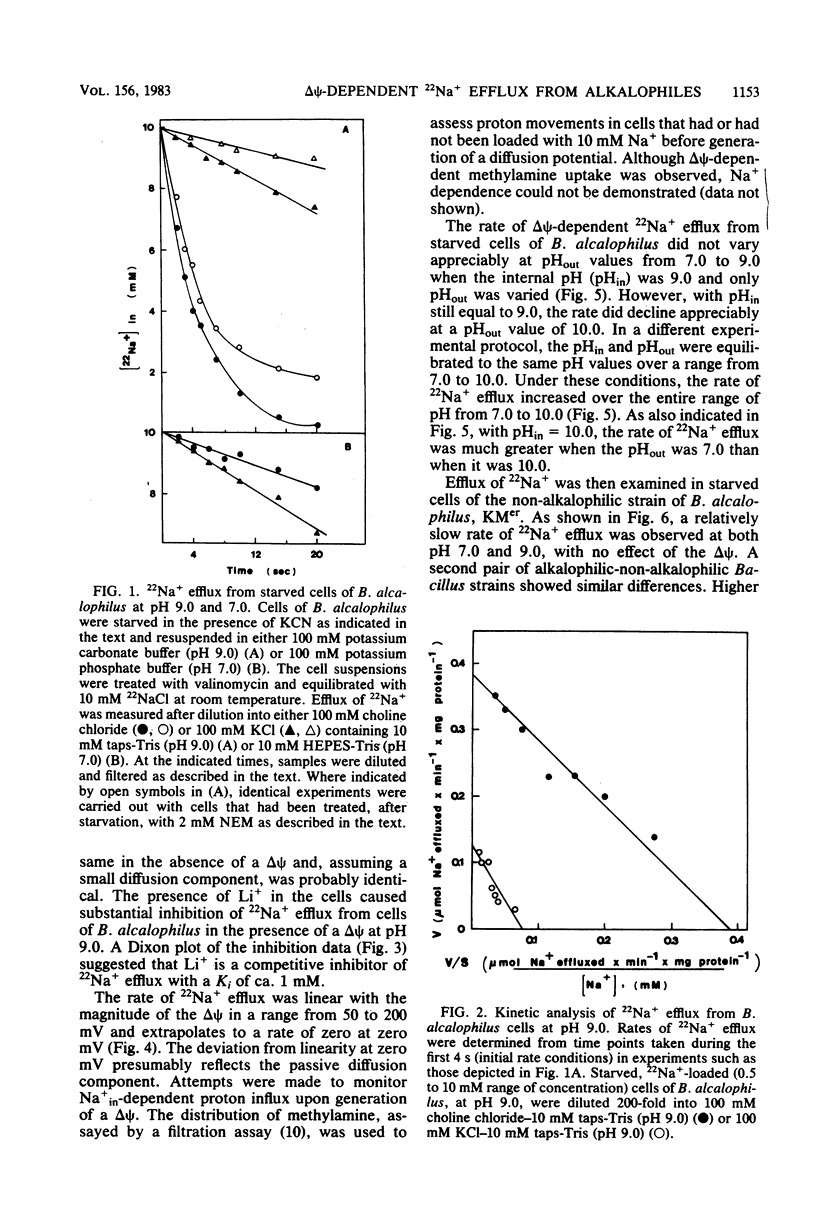
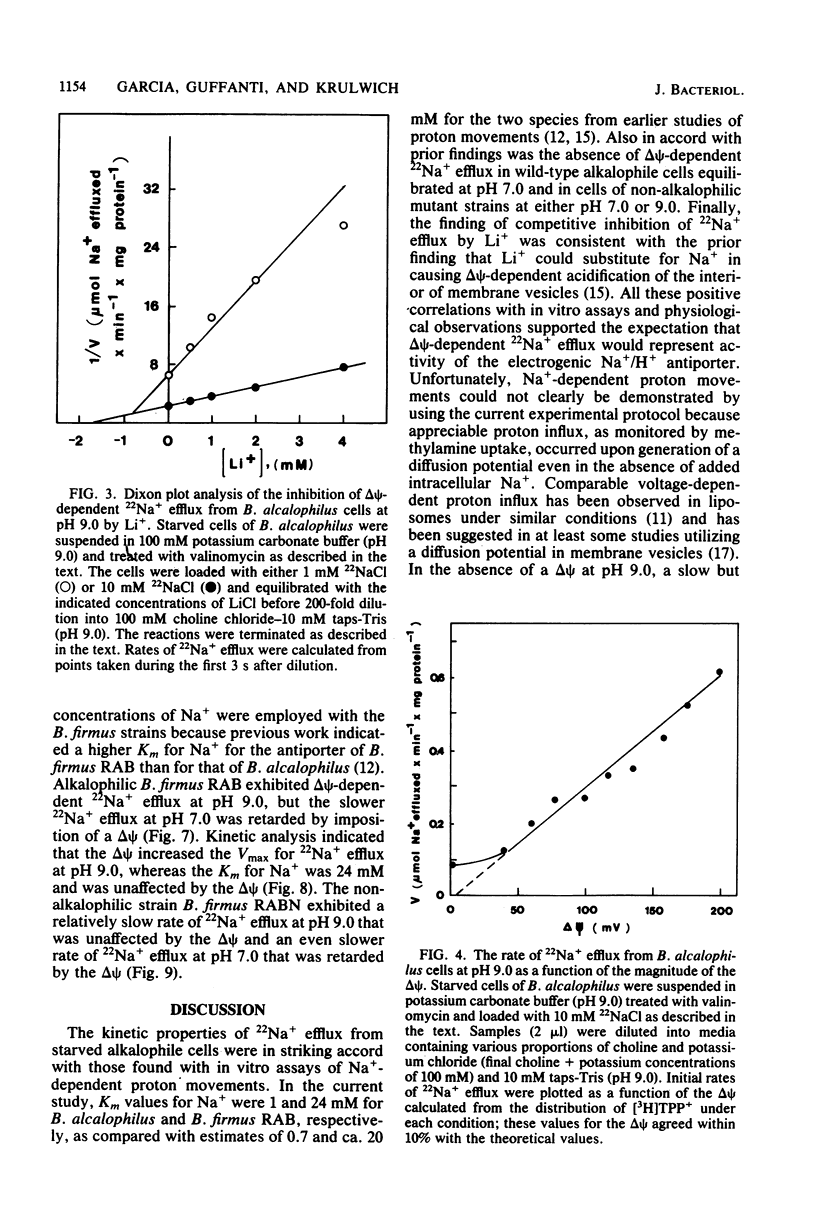
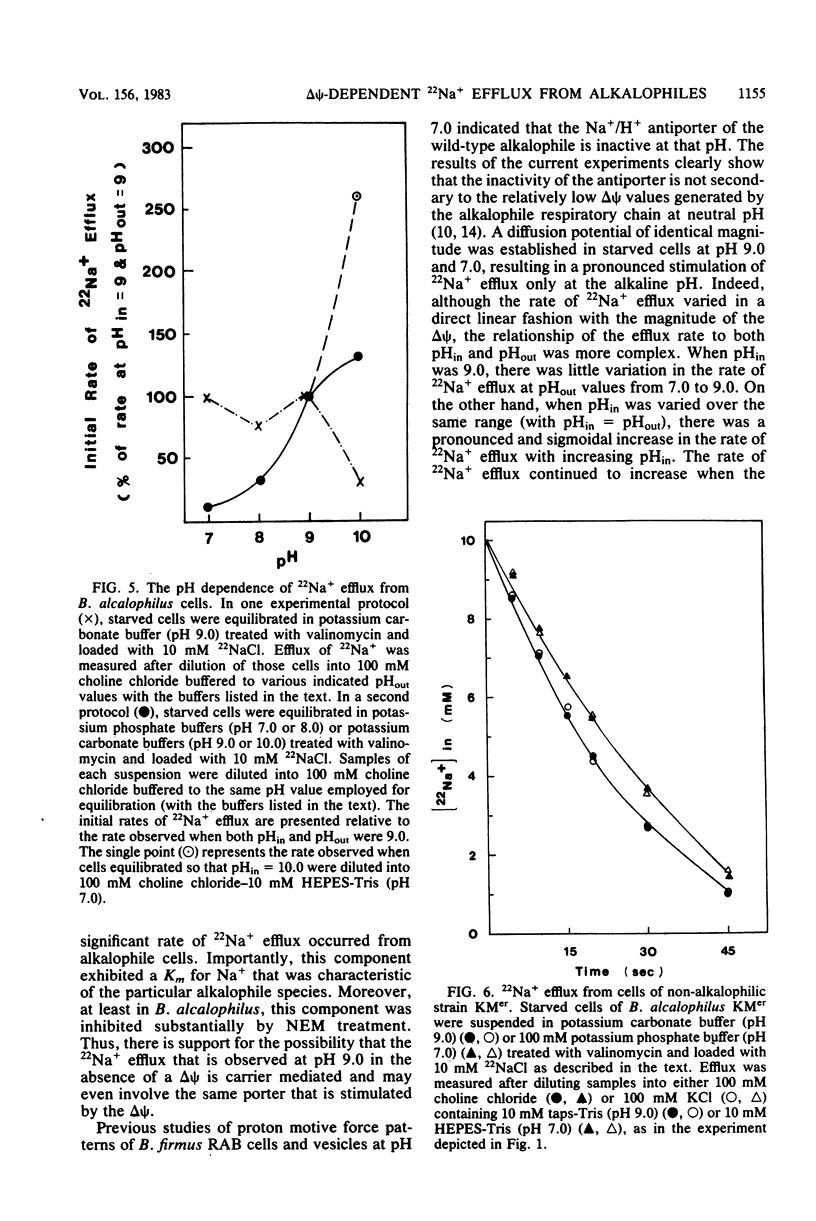
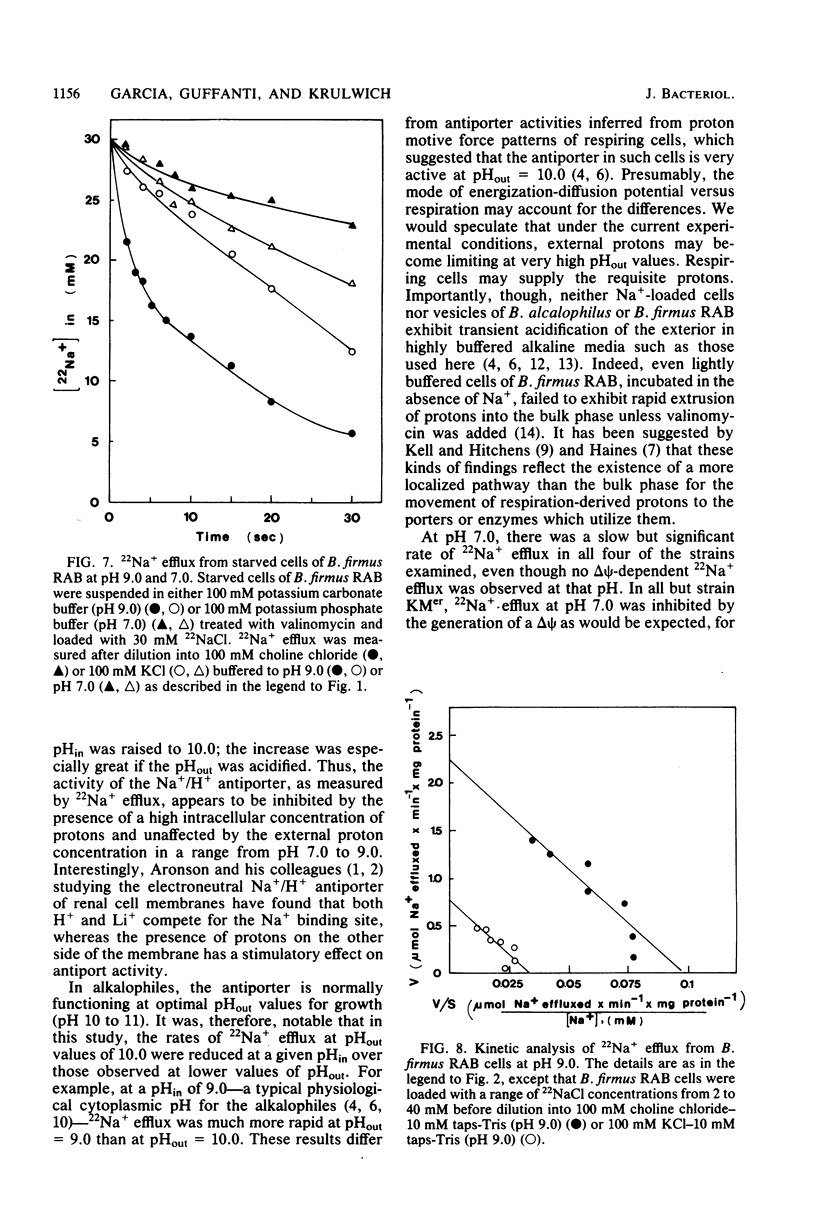
The Na+/H+ antiporter of Bacillus alcalophilus was studied by measuring 22Na+ efflux from starved, cyanide-inhibited cells which were energized by means of a valinomycin-induced potassium diffusion potential, positive out (delta psi). In the absence of a delta psi, 22Na+ efflux at pH 9.0 was slow and appreciably inhibited by N-ethylmaleimide. Upon imposition of a delta psi, a very rapid rate of 22Na+ efflux occurred. This rapid rate of 22Na+ efflux was competitively inhibited by Li+ and varied directly with the magnitude of the delta psi. Kinetic experiments with B. alcalophilus and alkalophilic Bacillus firmus RAB indicated that the delta psi caused a pronounced increase in the Vmax for 22Na+ efflux. The Km values for Na+ were unaffected by the delta psi. Upon imposition of a delta psi at pH 7.0, a retardation of the slow 22Na+ efflux rate at pH 7.0 was caused by the delta psi. This showed that inactivity of the Na+/H+ antiporter at pH 7.0 was not secondary to a low delta psi generated by respiration at this pH. Indeed, 22Na+ efflux activity appeared to be inhibited by a relatively high internal proton concentration. By contrast, at a constant internal pH, there was little variation in the activity at external pH values from 7.0 to 9.0; at an external pH of 10.0, the rate of 22Na+ efflux declined. This decline at typical pH values for growth may be due to an insufficiency of protons when a diffusion potential rather than respiration is the driving force. Non-alkalophilic mutant strains of B. alcalophilus and B. firmus RAB exhibited a slow rate of 22Na+ efflux which was not enhanced by a delta psi at either pH 7.0 or 9.0.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Suhm M. A., Nee J. Interaction of external H+ with the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6767–6771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Cohn D. E., Kaback H. R., Krulwich T. A. Relationship between the Na+/H+ antiporter and Na+/substrate symport in Bacillus alcalophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1481–1484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Susman P., Blanco R., Krulwich T. A. The protonmotive force and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in an obligately alkalophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):708–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines T. H. Anionic lipid headgroups as a proton-conducting pathway along the surface of membranes: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):160–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Bioenergetic properties and viability of alkalophilic Bacillus firmus RAB as a function of pH and Na+ contents of the incubation medium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1096–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1096-1104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Hoffstein J. A sodium requirement for growth, solute transport, and pH homeostasis in Bacillus firmus RAB. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1885–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Mandel K. G., Bornstein R. F., Guffanti A. A. A non-alkalophilic mutant of Bacillus alcalophilus lacks the Na+/H+ antiporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. J., Krulwich T. A., Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Respiration-dependent proton translocation in alkalophilic Bacillus firmus RAB and its non-alkalophilic mutant derivative. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2109–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Monovalent cation/proton antiporters in membrane vesicles from Bacillus alcalophilus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7391–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Kaback H. R. Sodium-dependent methyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside transport in membrane vesicles isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2130–2136. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


