Abstract
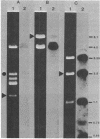
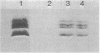
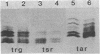
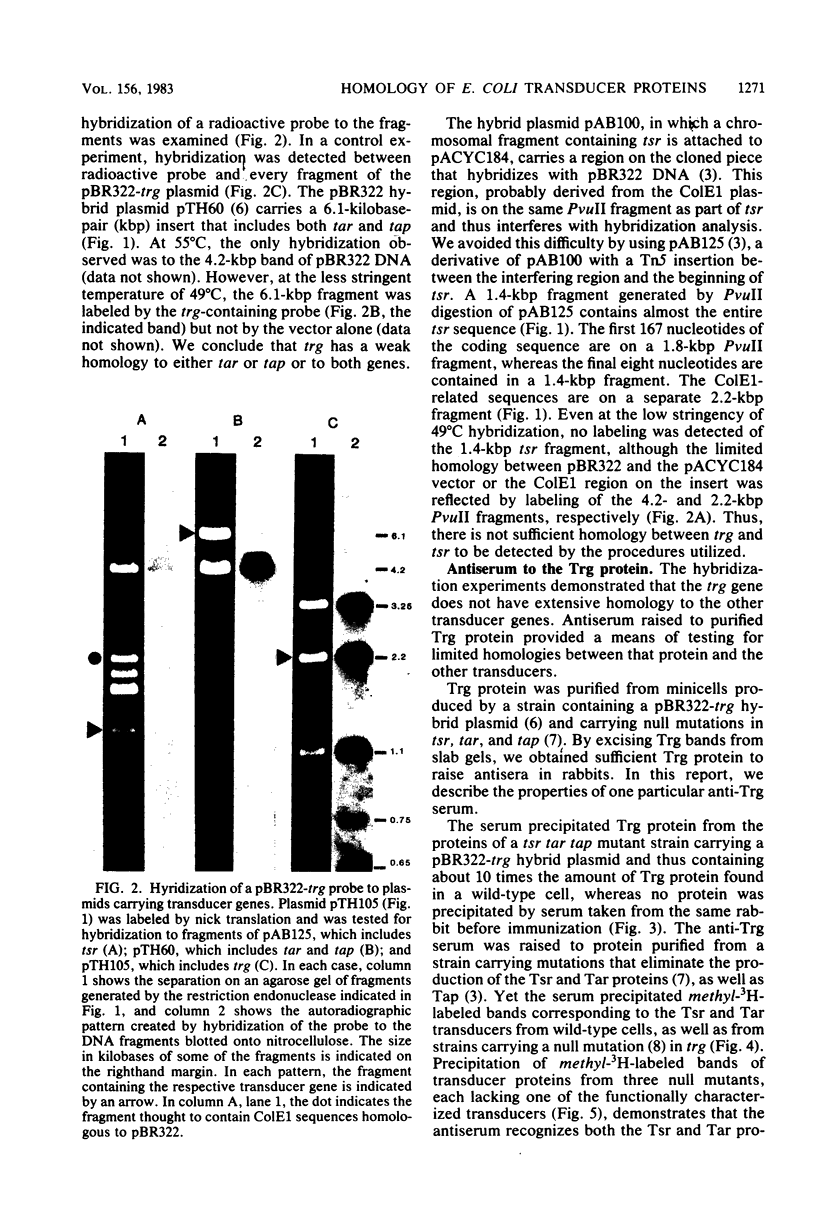
Transducers are transmembrane proteins that are central to the chemotactic system of Escherichia coli. The proteins transduce ligand recognition into an excitatory signal and function in adaptation as methyl-accepting proteins. The transducer genes tsr, tar, and tap have extensive homology with each other. However, previous studies revealed little indication of homology between those three transducer genes and a fourth gene, trg. We investigated the relationship between trg and the other genes by blot-hybridization experiments and the relationship between Trg and the other transducer proteins by immune precipitation and experiments with an antiserum raised to purified Trg protein. In experiments in which 35% mismatch would be tolerated, weak hybridization of trg was detected to a DNA fragment containing tar and tap but not to a fragment containing tsr. In experiments in which only 30% mismatch would be tolerated, no trg hybridization was apparent either to total chromosomal DNA or to DNA from hybrid plasmids carrying the other transducer genes. An anti-Trg serum formed immune precipitates with the Tsr and Tar proteins as well as with the Trg protein to which it was raised. We conclude that there is homology between Trg and the other transducer, but the homology is more limited than that shared among the other transducers. Furthermore, we found no indication of additional transducer genes closely related to trg. Thus, the trg gene is a somewhat distant cousin within a single transducer gene family of E. coli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouché J. P., Gélugne J. P., Louarn J., Louarn J. M., Kaiser K. Relationships between the physical and genetic maps of a 470 x 10(3) base-pair region around the terminus of Escherichia coli K12 DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90414-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Kendall K., Simon M. I. Structure of the serine chemoreceptor in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):623–626. doi: 10.1038/301623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Krikos A., Simon M. Sensory transducers of E. coli are encoded by homologous genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Dahlquist F. W. Structural studies of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Escherichia coli: evidence for multiple methylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2434–2438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Curtiss R., 3rd Production, properties and utility of bacterial minicells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:1–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Engström P., Wolf-Watz H., Iino T., Hazelbauer G. L. Cloning of trg, a gene for a sensory transducer in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):372–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.372-383.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P., Harayama S. Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein III and transducer gene trg. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.43-49.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P. Multiple forms of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins distinguished by a factor in addition to multiple methylation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.35-42.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:33–70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W., Brunovskis I., Summers W. C. DNA base sequence homology between coliphages T7 and phiII and between T3 and phiII as determined by heteroduplex mapping in the electron microscope. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90330-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Lugtenberg B. Recognition site for phosphorus-containing compounds and other negatively charged solutes on the PhoE protein pore of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Van Scharrenburg G., Lugtenberg B. Antigenic relationships between pore proteins of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Synthesis of exported proteins by membrane-bound polysomes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]