Abstract
Upon fractionating Saccharomyces cerevisiae asynchronous cultures by sucrose density gradient centrifugation in a zonal rotor and examining the exo-1,3-β-glucanase and deoxyribonucleic acid content of the cells, a periodic step increase in the activity of this enzyme was observed, indicating a discontinuous pattern of synthesis or activation of exo-1,3-β-glucanase during the mitotic cycle at the transition from the S to the G2 phase. Similar results were obtained for endo-1,3-β-glucanase by assaying activity against oxidized laminarin in permeabilized cells, suggesting that the synthesis of endo-1,3-β-glucanase is controlled in the same way. When a and α strains were mated, the specific activity of cell extracts against laminarin, oxidized laminarin, and pustulan remained constant while zygote formation was taking place. However, when growth resumed, active synthesis of 1,3-β-glucanases took place as shown by the occurrence of a significant increase in the specific activity against the three substrates. Specific changes in the level of glucan degradative enzymes, not observed in a haploid parental strain, occurred when the diploid S. cerevisiae AP-1 was induced to sporulate. The sporulation process triggered the activation of first the pustulan degradative capacity and then the capacity to hydrolyze oxidized laminarin. The specific activity against this substrate was 10 times higher than that against pustulan.
Full text
PDF

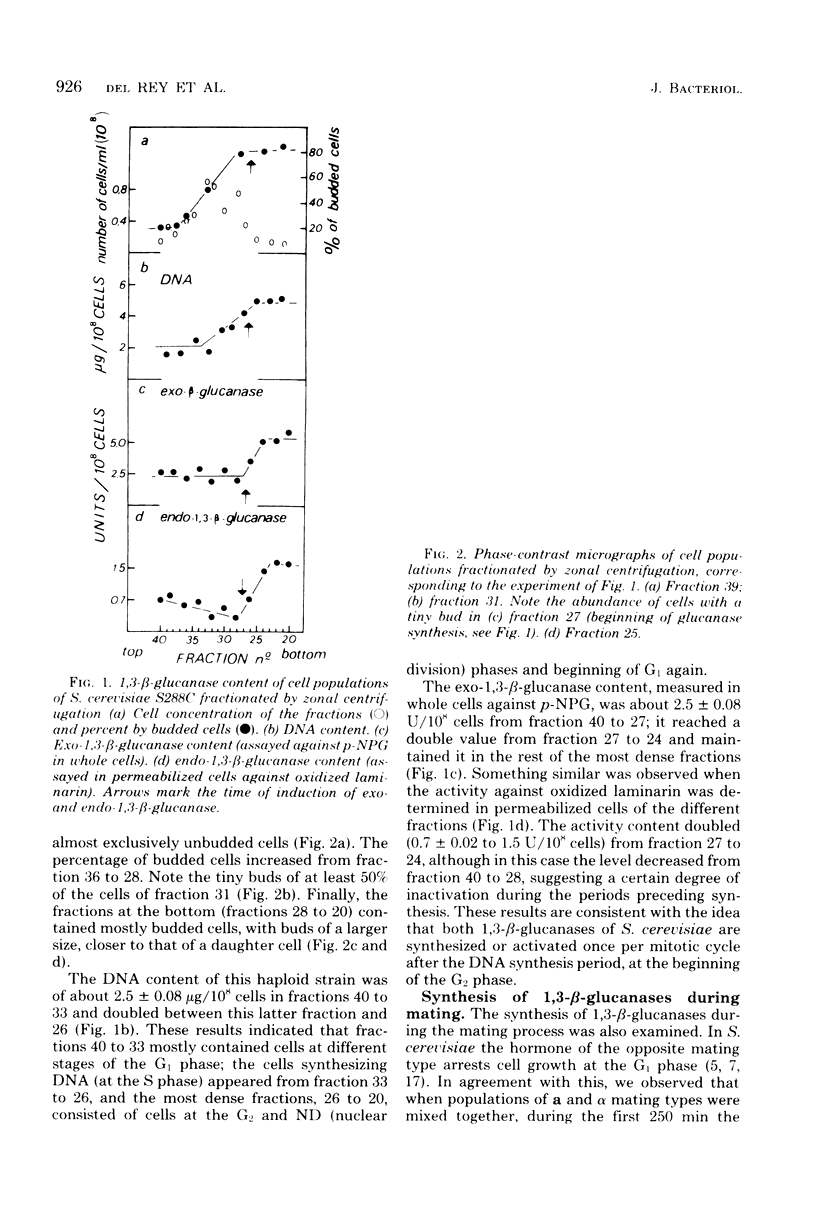
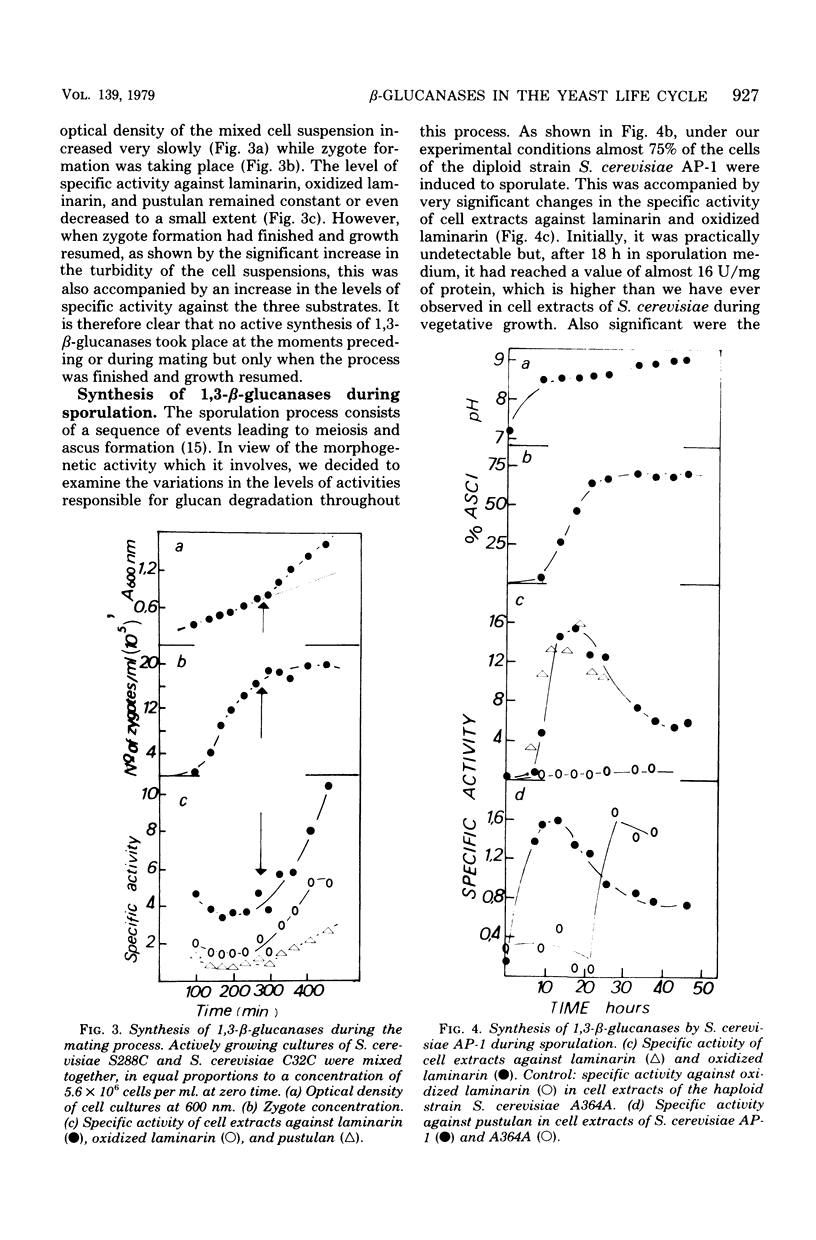
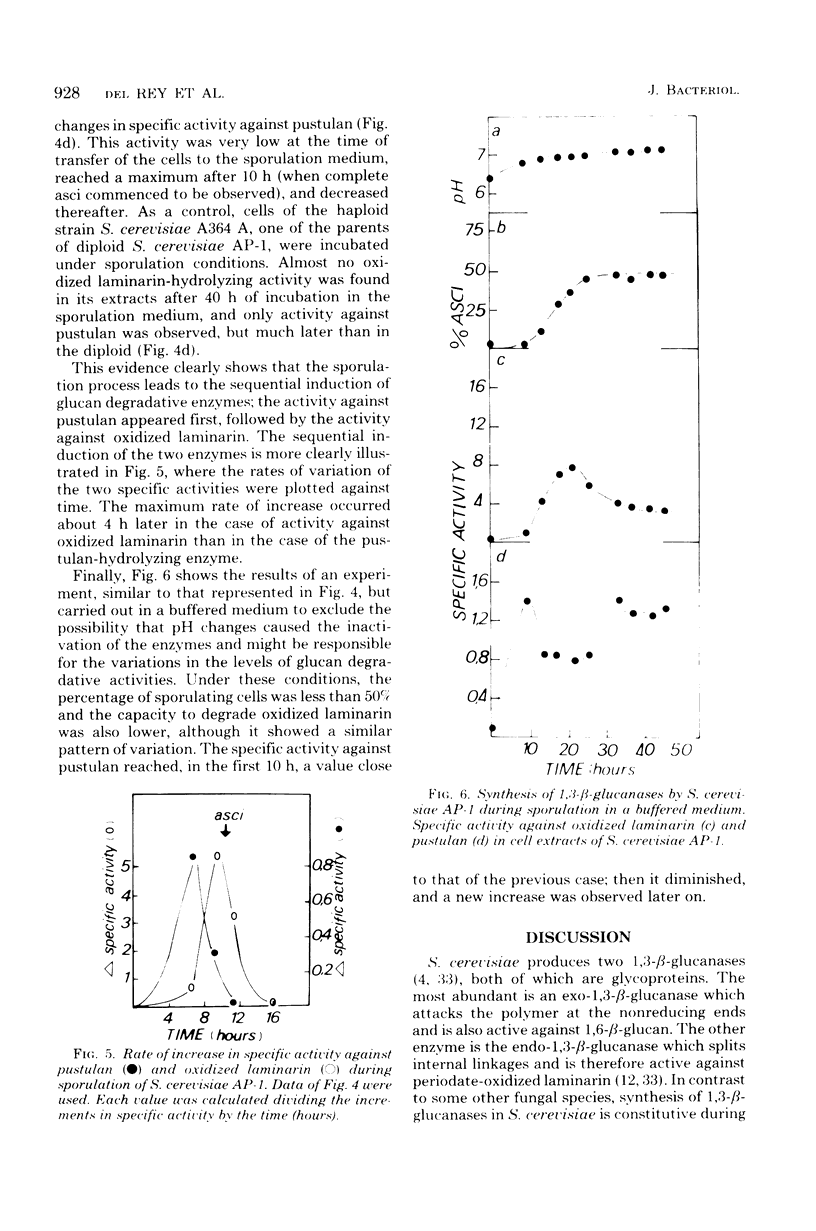



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz H., Weiser U. Protein degradation during yeast sporulation. Enzyme and cytochrome patterns. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):385–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H., Weisner U. Protein degradation and proteinases during yeast sporulation. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):65–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biely P., Krátký Z., Bauer S. Interaction of concanavalin A with external mannan-proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Glycoprotein nature of beta-glucanases. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):75–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biliński T., Jachymczyk W., Litwińska J., Zuk J., Gajewski W. Mutual inhibition of DNA synthesis in a- and alpha-cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during conjugation. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 May;82(1):97–101. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Biochemical and cellular changes occuring during conjugation in Hansenula wingei. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1019–1025. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1019-1025.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Magee P. T. Glycogenolytic enzymes in sporulating yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.844-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortat M., Matile P., Wiemken A. Isolation of glucanase-containing vesicles from budding yeast. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;82(3):189–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00412191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. G., McLaughlin C. S. Rate of macromolecular synthesis through the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas V., Biely P., Bauer S. Extracellular beta-glucanases of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 15;321(1):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth E., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Morphogenesis of ascospores in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):869–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.869-880.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O., Carter B. L., Tauro P. Synthesis of enzymes during the cell cycle. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6(0):47–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):164–198. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.164-198.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Synchronization of haploid yeast cell cycles, a prelude to conjugation. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. F. Lysis of yeast cell walls induced by 2-deoxyglucose at their sites of glucan synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1169–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1169-1172.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. M., Roth R. Carbohydrate metabolism during ascospore development in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.8-14.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Halvorson H. O. Proteinase activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):863–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.863-869.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. K., Lloyd D. Oscillations of enzyme activities during the cell-cycle of a glucose-repressed fission-yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe 972h-. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):195–207. doi: 10.1042/bj1360195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. Carbohydrate accumulation during the sporulation of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):53–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.53-57.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos T., del Rey F., Conde J., Villanueva J. R., Nombela C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant defective in exo-1,3-beta-glucanase production. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.333-338.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian J., Carter B. L., Halvorson H. O. Use of yeast populations fractionated by zonal centrifugation to study the cell cycle. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1045-1050.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentandreu R., Elorza M. V., Villanueva J. R. Synthesis of yeast wall glucan. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Sep;90(1):13–20. doi: 10.1099/00221287-90-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. R., James T. W. Cell cycle analysis by culture fractionation. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Dec;75(2):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90454-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]