Abstract
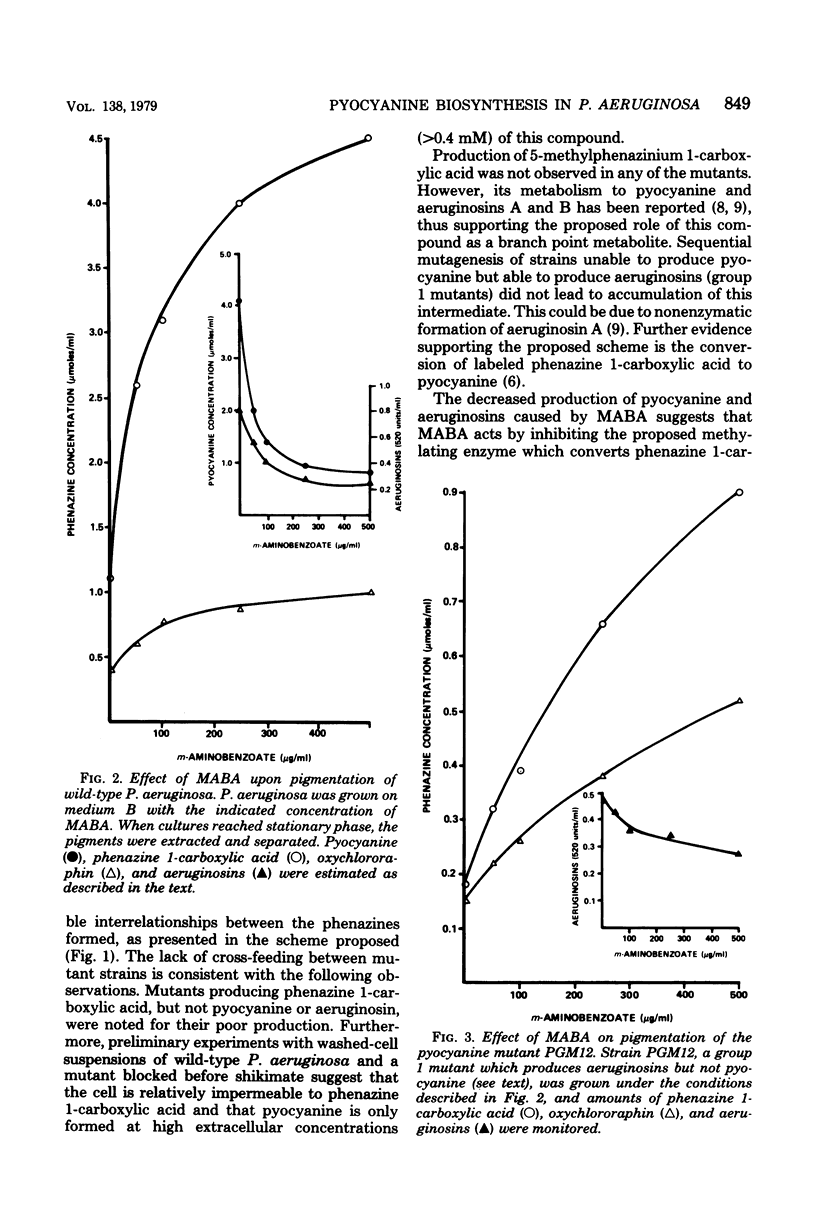
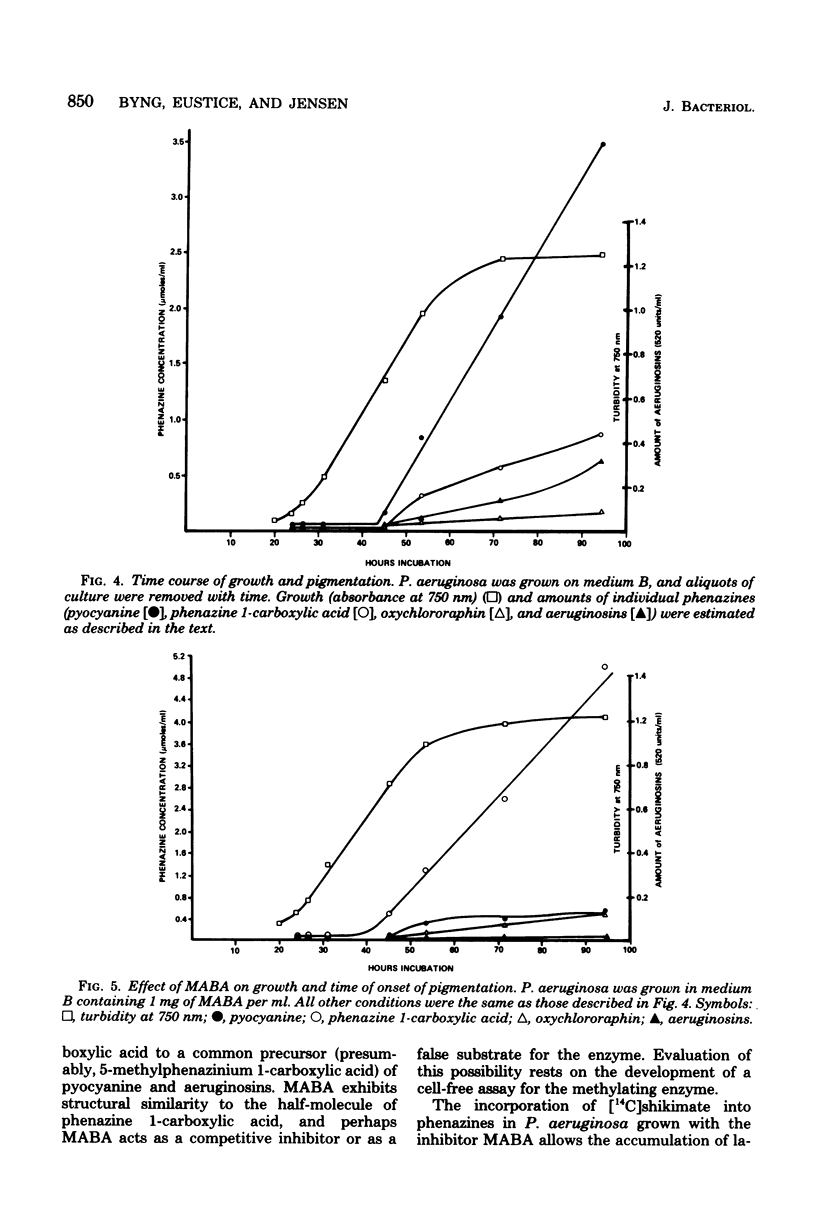
Pigmentation mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, selected by observed visual differences in coloration from the wild-type strain, were examined for altered patterns of phenazine synthesis. Three classes of mutants that were incapable of pyocyanine production were identified. Pigmentation patterns that were found to characterize the various mutant classes implicated precursor-product relationships, and a biochemical scheme covering the terminal reactions of pyocyanine biosynthesis is proposed. Among compounds tested as inhibitors of pigmentation, two effectively inhibited pyocyanine production production while allowing cell growth. p-Aminobenzoate inhibited total pigmentation; i.e., no other phenazine accumulated. m-Aminobenzoate inhibited a presumptive methylation step in pyocyanine biosynthesis, abolishing the formation of pyocyanine and aeruginosin pigments but increasing the yields of phenazine 1-carboxylic acid and oxychlororaphin. D-[2,3,4,5(n)-14C]shikimate was most efficiently incorporated into phenazines in the middle to late exponential phase of growth. Label was incorporated predominantly into pyocyanine in the absence of inhibitors and into phenazine 1-carboxylic acid when the organism was grown in the presence of m-aminobenzoate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byng G. S., Turner J. M. Incorporation of [14C]shikimate into plenazines and their further metabolism by Pseudomonas phenazinium. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj1640139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byng G. S., Turner J. M. Isolation of pigmentation mutants of Pseudomonas phenazinium. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Nov;97(1):57–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Carson M., Jensen R. A. The branch point metabolite for pyocyanine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):581–583. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson M., Jensen R. A. Phenotype recognition of pyocyanine mutants in pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):312–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.312-314.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. C., Blackwood A. C. Simultaneous production of three phenazine pigments by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mac 436. Can J Microbiol. 1969 May;15(5):439–444. doi: 10.1139/m69-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK L. H., DEMOSS R. D. On the biosynthesis of pyocyanine. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jun;77(6):776–782. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.6.776-782.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flood M. E., Herbert R. B., Holliman F. G. Pigments of Pseudomonas species. V. Biosynthesis of pyocyanin and the pigments of Ps. aureoaciens. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1972;4:622–626. doi: 10.1039/p19720000622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLOWAY B. W. Genetic recombination in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Dec;13(3):572–581. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansford G. S., Holliman F. G., Herbert R. B. Pigments of Pseudomonas species. IV. In vitro and in vivo conversion of 5-methylphenazinium-1-carboxylate into aeruginosin A. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1972;1:103–105. doi: 10.1039/p19720000103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliman F. G. Pigments of pseudomonas species. I. Structure and synthesis of aeruginosin A. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1969;18:2514–2516. doi: 10.1039/j39690002514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein U., McCamey D. A. Biosynthesis of phenazines. II. Incorporation of (6-14C)-D-shikimic acid into phenazine-1-carboxylic acid and iodinin. J Org Chem. 1973 Sep 21;38(19):3415–3417. doi: 10.1021/jo00959a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. M., Campbell J. J. A new resuspension medium for pyocyanine production. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jun;15(6):595–598. doi: 10.1139/m69-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. M., Campbell J. J. Evaluation of shikimic acid as a precursor of pyocyanine. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jun;15(6):535–541. doi: 10.1139/m69-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner D., Gerber N. N., Bartha R. Pattern of phenazine pigment production by a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):690–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.690-692.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley R. P., Halliwell J. E., Campbell J. J., Ingledew W. M. The branchpoint of pyocyanine biosynthesis. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Sep;18(9):1357–1363. doi: 10.1139/m72-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEIKH N. M., MACDONALD J. C. BIOGENESIS OF THE N-METHYL GROUP OF PYOCYANINE. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Dec;10:861–866. doi: 10.1139/m64-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



