Abstract
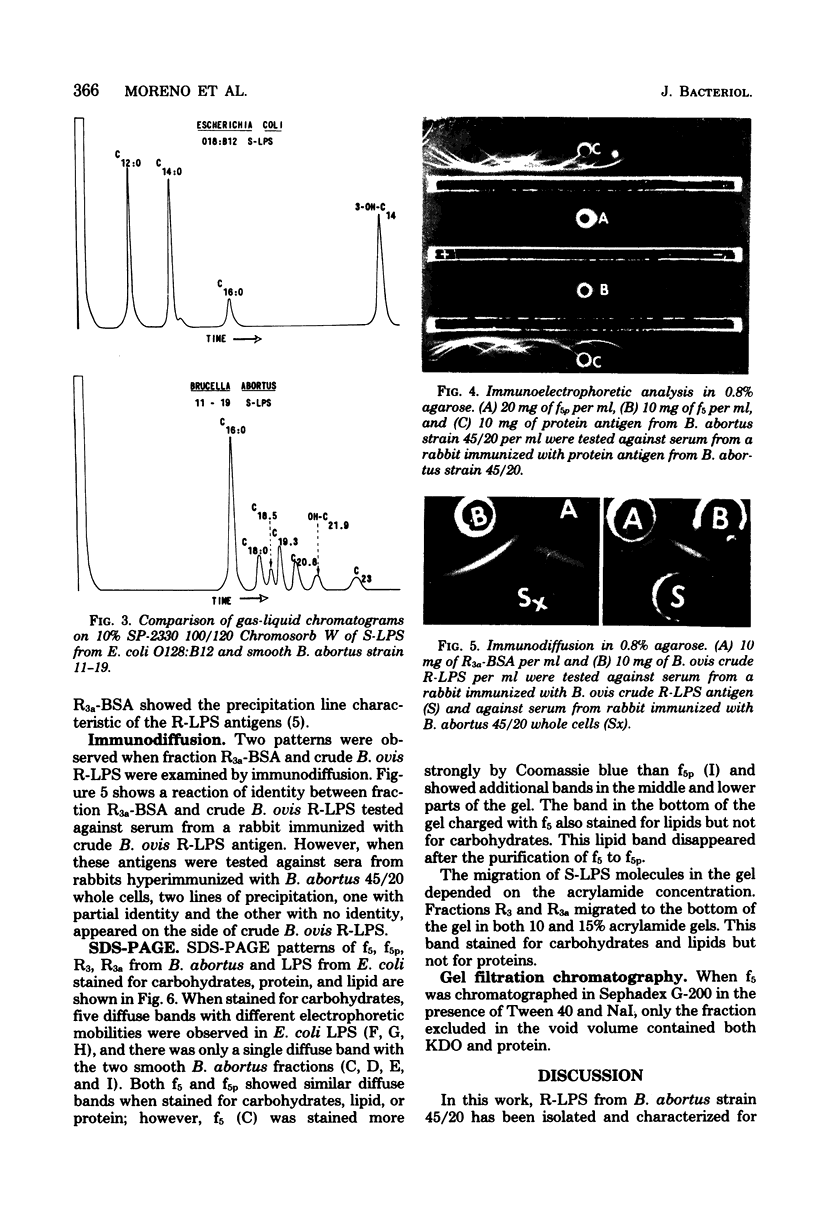
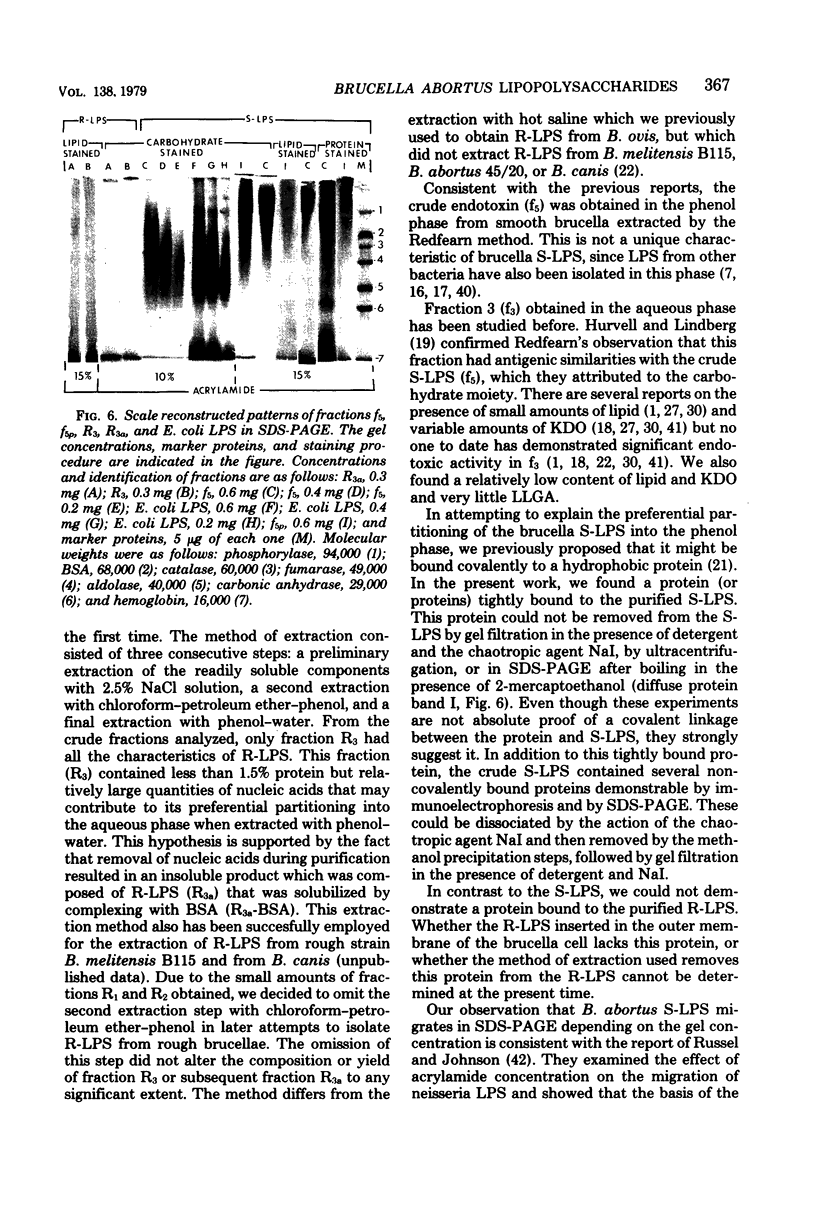
In an attempt to obtain pure and well characterized smooth lipopolysaccharide (S-LPS) and rough lipopolysaccharide (R-LPS), smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus were extracted by two different modifications of the phenol-water method. S-LPS was obtained in the phenol phase, and R-LPS was obtained in the aqueous phase. Further purification was accomplished by treatment with enzymes, detergents, NaI as a chaotropic agent to separate non-covalently bound contaminants, and by gel filtration. The degree of purity of the molecules was determined by chemical and immunological analysis and by electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Lipid identification by gas-liquid chromatography showed seven major fatty acids. Palmitic acid accounts for about 50%, stearic acid accounts for about 10%, and hydroxylated fatty acids account for less than 5% of total fatty acids. 2-Keto-3-deoxyoctonate but not heptose was detected in the sugar analysis. Protein was found to be firmly bound to S-LPS but not to R-LPS.
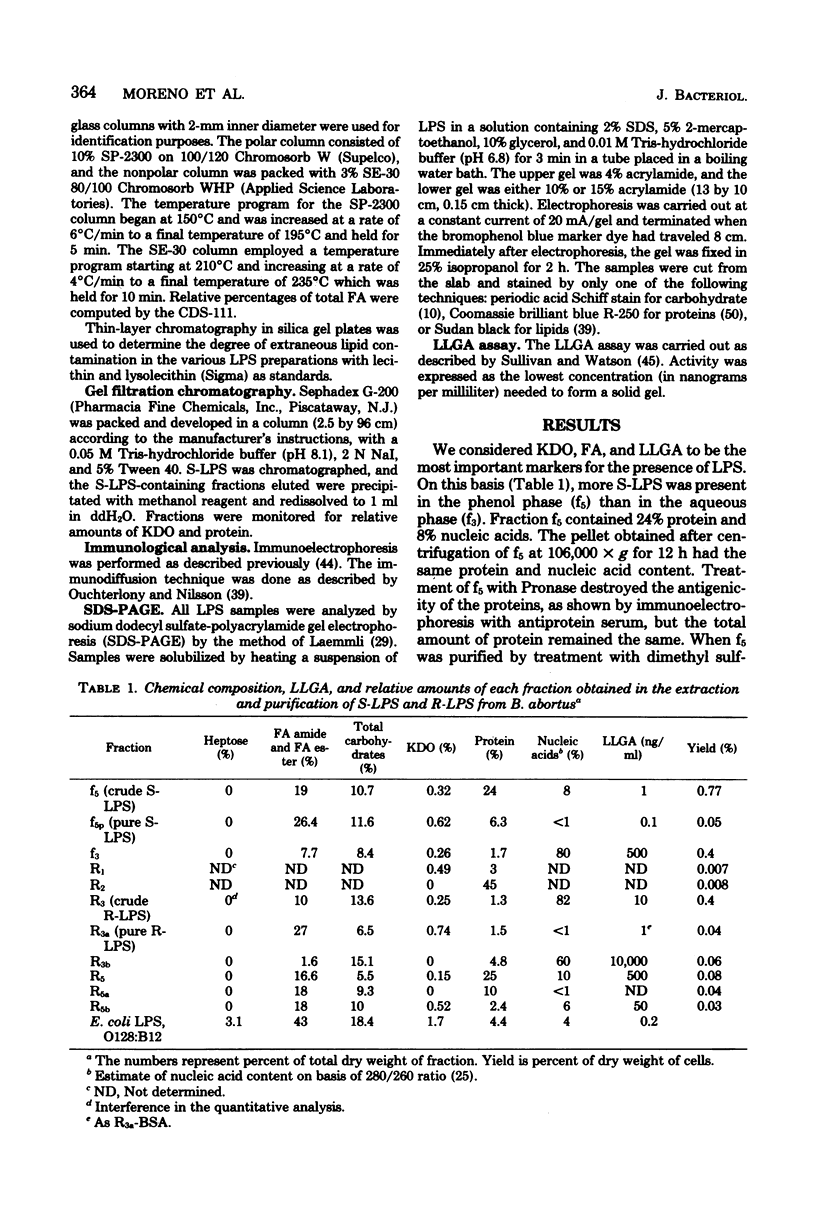
Full text
PDF
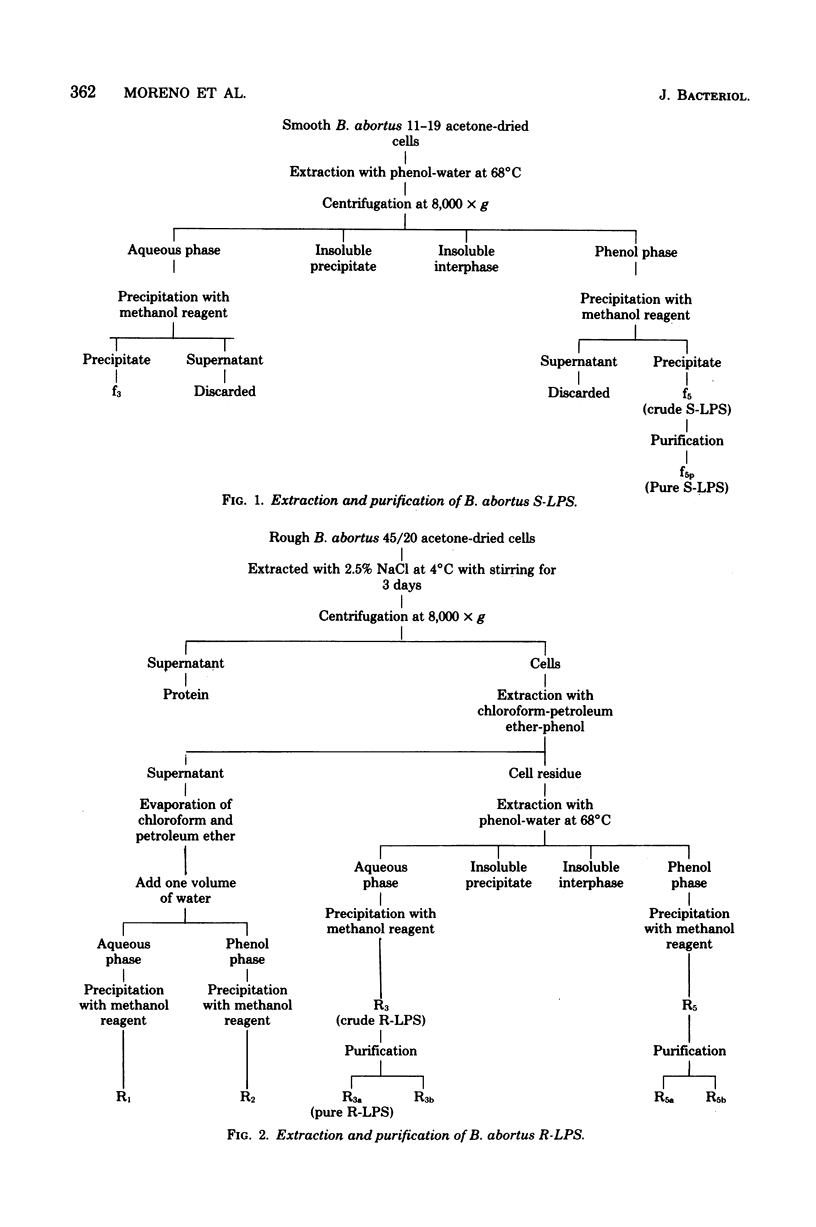




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON A. J., CARTER H. E. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE LIPID A COMPONENT OF THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:411–418. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Chemical composition and biological properties of the endotoxin of Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):895–902. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.895-902.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Hypoferremia in mice and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.903-910.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser D. V., Wheat R. W., Foster J. W., Leong D. Occurrence of quinovosamine in lipopolysaccharides of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):772–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.772-774.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Qualitative and quantitative colorimetric determination of heptoses. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):983–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Leong D., Wilson J. B. Surface antigens of smooth brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.893-901.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C. Physical state and biological activity of lipopolysaccharides. Toxicity and immunogenicity of the lipid A component. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):214–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biological activities of lipid A complexed with bovine-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):230–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman J., Ashwell G. Isolation of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide from Xanthomonas campestris containing 3-acetamido-3,6-dideoxy-D-galactose and D-rhamnose. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1424–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert R. E., Hurlbert I. M. Biological and physicochemical properties of the lipopolysaccharide of Chromatium vinosum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):983–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.983-994.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunochemical studies on phenol-water extracted lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Biological and chemical investigations of lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):105–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Studies of Brucella lipopolysaccharide. Dev Biol Stand. 1976;31:62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Diaz R., Berman D. T. Endotoxic activity of rough organisms of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1638–1641. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1638-1641.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Diaz R., Taylor A. G. Characterization of allergens prepared from smooth and rough strains of Brucella melitensis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Oct;54(5):492–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellerman G. D., Foster J. W., Badakhsh F. F. Comparison of Chemical Components of Cell Walls of Brucella abortus Strains of Low and High Virulence. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):237–243. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.237-243.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacave C., Asselineau J., Serre A., Roux J. Comparaison de la composition chimique d'une fraction lipopolysaccharidique et d'une fraction polysaccharidique isolées de Brucella melitensis. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):189–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacave C., Promé J. C., Asselineau J., Roux J., Serre A. Sur les fractions lipopolysaccharidiques extraites par le phenol de Brucella melitensis. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 May 11;270(19):2380–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Diaz R., Milner K., Rudbach J., Wilson J. B. Some structural and biological properties of Brucella endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):174–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.174-182.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Diaz R., Wilson J. B. Identification of the toxic component of Brucella abortus endotoxin and its labeling with radioactive chromate. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):612–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.612-617.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limjuco G. A., Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Maigetter R. Z., King J. J., Carlo D. J. Studies on the chemical composition of lipopolysaccharide from Neisseria meningitidis group B. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):187–191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Sandulache R., Pop A., Cerbu A. Biochemical basis of the serological cross-reactions between Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Dec;126(4):435–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Bergman R. K., Robbins K. E. Comparison of the histamine hypersensitivity and the Limulus amoebocyte lysate tests for endotoxin activity. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):292–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.292-294.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. M., Jones L. M., Varela-Diaz V. M. Studies of antigens for complement fixation and gel diffusion tests in the diagnosis of infections caused by Brucella ovis and other Brucella. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):894–902. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.894-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN J. S., ROUSER G. ANALYSIS OF HYDROXY FATTY ACIDS BY GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY. Anal Biochem. 1964 Mar;7:288–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff R. A., Wheat R. W. Carbohydrate composition of the phenol-soluble lipopolysaccharides of Citrobacter freundii. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2035–2043. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2035-2043.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renoux G., Renoux M., Tinelli R. Phenol-water fractions from smooth Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis: immunochemical analysis and biologic behavior. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):139–148. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Johnson K. G. SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):2013–2018. doi: 10.1139/m75-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Jones L. M., Speth S. L., Berman D. T. Antibody response to antigens distinct from smooth lipopolysaccharide complex in Brucella infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.994-1002.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. D., Jr, Watson S. W. Factors affecting the sensitivity of Limulus lysate. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.1023-1026.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Suto T., Isayama Y., Azuma R., Hatakeyama H. Chemo-taxonomical studies on fatty acids of "Brucella" species. Ann Sclavo. 1977 Jan-Feb;19(1):67–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]