Abstract
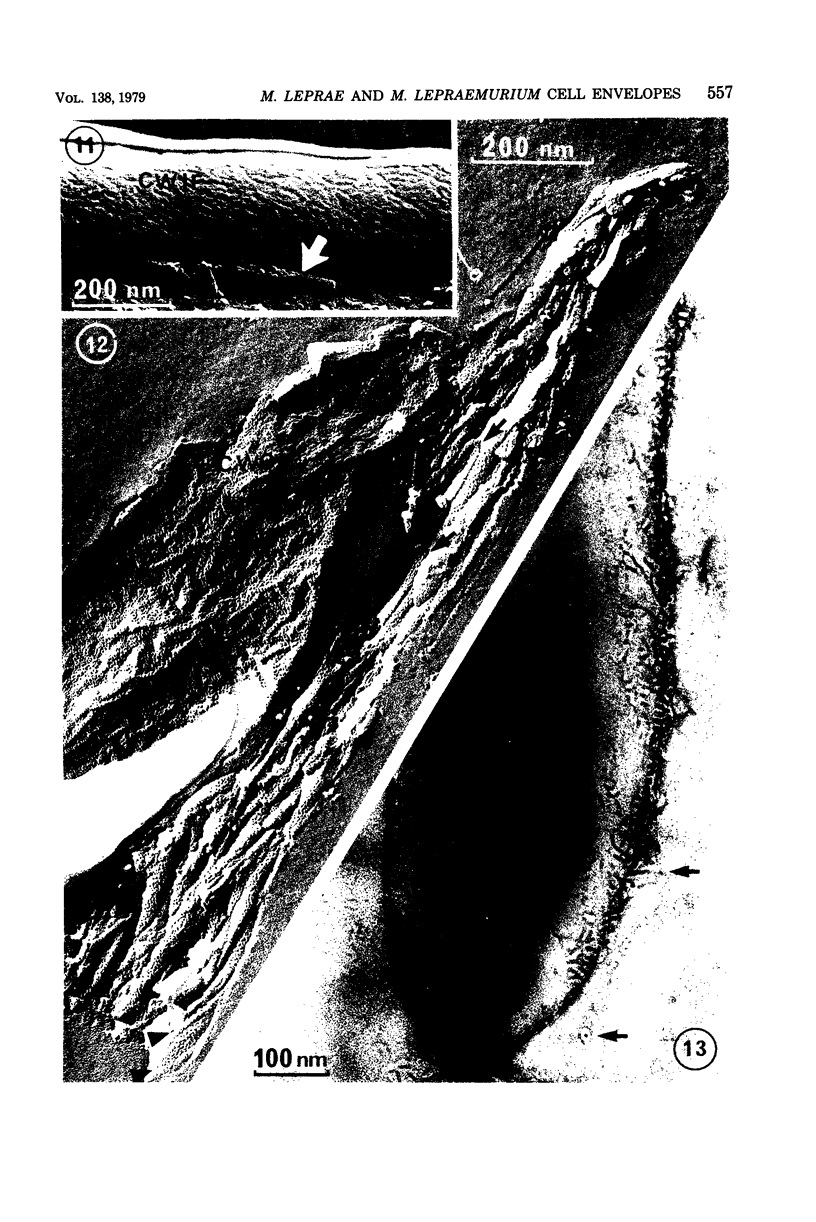
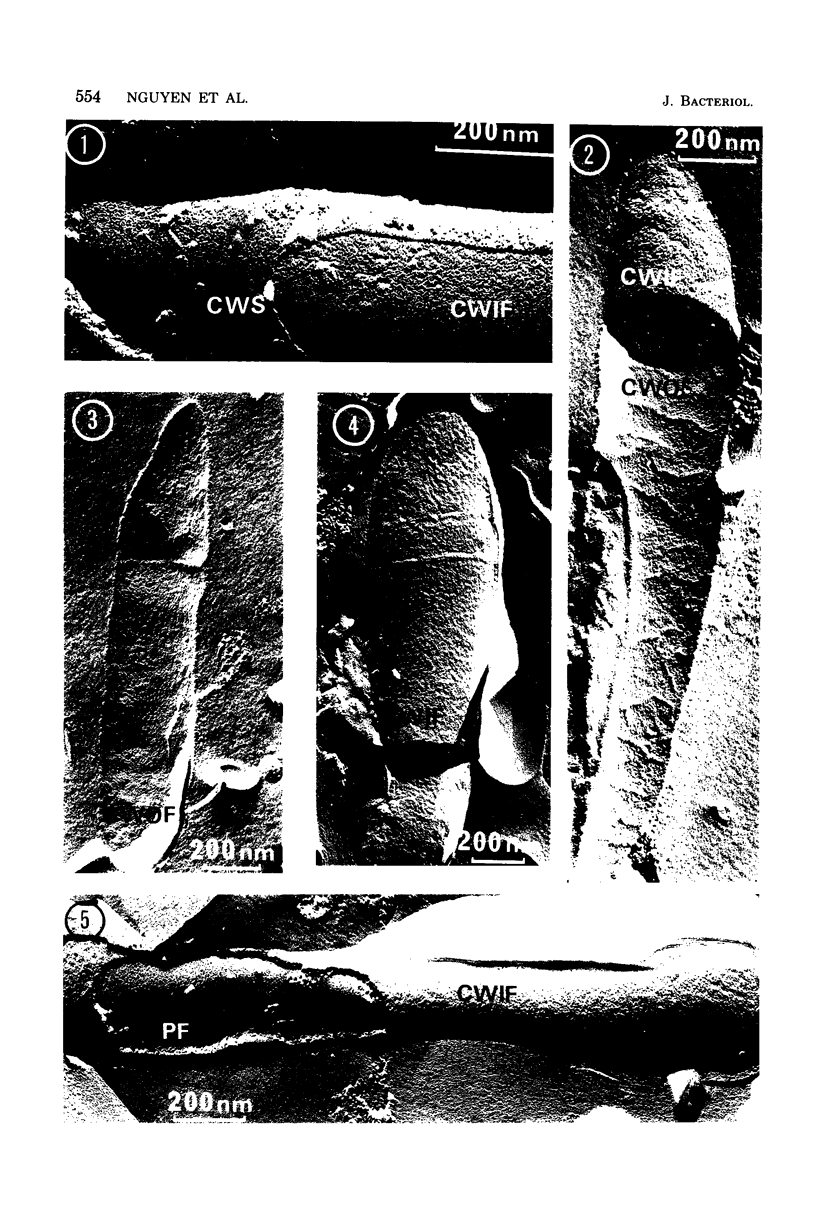
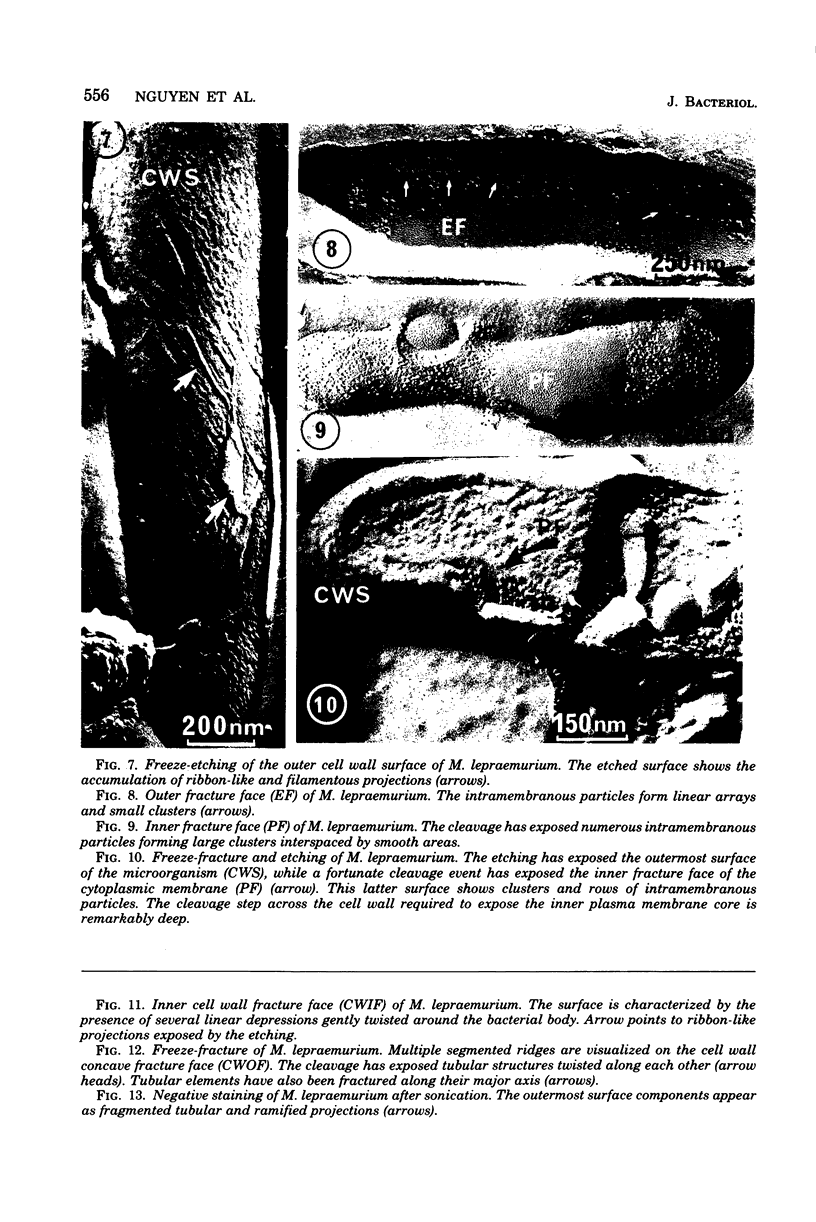
The structural properties of the cell envelopes of Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepraemurium were investigated by freeze-fracture, freeze-etching, and negative-staining techniques. Freeze-fracture split the cell wall and exposed the internal features of the peptidoglycolipid mycosidic filamentous network. The cell membrane was also split into two asymmetric faces. The external fracture face was characterized by linear arrays of intramembranous particles, whereas the protoplasmic fracture face showed randomly distributed clusters of particulate entities. Comparative analysis of the ultrastructural features observed in M. leprae and M. lepraemurium indicated that the organization of the cell envelope in these two species differed particularly with respect to the amount and complexity of the superficial peptidoglycolipid and mycosidic integument, which is poorly developed in the mycobacterium responsible for human disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma I., Yamamura Y., Tanaka Y., Kosaka K., Mori T. Cell wall of Mycobacterium lepraemurium strain Hawaii. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.515-518.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L., Kim K. S. Mycobacterium. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):217–372. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.217-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Jr, Willison J. H., Richardson C. L. Cellulose biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum: visualization of the site of synthesis and direct measurement of the in vivo process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4565–4569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P. Cell walls of Mycobacterium leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1976 Jan-Jun;44(1-2):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuchi A., Tokunaga T. Nature of the receptor substance of Mycobacterium smegmatis for D4 bacteriophage adsorption. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):404–411. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.404-411.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., White R. G. Surface peptido-glycolipid filaments on Mycobacterium leprae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Oct;9(4):539–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., McClatchy J. K., Martens B., Brokl O. Mycosides C: behavior as receptor site substance for mycobacteriophage D4. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):999–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.999-1003.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B. Phagocyte lysosomes: interactions with infectious agents, phagosomes, and experimental perturbations in function. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:507–533. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Chatterjee A. K., Sanderson K. E., Costerton J. W. Comparison of the cell envelope structure of a lipopolysaccharide-defective (heptose-deficient) strain and a smooth strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):930–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.930-941.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Salton M. R., Barksdale L. Ultrastructure of superficial mycosidic integuments of Mycobacterium sp. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):739–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.739-743.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. E. The fine structure of the cerebroside occurring in Gaucher's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):484–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Owen P. Bacterial membrane structure. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:451–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Shockman G. D., Higgins M. L. Structural arrangement of polymers within the wall of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):372–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.372-386.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vásquez C., Barrantes F. J., La Torre J. L., de Robertis E. Electron microscopy of proteolipid macromolecules from cerebral cortex. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]