Abstract
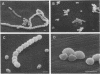
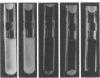
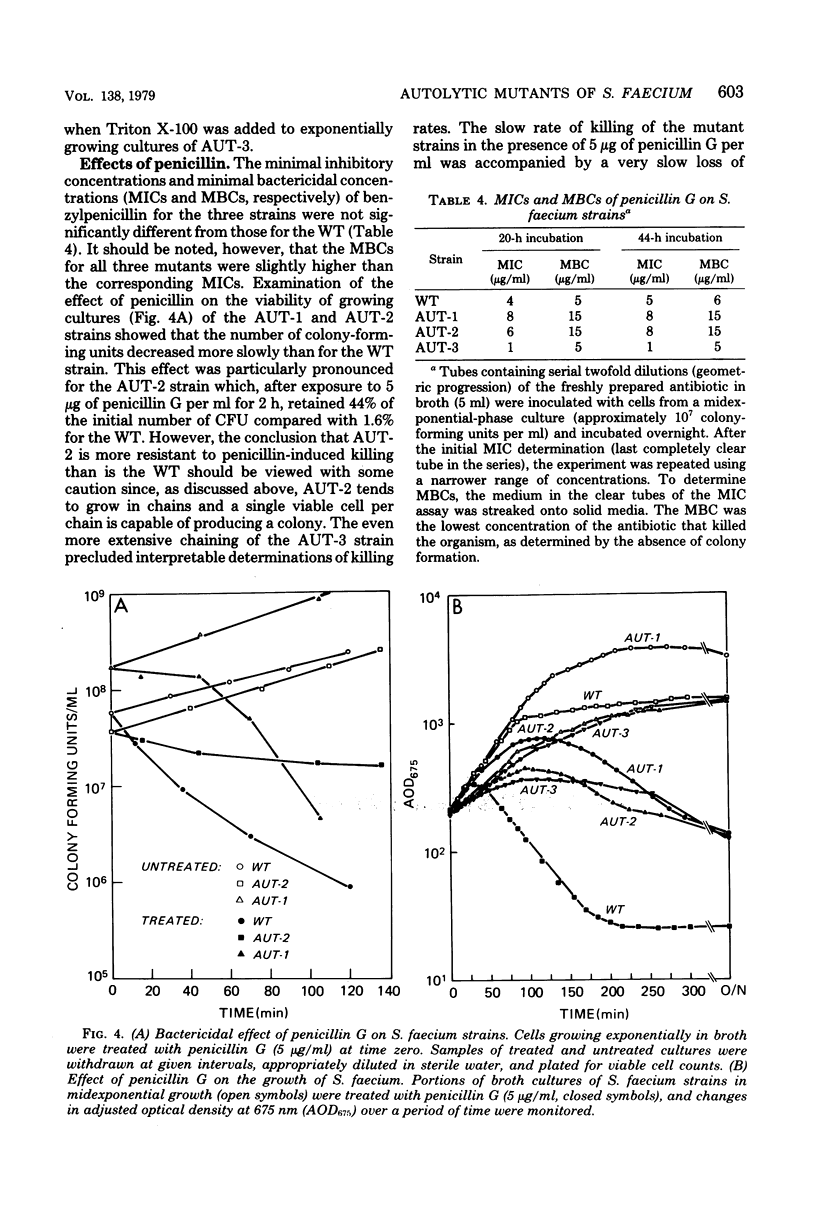
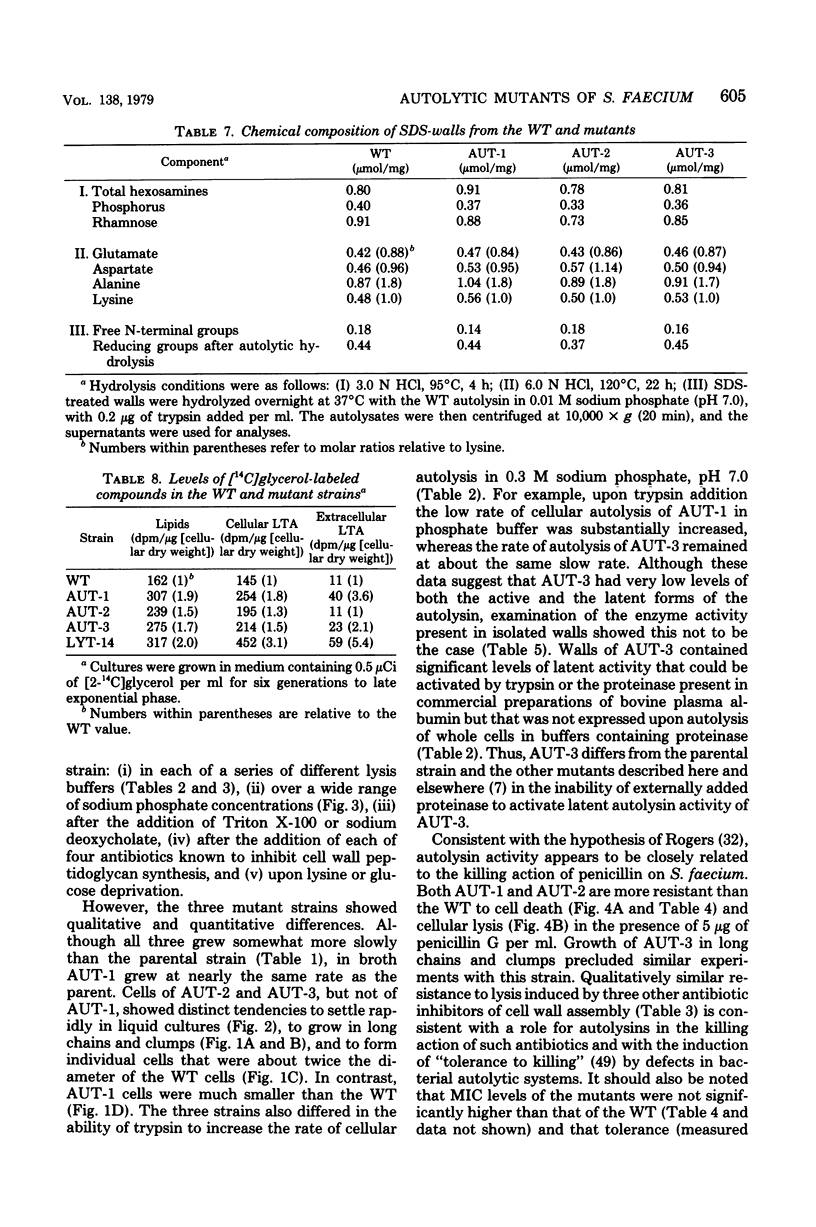
Three autolytic-defective mutants of Streptococcus faecium (S. faecalis ATCC 9790) were isolated. All three autolytic-defective mutants exhibited the following properties relative to the parental strain: (i) slower growth rates, especially in chemically defined medium; (ii) decreased rates of cellular autolysis and increased survival after exposure to antibiotics which block cell wall biosynthesis; (iii) decreased rates of cellular autolysis when treated with detergents, suspended in autolysis buffers, or grown in medium lacking essential cell wall precursors; (iv) a reduction in the total level of cellular autolytic enzyme (active plus latent forms of the enzyme); (v) an increased ratio of latent to active forms of autolysin; and (vi) increased levels of both cellular lipoteichoic acid and lipids.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. C., Wilson C. R., Lukehart S., Young F. E., Shiflett M. A. Analysis of autolysins in temperature-sensitive morphological mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):166–173. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.166-173.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N., Wong W., Young F. E., Gilpin R. W. Isolation and characterization of a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus deficient in autolytic activity. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):961–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.961-967.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Daneo-Moore L., Wicken A. J., Shockman G. D. Effect of lipoteichoic acid and lipids on lysis of intact cells of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1582–1584. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1582-1584.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Holtje J. V., Wicken A. J., Tomasz A., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of bacterial wall lysins by lipoteichoic acids and related compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90791-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Wicken A. J., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of wall autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis by lipoteichoic acid and lipids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):192–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.192-197.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover M. J., Thompson J. S., Shockman G. D. Autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis: release of soluble enzyme from cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90459-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Redman B. E., Shockman G. D. Autolytic defective mutant of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):631–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.631-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Cellular lysis of Streptococcus faecalis induced with triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.153-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P. Autolysin(s) of Bacillus subtilis as dechaining enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.494-499.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Beckman M. M., Cunningham W. P. Ultrastructural studies on a mutant of Bacillus subtilis whose growth is inhibited due to insufficient autolysin production. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1247–1257. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1247-1257.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Beckmann M. M. Mutant of Bacillus subtilis with a temperature-sensitive autolytic amidase. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):798–803. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.798-803.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein J. E., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzyme-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1427–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1427-1442.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. H., Kessler R. E., Tabak L. A., Shockman G. D. Limulus lysate activity of lipoteichoic acids. J Dent Res. 1977 Dec;56(12):1500–1500. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560121501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Rogers H. J. Characterization of Bacillus licheniformis 6346 mutants which have altered lytic enzyme activities. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):358–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.358-368.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinks R. P., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Cellular autolytic activity in synchronized populations of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.822-829.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Autolytic formation of protoplasts (autoplasts) of Streptococcus faecalis; location of active and latent autolysin. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1482–1493. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1482-1493.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Shockman G. D. Precursor-product relationship of intracellular and extracellular lipoteichoic acids of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.869-877.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Chan L., Glaser L. Turnover of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1820–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieringer R. A., Ambron R. T. A method for the specific labeling of the glycerol in glyceride-containing lipids of Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790. J Lipid Res. 1973 May;14(3):370–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Porres-Juan J. M., Shockman G. D. Dissociation of an autolytic enzyme-cell wall complex by treatment with unusually high concentrations of salt. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1134–1140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D., Higgins M. L., Porres-Juan J. Some properties of two autolytic-defective mutants of Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):423–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.423-431.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Relationship between the latent form and the active form of the autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):617–624. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.617-624.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Leonard C. G., Cole R. M. Autolytic activity associated with competent group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):257–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.257-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Bacterial growth and the cell envelope. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):194–214. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.194-214.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Forsberg C. W. Role of autolysins in the killing of bacteria by some bactericidal antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1235-1243.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Pooley H. M., Thurman P. F., Taylor C. Wall and membrane growth in bacilli and their mutants. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Sep;125 B(2):135–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D., KOLB J. J., TOENNIES G. Relations between bacterial cell wall synthesis, growth phase, and autolysis. J Biol Chem. 1958 Feb;230(2):961–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wheeler N., Laverdiere M., Blazevic D., Wilkinson B. J. A new type of penicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Cheney M. C. Autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. V. Nature of the autolysin-cell wall complex and its relationship to properties of the autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1199–1207. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1199-1207.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Conover M. J., Kolb J. J., Phillips P. M., Riley L. S., Toennies G. LYSIS OF STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81(1):36–43. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.36-43.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Thompson J. S., Conover M. J. The autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. II. Partial characterization of the autolysin and its substrate. Biochemistry. 1967 Apr;6(4):1054–1065. doi: 10.1021/bi00856a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soper J. W., Winter C. G. Role of cell wall antolysin in chain formation by a mutant strain of Streptococcus faecalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Shockman G. D. A modification of the Park and Johnson reducing sugar determination suitable for the assay of insoluble materials: its application to bacterial cell walls. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toennies G., Das D. N., Feng F. New observations on the determination of bacterial lipid phosphorus. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):484–485. doi: 10.1139/m68-079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Biological consequences of the replacement of choline by ethanolamine in the cell wall of Pneumococcus: chanin formation, loss of transformability, and loss of autolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):86–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Waks S. Mechanism of action of penicillin: triggering of the pneumococcal autolytic enzyme by inhibitors of cell wall synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Westphal M. Abnormal autolytic enzyme in a pneumococus with altered teichoic acid composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2627–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberger C. L., Angelo N. Purificationa and properties of a fructose-1,6-diphosphate-activated lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.717-724.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]