Abstract
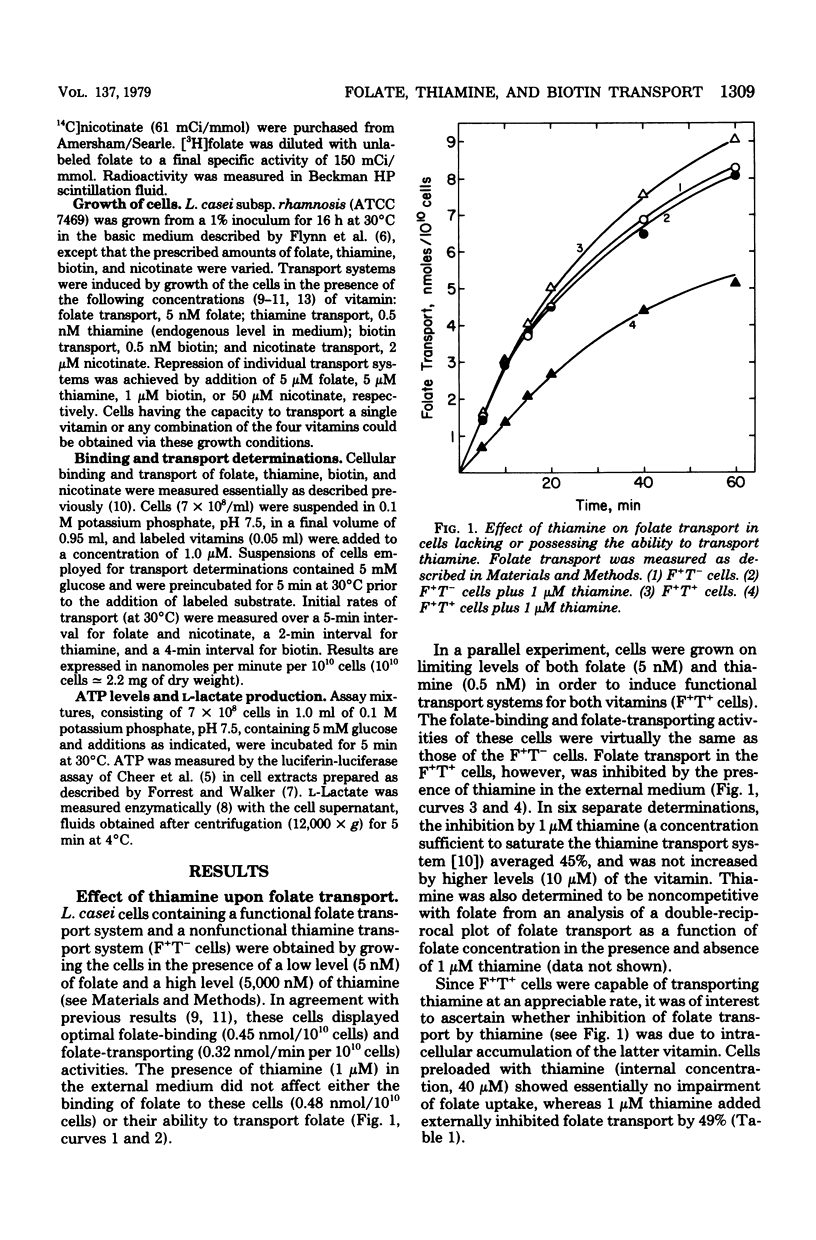
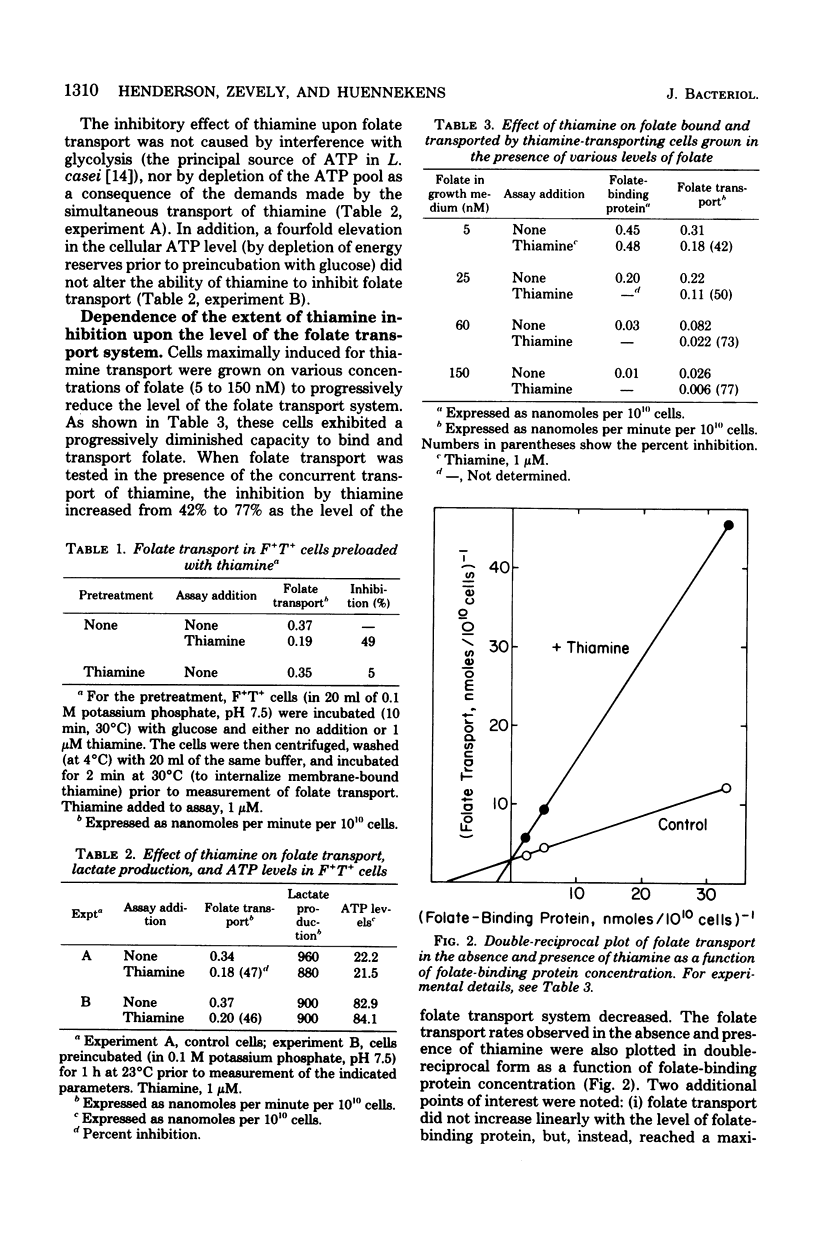
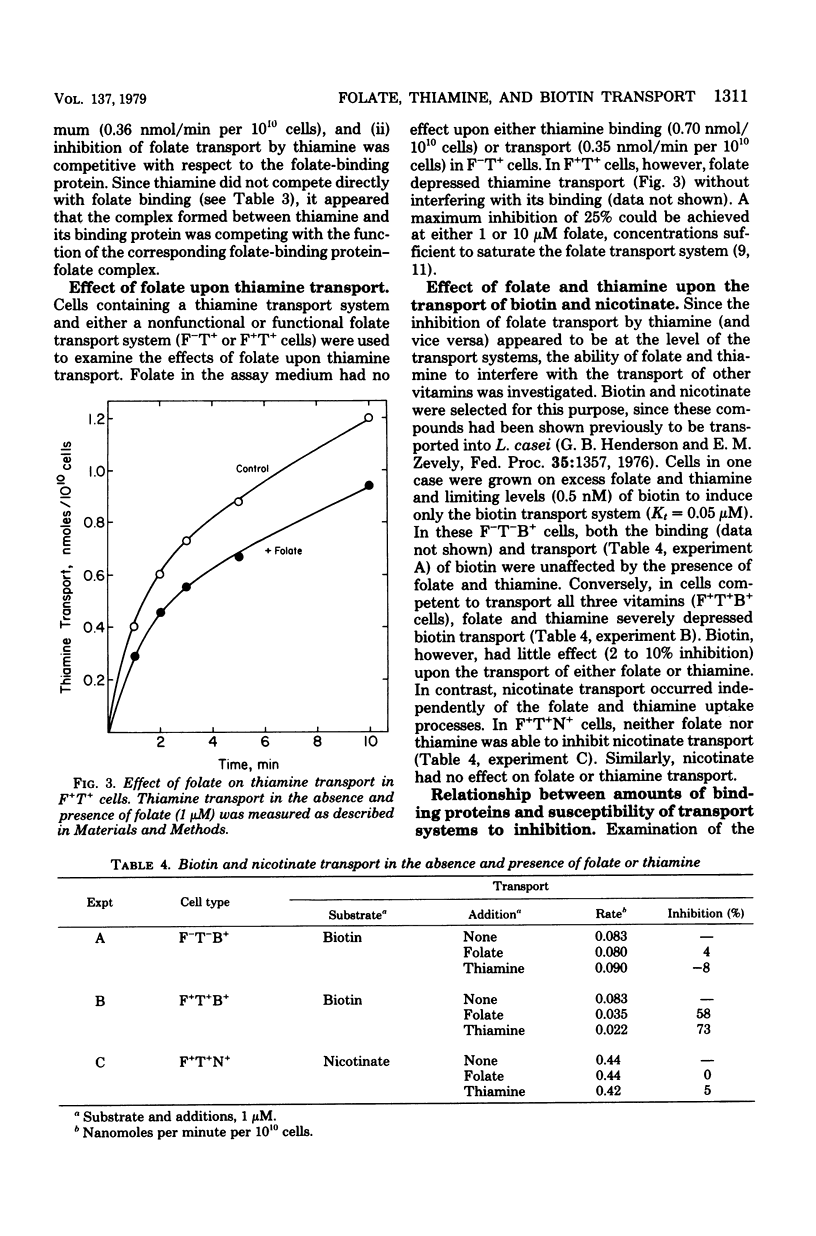
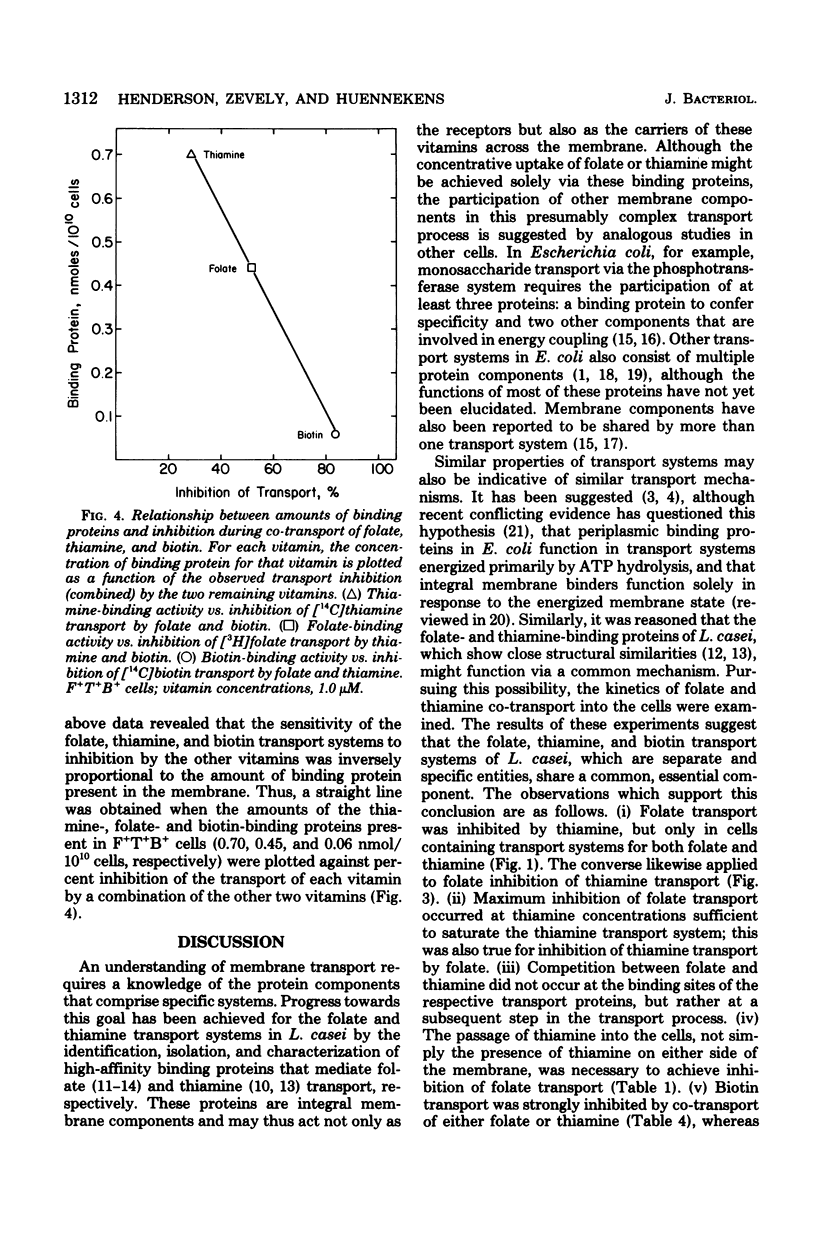
Lactobacillus casei cells have been shown previously to utilize two separate binding proteins for the transport of folate and thiamine. Folate transport, however, was found to be strongly inhibited by thiamine in spite of the fact that the folate-binding protein has no measurable affinity for thiamine. This inhibition, which did not fluctuate with intracellular adenosine triphosphate levels, occurred only in cells containing functional transport systems for both vitamins and was noncompetitive with folate but competitive with respect to the level of folate-binding protein. Folate uptake in cells containing optimally induced transport systems for both vitamins was inhibited by thiamine (1 to 10 μM) to a maximum of 45%; the latter value increased to 77% in cells that contained a progressively diminished folate transport system and a normal thiamine system. Cells preloaded with thiamine could transport folate at a normal rate, indicating that the inhibition resulted from the entry of thiamine rather than from its presence in the cell. In a similar fashion, folate (1 to 10 μM) did not interfere with the binding of thiamine to its transport protein, but inhibited thiamine transport (to a maximum of 25%). Competition also extended to biotin, whose transport was strongly inhibited (58% and 73%, respectively) by the simultaneous uptake of either folate or thiamine; biotin, however, had only a minimal effect on either folate or thiamine transport. The nicotinate transport system was unaffected by co-transport with folate, thiamine, or biotin. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the folate, thiamine, and biotin transport systems of L. casei each function via a specific binding protein, and that they require, in addition, a common component present in limiting amounts per cell. The latter may be a protein required for the coupling of energy to these transport processes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Heppel L. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the shock-sensitive and shock-resistant amino acid permeases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7747–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheer S., Gentile J. H., Hegre C. S. Improved methods for ATP analysis. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):102–114. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORREST W. W., WALKER D. J. SYNTHESIS OF RESERVE MATERIALS FOR ENDOGENOUS METABOLISM IN STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1448–1452. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1448-1452.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B., Huennekens F. M. Transport of folate compounds into Lactobacillus Casei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):722–728. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B., Zevely E. M. Binding and transport of thiamine by Lactobacillus casei. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1190–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1190-1196.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B., Zevely E. M., Huennekens F. M. Folate transport in Lactobacillus casei: solubilization and general properties of the binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):712–717. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B., Zevely E. M., Huennekens F. M. Purification and properties of a membrane-associated, folate-binding protein from Lactobacillus casei. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3760–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B., Zevely E. M., Kadner R. J., Huennekens F. M. The folate and thiamine transport proteins of Lactobacillus casei. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(2):239–247. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. I. Isolation of a phosphotransferase system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1393–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. II. Characterization of constitutive membrane-bound enzymes II of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1407–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S. G., Ames G. F. The hisP protein, a known histidine transport component in Salmonella typhimurium, is also an arginine transport component. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.107-113.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L., Anderson J. J., Mayo M. M., Quay S. C. Leucine binding protein and regulation of transport in E. coli. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(3):419–431. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. R., Rotman B. Evidence for binding protein-independent substrate translocation by the methylgalactoside transport system of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):423–427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Postma P. W. The energetics of bacterial active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:523–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. P., Bragg P. D. Energetics of galactose, proline, and glutamine transport in a cytochrome-deficient mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(3):389–398. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



