Abstract
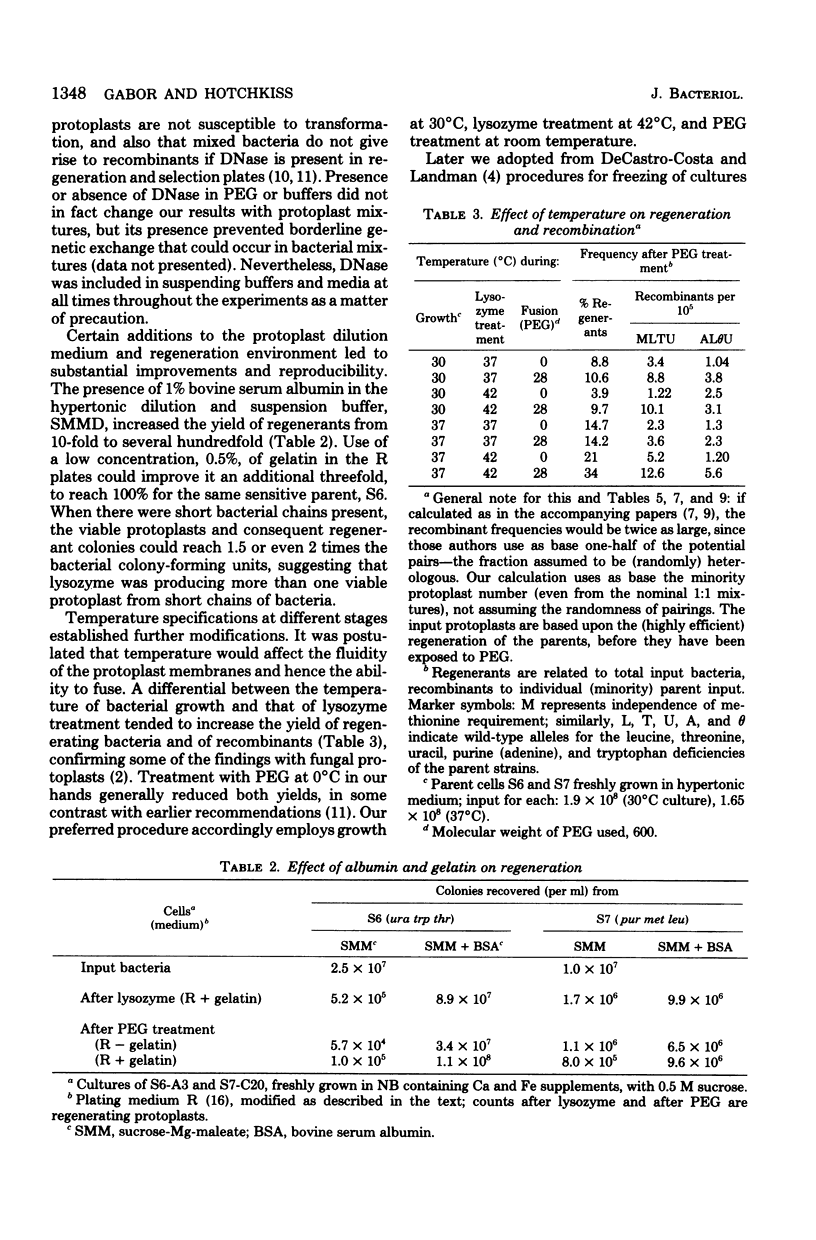
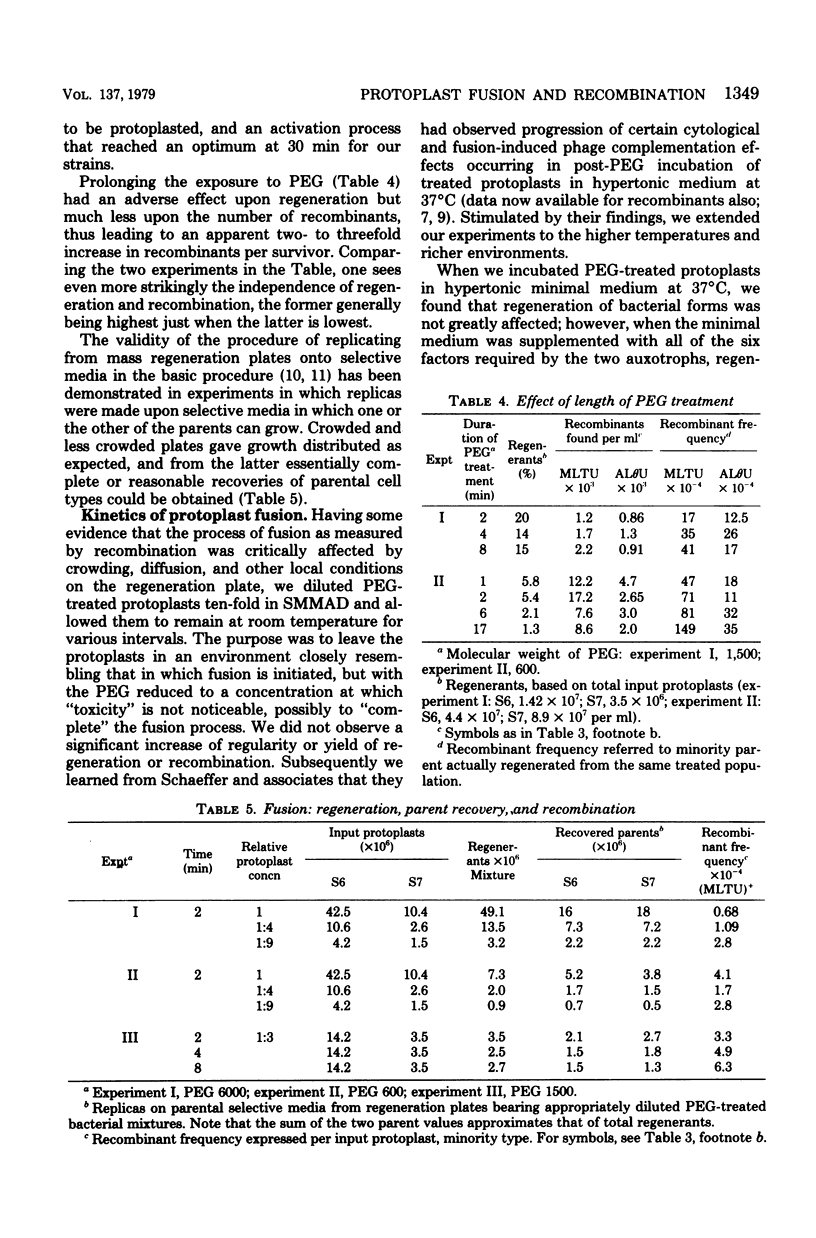
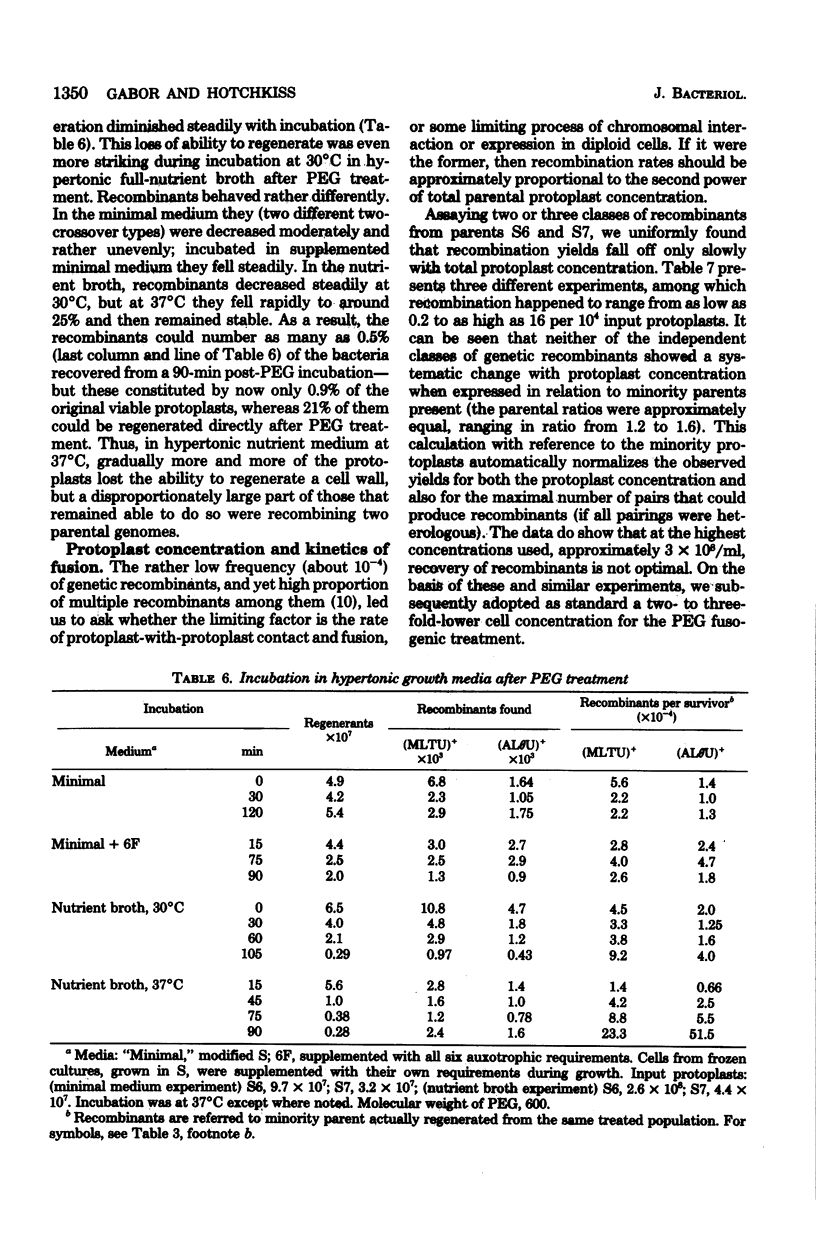
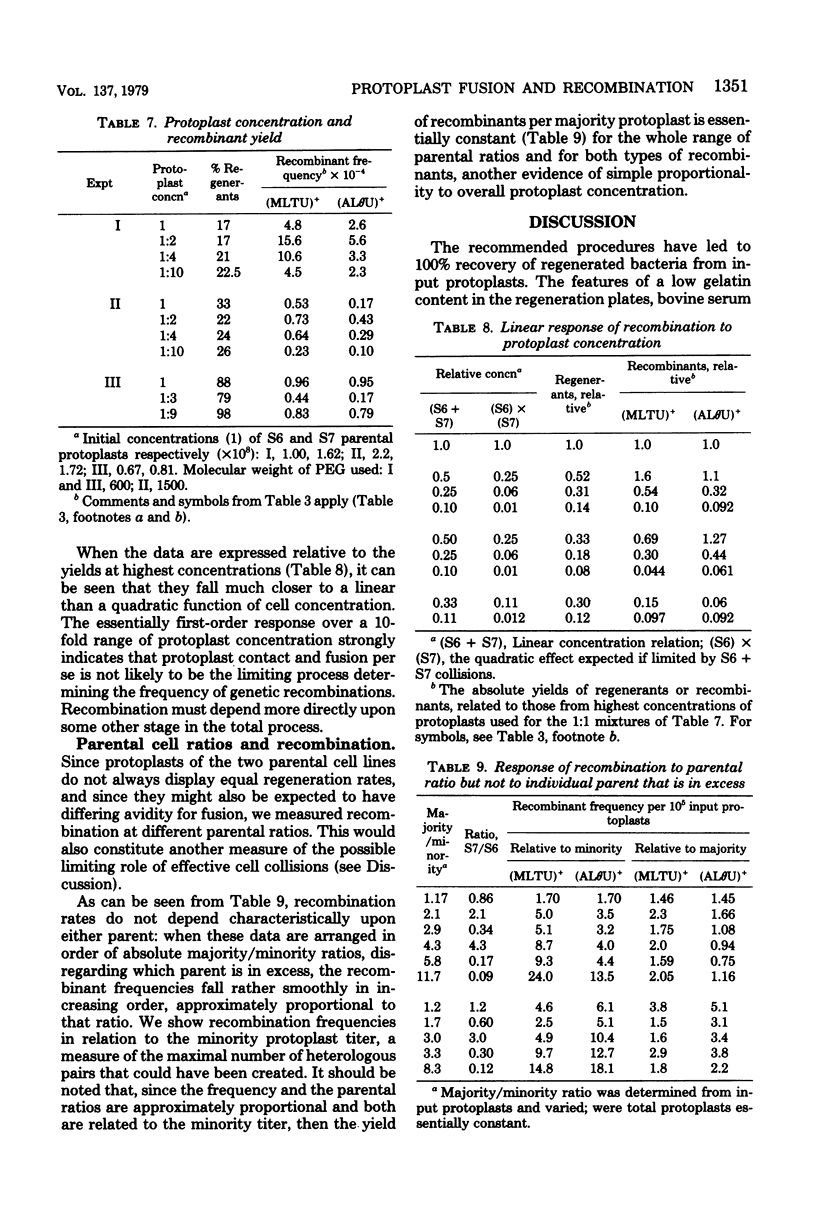
Bacterial protoplast fusion, induced by polyethylene glycol, has been made more regular and convenient by further specification and improvement of various steps in the previously used procedure. These have made it possible to obtain regularly 100% regeneration of Bacillus subtilis cells from protoplasts before treatment with polyethylene glycol and yields of 10 to 75% from polyethylene glycol-treated protoplasts. Genetic recombination frequencies do not increase correspondingly. Also, when regeneration is reduced by various experimental conditions, recombination does not decrease in proportion. It is concluded that regeneration of recombinant-forming cells is independently determined and not closely related to the average regeneration for the population. Kinetic studies with varying individual parental or total protoplast concentrations strongly indicate that protoplast collision and contact is not the limiting factor determining the number of genetic recombinants obtained. Recombination approximates a linear, rather than quadratic, function of the total or of the majority protoplast population present, from which it is concluded that fusion events are always adequate to produce substantially more potential recombinants than are registered. The strong effect of the majority/minority ratio upon the number of minority cells that become recombinant is independent of which parent is in excess. This shows in a direct and physiological way that both parents are equivalent partners in their genetic contributions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anné J., Peberdy J. F. Conditions for induced fusion of fungal protoplasts in polyethylene glycol solutions. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Nov 7;105(3):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00447138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., O'Malley K. A., Wheeler T. B. Polyethylene glycol-induced mammalian cell hybridization: effect of polyethylene glycol molecular weight and concentration. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF01538965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCastro-Costa M. R., Landman O. E. Inhibitory protein controls the reversion of protoplasts and L forms of Bacillus subtilis to the walled state. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):678–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.678-689.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Alföldi L. Fusion of protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2147–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Demiri E., Alföldi L. Polyethylene glycol-induced fusion of heat-inactivated and living protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):68–70. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.68-70.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Lheritier A. M., Sanchez-Rivas C., Schaeffer P. Electron microscopic study of Bacillus subtilis protoplast fusion. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1354–1361. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1354-1361.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Rivas C., Garro A. J. Bacterial fusion assayed by a prophage complementation test. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1340-1345.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Cami B., Hotchkiss R. D. Fusion of bacterial protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Hotchkiss R. D. Fusion of bacterial protoplasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;20:149–158. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)62017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tichy P., Landman O. E. Transformation in quasi spheroplasts of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.42-51.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wax R., Freese E. Initiation of the germination of Bacillus subtilis spores by a combination of compounds in place of L-alanine. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):433–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.433-438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Bott K. F. Effects of lysozyme on competence for Bacillus subtilis transfection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):464–475. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Rogers H. J. Isolation and characterization of cell wall-defective variants of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):456–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.456-465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Arndt W. F. PRODUCTION OF PROTOPLASTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI BY LYSOZYME TREATMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):586–590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



