Abstract
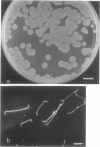
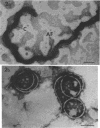
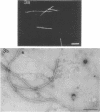
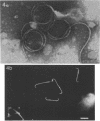
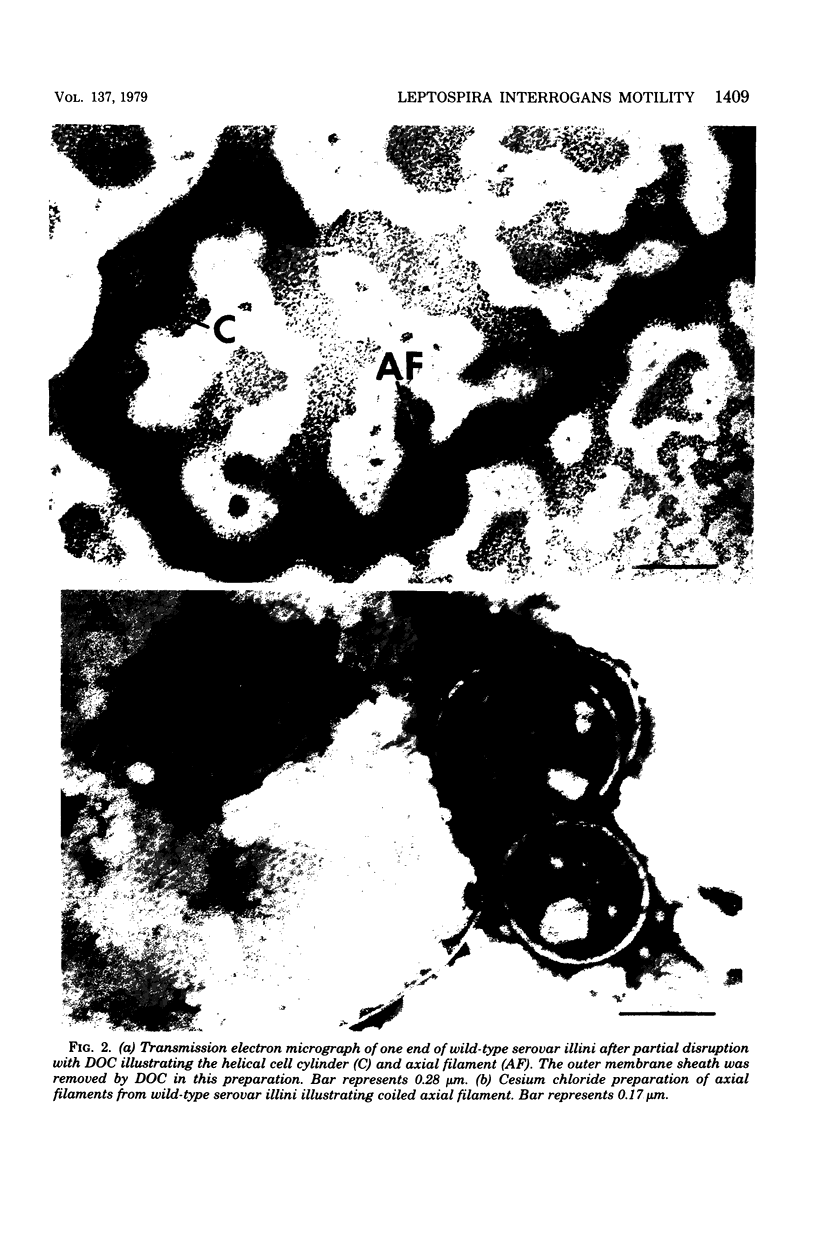
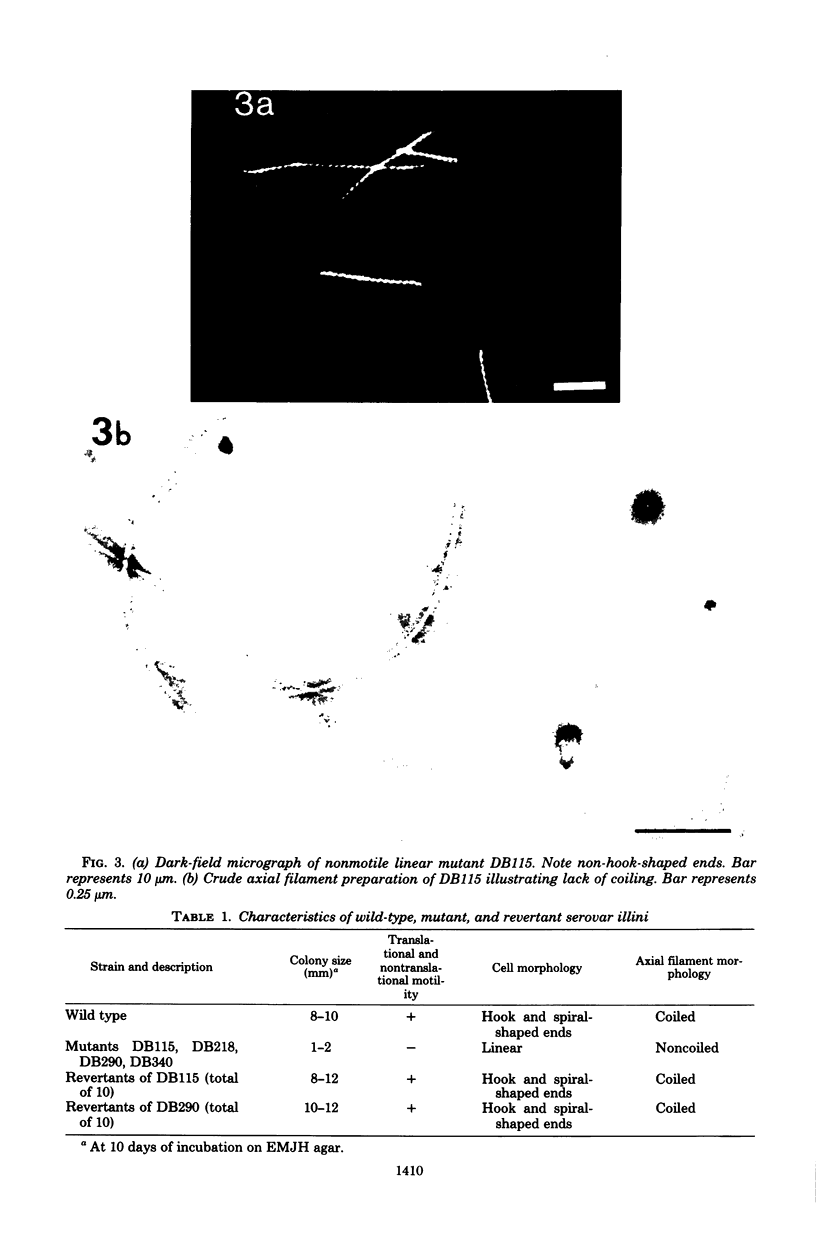
Motility mutants of Leptospira interrogans serovar illini were isolated and analyzed by dark-field and electron microscopy. Mutants were obtained by screening for small colonies after nitrosoguanidine treatment. One class of mutants did not have hook- or spiral-shaped ends. In addition, the axial filaments from these mutants were not coiled. An analysis of revertants of two of the mutants in this class indicated that the mutations were pleiotropic with respect to motility, hook- and spiral-shaped ends, and axial filament coiling. We conclude that the axial filaments and the hook- and spiral-shaped ends are involved in L. interrogans motility.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bharier M. A., Rittenberg S. C. Chemistry of axial filaments of Treponema zuezerae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):422–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.422-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch-Andersen A., Hovind Hougen K., Borg-Petersen C. Electron microscopy of Leptospira. 1. Leptospira strain Pomona. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):665–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E. Physiology and evolution of spirochetes. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):181–204. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.181-204.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A., Faine S. Electron-microscopic evidence for reactions of axial filaments of Leptospira with IgM and IgG antibodies. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(4):571–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon N. W., Johnson R. C., Peterson D. Amino acid biosynthesis in the spirochete Leptospira: evidence for a novel pathway of isoleucine biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):203–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.203-211.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox P. J., Twigg G. I. Leptospiral motility. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):260–261. doi: 10.1038/250260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAINE S., VANDERHOEDEN J. VIRULENCE-LINKED COLONIAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL VARIATION IN LEPTOSPIRA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1493–1496. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1493-1496.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerola N., Ingraham J. L., Cerdá-Olmedo E. Induction of closely linked multiple mutations by nitrosoguanidine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):122–125. doi: 10.1038/newbio230122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K. Determination by means of electron microscopy of morphological criteria of value for classification of some spirochetes, in particular treponemes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1976;(255):1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C. The spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Asakura S. Helical transformations of Salmonella flagella in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):167–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauman R. K., Holt S. C., Cox C. D. Purification, ultrastructure, and composition of axial filaments from Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):264–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.264-280.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON C. F., WHITE F. H. ULTRASTRUCTURAL VARIATIONS BETWEEN HOOKED AND NONHOOKED LEPTOSPIRES. J Infect Dis. 1964 Feb;114:69–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W., Koffler H. Bacterial flagella. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:219–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy D. N., Hanson L. E. Agar overlay method for growth of leptospires in solid medium. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jul;32(7):1125–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy D. N., Hanson L. E. Colonial and morphologic variations of Leptospira illini strain 3055. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Aug;33(8):1723–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]