Abstract
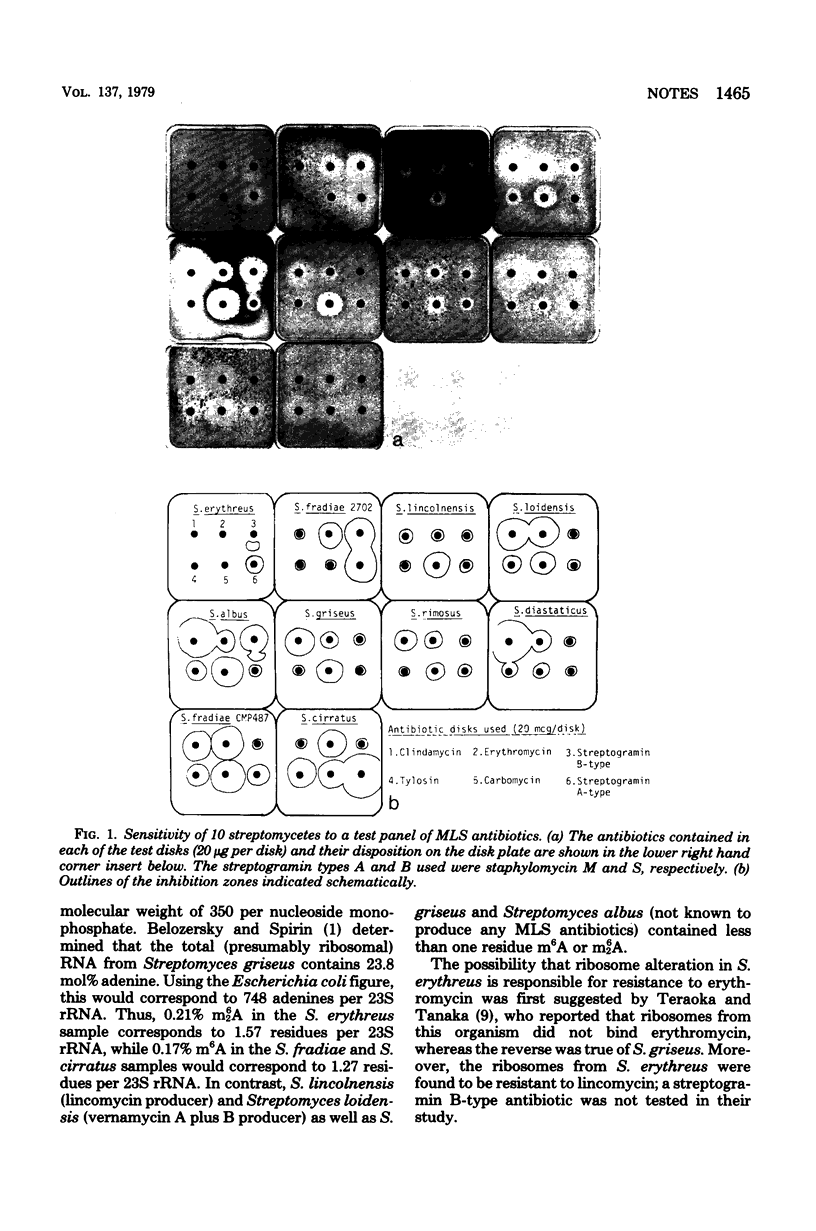
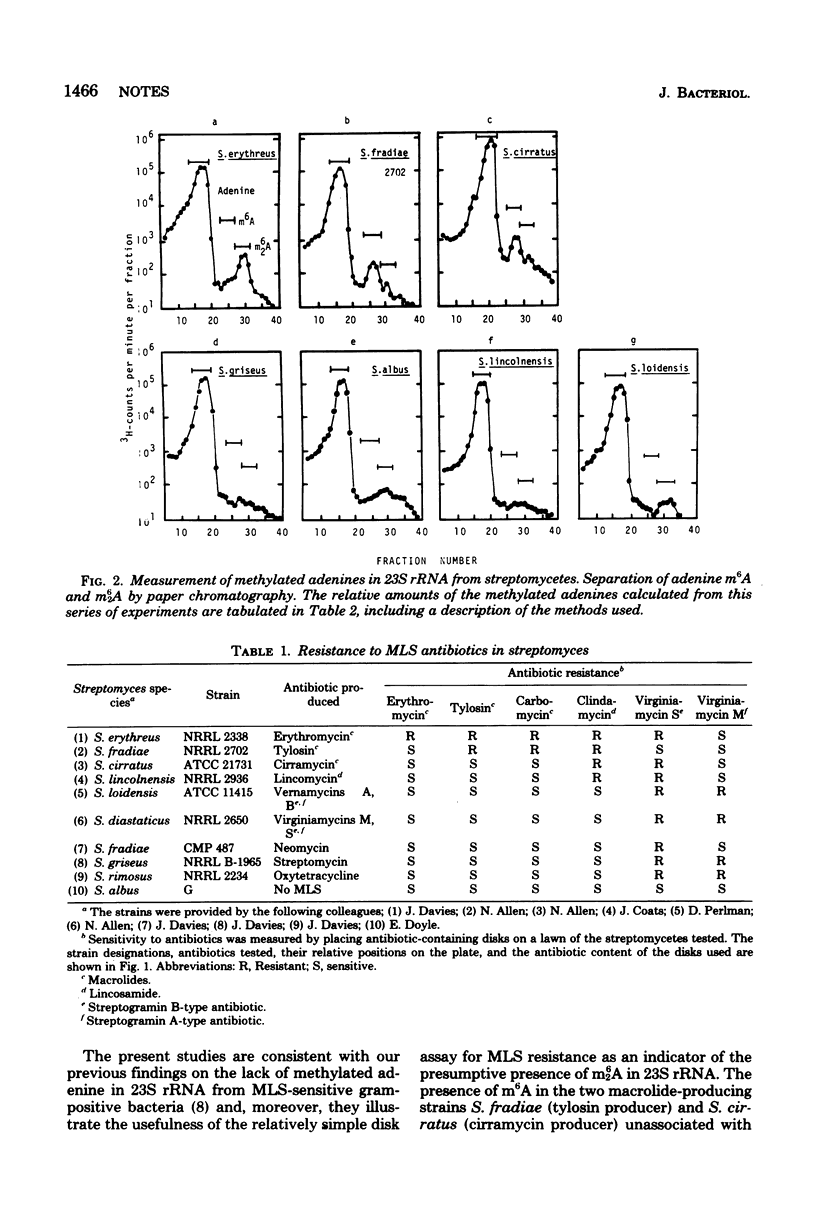
Coresistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin B-type (MLS) antibiotics by a common biochemical mechanism characterizes clinically resistant pathogens. Of 10 streptomycetes tested for resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin B-type antibiotics, only 1, Streptomyces erythreus, the organism used for production of erythromycin, was found resistant to all three classes; moreover, it was the only streptomycete in the series tested found to contain N6-dimethyladenine (m62A) in 23S ribosomal ribonucleic acid, the structural alteration of ribosomal ribonucleic acid associated with clinical resistance. Of the seven streptomycetes tested for the presence of m62A and N6-methyladenine (m6A), two, S. fradiae and S. cirratus, which produce the macrolide antibiotics tylosin and cirramycin, respectively, were found to contain m6A, but not m62A. The remaining strains tested, including strains which produce lincomycin and streptogramins, contained neither m6A nor m62A.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELOZERSKY A. N., SPIRIN A. S. A correlation between the compositions of deoxyribonucleic and ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1958 Jul 12;182(4628):111–112. doi: 10.1038/182111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Franke A. E. Characterization of a plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):534–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P. M., Carlier C., Chabbert Y. A. Plasmid-linked tetracycline and erythromycin resistance in group D "streptococcus". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bouanchaud D. H., Bieth G., Chabbert Y. A. R plasmids in Streptococcus agalactiae (group B). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):795–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B. Altered methylation of ribosomal RNA in an erythromycin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B., Fahnestock S. R., Nomura M. Alteration of 23 S ribosomal RNA and erythromycin-induced resistance to lincomycin and spiramycin in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Systematic difference in the methylation of ribosomal ribonucleic acid from gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):771–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.771-774.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tanaka K. Properties of ribosomes from Streptomyces erythreus and Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):316–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.316-321.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Siddhikol C., Lai C. J., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: requirements for induction. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):835–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.835-847.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]