Abstract
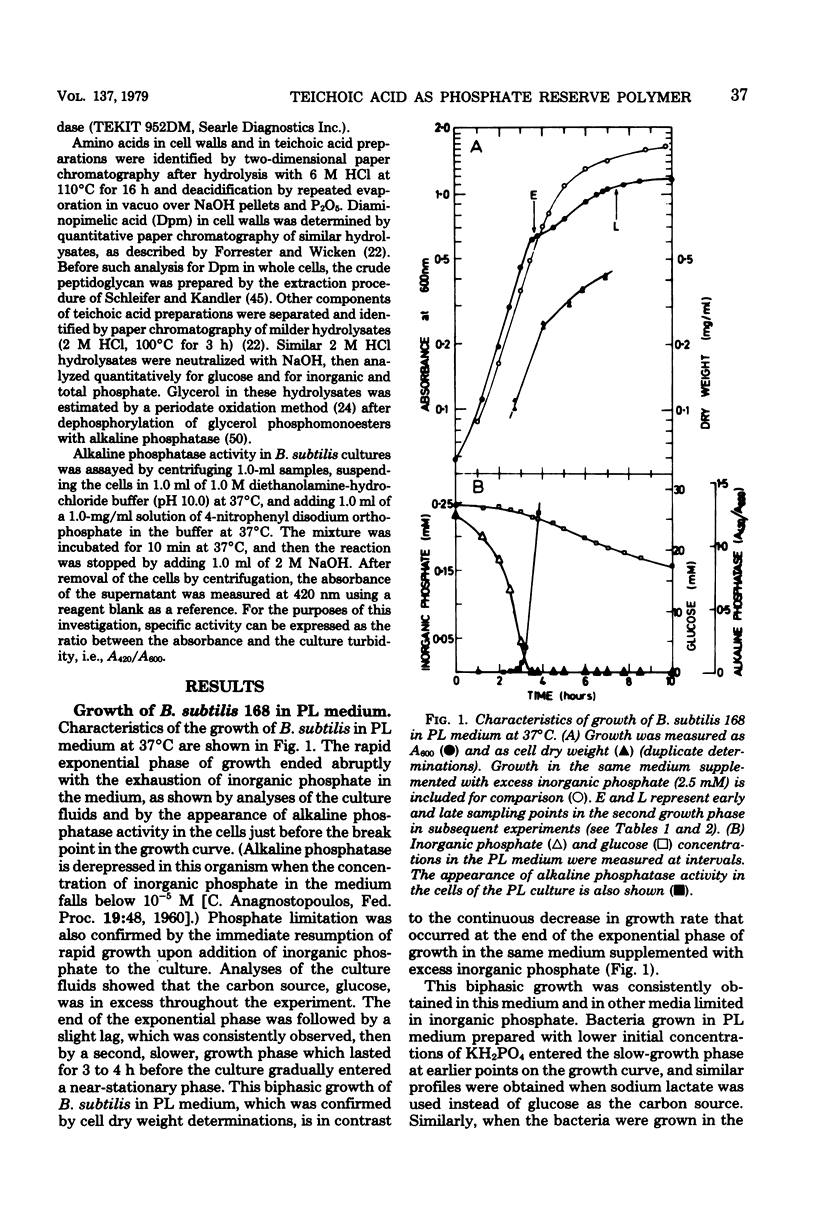
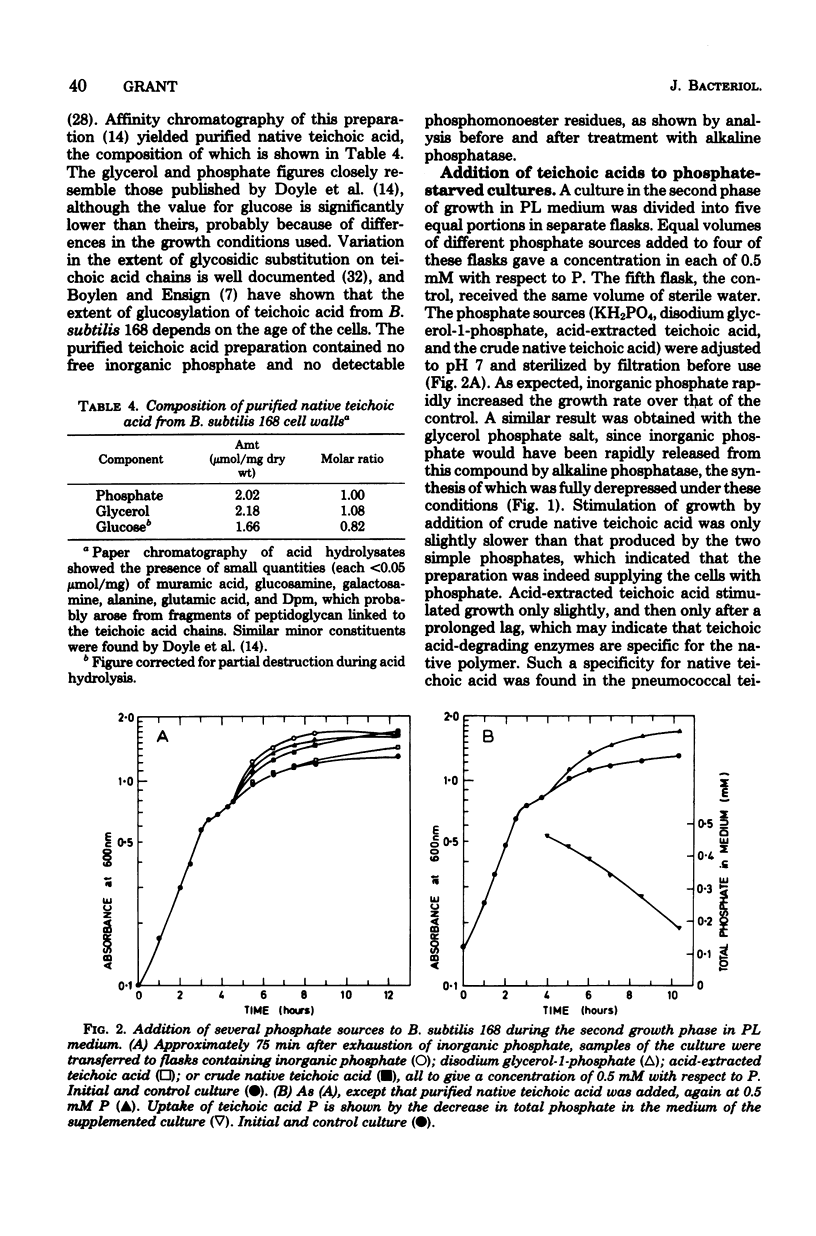
Although exponential growth of Bacillus subtilis 168 in a phosphate-limited medium halted with the exhaustion of inorganic phosphate, the bacteria continued to grow at a slower rate for a further 3 to 4 h at 37 degrees C. This postexponential growth in the absence of an exogenous phosphate supply was accompanied by a loss of teichoic acid from the cell walls of the bacteria. Quantitative analysis of walls and culture fluids showed that the phosphate loss from the walls could not be accounted for by an increase in phosphate-containing compounds in the medium, which implied that the cells were using their own wall teichoic acids to supply phosphate necessary for growth. Addition of exogenous teichoic acid to phosphate-starved cultures resulted in stimulation of growth and in the simultaneous disappearance of teichoic acid phosphate from the medium. It is proposed that teichoic acids, which can contain more than 30% of the total phosphorus of exponential-phase cells, can be used as a reserve phosphate source when the bacteria are starved for inorganic phosphate.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Coapes H. E. Bacteriophage SP50 as a marker for cell wall growth in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1195-1206.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H., Brooks D., Young F. E. Regulation of the bacterial cell wall: analysis of a mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in biosynthesis of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.281-290.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylen C. W., Ensign J. C. Ratio of teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in cell walls of Bacillus subtilis following spire germination and during vegetative growth. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):421–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.421-427.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Doyle R. J., Streips U. N. Comparison of various procedures for removing proteins and nucleic acids from cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(6):479–488. doi: 10.1080/00327487608069130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaloupka J., Krecková P. Characterization of degradation products of the cell wall released during growth and sporulation of Bacillus megaterium. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1974;19(4):292–300. doi: 10.1007/BF02873221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain S. Variations d'activités enzymatiques chez Bacillus megaterium dans différentes conditions de sporulation. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 Nov 17;281(20):1529–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Birdsell D. C., Young F. E. Isolation of the teichoic acid of Bacillus subtilis 168 by affinity chromatography. Prep Biochem. 1973;3(1):13–18. doi: 10.1080/00327487308061485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., McDannel M. L., Helman J. R., Streips U. N. Distribution of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):152–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The location of N-acetylgalactosamine in the walls of Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):691–696. doi: 10.1042/bj1300691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Tempest D. W. Control of teichoic acid and teichuronic acid biosyntheses in chemostat cultures of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(1):1–5. doi: 10.1042/bj1110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The wall content and composition of Bacillus substilis var. niger grown in a chemostat. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):367–373. doi: 10.1042/bj1180367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrati-Elizur E. Spontaneous transformation in Bacillus subtilis. Genet Res. 1968 Feb;11(1):83–96. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielder F., Glaser L. Assembly of bacterial cell walls. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 28;300(4):467–485. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester I. T., Wicken A. J. The chemical composition of the cell walls of some thermophilic bacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jan;42(1):147–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-1-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Wyrick P. B., Ward J. B., Rogers H. J. Effect of phosphate limitation on the morphology and wall composition of Bacillus licheniformis and its phosphoglucomutase-deficient mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):969–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.969-984.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAHAN D. J., OLLEY J. N. Chemical nature of monophosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):813–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Inorganic polyphosphates in biology: structure, metabolism, and function. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):772–794. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.772-794.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. Autolysis of isolated cell walls of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346 and Bacillus subtilis Marburg Strain 168. Separation of the products and characterization of the mucopeptide fragments. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):849–860. doi: 10.1042/bj1190849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Pavlik J. G., Rogers H. J., Tanner P. J. Organization of polymers in the cell walls of some bacilli. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):642–644. doi: 10.1038/219642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey H., Sueda S., Cheah S. C., Baddiley J. Control of teichoic acid synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 9945. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):169–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Teichoic acid phosphorylcholine esterase. A novel enzyme activity in pneumococcus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):7032–7034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata S., Tochikubo K., Kato K., Hirata T., Kotani S., Yagi K. Microorganism capable of decomposing N-acetylglucosaminyl ribitol teichoic acid of Staphylococcus aureus. Jpn J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;20(2):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1976.tb00918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hégarat J. C., Anagnostopoulos C. Purification, subunit structure and properties of two repressible phosphohydrolases of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):525–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Chan L., Glaser L. Turnover of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1820–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Glaser L. On the mode of in vivo assembly of the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1180–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Glaser L. Periplasmic nucleoside diphosphate sugar hydrolase from Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 3;9(5):1140–1147. doi: 10.1021/bi00807a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Glaser L. Turnover of the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis W-23 during logarithmic growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 22;39(4):699–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Layered distribution, according to age, within the cell wall of bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1139–1147. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1139-1147.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Turnover and spreading of old wall during surface growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1127–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1127-1138.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Medveczky N., La Nauze J. M. Phosphate transport in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger R. F. Control of teichoic and teichuronic acid biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis 168trp. Evidence for repression of enzyme synthesis and inhibition of enzyme activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):516–524. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Tsugita A. Phosphoesterases of Bacillus subtilis. I. Purification and properties of phosphodiesterases. J Biochem. 1966 Oct;60(4):372–380. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKEN A. J., BADDILEY J. Structure of intracellular teichoic acids from group D streptococci. Biochem J. 1963 Apr;87:54–62. doi: 10.1042/bj0870054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels J. G. Control of cell-wall glucan degradation during development in Schizophyllum commune. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1966;32(4):341–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02097484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise E. M., Jr, Glickman R. S., Teimer E. Teichoic acid hydrolase activity in soil bacteria (Bacillus subtilis-sporulation-phosphodiesterase-polyamines-concanavalin A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):233–237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W., Young F. E., Chatterjee A. N. Regulation of bacterial cell walls: turnover of cell wall in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):837–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.837-843.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. A., Tristram H. Localization in the Cell and Extraction of Alkaline Phosphatase from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1045-1051.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Variation in the chemical composition of the cell walls of Bacillus subtilis during growth in different media. Nature. 1965 Jul 3;207(992):104–105. doi: 10.1038/207104b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rio L. A., Berkeley R. C. Exo-beta-N-acetylmuramidase--a novel hexosaminidase. Production by Bacillus subtilis B, purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):3–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



