Abstract
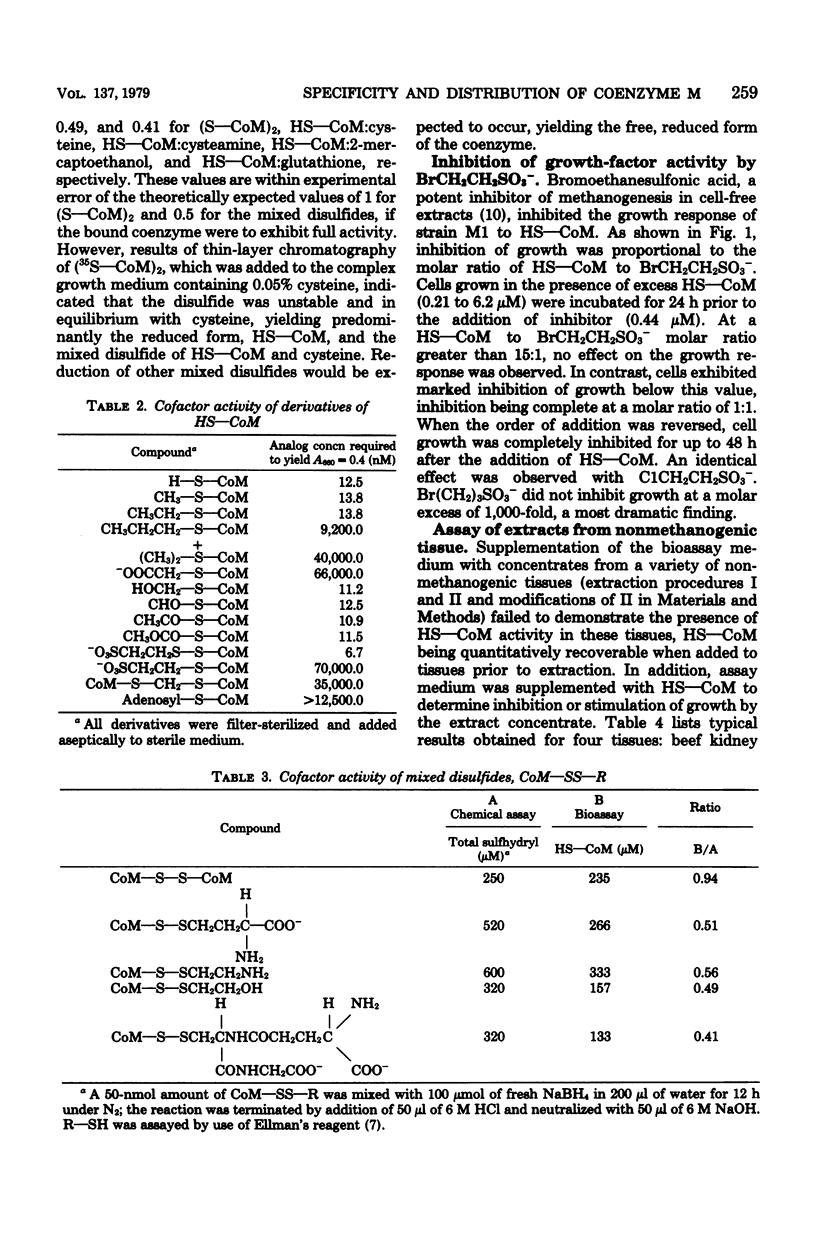
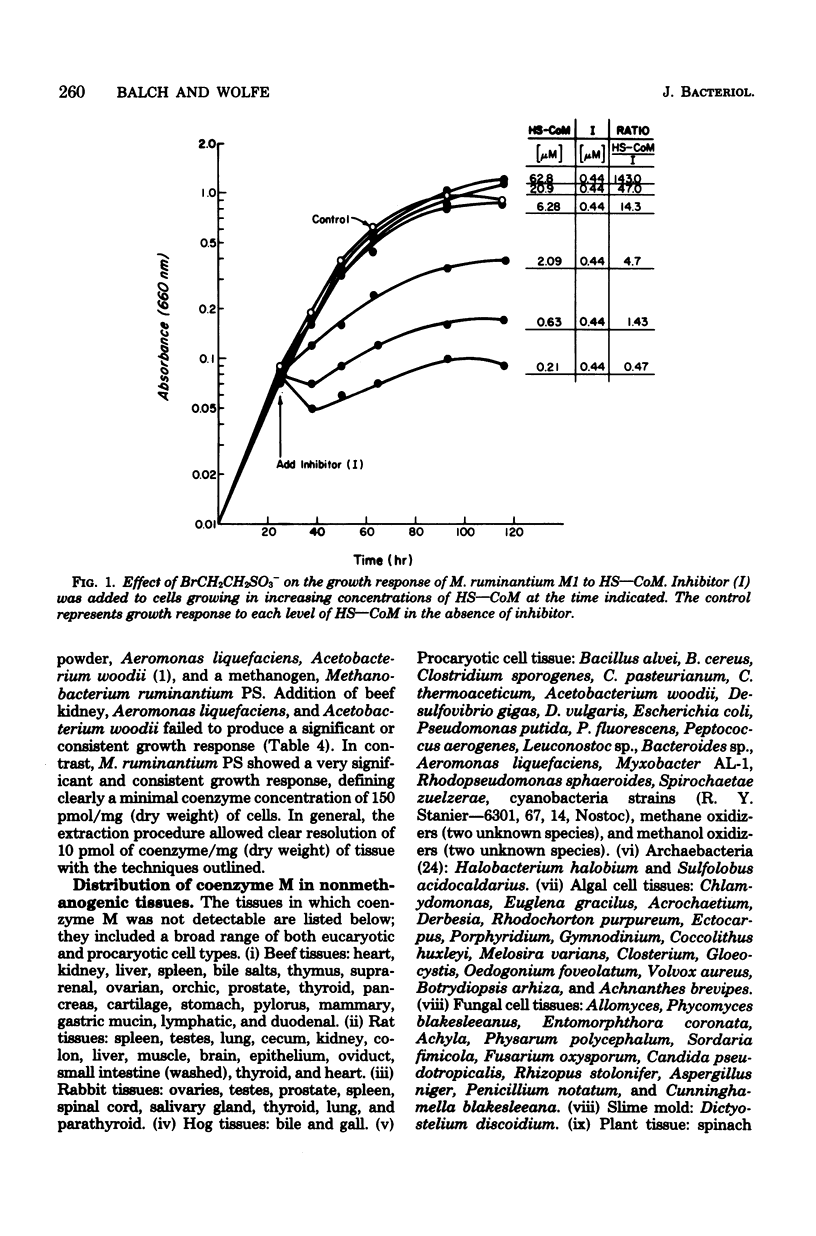
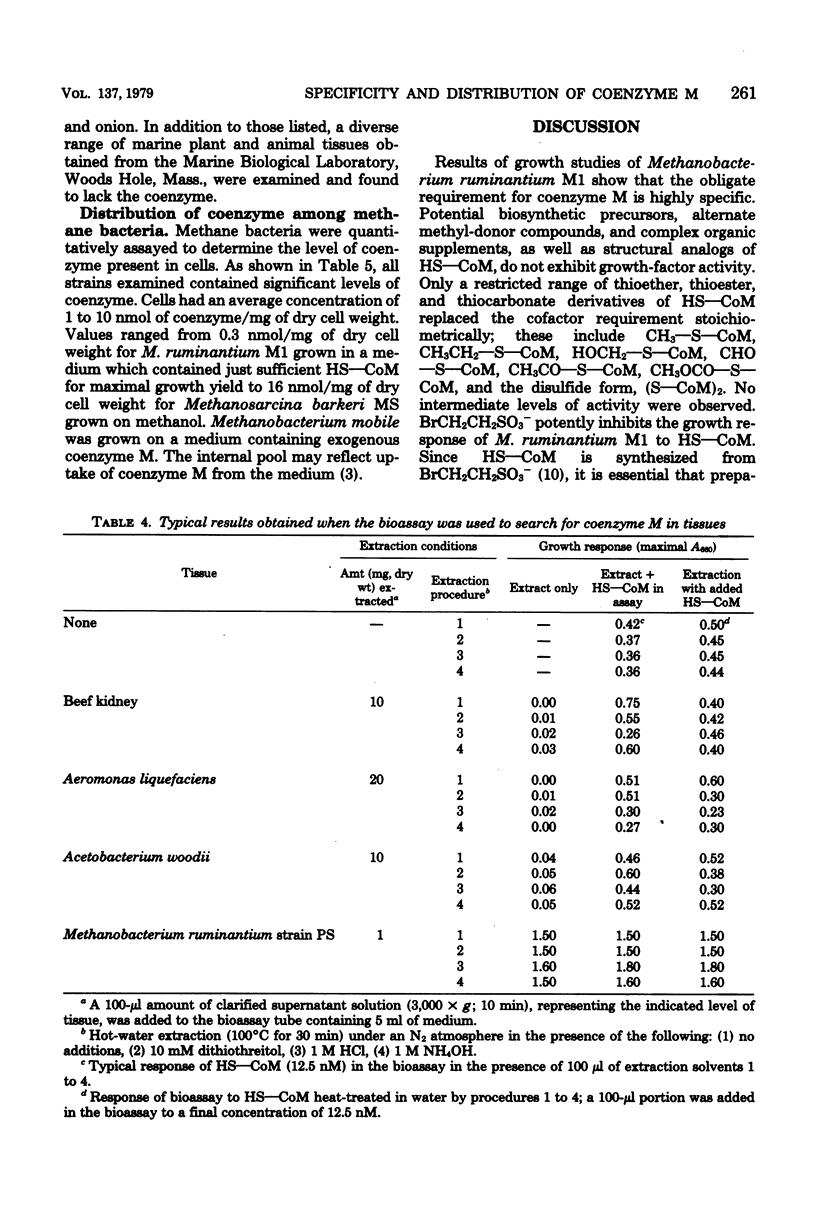
The specificity of the growth requirement of Methanobacterium ruminantium strain M1 for a new coenzyme, 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS--CoM), was examined. A variety of derivatives, analogs, and potential biosynthetic precursors of coenzyme M were tested; only a restricted range of thioether, thioester, and thiocarbonate derivatives of the cofactor were found to replace the HS--CoM requirement. Bromoethanesulfonic acid (BrCH2CH2SO3-), a halogenated analog of HS--CoM, potently inhibited the growth response. No coenzyme was detectable in a wide range of nonmethanogenic eucaryotic tissues and procaryotic organisms. However, all methanogens available in pure culture exhibited high levels of coenzyme M which ranged from 0.3 to 16 nmol/mg of dry weight.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. Transport of coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid) in Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):264–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.264-273.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best A. N. Composition and Characterization of tRNA from Methanococcus vannielii. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.240-250.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S. Hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacteria. I. Cultivation and methanogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1118–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1118-1123.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. A colorimetric method for determining low concentrations of mercaptans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Apr;74(2):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirich L. D., Vogels G. D., Wolfe R. S. Proposed structure for coenzyme F420 from Methanobacterium. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4583–4593. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S., Woese C. R. Classification of methanogenic bacteria by 16S ribosomal RNA characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4537–4541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Romesser J. A., Wolfe R. S. Preparation of coenzyme M analogues and their activity in the methyl coenzyme M reductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. B., Bowers B., Stadtman T. C. Methanococcus vannielii: ultrastructure and sensitivity to detergents and antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1357–1363. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1357-1363.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. B., Stadtman T. C. Methanococcus vannielii: culture and effects of selenium and tungsten on growth. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1404–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1404-1406.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandler O., Hippe H. Lack of peptidoglycan in the cell walls of Methanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol. 1977 May 13;113(1-2):57–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00428580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandler O., König H. Chemical composition of the peptidoglycan-free cell walls of methanogenic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):141–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00415722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrum L. J., Luehrsen K. R., Woese C. R. Are extreme halophiles actually "bacteria"? J Mol Evol. 1978 May 12;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01768019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R. A., Singer M. E. Ether-containing lipids of methanogenic bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):716–722. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90933-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postgate J. R. Methane as a minor product of pyruvate metabolism by sulphate-reducing and other bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(3):293–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S., Bryant M. P. Coenzyme M, essential for growth of a rumen strain of Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):974–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.974-975.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Holzer G., Fox G. E., Oro J. Phytanyl-glycerol ethers and squalenes in the archaebacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01734487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


