Abstract
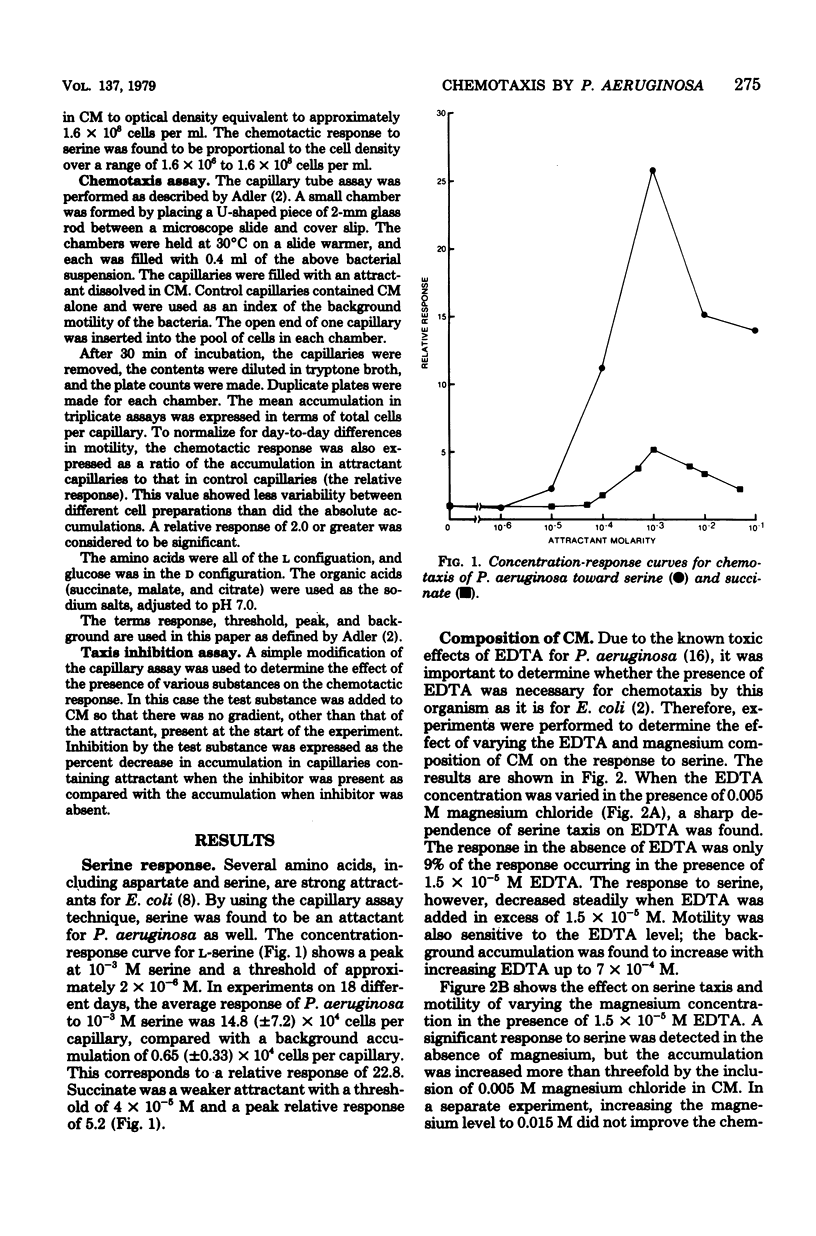
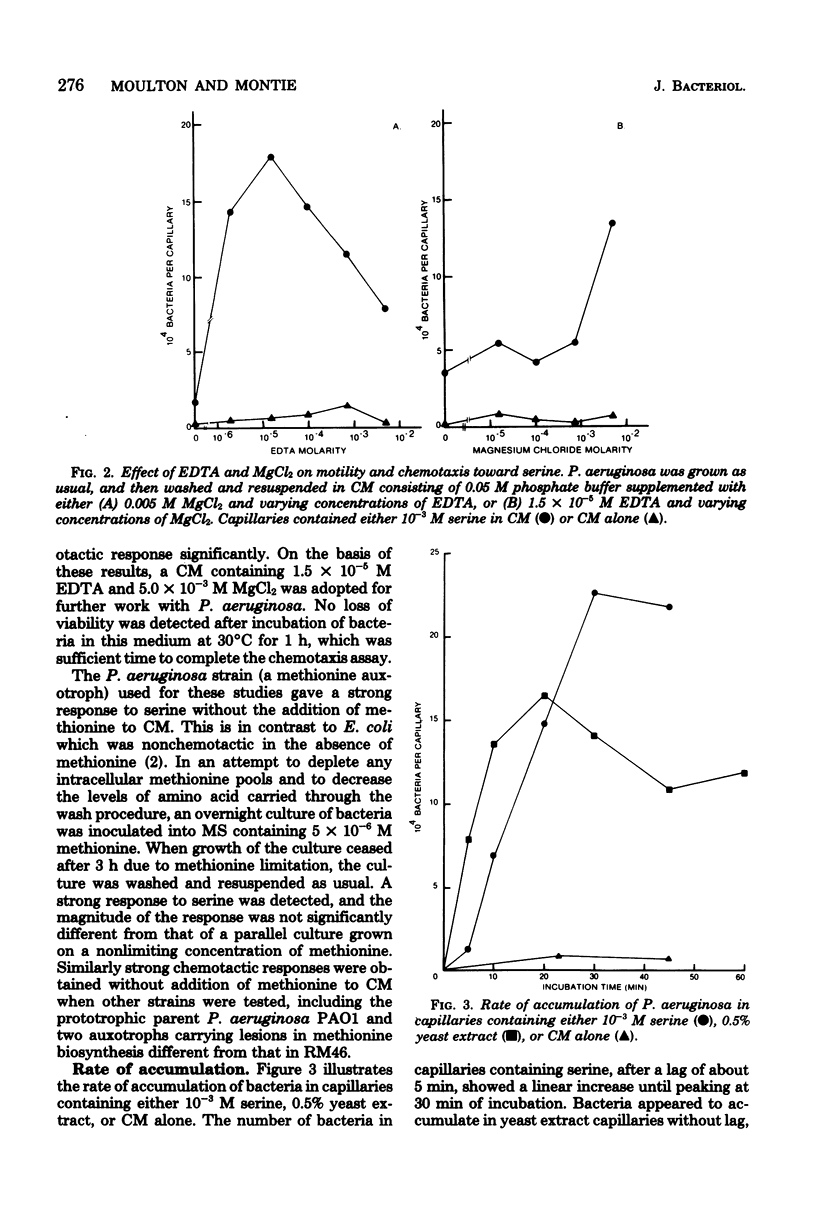
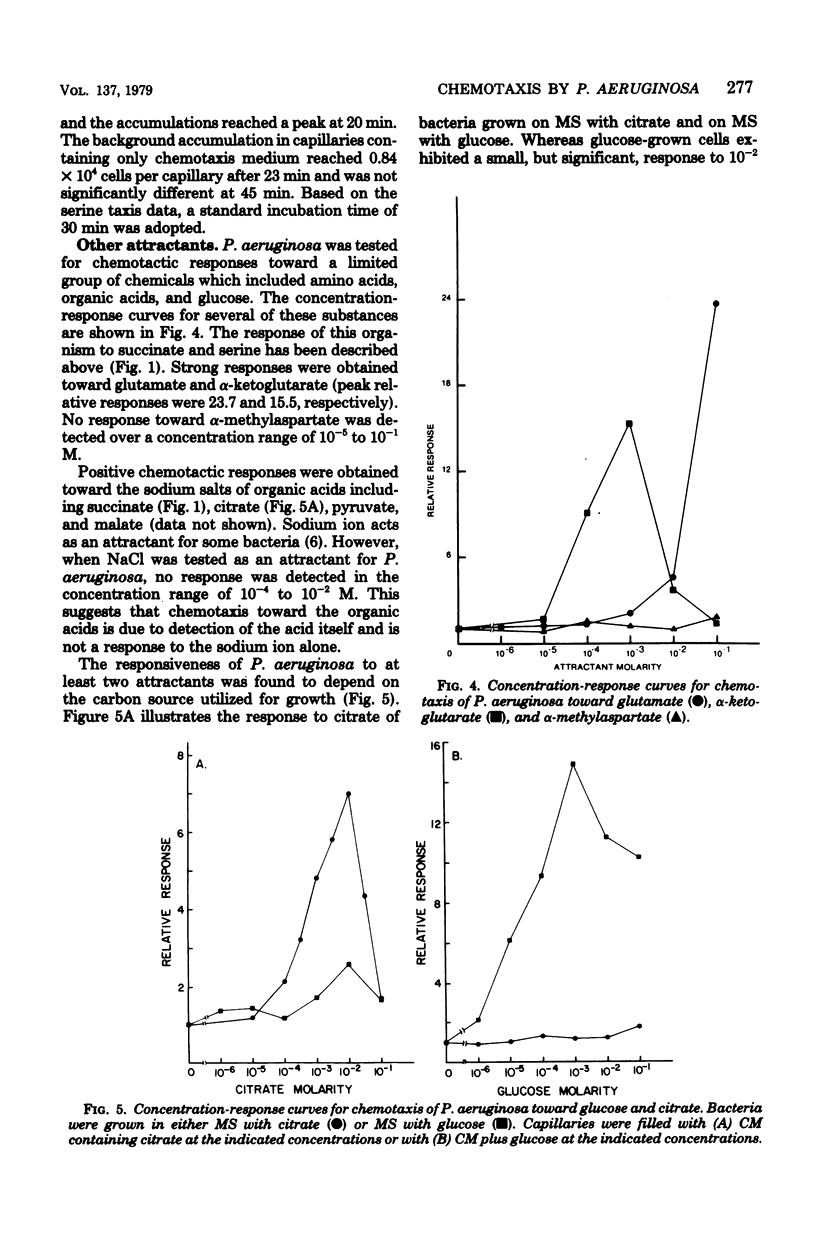
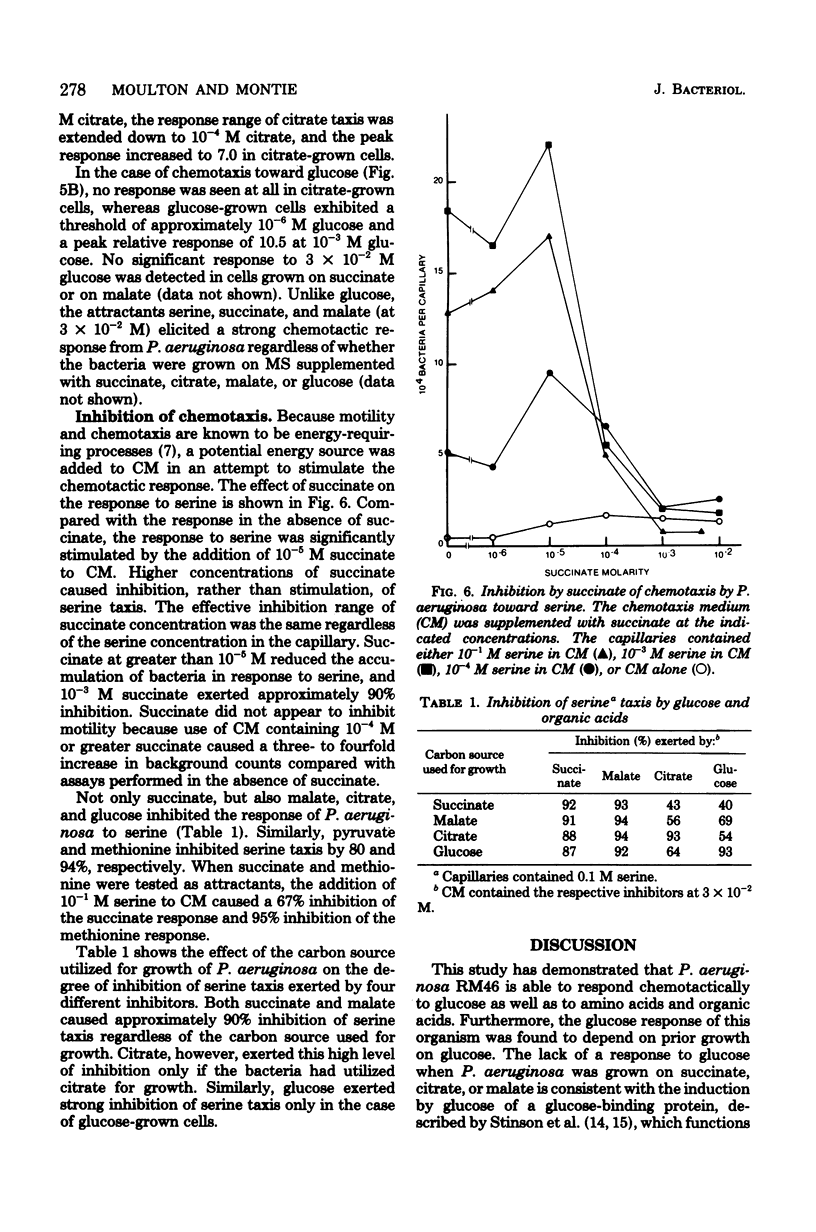
Chemotaxis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa RM46 has been studied, and conditions required for chemotaxis have been defined, by using the Adler capillary assay technique. Several amino acids, organic acids, and glucose were shown to be attractants of varying effectiveness for this organism. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid was absolutely required for chemotaxis, and magnesium was also necessary for a maximum response. Serine taxis was greatest when the chemotaxis medium contained 1.5 X 10(-5) M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 0.005 M magnesium chloride. It was not necessary to include methionine in the chemotaxis medium. The strength of the chemotactic responses to glucose and to citrate was dependent on prior growth of the bacteria on glucose and citrate, respectively. Accumulation in response to serine was inhibited by the addition of succinate, citrate, malate, glucose, pyruvate, or methionine to the chemotaxis medium. Inhibition by succinate was not dependent on the concentration of attractant in the capillary. However, the degree to which glucose and citrate inhibited serine taxis was dependent on the carbon source utilized for growth. Further investigation of this inhibition may provide information about the mechanisms of chemotaxis in P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemoreceptors in bacteria. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1588–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chet I., Mitchell R. The relationship between chemical structure of attractants and chemotaxis by a marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Aug;22(8):1206–1208. doi: 10.1139/m76-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr A response regulator model in a simple sensory system. Science. 1977 Jun 3;196(4294):1055–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.870969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarre A. G., Straley S. C., Conti S. F. Chemotaxis toward amino acids by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):201–207. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.201-207.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Sensory electrophysiology of bacteria: relationship of the membrane potential to motility and chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4752–4756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Becker J. M. Peptide utilization in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence for membrane-associated peptidase. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):165–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.165-171.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. T., Konetzka W. A. Chemotaxis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):427–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.427-429.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Cohen M. A., Merrick J. M. Purification and properties of the periplasmic glucose-binding protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):672–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.672-681.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



