Abstract
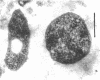
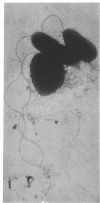
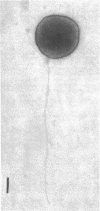
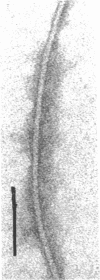
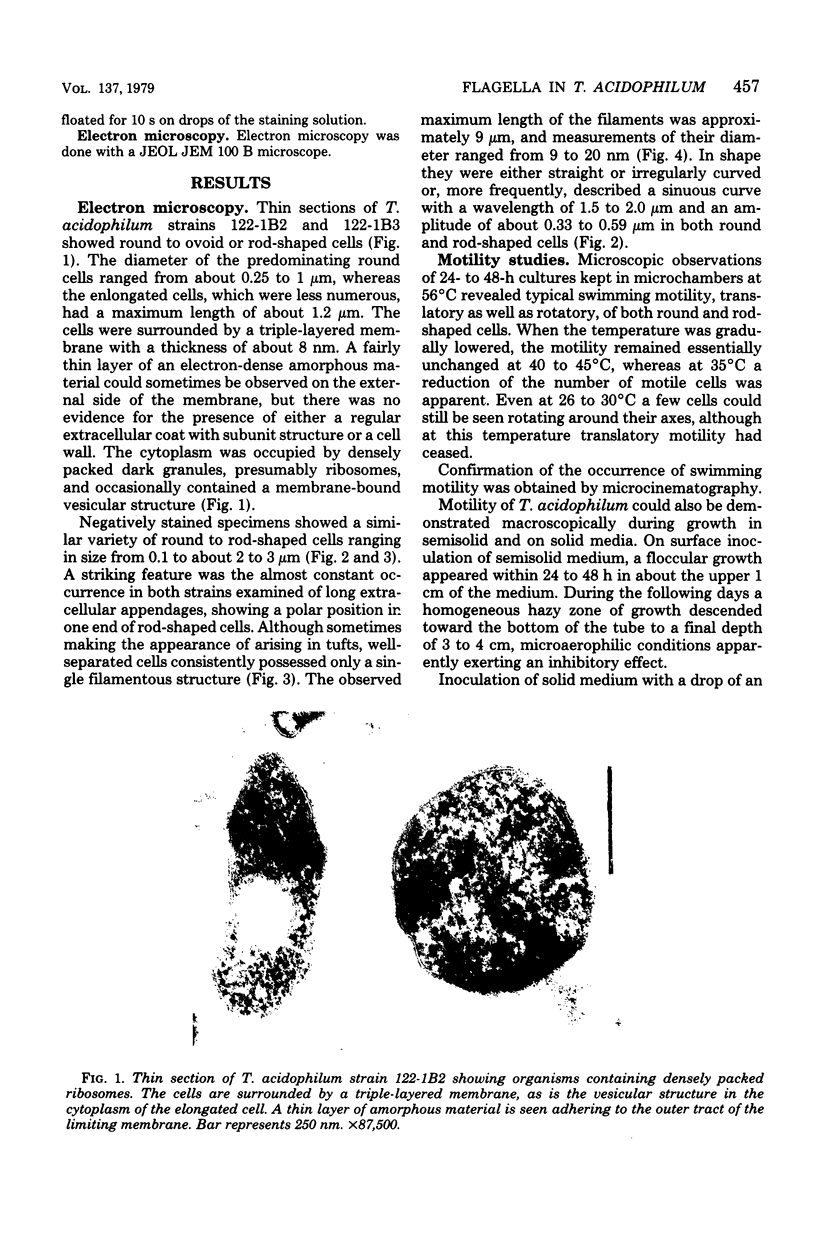
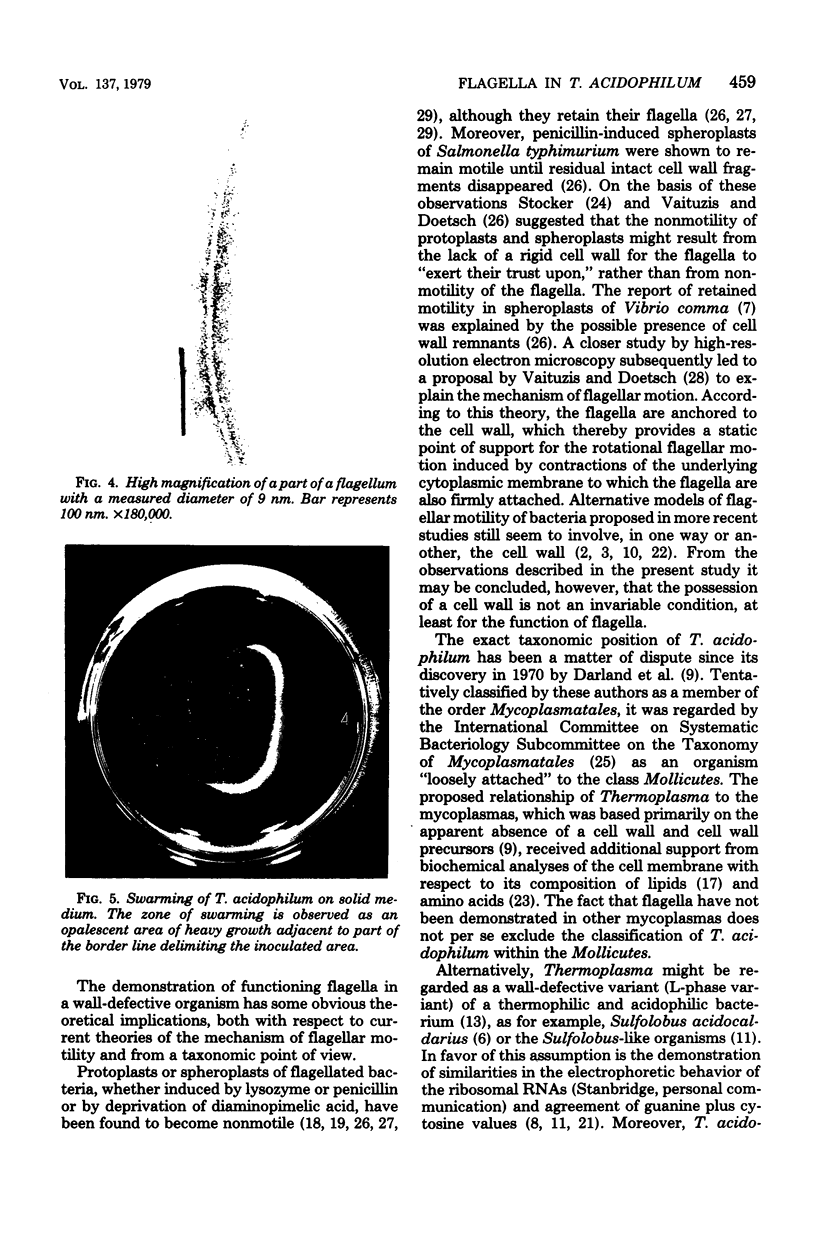
Electron microscopy of thin sections of Thermoplasma acidophilum confirmed previous observations of the absence of a typical cell wall in this organism. Negatively stained specimens revealed the almost consistent occurrence in both strains examined of monotrichously arranged flagella, about 9 micrometer long, which describe a sinuous curve with a wavelength of 1.5 to 2.0 micrometer and an amplitude of 0.33 to 0.59 micrometer. Motility of T. acidophilum could be demonstrated microscopically by microcinematography and macroscopically. The theoretical implications of the demonstration of functioning flagella in a wall-defective organism are discussed in the light of current theories of the mechanism of flagellar motility and from a taxonomic point of view.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C., Anderson R. A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):380–382. doi: 10.1038/245380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Dynamic properties of bacterial flagellar motors. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):77–79. doi: 10.1038/249077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T., Birch-Andersen A., Freundt E. A. Morphology and ultrastructure of human T-mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):254–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.254-259.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt W. Growth morphology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strain FH on glass surface. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):338–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE B. R., WILLIAMS R. P. PREPARATION OF SPHEROPLASTS FROM VIBRIO COMMA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:838–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.838-841.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darland G., Brock T. D., Samsonoff W., Conti S. F. A thermophilic, acidophilic mycoplasma isolated from a coal refuse pile. Science. 1970 Dec 25;170(3965):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3965.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Attachment of flagellar basal bodies to the cell envelope: specific attachment to the outer, lipopolysaccharide membrane and the cyoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):396–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.396-407.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holländer R., Wolf G., Mannheim W. Lipoquinones of some bacteria and mycoplasmas, with considerations on their functional significance. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1977;43(2):177–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00395672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn T. L., Bovee E. C. Movement and locomotion of microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:21–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., ST CLAIR J. Protoplasts and L-type growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):143–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.143-160.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Smith P. F., Mayberry W. R. Lipids of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1193-1200.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Langworth T. A., Mayberry W. R., Houghland A. E. Characterization of the membranes of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1019–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1019-1028.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAITUZIS Z., DOETSCH R. N. FLAGELLA OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1586–1593. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1586-1593.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Doetsch R. N. Flagella of Escherichia coli spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2103–2104. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2103-2104.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Doetsch R. N. Relationship between cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, and bacterial motility. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):512–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.512-521.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. The isolation of protoplasts from Bacillus megaterium by controlled treatment with lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.688-695.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Extremely thermophilic acidophilic bacteria convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):156–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Ultrastructure of an extremely thermophilic acidophilic micro-organism. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):165–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]