Abstract
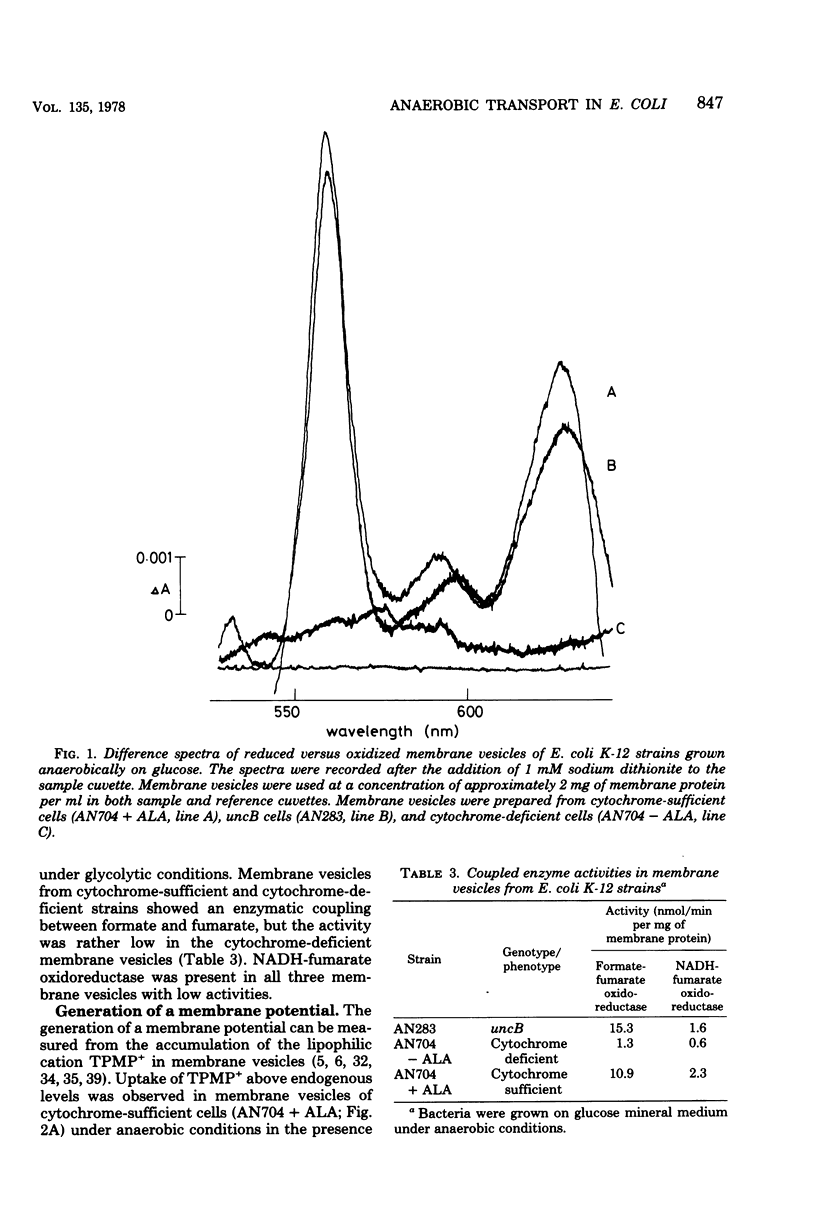
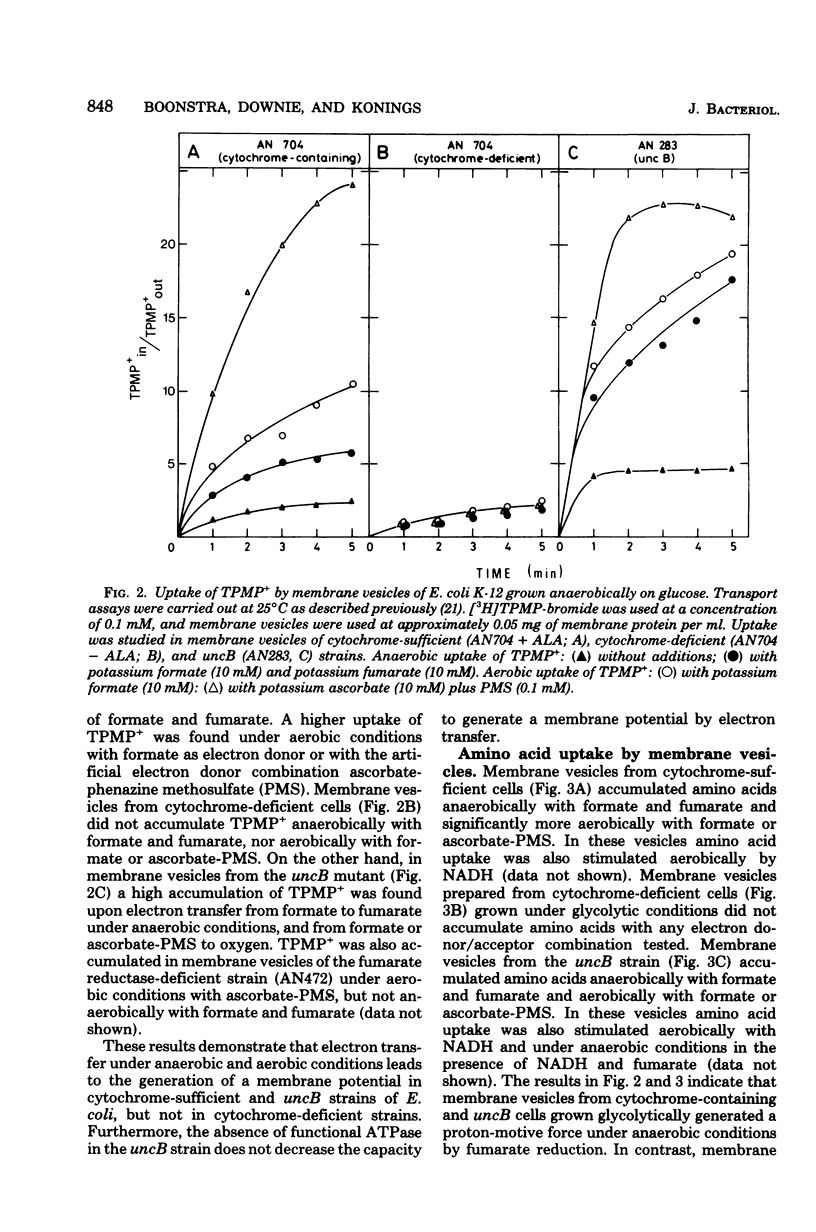
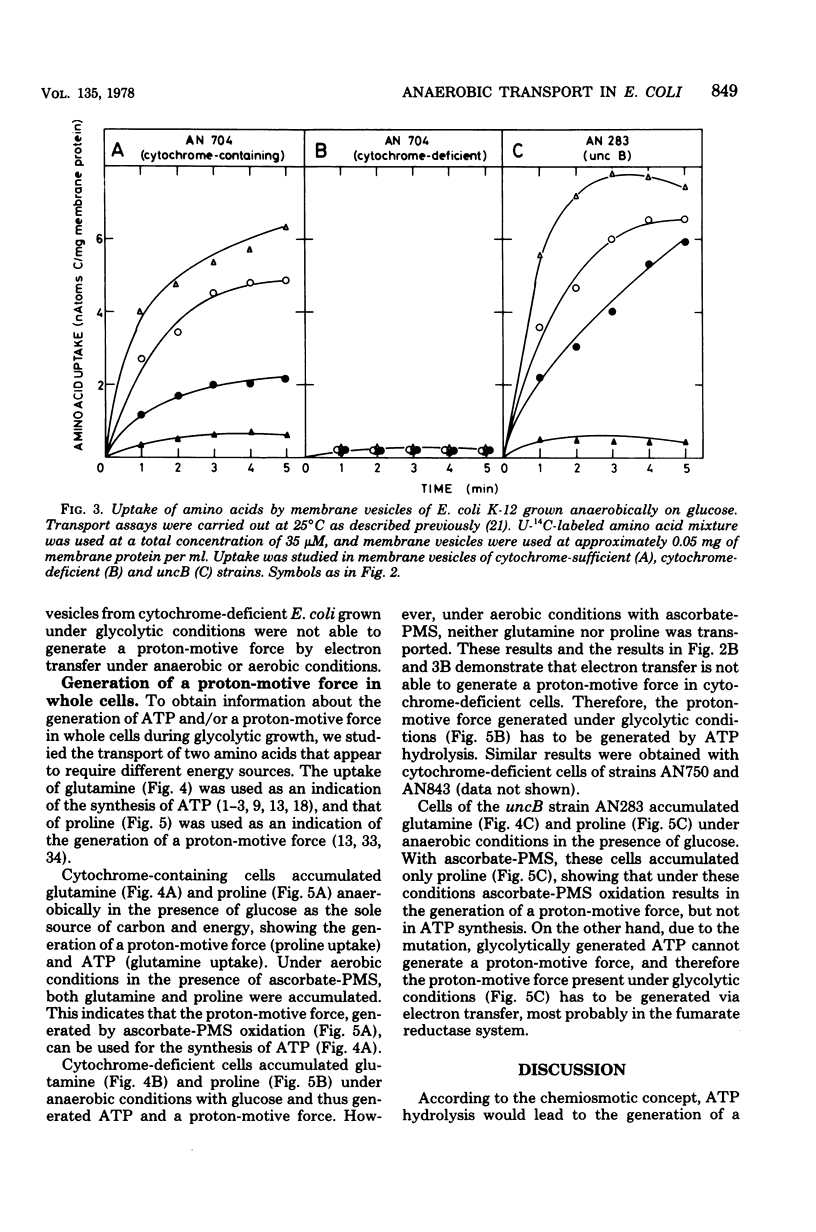
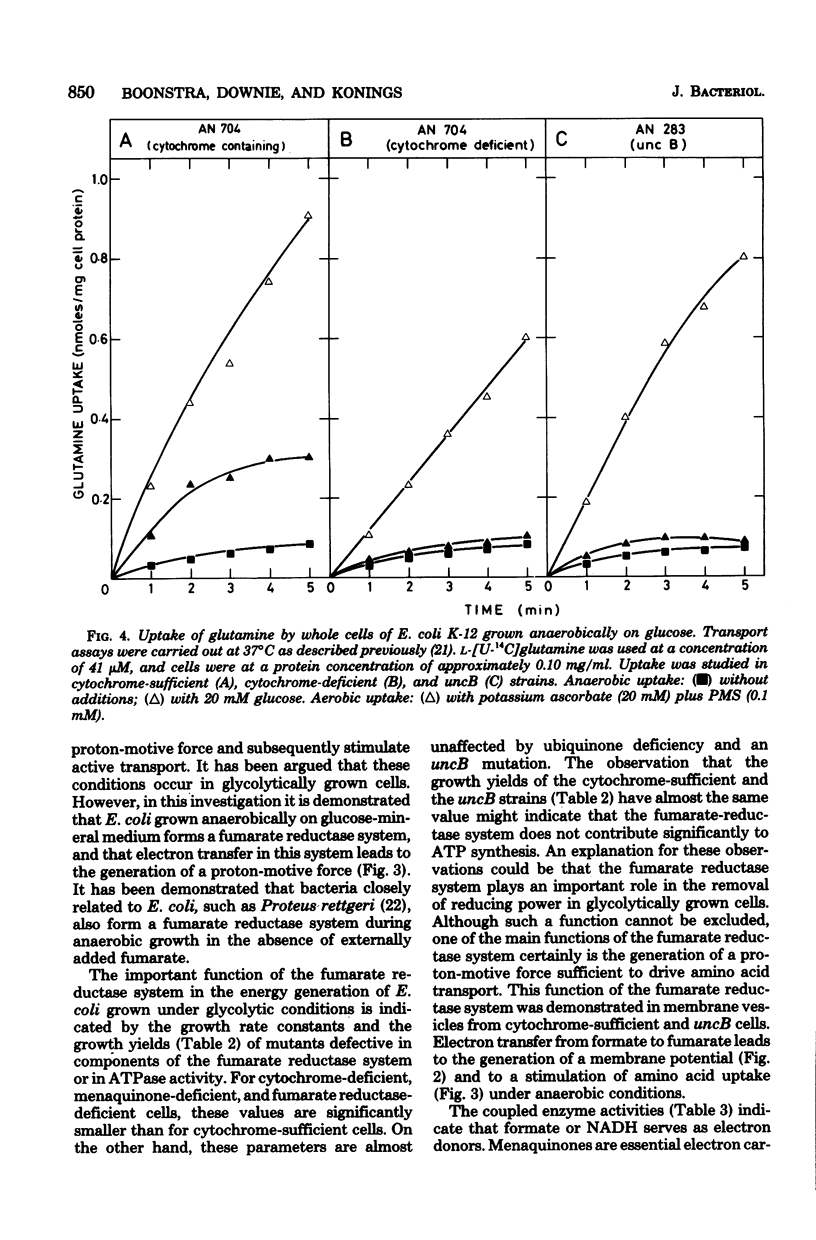
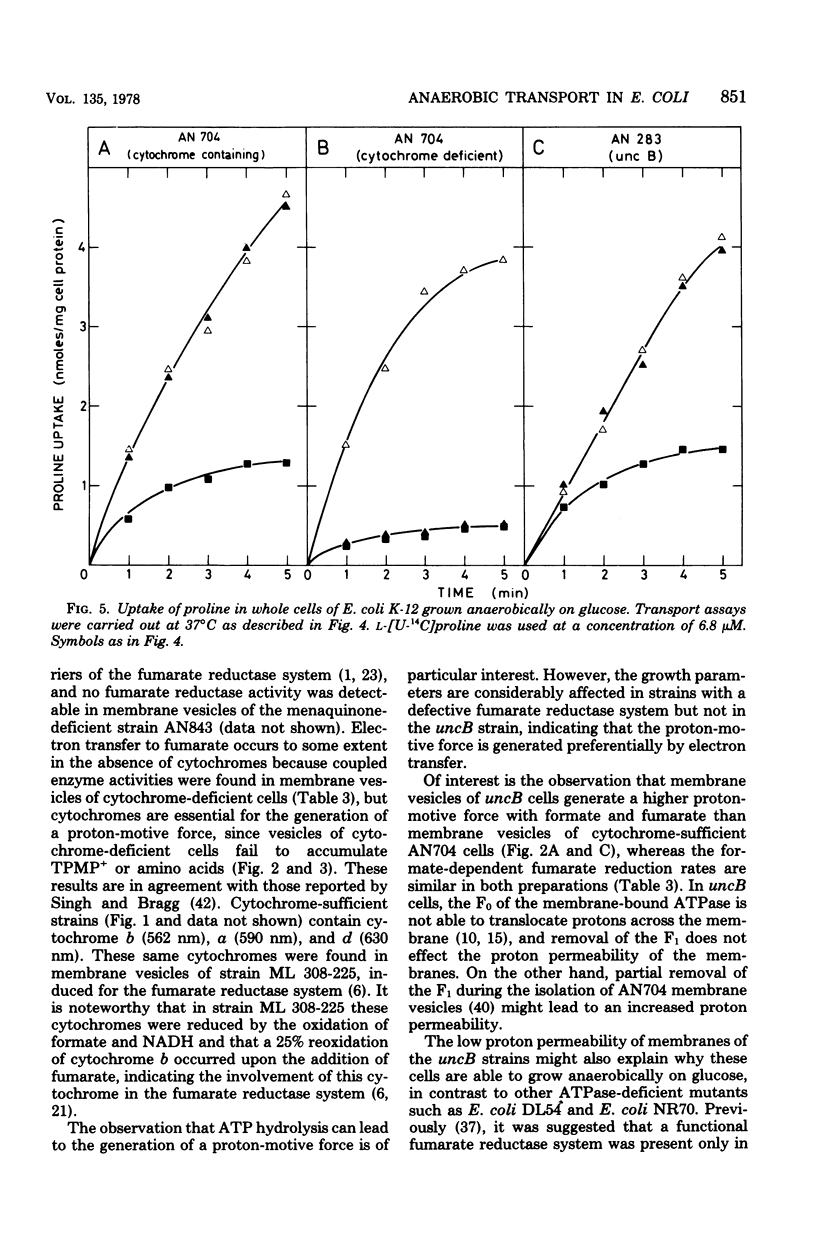
Escherichia coli K-12, grown under anaerobic conditions with glucose as the sole source of carbon and energy without any terminal electron acceptor added, contains a fumarate reductase system in which electrons are transferred from formate or reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide via menaquinone and cytochromes to fumarate reductase. This fumarate reductase system plays an important role in the metabolic energy supply of E. coli, grown under so-called “glycolytic conditions,” as is indicated by the growth yields and maximal growth rates of mutants impaired in electron transfer or adenosine triphosphatase (uncB). In mutants deficient in menaquinone, cytochromes, or fumarate reductase, these values are considerably lower than in mutants deficient in ubiquinone or a functional adenosine triphosphatase. Electron transfer in this fumarate reductase system leads to the generation of a membrane potential, as is indicated by the uptake of the lipophilic cation triphenylmethylphosphonium by membrane vesicles prepared from cytochrome-sufficient and uncB cells. The generation of a proton-motive force by the fumarate reductase system was also demonstrated by the uptake of amino acids under anaerobic conditions in membrane vesicles of cytochrome containing and uncB cells grown under glycolytic conditions. Membrane vesicles of cytochrome-deficient cells failed to accumulate triphenyl-methylphosphonium and amino acids under these conditions, indicating that cytochromes are essential for the generation of a proton-motive force. Using glutamine uptake as an indication of the generation of ATP and proline uptake as an indication of the generation of a proton-motive force, it was demonstrated in whole cells that the proton-motive force is formed by ATP hydrolysis in cytochrome-deficient cells and by electron transfer in the uncB cells. In cytochrome-containing cells it was not possible to distinguish between these two possibilities, but the growth parameters suggest that, under glycolytic conditions, the proton-motive force is generated via electron transfer in the fumarate reductase system rather than via ATP hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews S., Cox G. B., Gibson F. The anaerobic oxidation of dihydroorotate by Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 12;462(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Heppel L. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the shock-sensitive and shock-resistant amino acid permeases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7747–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Huttunen M. T., Konings W. N. Anaerobic transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6792–6798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient by nitrate respiration in membrane vesicles from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):361–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Sips H. J., Konings W. N. Active transport by membrane vesicles from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli energized by electron transfer to ferricyanide and chlorate. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K-12: the genetic and biochemical characterisations of a strain carrying a mutation in the uncB gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. H., Hamilton W. A. Magnitude of the protonmotive force in respiring Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1224–1231. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1224-1231.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L. Energetics of glycylglycine transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.139-146.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Crane F. L., Downie J. A., Radik J. Different effects of inhibitors on two mutants of Escherichia coli K12 affected in the Fo portion of the adenosine triphosphatase complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 12;462(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F. Studies on electron transport and energy-linked reactions using mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 30;346(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Cox G. B. Sequence of b cytochromes relative to ubiquinone in the electron transport chain of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):477–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.477-484.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S. J., Rosenberg H. Energy coupling to active transport in anaerobically grown mutants of Escherichia Coli K12. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):731–734. doi: 10.1042/bj1540731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan S. M., Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Energy transduction in Escherichia coli: physiological and biochemical effects of mutation in the uncB locus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.108-113.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Molecular biology and energetics of membrane transport. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):575–593. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Kin E., Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. X. Sources of energy and energy coupling reactions of the active transport systems for isoleucine and proline in E. coli. J Biochem. 1974 Aug;76(2):251–261. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N. Active transport of solutes in bacterial membrane vesicles. Adv Microb Physiol. 1977;15:175–251. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Kaback H. R. Anaerobic transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3376–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger A. Electron-transport phosphorylation coupled to fumarate reduction in anaerobically grown Proteus rettgeri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 22;347(2):273–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Guest J. R. Mutants of Escherichia coli K12 unable to use fumarate as an anaerobic electron acceptor. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):145–160. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., COHEN-BAZIRE G., COHN M. Sur la biosynthèse de la beta-galactosidase (lactase) chez Escherichia coli; la spécificité de l'induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1951 Nov;7(4):585–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(51)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Performance and conservation of osmotic work by proton-coupled solute porter systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):63–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01516051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Possible molecular mechanisms of the protonmotive function of cytochrome systems. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 21;62(2):327–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton N. A., Cox G. B., Gibson F. The function of menaquinone (vitamin K 2 ) in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 20;244(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis F. J., Kanner B. I., Gutnick D. L., Postma P. W., van Dam K. Energy conservation in membranes of mutants of Escherichia coli defective in oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 19;325(1):62–71. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):848–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. pH-dependent changes in proton:substrate stoichiometries during active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4270–4275. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., McClees J. S. Active transport of calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5042–5046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Cox G. B., Butlin J. D., Gutowski S. J. Metabolite transport in mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in electron transport and coupled phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):417–423. doi: 10.1042/bj1460417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schairer H. U., Haddock B. A. -Galactoside accumulation in a Mg 2+ -,Ca 2+ -activated ATPase deficient mutant of E.coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):544–551. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Localization of D-lactate dehydrogenase in native and reconstituted Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4291–4296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Postma P. W. The energetics of bacterial active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:523–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. P., Bragg P. D. Anaerobic transport of amino acids coupled to the glycerol-3-phosphate-fumarate oxidoreductase system in a cytochrome-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 12;423(3):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Characterization of an active transport system for calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7687–7692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. The proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80880-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



