Abstract
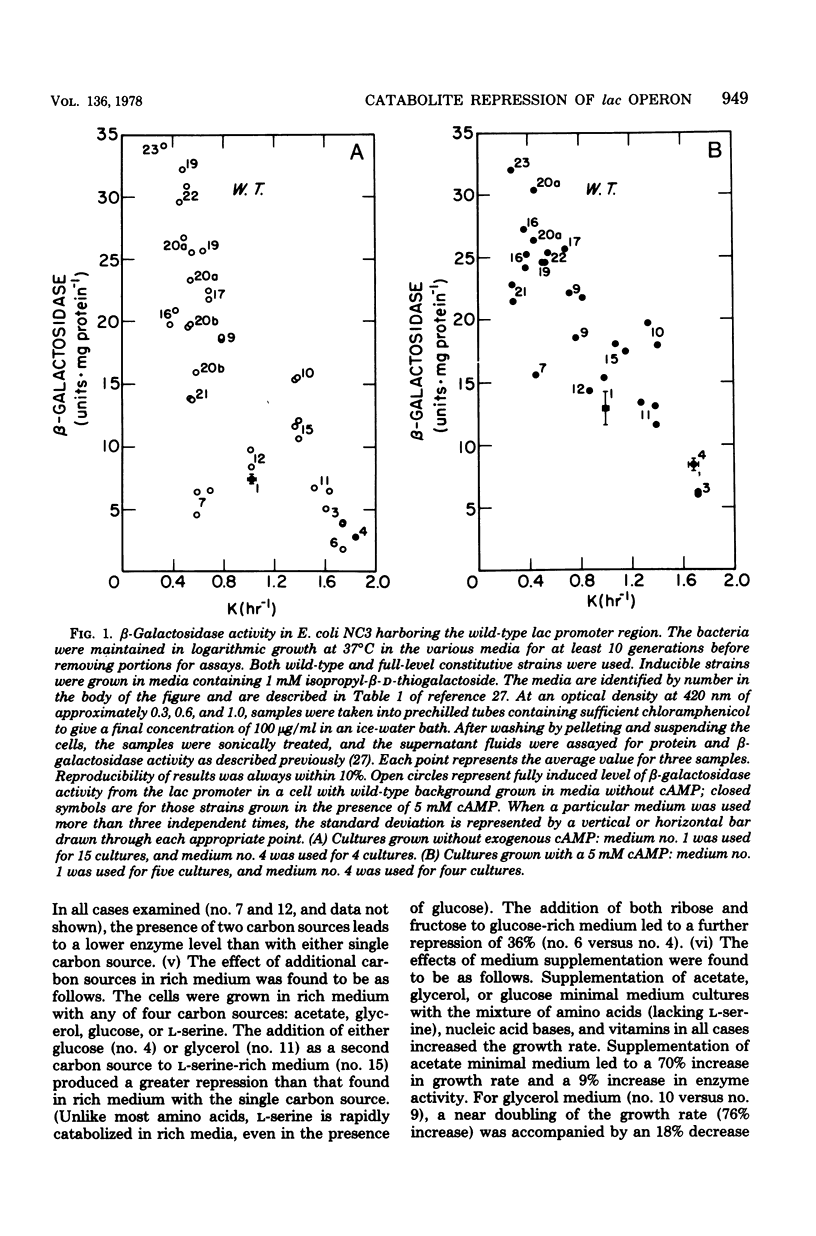
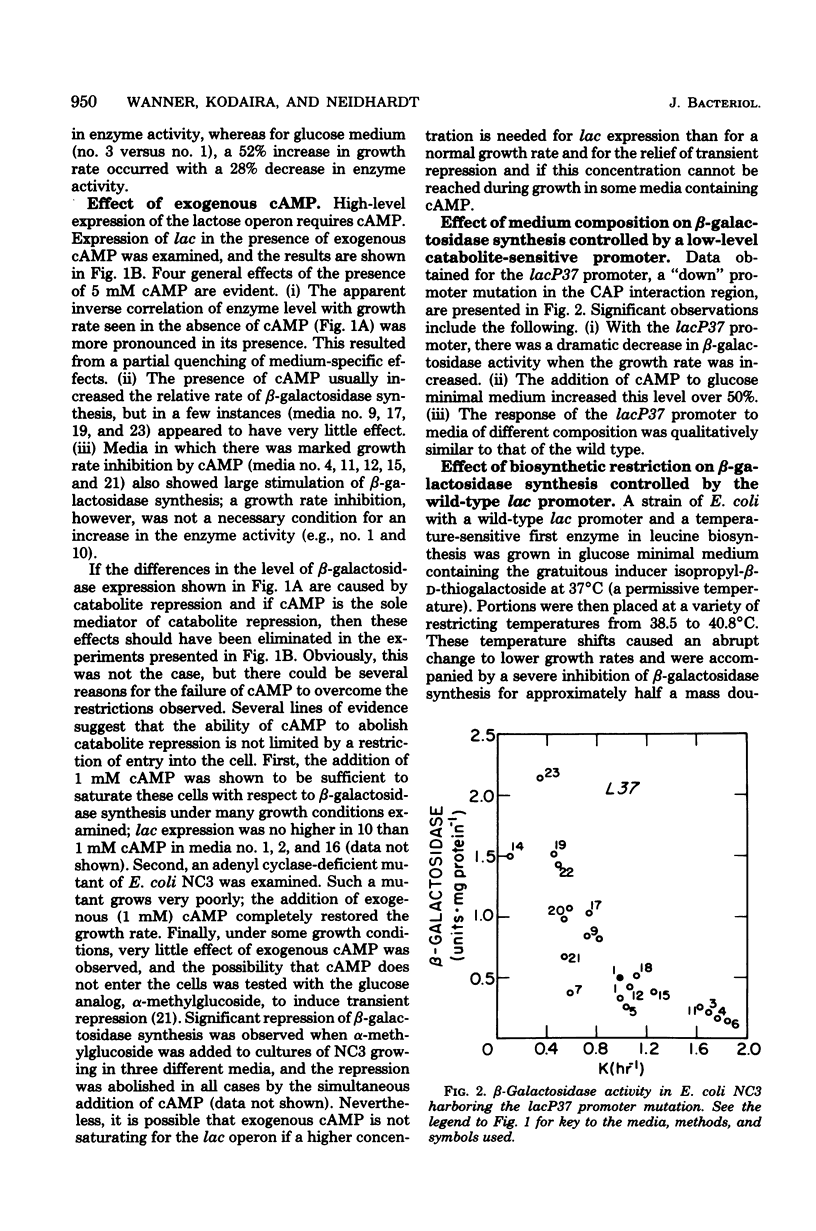
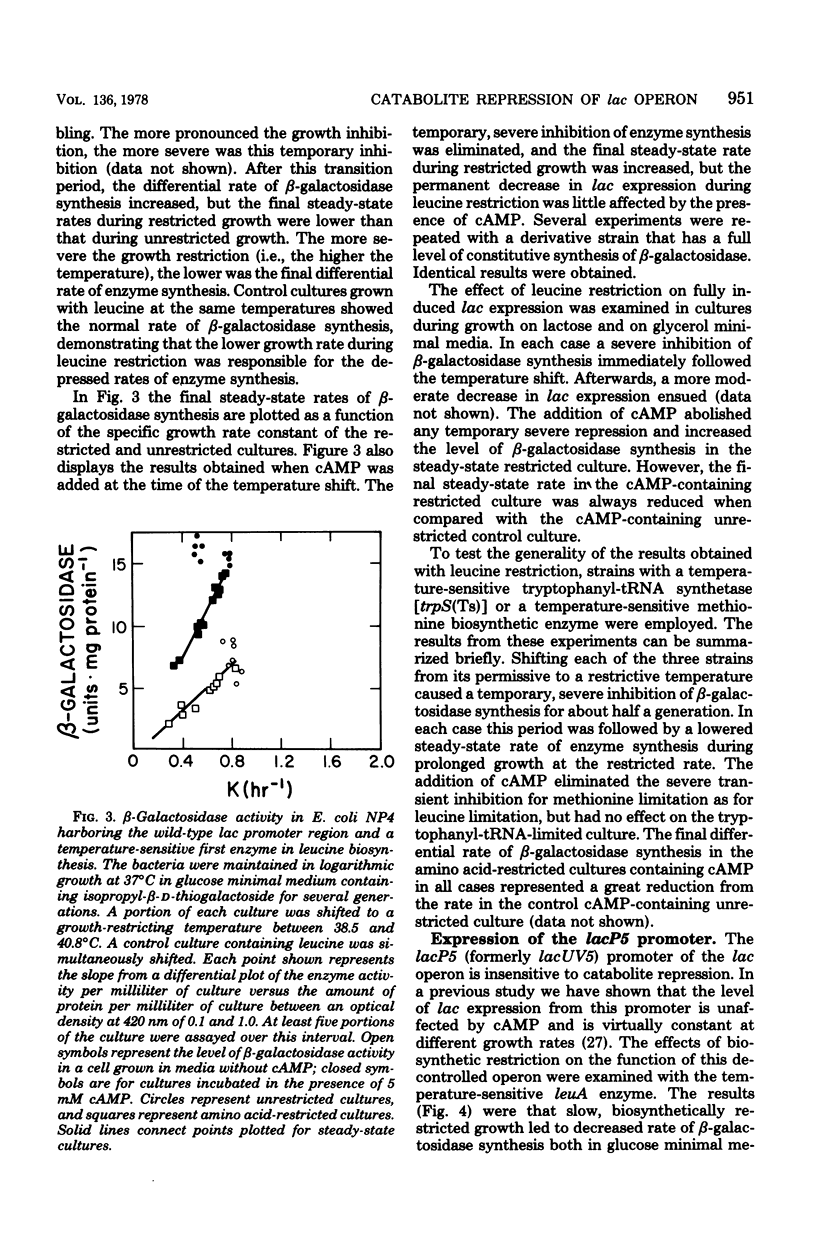
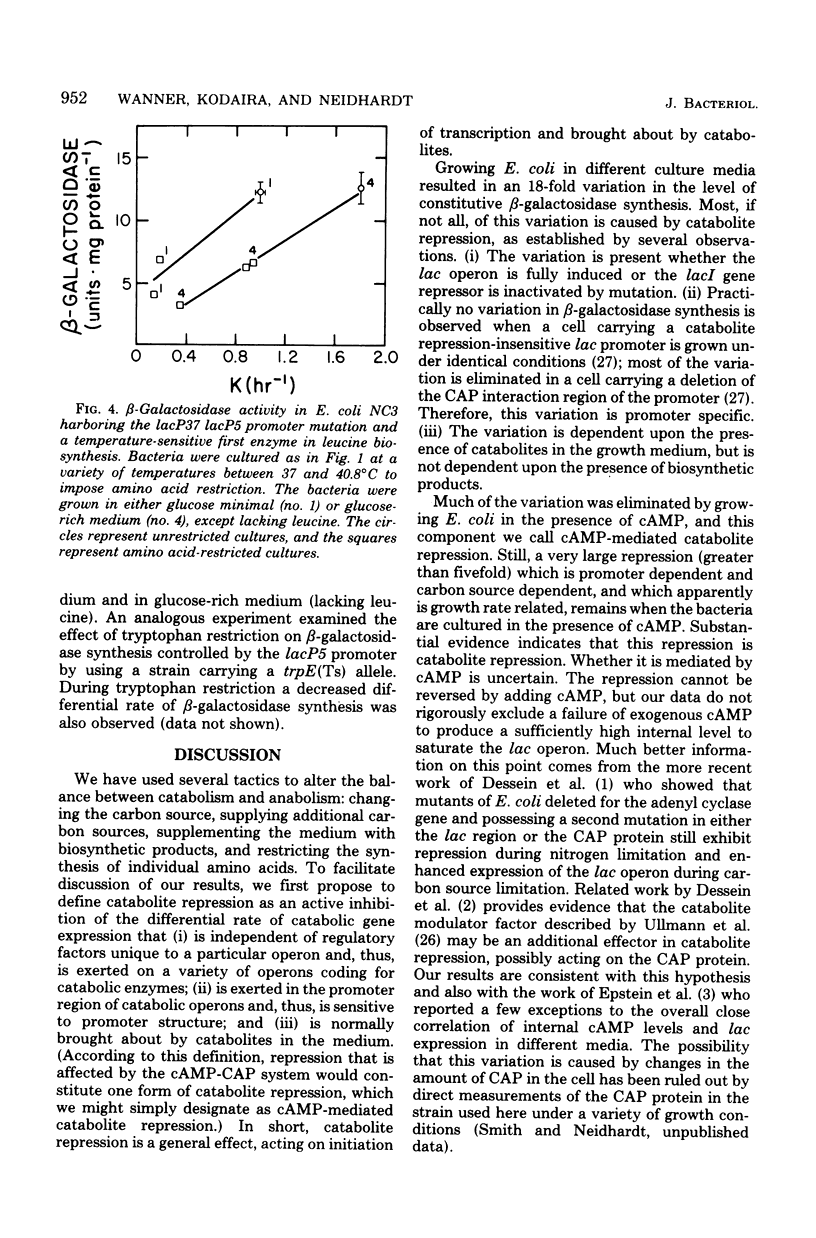
The physiological state of Escherichia coli with respect to (permanent) catabolite repression was assessed by measuring the steady-state level of β-galactosidase in induced or in constitutive cells under a variety of growth conditions. Four results were obtained. (i) Catabolite repression had a major effect on fully induced or constitutive expression of the lac gene, and the magnitude of this effect was found to be dependent on the promoter structure; cells with a wild-type lac promoter showed an 18-fold variation in lac expression, and cells with the lacP37 (formerly lac-L37) promoter exhibited several hundred-fold variation. (ii) Exogenous adenosine cyclic 3′,5′-monophosphoric acid (cAMP) could not abolish catabolite repression, even though several controls demonstrated that cAMP was entering the cells in significant amounts. (Rapid intracellular degradation of cAMP could not be ruled out.) (iii) Neither the growth rate nor the presence of biosynthetic products altered the degree of catabolite repression; all variation could be related to the catabolites present in the growth medium. (iv) Slowing by imposing an amino acid restriction decreased the differential rate of β-galactosidase synthesis from the wild-type lac promoter when bacteria were cultured in either the absence or presence of cAMP; this decreased lac expression also occurred when the bacteria harbored the catabolite-insensitive lacP5 (formerly lacUV5) promoter mutation. These findings support the idea that (permanent) catabolite repression is set by the catabolites in the growth medium and may not be related to an imbalance between catabolism and anabolism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dessein A., Schwartz M., Ullmann A. Catabolite repression in Escherichia coli mutants lacking cyclic AMP. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 1;162(1):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00333853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessein A., Tillier F., Ullmann A. Catabolite modulator factor: physiological properties and in vivo effects. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 1;162(1):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00333854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmer M., deCrombrugghe B., Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic AMP receptor protein of E. coli: its role in the synthesis of inducible enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Rothman-Denes L. B., Hesse J. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate as mediator of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2300–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE ENZYMIC ACTIVITIES OF BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1943 Sep;7(3):139–173. doi: 10.1128/br.7.3.139-173.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B., NEIDHARDT F. C. Inhibitory effect of glucose on enzyme formation. Nature. 1956 Oct 13;178(4537):801–802. doi: 10.1038/178801b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. The repression of constitutive beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli by glucose and other carbon sources. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:489–493. doi: 10.1042/bj0820489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses V., Prevost C. Catabolite repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):336–353. doi: 10.1042/bj1000336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., MAGASANIK B. Effect of mixtures of substrates on the biosynthesis of inducible enzymes in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):260–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.260-263.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Pedersen S., Reeh S. Chemical measurement of steady-state levels of ten aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):378–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.378-387.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen K. Phenomenon of transient repression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1201–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1201-1209.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Bloch P. L., Reeh S., Neidhardt F. C. Patterns of protein synthesis in E. coli: a catalog of the amount of 140 individual proteins at different growth rates. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., De Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP regulates catabolite and transient repression in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):810–812. doi: 10.1038/223810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Iida S. Mutants of Escherichia coli permeable to actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2315–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstone A. E., Arditti R. R., Magasanik B. Catabolite-insensitive revertants of lac promoter mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):773–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Loomis W. F., Jr, Magasanik B. Transient repression of the lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):2001–2011. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.2001-2011.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Magasanik B. Molecular basis of transient repression of beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.550-556.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. Are cyclic AMP effects related to real physiological phenomena? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):348–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90936-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Monod J. Cyclic AMP as an antagonist of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1968 Nov;2(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Tillier F., Monod J. Catabolite modulator factor: a possible mediator of catabolite repression in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3476–3479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Kodaira R., Neidhardt F. C. Physiological regulation of a decontrolled lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):212–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.212-222.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



