Abstract
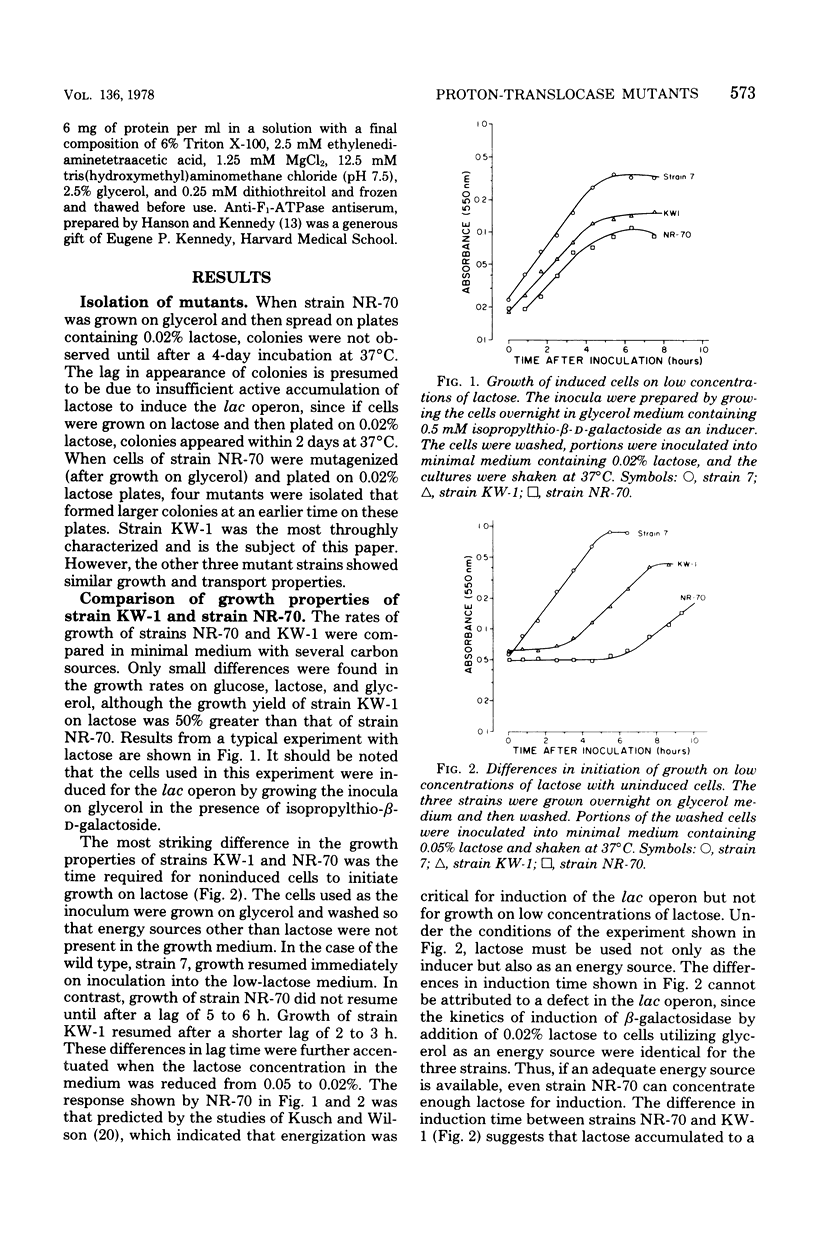
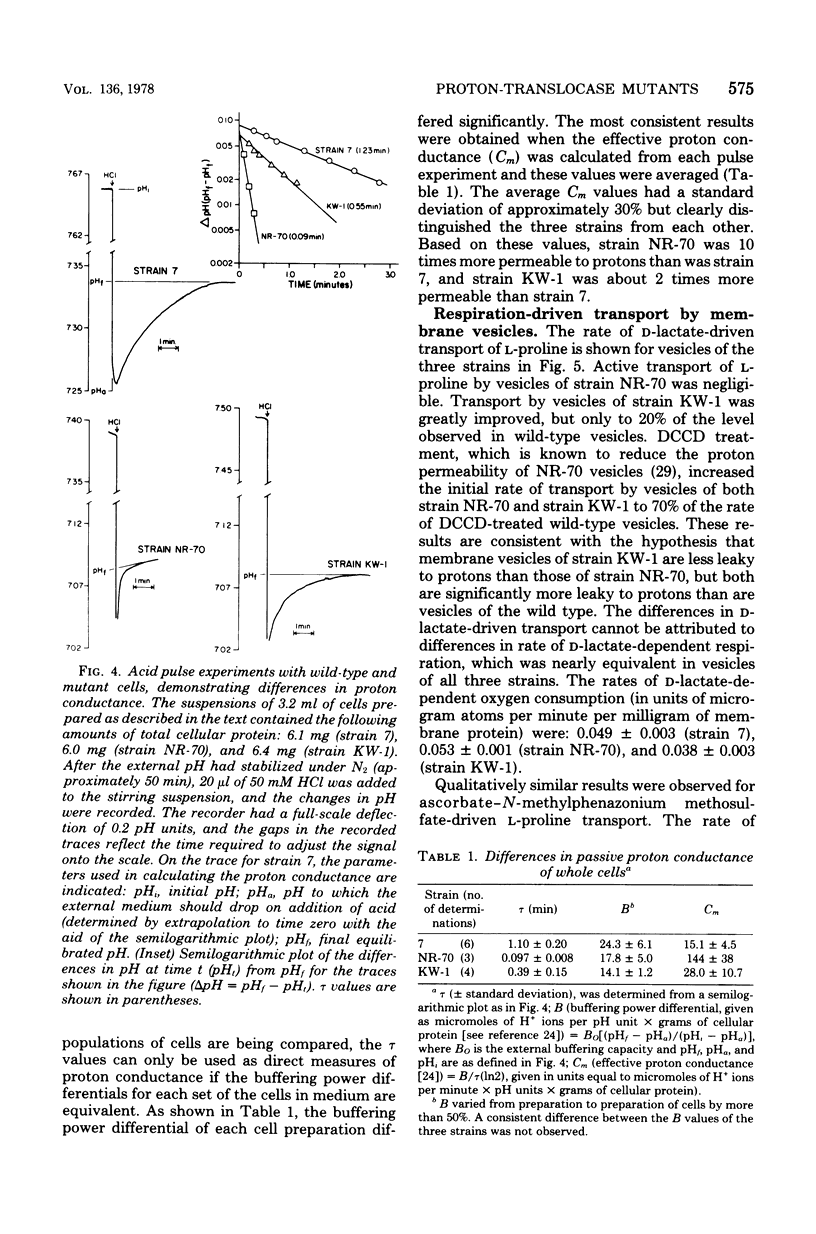
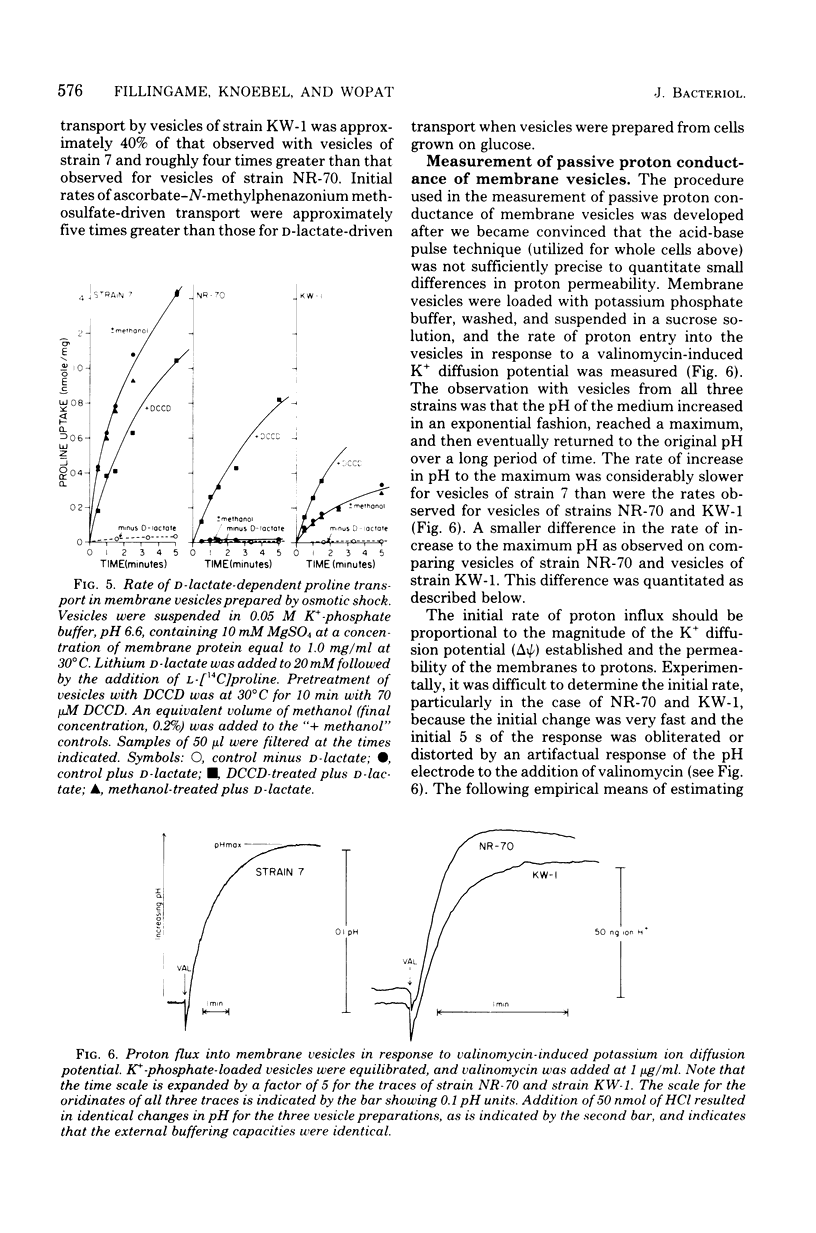
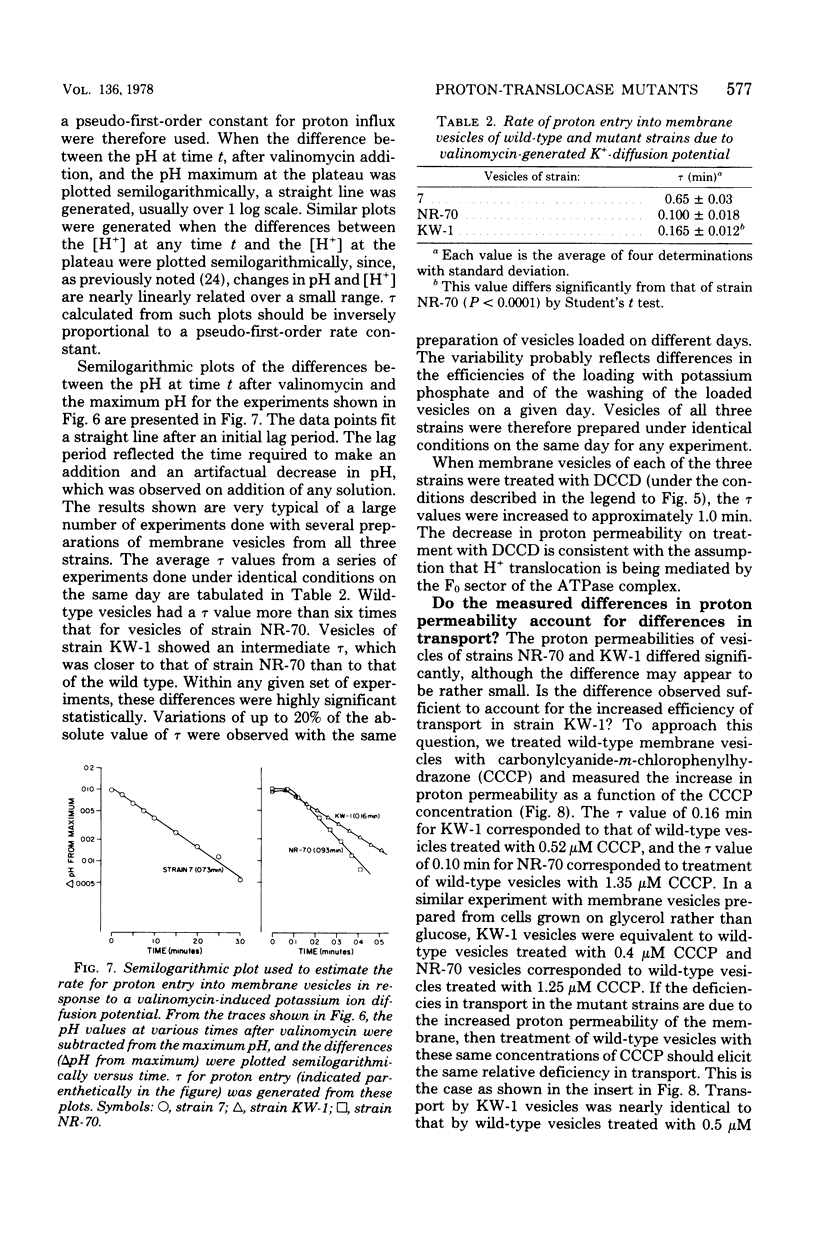
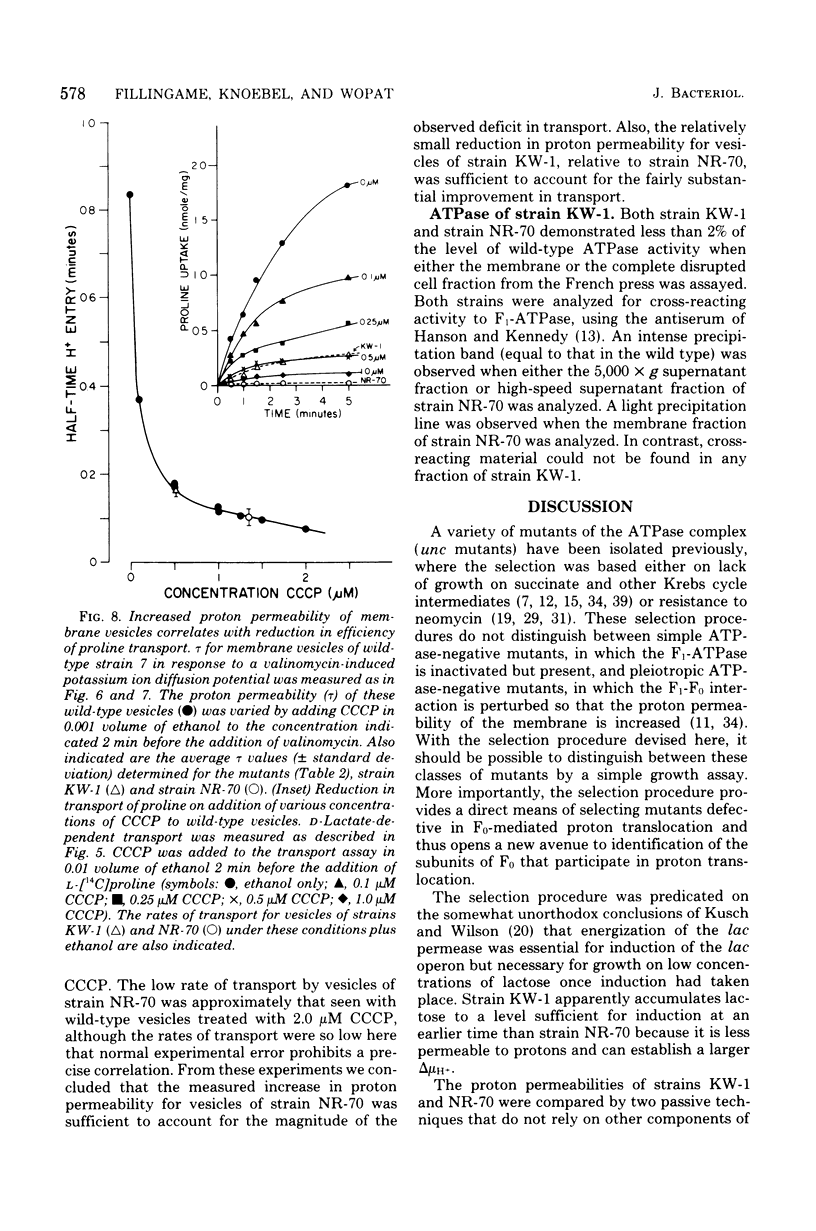
A technique for selecting mutants of Escherichia coli in which the proton-translocating sector of the adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) complex has been inactivated is reported. The procedure uses a strain of E. coli (NR-70) lacking the extrinsic (F1) sector of the ATPase complex and which in consequently permeable to protons (B. P. Rosen, J. Bacteriol. 116:1124--1129, 1973). After growing strain NR-70 under noninducing conditions for the lac operon, cells were mutagenized and plated on minimal medium containing low concentrations of lactose. Several mutants of strain NR-70 were isolated as large colonies on these plates, apparently because they could concentrate lactose more efficiently. A description of one of the mutants, strain KW-1, is reported here. The most distinguishing difference in growth properties of the two strains was that, when transferred to medium containing low concentrations of lactose, strain KW-1 induced the lac operon with a shorter lag time than strain NR-70. The mutation in strain KW-1 leading to more rapid growth on lactose was cotransducible with the asn and unc loci, at 83 min on the E. coli genetic map. Intact cells of strain KW-1 actively transported L-proline as well as did wild-type cells, whereas cells of strain NR-70 were markedly deficient in L-proline transport. The improvement in the transport capacity of strain KW-1 correlated with a marked decrease in proton permeability relative to that of strain NR-70. Based on an acid-base pulse technique that measured the proton conductance of the membranes of intact cells, strain NR-70 was at least 10 times more permeable to protons than was the wild type, whereas strain KW-1 was only 2 times more permeable. The transport properties and proton conductance were also compared with membrane vesicles prepared by osmotic shock. With either D-lactate or ascorbate-N-methylphenazonium methosulfate as respiratory substrates, vesicles of strain KW-1 transported L-proline much more rapidly than did vesicles of strain NR-70, but still at rates less rapid than those of the wild type. The passive proton conductance of the membrane vesicles was quantitated by measuring the rate of H+ influx into vesicles in response to a valinomycin-generated K+ diffusion potential. The proton permeability of vesicles of strain KW-1 was reduced 1.5-fold relative to vesicles of strain NR-70, but these vesicles were still four times more permeable to protons than was the wild type. Vesicles of strain KW-1 corresponded to wild-type vesicles treated with 0.5 micrometer carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) and vesicles of strain NR-70 corresponded to wild-type vesicles treated with 1.4 micrometer CCCP. Treatment of wild-type vesicles with these concentrations of CCCP caused decreases in transport comparable to those observed in the mutants. Strain KW-1 lacked ATPase activity. Cross-reacting material to F1-ATPase was not found in strain KW-1 by double immunodiffusion analysis.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K., Harold F. M., Simoni R. D. Impairment and restoration of the energized state in membrane vesicles of a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4587–4593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. I. The site of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5518–5522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragg P. D., Hou C. Purification of a factor for both aerobic-driven and ATP-driven energy-dependent transhydrogenases of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 15;28(3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80738-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K-12: the genetic and biochemical characterisations of a strain carrying a mutation in the uncB gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Schwartz J. H. The asparagine synthetase of Escherhic coli. I. Biosynthetic role of the enzyme, purification, and characterization of the reaction products. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4112–4121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F. Studies on electron transport and energy-linked reactions using mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 30;346(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. Identification of the dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-reactive protein component of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate energy-transducing system of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):870–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.870-883.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Sternweis P. C., Heppel L. A. Purification and properties of reconstitutively active and inactive adenosinetriphosphatase from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Cox G. B., Downie J. A., Radik J. A mutation affecting a second component of the F0 portion of the magnesium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli K12. The uncC424 allele. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):193–198. doi: 10.1042/bj1640193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A., Jones C. W. Bacterial respiration. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):47–99. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.47-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. L., Kennedy E. P. Energy-transducing adenosine triphosphatase from Escherichia coli: purification, properties, and inhibition by antibody. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.772-781.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare J. F. Purification and characterization of a dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase complex from membranes of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1329–1337. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90505-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan S. M., Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Energy transduction in Escherichia coli: physiological and biochemical effects of mutation in the uncB locus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.108-113.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Gutnick D. L. Use of neomycin in the isolation of mutants blocked in energy conservation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):287–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.287-289.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusch M., Wilson T. H. Defective lactose utilization by a mutant of Escherichia coli energy-uncoupled for lactose transport. The advantages of active transport versus facilitated diffusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 7;311(1):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. A., Simon M., Hong J. S. Characterization of Escherichia coli mutant incapable of maintaining a transmembrane potential. MetC ecfts mutations. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4056–4067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Futai M., Anraku Y. Biochemical characterization of the uncA phenotype of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90729-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Sone N., Hirata H., Yoshida M., Kagawa Y. Purified proton conductor in proton translocating adenosine triphosphatase of a thermophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6125–6131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Kaback H. R. The role of the carbodiimide-reactive component of the adenosine-5'-triphosphatase complex in the proton permeability of Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2741–2746. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., Adler L. W. The maintenance of the energized membrane state and its relation to active transport in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 14;387(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Beta-galactoside transport and proton movements in an adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1289–1296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90605-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., Brey R. N., Hasan S. M. Energy transduction in Escherichia coli: new mutation affecting the Fo portion of the ATP synthetase complex. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1030–1038. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1030-1038.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Restoration of active transport in an Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1124-1129.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryrie I. J. The yeast mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase complex. Purification, subunit composition, and some effects of protease inhibitors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Dec;184(2):464–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90456-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schairer H. U., Friedl P., Schmid B. I., Vogel G. The use of several energy-coupling reactions in characterizing mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in oxidative phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):257–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P. Acid-base titration across the plasma membrane of Micrococcus denitrificans: factors affecting the effective proton conductance and the respiratory rate. J Bioenerg. 1970 Jun;1(1):61–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01516089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebald W. Biogenesis of mitochondrial ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 21;463(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(77)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kanner B. I., Racker E. Purification and properties of the proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase complex of bovine heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2453–2461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Localization of D-lactate dehydrogenase in native and reconstituted Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4291–4296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Postma P. W. The energetics of bacterial active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:523–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Shandell A. Energy transduction in Escherichia coli. Genetic alteration of a membrane polypeptide of the (Ca2+,Mg2+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9421–9427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Yoshida M., Hirata H., Kagawa Y. Purification and properties of a dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase from a thermophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7917–7923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Energy transduction in Escherichia coli. The role of the Mg2+ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8409–8415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel G., Steinhart R. ATPase of Escherichia coli: purification, dissociation, and reconstitution of the active complex from the isolated subunits. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):208–216. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Thienen G., Postma P. W. Coupling between energy conservation and active transport of serine in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



