Abstract
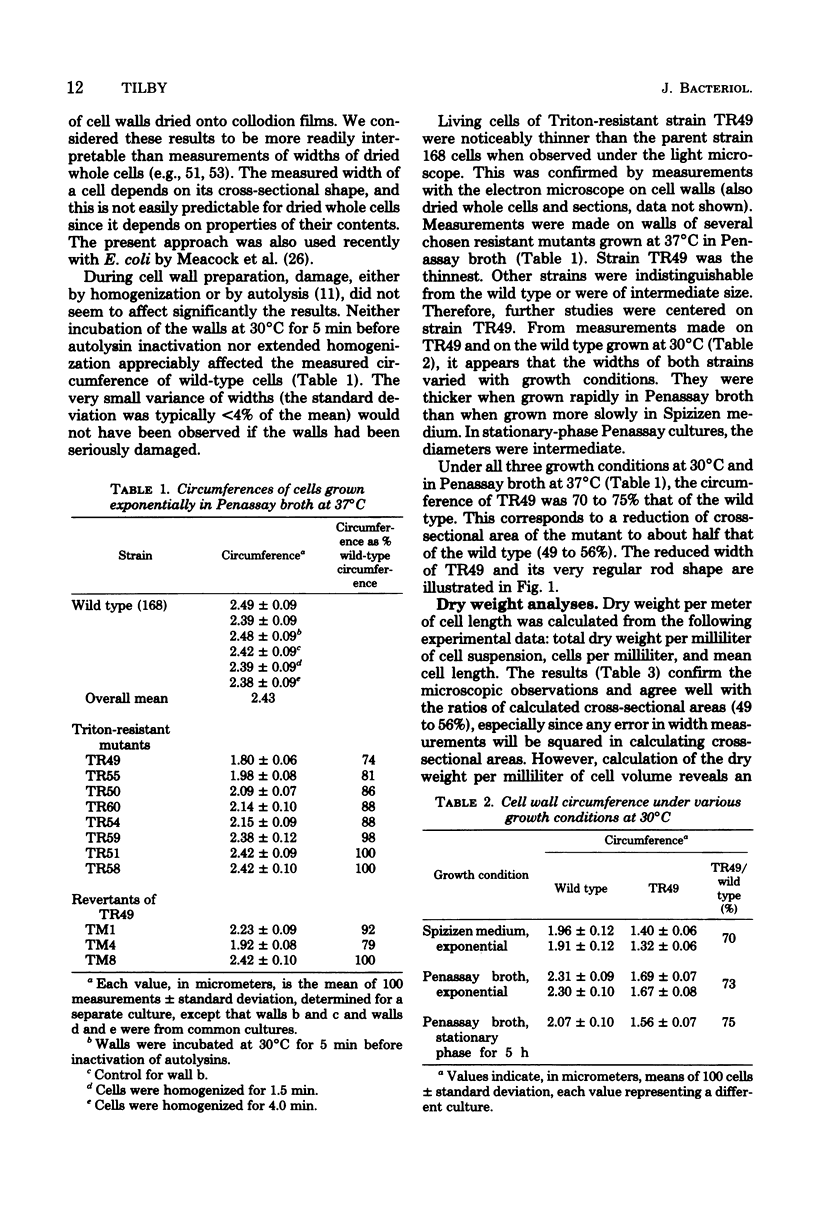
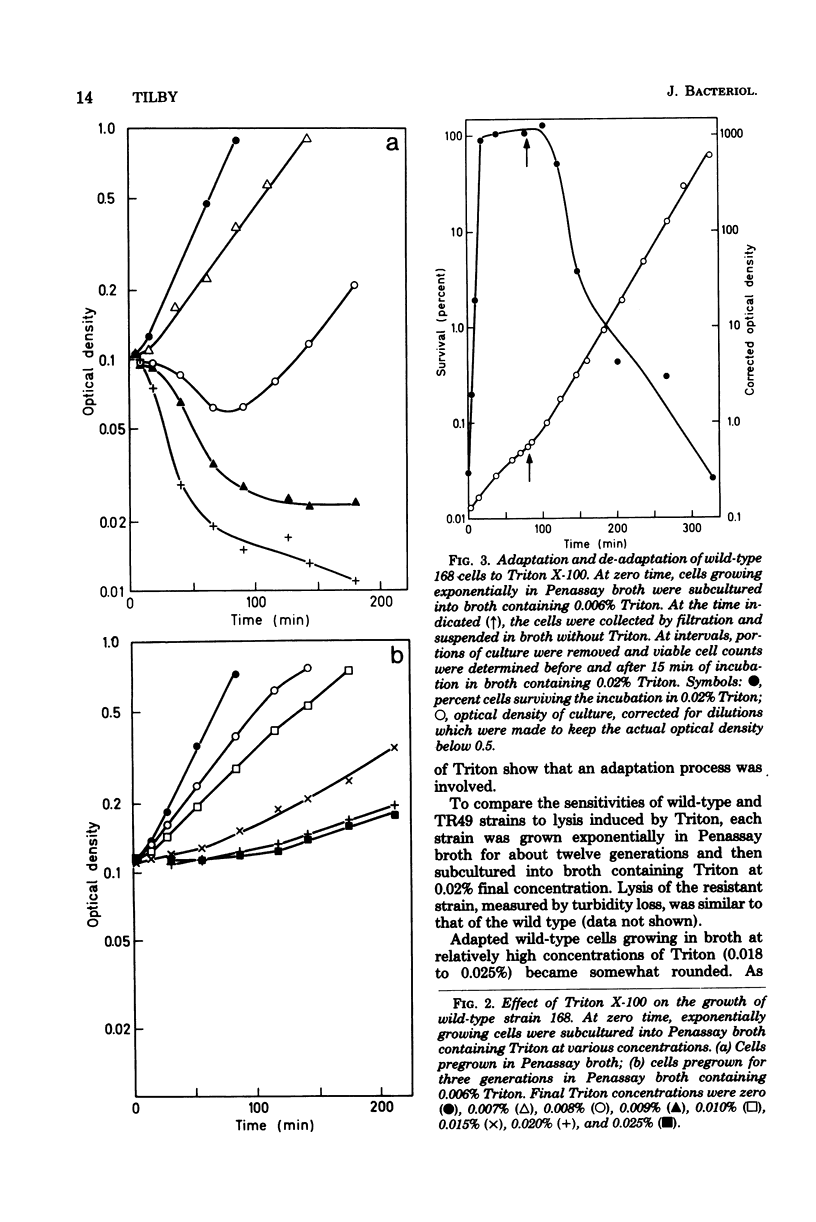
Variants of Bacillus subtilis resistant to the detergent Triton X-100 may exhibit: (i) normal cell morphology, (ii) reduced cell diameter, or (iii) helical cell shape. One variant of type ii was studied in some detail. Triton resistance, cell diameter reduction, and poor sporulation all may have resulted from a single mutation. High concentrations of Triton caused rapid lysis of wild-type cells. B. subtilis adapted to low Triton concentrations such that, upon subsequent exposure to higher concentrations, growth continued, although it bacame inhibited at very high concentrations. The variant studied retained its sensitivity to Triton-induced lysis but, after adaptation, grew at very high Triton levels. In this strain, cell diameter and cross-sectional area were reduced to about 73 and 50%, respectively, of those of wild type, yet the cells grew at normal rates, and DNA/protein/RNA ratios were largely unaltered. Peptidoglycan content per unit of cell surface area was higher in the variant than in the wild type under at least certain growth conditions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Terry C. E., Hardigree A. A. Giant cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):139–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.139-142.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARAC-NIETO M., OSPINA B., DUENAS A., MARTINEZ-PINTO I., MEJIA C., RODRIGUEZ E., HUNTER F. R. Permeability of erythrocytes to sugars. II. Effect of triton X-100. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1963 Jun;61:223–233. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030610303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohin J. P., Bohin A., Schaeffer P. Increased nitrate reductase A activity as a sign of membrane alteration in early blocked asporogenous mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Biochimie. 1976;58(1-2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80360-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohin J. P., Rigomier D., Schaeffer P. Ethanol sensitivity of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis: a new tool for the analysis of the sporulation process. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):934–940. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.934-940.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland J. C. Regulation of chromosome replication in Bacillus subtilis: effects of amino acid starvation in strain W23. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):595–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.595-603.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland J. C. Regulation of chromosome replication in Bacillus subtilis: marker frequency analysis after amino acid starvation. Science. 1971 Apr 9;172(3979):159–161. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3979.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuticke B. Transformation and restoration of biconcave shape of human erythrocytes induced by amphiphilic agents and changes of ionic environment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 10;163(4):494–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D., Begg K. J., Vicente M. Cell length, cell growth and cell division. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):328–333. doi: 10.1038/264328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Beckman M. M. Mutant of Bacillus subtilis demonstrating the requirement of lysis for growth. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):629–636. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.629-636.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P. Cell wall binding properties of the Bacillus subtilis autolysin(s). J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):488–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.488-493.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Sheu C. W., Galliers E. Function of lipophilic acids as antimicrobial food additives. Nature. 1973 Feb 2;241(5388):321–325. doi: 10.1038/241321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARY N. D., BARD R. C. Effect of nutrition on the growth and metabolism of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):501–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.4.501-512.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser L. Bacterial cell surface polysaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:91–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning U. L. Determination of cell shape in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:45–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning U., Rehn K., Braun V., Höhn B. Cell envelope and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Properties of a temperature-sensitive rod mutant. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 24;26(4):570–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O. Adaptation of membrane lipids to alcohols. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):670–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.670-678.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Kitagawa T. Effect of lipid composition on sensitivity of lipid membranes to Triton X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., ARBER W. Electron microscopical studies of phage multiplication. I. A method for quantitative analysis of particle suspensions. Virology. 1957 Apr;3(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Turbidity measurements of bacterial cultures in some available commercial instruments. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E. Salt-induced contraction of bacterial cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):775–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.775-781.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvin D. A. Control of DNA replication by membrane. Nature. 1968 Aug 3;219(5153):485–486. doi: 10.1038/219485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock P. A., Pritchard R. H., Roberts E. M. Effect of thymine concentration on cell shape in Thy- Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):320–328. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.320-328.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson N. H. Helical growth of Bacillus subtilis: a new model of cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1740–1744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGG J. E., ZELLE M. R. Isolation and characterization of a large cell possibly polyploid strain of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1957 Oct;74(4):477–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.4.477-484.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L. T., Marquis R. E. Electromechanical interactions in cell walls of gram-positive cocci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.92-101.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL E. O., ERRINGTON F. P. Generation times of individual bacteria: some corroborative measurements. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 May;31:315–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., McConnell M., Burdett I. D. The isolation and characterization of mutants of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis with disturbed morphology and cell division. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):155–171. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., MAALOE O., KJELDGAARD N. O. Dependency on medium and temperature of cell size and chemical composition during balanced grown of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):592–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Control of cell length in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):7–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.7-19.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlieper P., De Robertis E. Triton X-100 as a channel-forming substance in artificial lipid bilayer membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Nov;184(1):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K. P., Armitage J., Rowbury R. J. A change in cell diameter associated with an outer membrane lesion in a temperature-sensitive cell division mutant of Salmonella typhi-murium. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Sep;125 B(2):233–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Singer S. J. Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M., Schaechter M. Control of cell division in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):199–221. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.199-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilby M. J. Helical shape and wall synthesis in a bacterium. Nature. 1977 Mar 31;266(5601):450–452. doi: 10.1038/266450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Waks S. Enzyme replacement in a bacterium: phenotypic correction by the experimental introduction of the wild type enzyme into a live enzyme defective mutant pneumococcus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit J. N., Strominger J. L. Relation of detergent HLB number to solubilization and stabilization of D-alanine carboxypeptidase from Bacillus subtilis membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2997–3001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwer R. W., Nanninga N. Electron microscopy of isolated cell walls of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):195–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00425135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WON W. D. The production of "giant" cells of Pasteurella pestis by treatment with camphor. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):102–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.102-104.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberger C. L., Beaman A. J., Lee L. N. Tween 80 effect on glucosyltransferase synthesis by Streptococcus salivarius. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):231–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.231-239.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldringh C. L., de Jong M. A., van den Berg W., Koppes L. Morphological analysis of the division cycle of two Escherichia coli substrains during slow growth. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):270–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.270-279.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaritsky A., Pritchard R. H. Changes in cell size and shape associated with changes in the replication time of the chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):824–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.824-837.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




