Abstract
Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 (SCA2) belongs to the group of neurodegenerative diseases caused by expansion of a polyglutamine (polyQ) domain. Overexpression of mutant ataxin-2 causes cell death and Golgi dispersion in cell culture as well as morphologic and functional changes in mouse models. To further define the mechanism of ataxin-2 induced cell death, we compared the cytotoxic effects of different domains of normal and mutant ataxin-2. N-terminal truncated ataxin-2N- with expanded polyQ repeats did not form intranuclear inclusion and was less cytotoxic than the corresponding full-length ataxin-2. Ataxin-2del42[Q22], which lacks 42 amino acids (aa) within the Lsm-associated domain (LsmAD) necessary for Golgi localization, showed a diffuse cytoplasmic localization and was more toxic than wild type ataxin-2[Q22]. Mutant ataxin-2del42[Q108] displayed the same toxicity as ataxin-2[Q108], but did not disperse the Golgi apparatus to the extent seen with full-length mutant proteins. These observations confirm that ataxin-2 cytotoxicity increases with increasing polyQ expansion and Golgi dispersion, and indicate that, in contrast to other polyQ diseases, N-terminal fragments containing the polyQ repeat are less toxic than full-length ataxin-2. Deletion of 42 aa in the Lsm-AD in ataxin-2 results in cytotoxicity without significant abnormalities in the Golgi apparatus. These findings suggest that the C-terminal domains are important for ataxin-2 cytotoxicity and that Golgi abnormalities may not be primary in the pathogenic process.
Keywords: spinocerebellar ataxia type 2, SCA2, polyQ protein, neurodegenerative disease, Ls-associated domain, Golgi dispersion, cytotoxicity, COS1, overexpression, cell model
Introduction
Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 (SCA2) is a polyglutamine (polyQ) neurodegenerative disease that results from the expansion of a CAG trinucleotide repeat in the coding region of the ataxin-2 gene (Imbert, et al., 1996, Pulst, et al., 1996, Sanpei, et al., 1996). The normal SCA2 gene sequence contains 14–31 CAG repeats, and symptoms of SCA2 occur when the CAG repeats are increased to 32 or greater. Increasing the length of the polyQ repeat is associated with more severe clinical symptoms and an earlier onset (Estrada, et al., 1999, Imbert, et al., 1996, Pulst, et al., 1996, Pulst, et al., 2005, Sanpei, 1999). Mice expressing mutant ataxin-2 with 58 glutamines (ataxin-2[Q58]) showed progressive functional deficits accompanied by loss of the Purkinje cell dendritic arbor and finally loss of Purkinje cells (Huynh, et al., 2000).
Ataxin-2 is a basic protein except for the acidic domain (amino acids 280–481) downstream of the polyQ repeat (Shibata, et al., 2000). Within the acidic domain are a putative caspase-3 motif (aa396–399), RNA splicing motifs (Lsm; like sm; aa254–345) and an Lsm-associated domain (LsmAD, aa353–475). The Lsm/LsmAD contains a putative clathrin-mediated transGolgi signal (aa414–416), and an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit signal (aa426–428). In addition, ataxin-2 also contains a PABP/Pab1 binding motif (PAM2) downstream of the LsmAD (aa908–925). The yeast homolog of ataxin-2, Pbp1, which also contains the Lsm domain similar to ataxin-2, regulates polyadenylation and binds to the yeast poly(A) binding protein, Pabp1 (Mangus, et al., 1998, Mangus, et al., 2003). Pabp1 is an ortholog of the human poly(A)-binding protein 1 (PABP1) which also binds to human ataxin-2 (Ralser, et al., 2005). The presence of the Lsm domain in both human and yeast ataxin-2 suggests that ataxin-2 can bind to RNA and regulate RNA metabolism and/or RNA processing in common with other Lsm domain proteins (Albrecht, et al., 2004). The identification of A2BP1 (ataxin-2 binding protein 1) as an interactor of ataxin-2 by yeast two-hybrid assays (Shibata, et al., 2000) further supports the notion that ataxin-2 is involved in RNA regulation. A2BP1 also contains RNA-recognition domains. The C. elegans ortholog of A2BP1, Fox-1 interacts with RNA and controls tissue specific alternative splicing (Jin, et al., 2003).
In polyQ diseases as well as in other neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson and Alzheimer disease, neuronal death is associated with cytoplasmic or intranuclear aggregation or accumulation of mutant proteins (DiFiglia, et al., 1997, Huynh, et al., 1999, Huynh, et al., 2000, Klement, et al., 1998, Koyano, et al., 2002, Koyano, et al., 2000, Paulson, et al., 1997, Uchihara, et al., 2001). Although intranuclear aggregates are seen in a small number of brain stem neurons in SCA2 patients (Koyano, et al., 2002, Koyano, et al., 2000) and COS1 cells transiently transfected with ataxin-2[Q108] (Huynh, et al., 2003), cytoplasmic aggregates predominate without the formation of large inclusion bodies, and no nuclear inclusions have been observed in Purkinje neurons of SCA2 patients (Huynh, et al., 1999, Huynh, et al., 2000, Koyano, et al., 2002). Co-expression with parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, alleviated the cytotoxicity of mutant ataxin-2 (Huynh, et al., 2006).
Wild type ataxin-2[Q22] colocalized with a transGolgi 58K marker and was found in the Golgi/endosomal fraction after differential centrifugation (Huynh, et al., 1999, Huynh, et al., 2003, Shibata, et al., 2000). Deletion of a 42 amino acid (aa) domain (ataxin-2del42 [Q22]) that resides within the LsmAD resulted in loss of Golgi association (Huynh, et al., 2003). Ataxin-2 with an expanded polyQ repeat disrupted the normal morphology of the Golgi complex and increased cell death.
We now report the subcellular distribution, Golgi morphology and viability of COS cells transfected with different ataxin-2 domains. These experiments were carried out with proteins containing the normal 22 glutamine repeat domain and proteins with the polyQ domain expanded to 58 and 108Q.
Materials and Methods
Plasmid Construction
The pEGFPC2-ataxin-2[Q22], pEGFPC2-ataxin-2[Q58], and pGFP-ataxin-2[Q108] plasmids were constructed as previously described (Huynh et al., 2003), and confirmed by sequencing. To construct the pEGFPC2-ataxin-2N[Q22] plasmid, the pEGFP-SCA2[Q22] vector containing the full-length ataxin-2 was digested with BamHI, which cuts at nucleotide 1349. This plasmid was designated pEGFPC2-ataxin-2[Q22]N. The ataxin-2del42 [Q22] plasmid was constructed by digesting the plasmid pGFPC2-SCA2[Q22] with SnaBI and XhoI at nucleotides 1404 and 1530, respectively. This restriction digest removed amino acid residues 414 to 456 within the LsmAD. The deleted amino acid sequence contains a putative clathrin-mediated transGolgi signal (aa residues 414–416) and a putative ER exit signal (aa residues 426–428) (Figueroa and Pulst, 2003, Pulst, et al., 1996). The XhoI 5’-overhang was blunt-ended by T4 DNA polymerase, and was religated in-frame with the SnaBI-digested blunt-end by T4 DNA ligase. This plasmid construct was designated pEGFPC2-ataxin-2del42[Q22]. This plasmid was inadvertently described as carrying a 43 aa deletion instead of a 42 aa deletion by Huynh et al. (2003). Plasmids pEGFC2-ataxin-2del42[Q58] and pEGFPC2-ataxin-2del42[Q108] were generated by transferring the 3’-terminal BamHI restricted fragment of pEGFPC2-ataxin-2del42[Q22] to the 5’-BamHI restricted fragment of either pEGFC-ataxin-2[Q58] or pEGFPC2-ataxin-2[Q108].
Sequence analysis of all ataxin-2 constructs confirmed the presence of the respective CAG repeats and the sites of N-terminal truncation or interstitial deletion. Sequence analysis of the C-terminus identified presence of an additional 6 nucleotides encoding Gly-Lys not reported in the original SCA2 cDNA sequence. We have subsequently found that they are due to use of an alternative splice site in the intron between exons 18 and 19. This cDNA splice variant is abundant in human and mouse brain and was originally reported in the mouse cDNA sequence (Nechiporuk et al. 1998). It has been reported for several other species as well.
Cell Culture
All culture media (DMEM, FBS, and Penicillin/Streptomycin) were purchased from Invitrogen Inc. COS1 cells were grown in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS and penicillin/streptomycin in an incubator at 37C° and 5% CO2. Cells were seeded at a subcultivation ratio of 1:3 to 1:6 every 3 days. One day prior to transfection, 200,000 cells were seeded on polylysine coated 1 cm2 coverslip placed in 6-wells dishes.
Transient Transfection
Plasmid DNA was mixed with polyfect transfection reagent and transiently transfected into overnight COS1 cell cultures according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Qiagen). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were collected for either cell death assay or immunofluorescent staining. To achieve equal transfection efficiencies for all plasmids, we measured DNA concentrations by spectrophotometry, and independent confirmation by serial dilutions of ethidium-bromide stained agarose gels. Equal molar ratios of the plasmids were used for each experiment.
Trypan Blue Exclusion Assay
We used the trypan blue exclusion assay to determine cell death. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were incubated with an equal volume of 0.4% trypan blue for 5 minutes. Labels were covered to blind the individual (SN) scoring the assay. Trypan blue will stain dead cells, while live cells exclude the dye. Cells were viewed under the Zeiss Axiovert 100 fluorescence microscope. GFP-positive cells stained with trypan blue were counted. Percentage of cell death was calculated by dividing the number of GFP-positive cells stained with trypan blue by the total number of GFP positive transfected cells. Two experiments were performed in triplicate. To combine different experiments, experiments were normalized by dividing the death rate seen for a given construct by the average of cell death in cells transfected with pEGFP vector in each experiment.
7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) assay
Cells were plated in triplicate per experiment. 24 to 72 hours after transfection, cells were washed once with cold PBS. Cells were then incubated with 1 ml of cold PBS containing 1 μg/ml of 7-AAD per 1 X 106 for 5 to 20 minutes. Cell viability was analyzed by flow cytometry using an excitation/emission wavelengths of 488 nm/508 nm for GFP and 488/650 nm for 7-AAD. A total of 10,000 events were counted for each sample. Cytotoxicity was calculated by dividing the number of 7-AAD positive cells by the total number of GFP positive cells.
Immunofluorescent Staining and Golgi Score
After 24 hours following transfection, cells were fixed with cold 4% PFA for 20 minutes. They were then washed three times with cold DPBS and unmasked for 5 minutes with 0.2% Triton X-100 in DPBS, washed and incubated with blocking buffer (3% normal goat serum, 0.05% Triton X-100, DBPS) for 30 minutes at RT. Cells were then incubated with a 1/50 dilution of mouse antiGolgi58 (Sigma) in blocking buffer overnight at 4°C. On the 2nd day, cells were washed 4 times with cold DPBS, and then incubated with a 1/150 dilution of goat TRITC-conjugated antimouse IgG in blocking buffer for 1 hour at RT. The slides were washed 6 times with cold DPBS for 5 minutes each. Slides were mounted with Prolong Reagent (Invitrogen/Molecular Probe).
To score Golgi co-localization and Golgi dispersion, GFP-SCA2 transfected cells were stained with mouse antiGolgi58K antibody (Sigma), and visualized with Rhodamine-conjugated antimouse IgG. Stained cells were then viewed by fluorescence microscopy. Transfected cells with the GFP-ataxin-2 localized within the Golgi58K labeling were scored, and normalized with the total number of transfected cells. Cells with a dispersed GFP-ataxin-2 distribution were scored as Golgi negative. A total of 94 to 155 transfected cells from three different slides (n=3) were scored. Labels on slides were covered to blind the scorer.
Statistical Analysis
All experiments were conducted in triplicate. The results of each set of two experiments were combined by normalizing cytotoxicity to that seen in cells transfected with GFP-vector. This was accomplished by dividing all the observed death rates in transfected cells by the mean death rate of cells transfected with GFP vector in the same experiment. Relative cytotoxicities for each group of experiments were analyzed by One-way ANOVA. If One-way ANOVA analysis was significant (P<0.05), a pairwise comparison was performed using Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test (GraphPad Prism software).
Results
PolyQ pathogenic expansion increases cytotoxicity
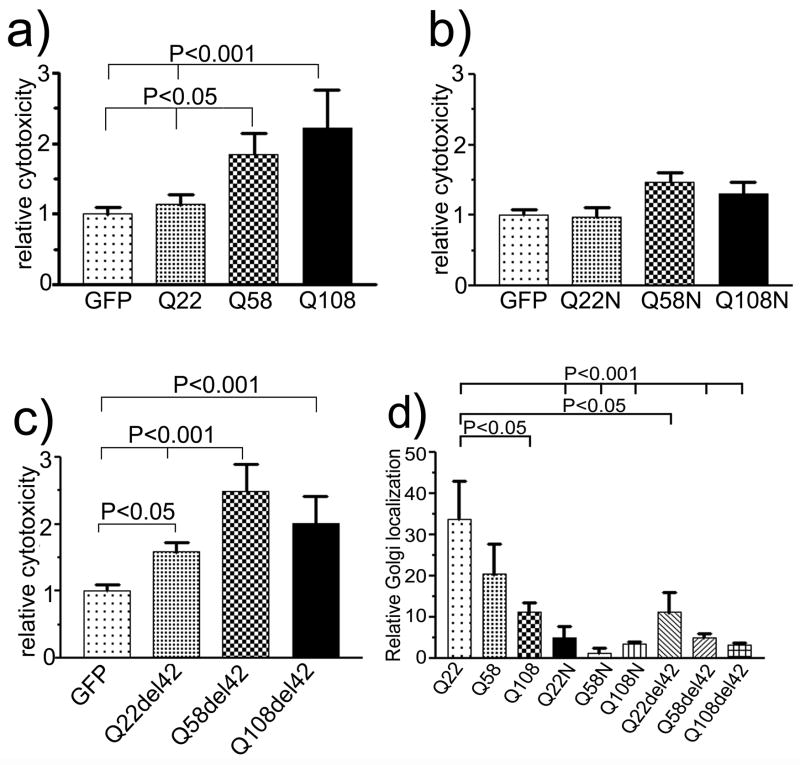
Since expansion of the polyQ repeat imparts increasing cytotoxicity to ataxin-2 (Huynh, et al., 2003), we transiently transfected COS1 cells with pEGFP-ataxin-2[Q22], pEGFP-ataxin-2[Q58], or pEGFP-ataxin-2[Q108] to confirm these observations (Fig. 1a). One-way ANOVA analysis (P<0.001) followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test showed that both ataxin-2[Q58] and ataxin-2[Q108] caused significant increases in cell death compared to wild type ataxin-2[Q22] and the GFP control. Compared with GFP vector (1.00 ± 0.102), wild type ataxin-2[Q22] (1.134 ±0.137; Tukey’s multiple comparison test, P>0.05) showed a non-significant increase in cell death, whereas ataxin-2[Q58] (P < 0.05) and ataxin-2[Q108] (P < 0.001) increased cell death to 1.84 ± 0.31 and 2.22 ± 0.54 fold (Mean ± SD), respectively (Fig. 1a). Although there was an increase in cell death in ataxin-2[Q108] relative to ataxin-2[Q58], the increase was not significant (P>0.05). At least 660 cells were counted at each data point. These results confirmed previous observations that ataxin-2 with an expanded polyQ domain was cytotoxic in vitro (Huynh, et al., 2003).
Figure 1.
Cytotoxicity in COS1 cells expressing ataxin-2 with different polyQ repeats. COS1 cells were transiently transfected with pEGFPC2 control plasmid and pEGFP-SCA2[Q22], pEGFP-SCA2[Q58], and pEGFP-SCA2[Q108]. After 24 hours, cell death was determined by trypan blue exclusion. Relative cytotoxicity was obtained by dividing the number of trypan blue and GFP-positive cells by the total number of counted GFP positive cells. This ratio was normalized by the ratio seen in cells transfected with the GFP vector control. (a) Cytotoxicity induced by normal and mutant full length ataxin-2. (b) Cytotoxicity induced by the N-terminal ataxin-2 fragment containing different polyQ repeats (Q22N, Q58N, Q108N), and (c) Cytotoxicity induced by full-length ataxin-2 with deletion of 42 aa in the Lsm-AD domain, (Q22del42, Q58del42, and Q108del42). Each histogram represents the Mean ± SD of two independent experiments performed in triplicate (n=6). One way ANOVA for data shown in Fig. 1a and c was significant (p<0.0001). (d) Relative Golgi localization of full-length (Q22, Q58, Q108), truncated (Q22N, Q58N, and Q108N), and deleted Lsm-AD domain (Q22del42, Q58del42, and Q108del42) ataxin-2 in COS1 cells. Relative Golgi localization was calculated by dividing the number of Golgi localized cells with the total number of transfected cells. Each histogram represents the Mean ± SD of 3 different slides. Compared with full-length wild type ataxin-2[Q22], polyQ repeat expansion, truncation or deletion of the Lsm-AD domain decrease association of ataxin-2 with the Golgi apparatus significantly (One-way ANOVA, P<0.0001). The P values obtained from Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test are shown above the respective bars.
Next, we examined the cytotoxicity of truncated N-terminal ataxin-2 fragments encompassing aa1–396 designated ataxin-2N. Ataxin-2N[Q22] did not show any increase in toxicity compared with vector control (Fig. 1b). Although an expanded polyQ domain increased cell death compared with ataxin-2N[Q22], the increase in cytotoxicity was relatively minor compared to full-length ataxin-2 (P>0.05) (Fig. 2a, 3a, 4a). In a separate set of experiments, we directly compared cytotoxicity of full-length and truncated ataxin-2N bearing 22, 58, or 108 glutamines (Figs. 2–4). These experiments confirmed that truncation of ataxin-2 at aa396 virtually abolished cytotoxicity.
Figure 2.
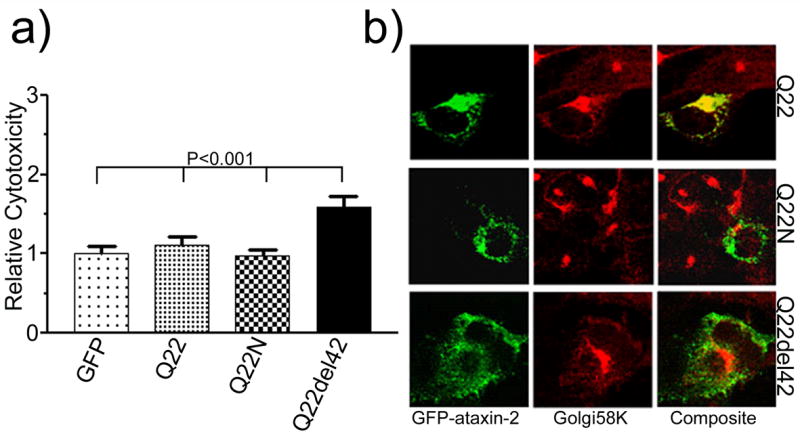
Cytotoxicity and subcellular localization of wild type ataxin-2. (a) Cytotoxicity of full-length ataxin-2[Q22] , truncated ataxin-2N[Q22], and LsmAD deleted ataxin-2del42[Q22] . Cell death (n=6) was analyzed by trypan blue exclusion assay. Each histogram represents the Mean ± SD of two independent experiments performed in triplicate (n=6). Deletion of the LS-AD domain (Q22del42) significantly increased cell death compared to GFP control, full-length (Q22), and truncated ataxin-2 (Q22del42) (One-way ANOVA, P<0.0001; the P values obtained from the Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test are shown above the respective bars). (b) Ataxin-2N[Q22] and ataxin-2del42[Q22] lose Golgi association. Transfected cells were stained with mouse anti-Golgi58K antibody and visualized with TRITC-conjugated antimouse IgG. Images were obtained by confocal laser microscopy using a 100X lense objective. Note that Golgi morphology is unperturbed in transfected cells when compared with untransfected cells.
Figure 3.
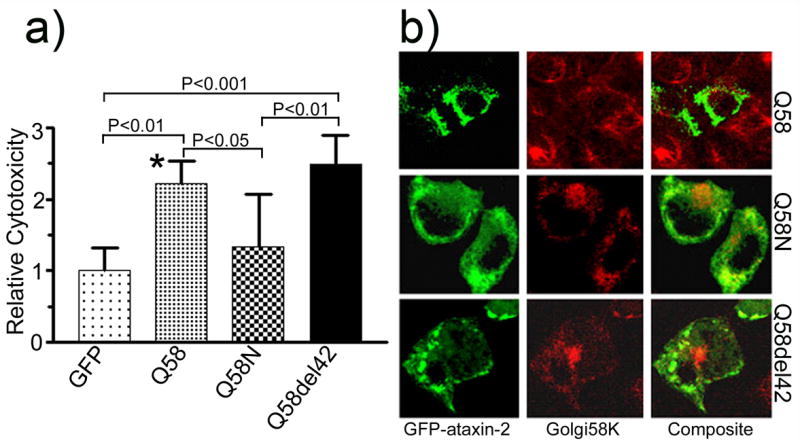
Cytotoxicity and subcellular localization of mutant ataxin-2[Q58]. (a) Full-length ataxin-2[Q58] and ataxin-2del42[Q58], but not ataxin-2N[Q58] show increased cell death compared with GFP vector control (One-way ANOVA P<0.0001). Each histogram represents the Mean ± SD of two independent experiments performed in triplicate (n=6, except for * where n=5). The P values obtained from the Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test are shown above the respective bars. (b) Transfection of full-length ataxin-2[Q58] disrupted Golgi labeling, while both truncated ataxin-2N[Q58] and Lsm-AD deleted ataxin-2del42[Q58] did not affect Golgi labeling. Note the prominent formation of perinuclear aggregates in cells transfected with ataxin-2del42[Q58].
Figure 4.
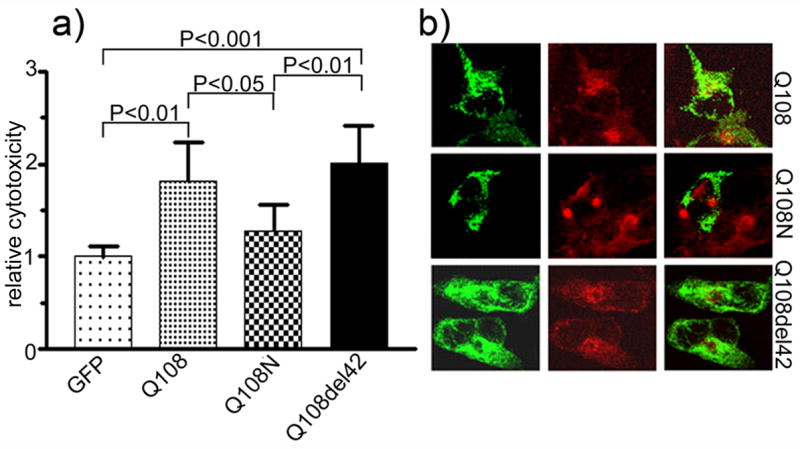
Cytotoxicity and subcellular localization of mutant ataxin-2[Q108]. Cytotoxicity (a) and subcellular distribution (b) of full-length ataxin-2[Q108], ataxin-2N[Q108], and ataxin-2del42[Q108]. Cell death (n=6) was analyzed by trypan blue exclusion assay. Each histogram represents the Mean ± SD. Both full-length and ataxin-2del42[Q108]a significantly increased cell death (One-way ANOVA, P<0.0001). The P values of the Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test are shown above the respective bars. The truncated ataxin-2 (Q108N) containing 108 glutamine repeats did not cause any significant cell death. Transfection of full-length ataxin-2[Q108] disrupted the Golgi apparatus, while both truncated (Q108N) and Lsm-AD deleted (Q108del42) ataxin-2 did not affect the Golgi apparatus.
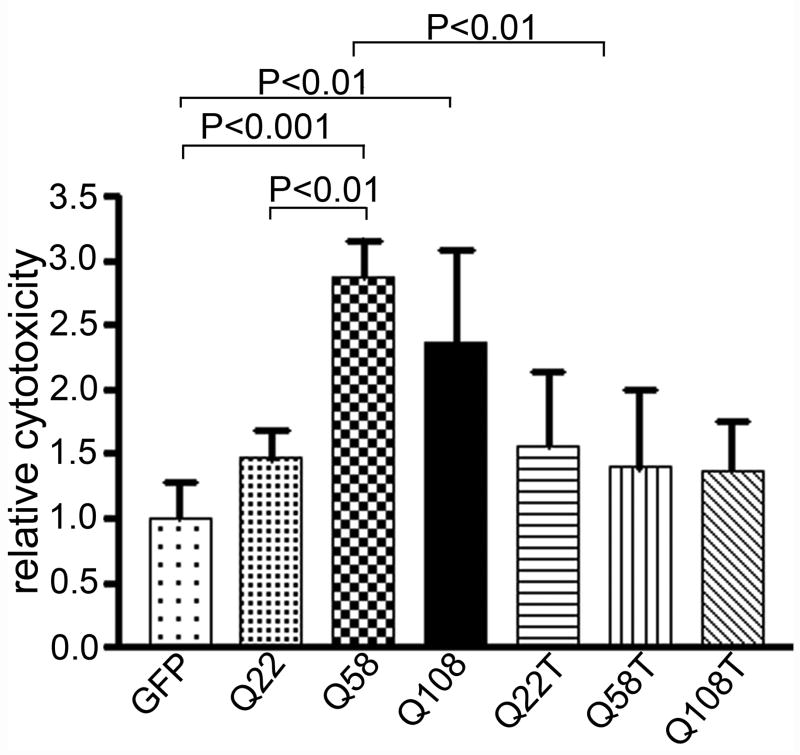
Similar results for full-length and truncated ataxin-2 were obtained in HEK293 cells using 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) exclusion followed by flow cytometric analysis (Figure 6). Deletion of a 42 amino acid fragment within the Lsm-Associated-Domain prevents Golgi dispersion induced by mutant ataxin-2. Using a scoring method for Golgi co-localization, co-localization decreased from 33.7 ± 9.2% (Mean ± SD) of cells for wild type ataxin-2[Q22] to 20.4 ± 12.9% for ataxin-2[Q58] (P>0.05) and to 11.4 ± 3.9% for ataxin-2[Q108] (P<0.05; Fig. 1d). Golgi localization for truncated and LsmD deleted constructs was less than 10% (Fig. 1d) and significantly different from wild type ataxin-2[Q22]. The Golgi apparatus remained intact in cells expressing ataxin-2[Q58]del42 and ataxin-2[Q108]del42 (Fig. 3b, 4b).
Figure 6.
Cytotoxicity of ataxin-2 by 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD). Cells were transfected with full-length and truncated pEGFP-SCA2 containing different polyQ repeats. 24 hours posttransfection, cells were washed once with cold PBS, and incubated with 300 ul (~1 x 106 cells/ml) of PBS containing 1 ug/ml for 5 to 20 minutes on ice. Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry. Percentage of cell death was determined by dividing the number of 7-AAD positive GFP expressing cells over the total number of GFP positive cells. Results were normalized with the average of cell death in cells expressing on the pEGFP plasmid (n =6). Relative cytotoxicity measured using the 7-AAD method and flow cytometry is similar to the trypan blue exclusion method. (One-way ANOVA, P<0.0001). The P values obtained from Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test are shown above the respective bars.
Deletion of 42 amino acids in the LsmAD enhances cytotoxicity of wild type ataxin-2
Ataxin-2 and the homologous Ataxin-2 related protein (A2RP) contain a highly conserved 42 aa domain (Figueroa and Pulst, 2003). Previous experiments had shown that deletion of this domain resulted in loss of colocalization of ataxin-2 with the 58K trans-Golgi marker (Huynh, et al., 2003). Analysis of cytotoxicity now indicated that deletion of this domain also increased cell death (Fig. 1c; one-way ANOVA p<0.0001). Pairwise comparisons confirmed that ataxin-2del42[Q22], [Q58], and [Q108] all had increased toxicity compared with vector control. Direct comparison of ataxin-2del42[Q22] with full-length ataxin-2[Q22] and truncated ataxin-2N[Q22] also indicated significantly increased cytotoxicity (Fig. 2a). When ataxin-2del42[Q58] and ataxin-2del42[Q108] were compared with the respective full-length mutant proteins (Fig. 3a, 4a), no further increase in cytotoxicity was observed (P>0.05). This potentially reflects a ceiling effect in our cell death assay.
Subcellular distribution and Golgi co-localization
Truncated polyQ proteins (huntingtin and ataxin-3) containing a pathologically expanded polyQ repeat are associated with increased cytotoxicity and increased aggregate formation in both the perinuclear and nuclear areas in various cellular models (Igarashi, et al., 2003, Martindale, et al., 1998, Ross, et al., 1999, Yoshizawa, et al., 2000). We therefore examined whether ataxin-2N or ataxin-2del42 assumed a different subcellular localization and examined this question for proteins with three different sizes of the polyQ domain (Q22, Q58, and Q108). We also examined co-localization of the respective protein with the trans-Golgi58K marker protein.
Quite surprisingly, the N-terminal fragment did not acquire a nuclear localization. Ataxin-2N[Q22] remained cytoplasmic and showed a diffuse cytoplasmic localization rather than aggregation and intranuclear localization (Fig. 2b). This remained true for truncated ataxin-2N[Q58] and ataxin-2N[Q108] (Fig. 3b, 4b). Ataxin-2del42 with an interstitial deletion of 42aa showed a cytoplasmic localization. In contrast to ataxin-2N, cells transfected with ataxin-2del42 showed increased formation of perinuclear aggregates, which became more evident in the presence of an expanded polyQ repeat (Fig. 3b,4b). Wild type ataxin-2 shows partial co-localization with markers of the trans-Golgi in vitro. To determine whether truncation or interstitial deletion would alter Golgi co-localization, we labeled transfected cells with a monoclonal antibody to the Golgi58K protein (Figs 2–5). As previously observed (Huynh, et al., 2003, Shibata, et al., 2000), GFP-tagged ataxin-2[Q22] colocalized with the anti-Golgi58K antibody in transfected cells (Fig. 2B). The morphology of the Golgi apparatus appeared normal in cells expressing wild type ataxin-2. In cells transfected with mutant full-length ataxin-2, Golgi co-localization was reduced and the Golgi staining itself was weaker (Figs. 3B, 4B). In contrast, cells expressing ataxin-2N and ataxin-2del42 retained normal Golgi staining, although co-localization was lost (Figs. 3B, 4B).
Figure 5.
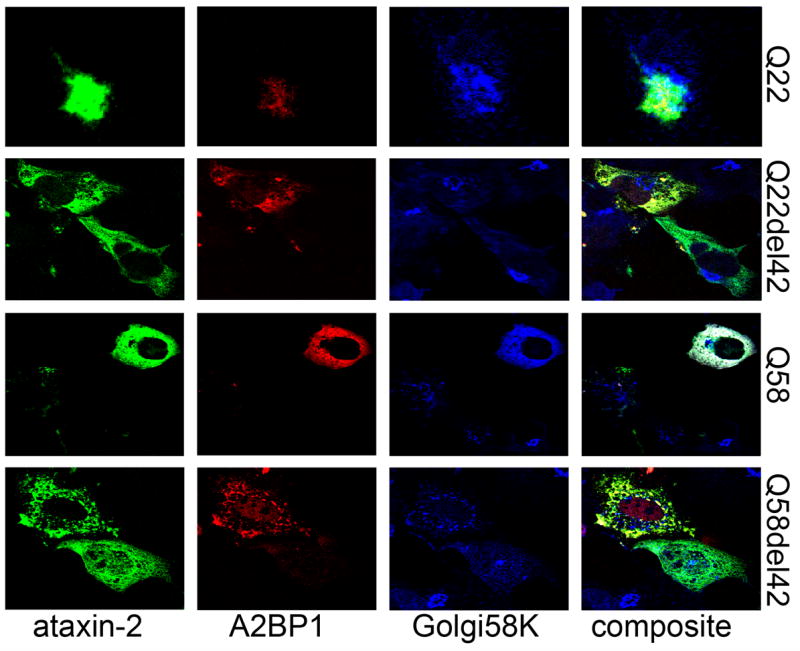
Co-localization of ataxin-2 and ataxin-2 binding protein 1 (A1BP1) in transiently transfected COS1 cells. Single confocal sections through the nucleus are shown. COS1 cells were co-transfected with pDsRed2-A2BP1 (Red) and pEGFP-ataxin-2 (Green). After 24 hours, cells were immunofluorescently stained with mouse anti-Golgi58 antibody, and visualized with C5 conjugated antimouse IgG (Blue). A2BP1 colocalizes with full-length ataxin-2[Q22] in the Golgi apparatus. Expansion of the polyQ repeats disrupts the Golgi apparatus but ataxin-2[Q58] still colocalizes with A2BP1 in Golgi elements. Deletion within the LsmAD prevents ataxin-2 and A2BP1 localization in the Golgi apparatus, and retains A2BP1 in the nucleus.
Ataxin-2 co-localization with ataxin-2 binding protein 1 (A2BP1)
To further define the relationship between ataxin-2 and its interactor, A2BP1, we coexpressed DsRed2-A2BP1 with GFP-ataxin-2 in COS1 cells, and analyzed the distribution of A2BP1 in cells expressing different forms of ataxin-2. DsRed2-A2BP1 colocalized with GFP-ataxin-2[Q22] and the 58K Golgi marker protein (Fig. 5, Q22) as previously demonstrated with endogenous ataxin-2 and A2BP1 (Shibata et al, 2000). In the absence of ataxin-2 co-expression, exogenous A2BP1 localizes predominantly in the nucleus in COS cells (data not shown). When coexpressed with ataxin-2[Q58], A2BP1 co-distributes with ataxin-2[Q58] in elements of the dispersed Golgi apparatus. A deletion within the LsmAD did not inhibit A2BP1 and ataxin-2 colocalization, and resulted in reduced co-localization of A2BP1 with the 58K Golgi marker protein (Fig. 5, Q22del42 and Q58del42); however, cells expressing ataxin-2del42 retained more A2BP1 in the nucleus than cells coexpressing A2BP1 and full-length ataxin-2 (Fig. 5, Q22del42 and Q58del42). These observations suggest that expansion of the polyQ repeat and deletion within the LsmAD alter the subcellular distribution of A2BP1.
Discussion
Expression of a number of proteins with expanded polyQ repeats causes cell death in cell culture and –to a lesser degree- in animal models (Huynh, et al., 1999, Huynh, et al., 2000, Huynh, et al., 2003, Igarashi, et al., 2003, Martindale, et al., 1998, Ross, et al., 1999, Shibata, et al., 2000, Yoshizawa, et al., 2000). Expression of mutant ataxin-2 results in the formation of cytoplasmic aggregates in transgenic mouse models and human patients as well as degeneration of Purkinje neurons in brains of SCA2 patients (Huynh, et al., 1999, Huynh, et al., 2000). Intranuclear inclusions are rare in SCA2 compared with other polyQ diseases and are seen mainly in pontine neurons (Koyano, et al., 2002, Koyano, et al., 2000). Expression of full-length mutant ataxin-2 in COS1 and PC12 cells causes activation of apoptosis and cytotoxicity associated with morphologic changes of the Golgi apparatus (Huynh DP, 2003). In this study we examined the subcellular localization of wild type and mutant ataxin-2 fragments either truncated or bearing an interstitial deletion and their effect on cell death. We found that mislocalization of ataxin-2 by deleting a 42 aa domain increased cytotoxicity without noticeably altering Golgi morphology and that an N-terminal fragment had reduced rather than increased cytotoxicity.
N-terminal fragment
Fragments containing the polyQ repeats of huntingtin (Igarashi, et al., 2003, Martindale, et al., 1998), atrophin (Nucifora, et al., 2003), and ataxin-3 (Yoshizawa, et al., 2000) have been observed to form intracellular aggregates and are usually associated with increased toxicity compared with their respective full-length proteins (Igarashi, et al., 2003, Martindale, et al., 1998, Nucifora, et al., 2003, Yoshizawa, et al., 2000). Our observations with an ataxin-2 N-terminal fragment containing the polyQ repeat contrasts with observations in the aforementioned diseases. First, N-terminal ataxin-2 did not acquire an intranuclear localization, but remained cytoplasmic. Even when this fragment contained an expanded polyQ domain, the subcellular localization remained diffusely cytoplasmic without increased aggregate formation. Second, cell death was much reduced compared with the corresponding full-length mutant ataxin-2 proteins (Fig. 1, 3, 4). This suggests that domains downstream of the polyQ repeat are important in ataxin-2 mediated cell death in vitro. Indeed, the interaction of ataxin-2 and A2BP1 is mediated via the C-terminal two-thirds of ataxin-2 (Shibata, et al., 2000).
Subcellular localization
For ataxin-1 (Klement, et al., 1998), proper subcellular localization is necessary for cell death; mutation of a nuclear localization signal prevents pathogenicity of mutant ataxin-1 in transgenic mice. We had previously shown that deletion of a 42 aa domain, which is highly conserved in A2RP and in orthologs in other species (Figueroa and Pulst, 2003), resulted in loss of the prominent co-localization of ataxin-2 with Golgi marker proteins (Huynh, et al., 2003). Based on results with ataxin-1, we had hypothesized that loss of this domain might reduce toxicity. Instead, mutant ataxin-2del42 remained cytotoxic. Furthermore, deletion of this domain in wild type ataxin-2[Q22], resulted in greatly increased cytotoxicity. This suggests that improper subcellular localization of ataxin-2 may be an important aspect of SCA2 pathogenesis. Indeed, ataxin-2[Q58] and [Q108] lack the subcellular distribution typical of the wild type protein. Furthermore, expansion of the polyQ repeat also alters the subcellular distribution of ataxin-2 binding protein 1, A2BP1 (Fig. 5, Shibata et al, 2000).
It is of interest that Golgi morphology in cells transfected with mutant ataxin-2[Q58]del42 and ataxin-2[Q108]del42 was normal, despite significant toxicity of the protein. This suggests that altered Golgi morphology seen with expression of mutant ataxin-2[Q58, Q108] may not be directly causative or may only be a contributing factor (Fig. 3, 4).
Our studies begin to suggest a model for ataxin-2 in vitro toxicity. We had previously suggested a function for ataxin-2 related to RNA metabolism/translation based on the presence of SM1 and SM2 domains in ataxin-2 and the presence of RNA-binding domains in ataxin-2 binding protein 1 (A2BP1/fox-1) (Shibata, et al., 2000). Recent studies have confirmed a role for ataxin-2 in stress granule formation and ribosomal functioning (Ralser, et al., 2005, Satterfield and Pallanck, 2006, Nonhoff, et al., 2007). Stress granules consist of unstranslated mRNAs and RNA stabilizing (e.g. Hu protein R) and destabilizing proteins (e.g. tristetraprolin) and are sites of arrested mRNA translation at times of cellular stress (Kedersha and Anderson, 2002). Proteins contained in stress granules are known to remain in equilibrium between their localization on subcellular organelles and their predominant presence in granules during stress (Kedersha, et al., 2000, Tarun and Sachs, 1996).
The N-terminal fragment lacks the domain necessary for Golgi localization, but also the domains necessary for A2BP1 binding. Thus, although mislocalized, it may lack domains to exert a deleterious role in RNA metabolism. Ataxin-2del42 on the other hand looses the Golgi association and may be more readily available for formation of stress granules. As it contains the C-terminus, it is still able to interact with A2BP1 and may show altered function in mRNA metabolism or affect A2BP1 subcellular localization. This model is also supported by the observation that coexpression of ataxin-2del42 or mutant ataxin-2 with exogenous A2BP1 resulted in altered localization of A2BP1 (Fig. 5). Finally, full-length ataxin-2 with an expanded polyQ domain assumes an abnormal subcellular localization due to direct or indirect effects of the mutant polyQ domain. In contrast to the N-terminal fragment, it contains the C-terminal domains important for binding of A2BP1 and other potential interactors. Subcellular fractionation experiments have indicated that mutant ataxin-2 remains in the P3 fraction which includes Golgi membranes (Huynh, et al., 2003). This may explain the abnormal Golgi staining observed in cells expressing ataxin-2[Q58] and its absence in cells expressing ataxin-2[Q58]del42. Direct examination of these ataxin-2 fragments in stress granule formation and or interaction with A2BP1 will be necessary to validate this model.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Kolja Wawrowsky at the Cedars-Sinai Imaging Core for assistance in confocal microscopy, and Dr. Karsten Strauss for the DsRed-A2BP1. This study was supported by NIH grant K01-NS047548-01A1 and the Carmen Warschaw Neuroscience Scholar Award to HPD, and the Carmen and Louis Warschaw endowment, F.R.I.E.N.D.S. of Neurology, and NIH grants RO1-NS33124, R21NS048083, and P50NS0338367 (project 4) to SMP.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Albrecht M, Golatta M, Wullner U, Lengauer T. Structural and functional analysis of ataxin-2 and ataxin-3. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:3155–3170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.DiFiglia M, Sapp E, Chase KO, Davies SW, Bates GP, Vonsattel JP, Aronin N. Aggregation of huntingtin in neuronal intranuclear inclusions and dystrophic neurites in brain. Science. 1997;277:1990–1993. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5334.1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Estrada R, Galarraga J, Orozco G, Nodarse A, Auburger G. Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 (SCA2): morphometric analyses in 11 autopsies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1999;97:306–310. doi: 10.1007/s004010050989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Figueroa KP, Pulst SM. Identification and expression of the gene for human ataxin-2-related protein on chromosome 16. Exp Neurol. 2003;184:669–678. doi: 10.1016/S0014-4886(03)00287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Huynh DP, Del Bigio MR, Ho DH, Pulst SM. Expression of ataxin-2 in brains from normal individuals and patients with Alzheimer's disease and spinocerebellar ataxia 2. Ann Neurol. 1999;45:232–241. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199902)45:2<232::aid-ana14>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huynh DP, Figueroa K, Hoang N, Pulst SM. Nuclear localization or inclusion body formation of ataxin-2 are not necessary for SCA2 pathogenesis in mouse or human. Nat Genet. 2000;26:44–50. doi: 10.1038/79162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huynh DP, Nguyen DT, Pulst-Korenberg JB, Brice A, Pulst SM. Parkin is an E3 ubiquitin-ligase for normal and mutant ataxin-2 and prevents ataxin-2-induced cell death. Exp Neurol. 2006 doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huynh DP, Yang HT, Vakharia H, Nguyen D, Pulst SM. Expansion of the polyQ repeat in ataxin-2 alters its Golgi localization, disrupts the Golgi complex and causes cell death. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:1485–1496. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Igarashi S, Morita H, Bennett KM, Tanaka Y, Engelender S, Peters MF, Cooper JK, Wood JD, Sawa A, Ross CA. Inducible PC12 cell model of Huntington's disease shows toxicity and decreased histone acetylation. Neuroreport. 2003;14:565–568. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200303240-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Imbert G, Saudou F, Yvert G, Devys D, Trottier Y, Garnier JM, Weber C, Mandel JL, Cancel G, Abbas N, Durr A, Didierjean O, Stevanin G, Agid Y, Brice A. Cloning of the gene for spinocerebellar ataxia 2 reveals a locus with high sensitivity to expanded CAG/glutamine repeats. Nat Genet. 1996;14:285–291. doi: 10.1038/ng1196-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jin Y, Suzuki H, Maegawa S, Endo H, Sugano S, Hashimoto K, Yasuda K, Inoue K. A vertebrate RNA-binding protein Fox-1 regulates tissue-specific splicing via the pentanucleotide GCAUG. Embo J. 2003;22:905–912. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kedersha N, Anderson P. Stress granules: sites of mRNA triage that regulate mRNA stability and translatability. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:963–969. doi: 10.1042/bst0300963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kedersha N, Cho MR, Li W, Yacono PW, Chen S, Gilks N, Golan DE, Anderson P. Dynamic shuttling of TIA-1 accompanies the recruitment of mRNA to mammalian stress granules. J Cell Biol. 2000;151:1257–1268. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.6.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Klement IA, Skinner PJ, Kaytor MD, Yi H, Hersch SM, Clark HB, Zoghbi HY, Orr HT. Ataxin-1 nuclear localization and aggregation: role in polyglutamine-induced disease in SCA1 transgenic mice. Cell. 1998;95:41–53. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81781-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Koyano S, Iwabuchi K, Yagishita S, Kuroiwa Y, Uchihara T. Paradoxical absence of nuclear inclusion in cerebellar Purkinje cells of hereditary ataxias linked to CAG expansion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;73:450–452. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.73.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Koyano S, Uchihara T, Fujigasaki H, Nakamura A, Yagishita S, Iwabuchi K. Neuronal intranuclear inclusions in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mangus DA, Amrani N, Jacobson A. Pbp1p, a factor interacting with Saccharomyces cerevisiae poly(A)-binding protein, regulates polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:7383–7396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.12.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mangus DA, Evans MC, Jacobson A. Poly(A)-binding proteins: multifunctional scaffolds for the post-transcriptional control of gene expression. Genome Biol. 2003;4:223. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-7-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Martindale D, Hackam A, Wieczorek A, Ellerby L, Wellington C, McCutcheon K, Singaraja R, Kazemi-Esfarjani P, Devon R, Kim SU, Bredesen DE, Tufaro F, Hayden MR. Length of huntingtin and its polyglutamine tract influences localization and frequency of intracellular aggregates. Nat Genet. 1998;18:150–154. doi: 10.1038/ng0298-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nechiporuk T, Huynh DP, Figueroa K, Sahba S, Nechiporuk A, Pulst SM. The mouse SCA2 gene: cDNA sequence, alternative splicing and protein expression. Hum Mol Gen. 1998;7:1301–1309. doi: 10.1093/hmg/7.8.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nonhoff U, Ralser M, Welzel F, Piccini I, Balzereit D, Yaspo ML, Lehrach H, Krobitsch S. Ataxin-2 Interacts with the DEAD/H-Box RNA Helicase DDX6 and Interferes with P-Bodies and Stress Granules. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:1385–1396. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-12-1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nucifora FC, Jr, Ellerby LM, Wellington CL, Wood JD, Herring WJ, Sawa A, Hayden MR, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ross CA. Nuclear localization of a non-caspase truncation product of atrophin-1, with an expanded polyglutamine repeat, increases cellular toxicity. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13047–13055. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211224200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Paulson HL, Perez MK, Trottier Y, Trojanowski JQ, Subramony SH, Das SS, Vig P, Mandel JL, Fischbeck KH, Pittman RN. Intranuclear inclusions of expanded polyglutamine protein in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. Neuron. 1997;19:333–344. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80943-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pulst SM, Nechiporuk A, Nechiporuk T, Gispert S, Chen XN, Lopes-Cendes I, Pearlman S, Starkman S, Orozco-Diaz G, Lunkes A, DeJong P, Rouleau GA, Auburger G, Korenberg JR, Figueroa C, Sahba S. Moderate expansion of a normally biallelic trinucleotide repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Nat Genet. 1996;14:269–276. doi: 10.1038/ng1196-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pulst SM, Santos N, Wang D, Yang H, Huynh D, Velazquez L, Figueroa KP. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2: polyQ repeat variation in the CACNA1A calcium channel modifies age of onset. Brain. 2005;128:2297–2303. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ralser M, Albrecht M, Nonhoff U, Lengauer T, Lehrach H, Krobitsch S. An integrative approach to gain insights into the cellular function of human ataxin-2. J Mol Biol. 2005;346:203–214. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ross CA, Wood JD, Schilling G, Peters MF, Nucifora FC, Jr, Cooper JK, Sharp AH, Margolis RL, Borchelt DR. Polyglutamine pathogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999;354:1005–1011. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sanpei K. [The function of spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2) gene product, ataxin-2 and the mechanism of pathogenesis for SCA2] Nippon Rinsho. 1999;57:822–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sanpei K, Takano H, Igarashi S, Sato T, Oyake M, Sasaki H, Wakisaka A, Tashiro K, Ishida Y, Ikeuchi T, Koide R, Saito M, Sato A, Tanaka T, Hanyu S, Takiyama Y, Nishizawa M, Shimizu N, Nomura Y, Segawa M, Iwabuchi K, Eguchi I, Tanaka H, Takahashi H, Tsuji S. Identification of the spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 gene using a direct identification of repeat expansion and cloning technique, DIRECT. Nat Genet. 1996;14:277–284. doi: 10.1038/ng1196-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Satterfield TF, Pallanck LJ. Ataxin-2 and its Drosophila homolog, ATX2, physically assemble with polyribosomes. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:2523–2532. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shibata H, Huynh DP, Pulst SM. A novel protein with RNA-binding motifs interacts with ataxin-2. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1303–1313. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.9.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tarun SZ, Jr, Sachs AB. Association of the yeast poly(A) tail binding protein with translation initiation factor eIF-4G. Embo J. 1996;15:7168–7177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Uchihara T, Fujigasaki H, Koyano S, Nakamura A, Yagishita S, Iwabuchi K. Non-expanded polyglutamine proteins in intranuclear inclusions of hereditary ataxias--triple-labeling immunofluorescence study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2001;102:149–152. doi: 10.1007/s004010100364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yoshizawa T, Yamagishi Y, Koseki N, Goto J, Yoshida H, Shibasaki F, Shoji S, Kanazawa I. Cell cycle arrest enhances the in vitro cellular toxicity of the truncated Machado-Joseph disease gene product with an expanded polyglutamine stretch. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:69–78. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]