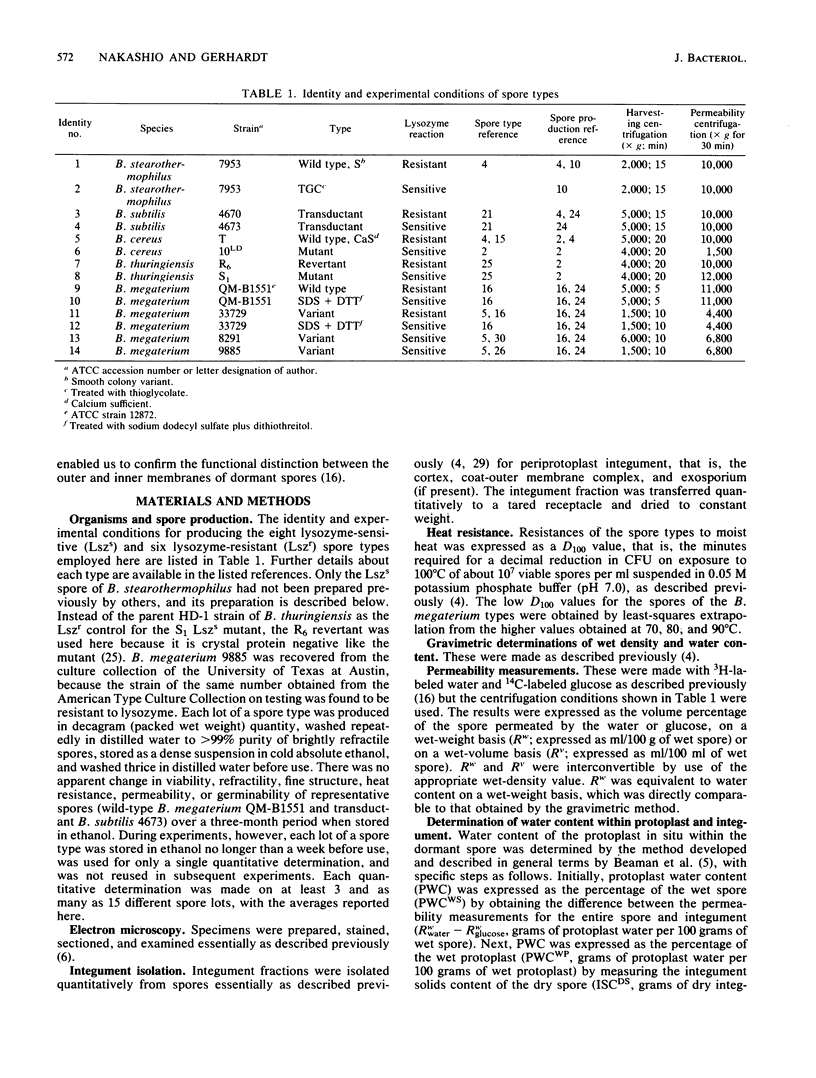
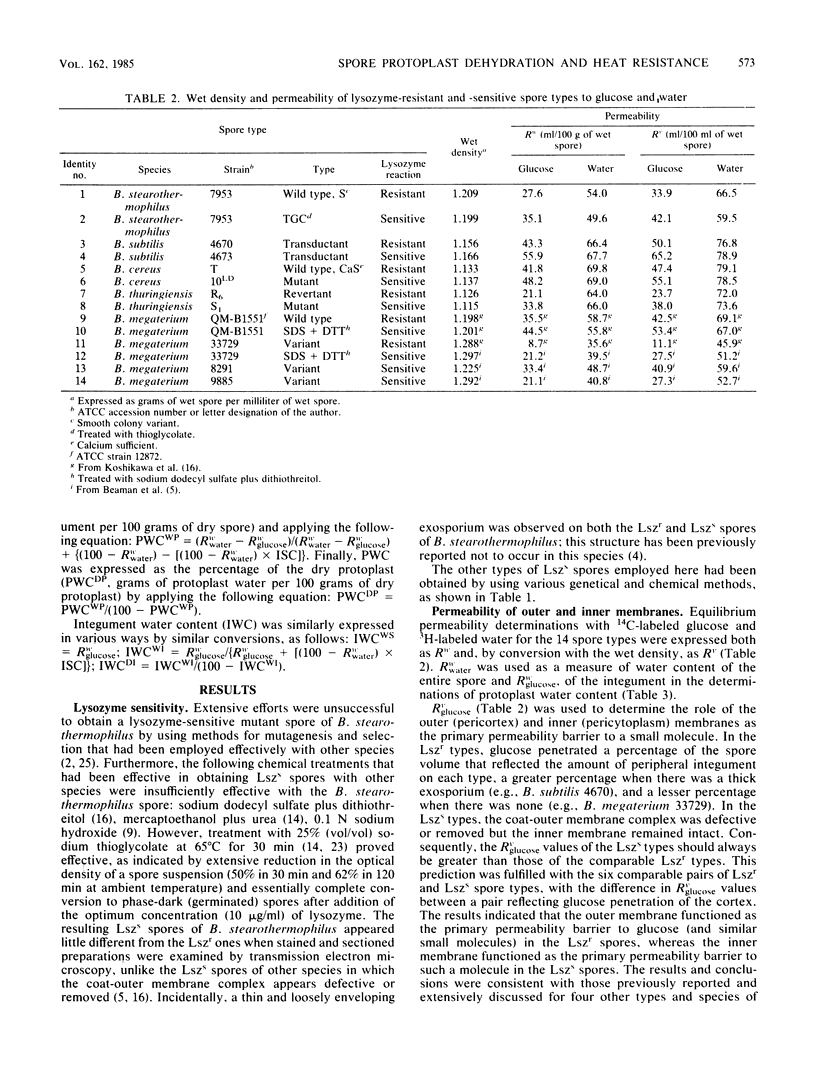
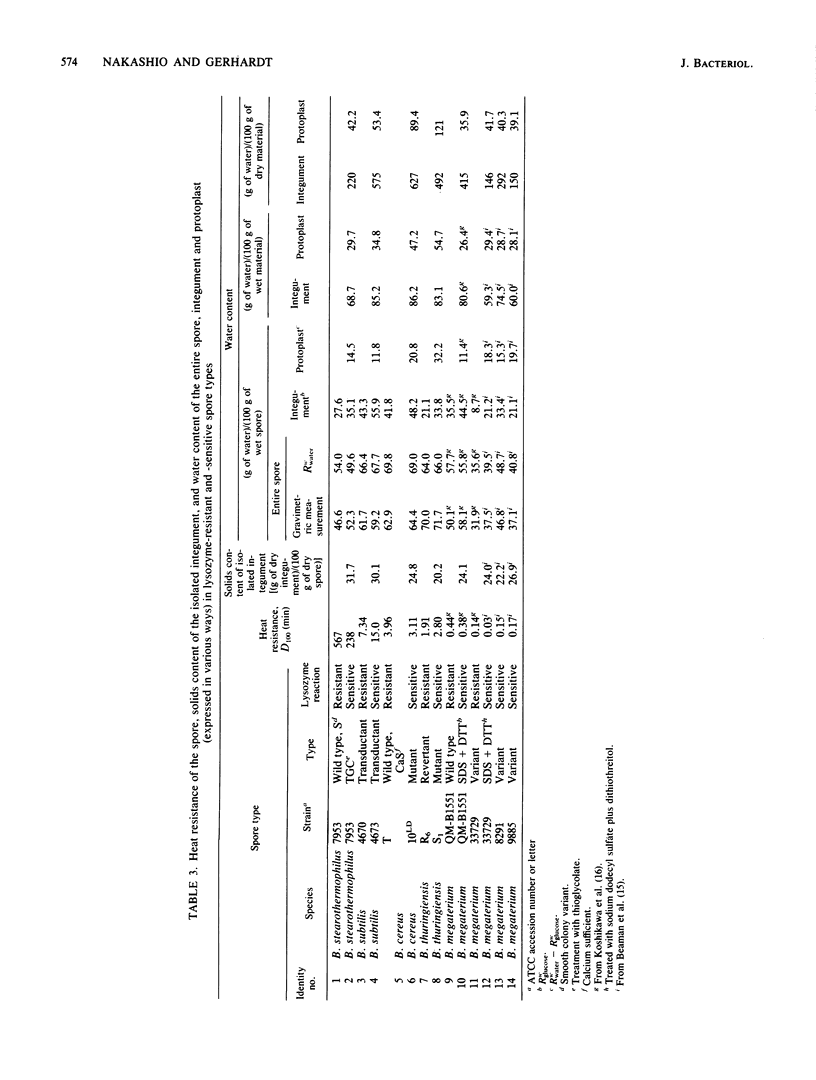
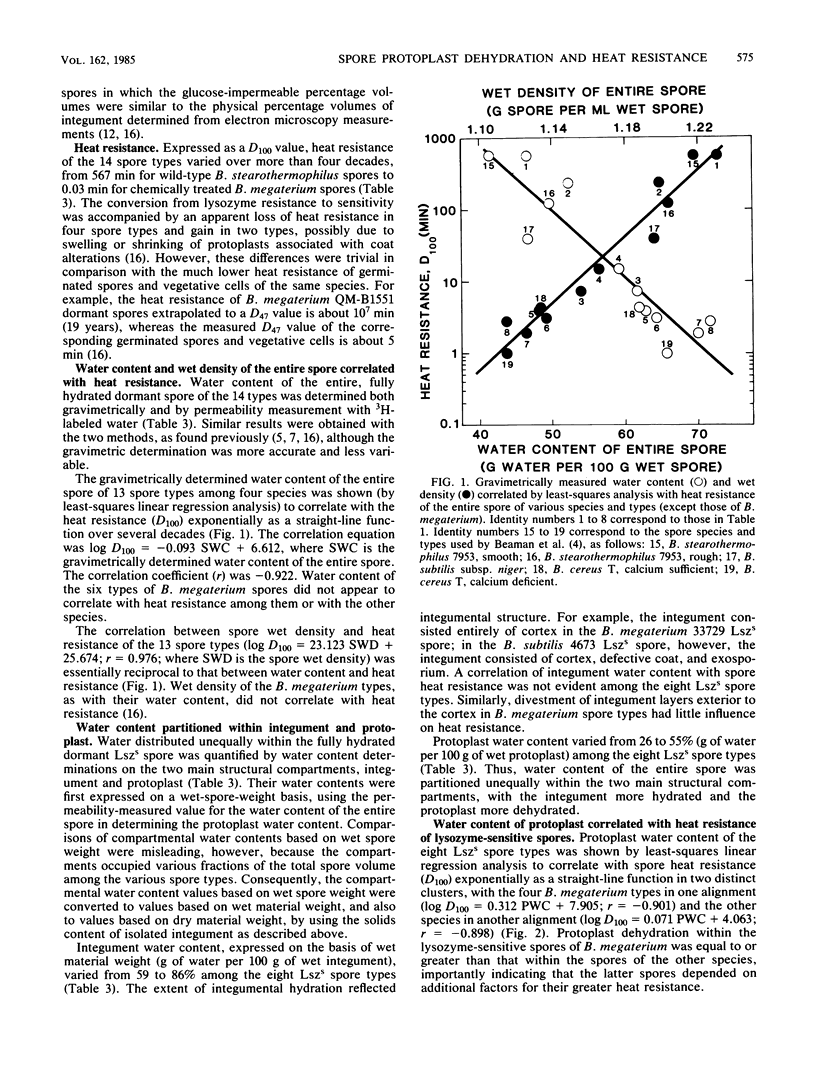
Abstract
Water content of the protoplast in situ within the fully hydrated dormant bacterial spore was quantified by use of a spore in which the complex of coat and outer (pericortex) membrane was genetically defective or chemically removed, as evidenced by susceptibility of the cortex to lysozyme and by permeability of the periprotoplast integument to glucose. Water content was determined by equilibrium permeability measurement with 3H-labeled water (confirmed by gravimetric measurement) for the entire spore, with 14C-labeled glucose for the integument outside the inner (pericytoplasm) membrane, and by the difference for the protoplast. The method was applied to lysozyme-sensitive spores of Bacillus stearothermophilus, B. subtilis, B. cereus, B. thuringiensis, and B. megaterium (four types). Comparable lysozyme-resistant spores, in which the outer membrane functioned as the primary permeability barrier to glucose, were employed as controls. Heat resistances were expressed as D100 values. Protoplast water content of the lysozyme-sensitive spore types correlated with heat resistance exponentially in two distinct clusters, with the four B. megaterium types in one alignment, and with the four other species types in another. Protoplast water contents of the B. megaterium spore types were sufficiently low (26 to 29%, based on wet protoplast weight) to account almost entirely for their lesser heat resistance. Corresponding values of the other species types were similar or higher (30 to 55%), indicating that these spores depended on factors additional to protoplast dehydration for their much greater heat resistance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDERTON G., SNELL N. Base exchange and heat resistance in bacterial spores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jan 31;10:139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. C. Properties of Bacillus cereus spore coat mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):354–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.354-365.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK S. H., GERHARDT P. Permeability of bacterial spores. IV. Water content, uptake, and distribution. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:960–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.960-967.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman T. C., Greenamyre J. T., Corner T. R., Pankratz H. S., Gerhardt P. Bacterial spore heat resistance correlated with water content, wet density, and protoplast/sporoplast volume ratio. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):870–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.870-877.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman T. C., Pankratz H. S., Gerhardt P. Ultrastructure of the exosporium and underlying inclusions in spores of Bacillus megaterium strains. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1198–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1198-1209.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury J. H., Foster J. R., Hammer B., Lindsay J., Murrell W. G. The source of the heat resistance of bacterial spores. Study of water in spores by NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 4;678(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Labbe R. G., Reich R. R. Germination of heat- and alkali-altered spores of Clostridium perfringens type A by lysozyme and an initiation protein. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):550–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.550-559.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz-James P. C., Young I. E. CYTOLOGICAL COMPARISON OF SPORES OF DIFFERENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78(6):755–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.755-764.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foerster H. F. Activation and germination characteristics observed in endospores of thermophilic strains of Bacillus. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Jun;134(3):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00407754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD G. W., HITCHINS A. D. SENSITIZATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES TO LYSOZYME AND TO HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WITH AGENTS WHICH RUPTURE DISULPHIDE BONDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:413–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt P., Beaman T. C., Corner T. R., Greenamyre J. T., Tisa L. S. Photometric immersion refractometry of bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):643–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.643-648.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO T., BLACK S. H., GERHARDT P. Development of fine structure, thermostability, and dipicolinate during sporogenesis in a bacillus. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:203–212. doi: 10.1139/m60-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshikawa T., Beaman T. C., Pankratz H. S., Nakashio S., Corner T. R., Gerhardt P. Resistance, germination, and permeability correlates of Bacillus megaterium spores successively divested of integument layers. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):624–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.624-632.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E., Bender G. R. Mineralization and heat resistance of bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):789–791. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.789-791.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. Germination properties of a spore coat-defective mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1106–1116. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1106-1116.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. B., Levinson H. S. Changes in spores of Bacillus megaterium treated with thioglycolate at a low pH and restoration of germinability and heat resistance by cations. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1017–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1017-1022.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XVII. Sulfhydryl and disulfide levels in dormancy and germination. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1155–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1155-1160.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahly D. P., Dingman D. W., Bulla L. A., Jr, Aronson A. I. Possible origin and function of the parasporal crystal in Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90745-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Rode L. J. Effect of lysozyme on resting spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.238-245.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARTH A. D., OHYE D. F., MURRELL W. G. Location and composition of spore mucopeptide in Bacillus species. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:593–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warth A. D. Relationship between the heat resistance of spores and the optimum and maximum growth temperatures of Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.699-705.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


