Abstract
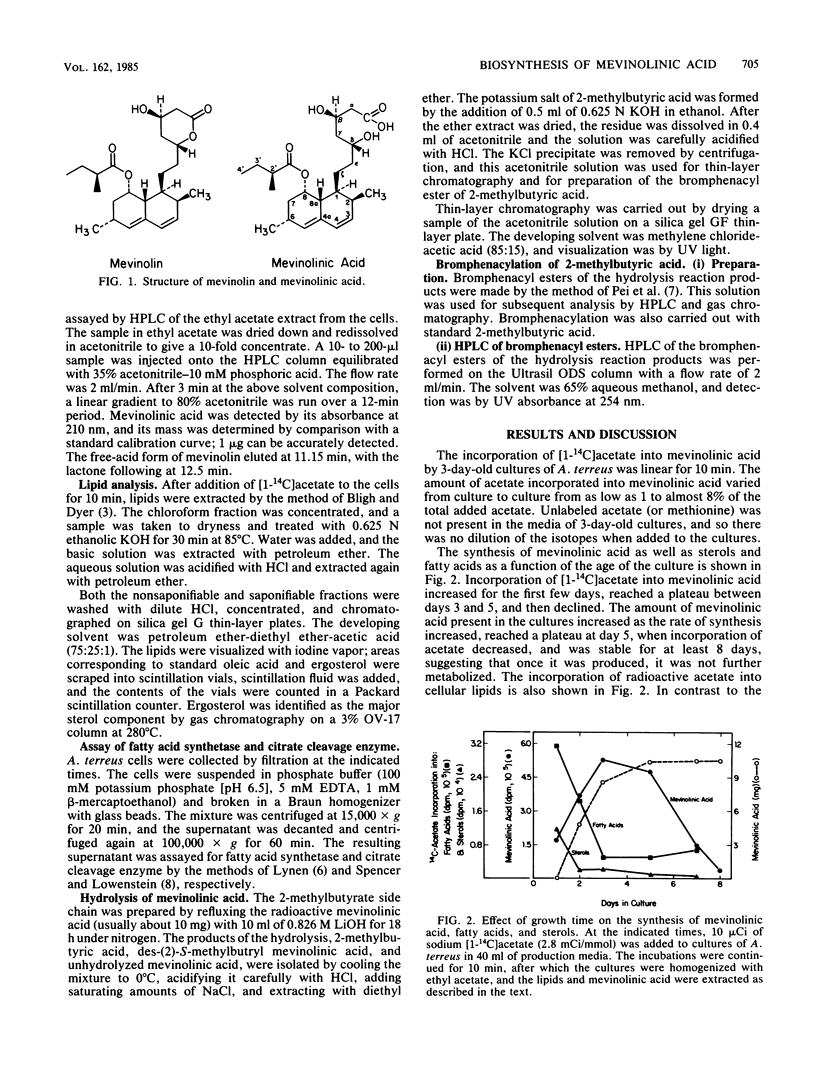
Mevinolinic acid, the open acid form of mevinolin, which is a metabolite of Aspergillus terreus, has been shown to be a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (Alberts et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77:3957-3961, 1980). The biosynthesis of mevinolinic acid was studied by examining the incorporation of [1-14C]acetate and [methyl-14C]methionine into the molecule. These isotopes were rapidly incorporated into mevinolinic acid, with [1-14C]acetate and [methyl-14C]methionine incorporation being linear for at least 10 and 30 min, respectively. A comparison of acetate incorporation into mevinolinic acid and fatty acids indicated that mevinolinic acid biosynthesis increased with a maximum between days 3 and 5 of growth; at this time cell growth had ceased and fatty acid biosynthesis was negligible. Hydrolysis of the mevinolinic acid and isolation of the products showed that [1-14C]acetate and [methyl-14C]methionine were incorporated into the 2-methylbutyric acid side chain as well as into the main (alcohol) portion of the molecule.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Grundy S. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Mevinolin and colestipol stimulate receptor-mediated clearance of low density lipoprotein from plasma in familial hypercholesterolemia heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimroth P., Walter H., Lynen F. Biosynthese von 6-Methylsalicylsäure. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):98–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei P. T., Kossa W. C., Ramachandran S., Henly R. S. High pressure reverse phase liquid chromatography of fatty acid p-bromophenacyl esters. Lipids. 1976 Nov;11(11):814–816. doi: 10.1007/BF02533409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobert J. A., Bell G. D., Birtwell J., James I., Kukovetz W. R., Pryor J. S., Buntinx A., Holmes I. B., Chao Y. S., Bolognese J. A. Cholesterol-lowering effect of mevinolin, an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):913–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI110530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. A., Lowenstein J. M. Citrate and the conversion of carbohydrate into fat. Fatty acid synthesis by a combination of cytoplasm and mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):5993–6002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



