Abstract
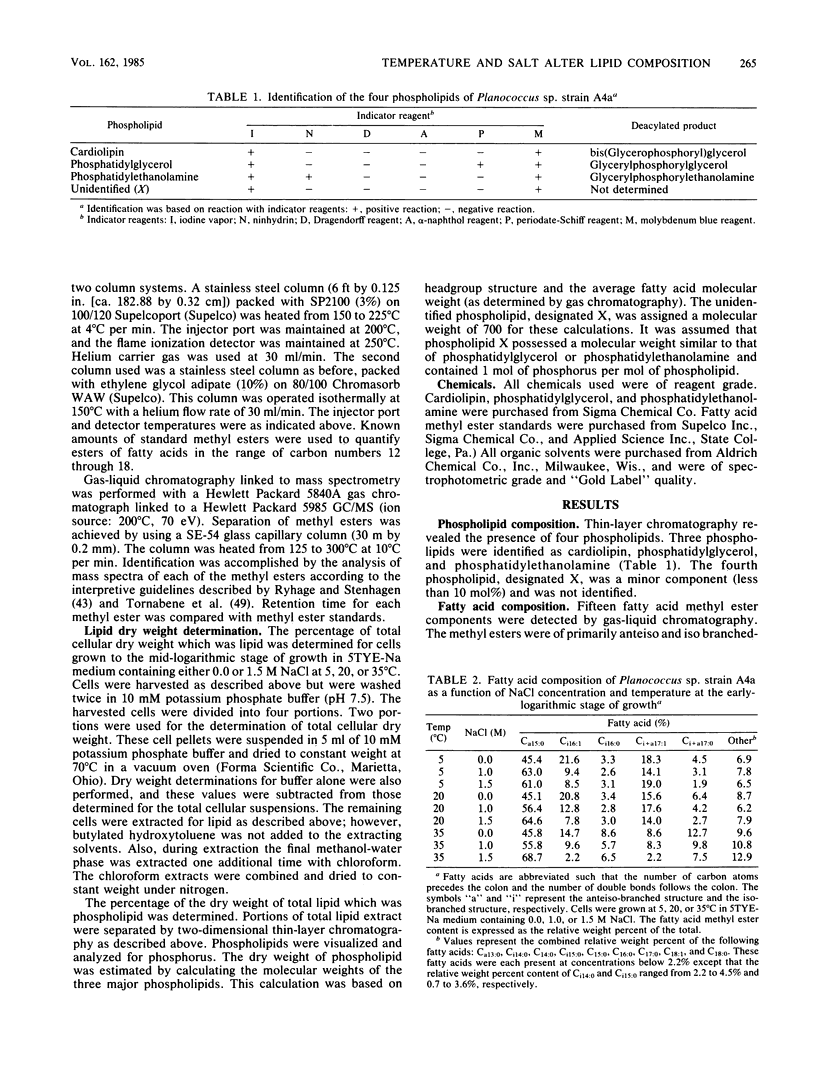
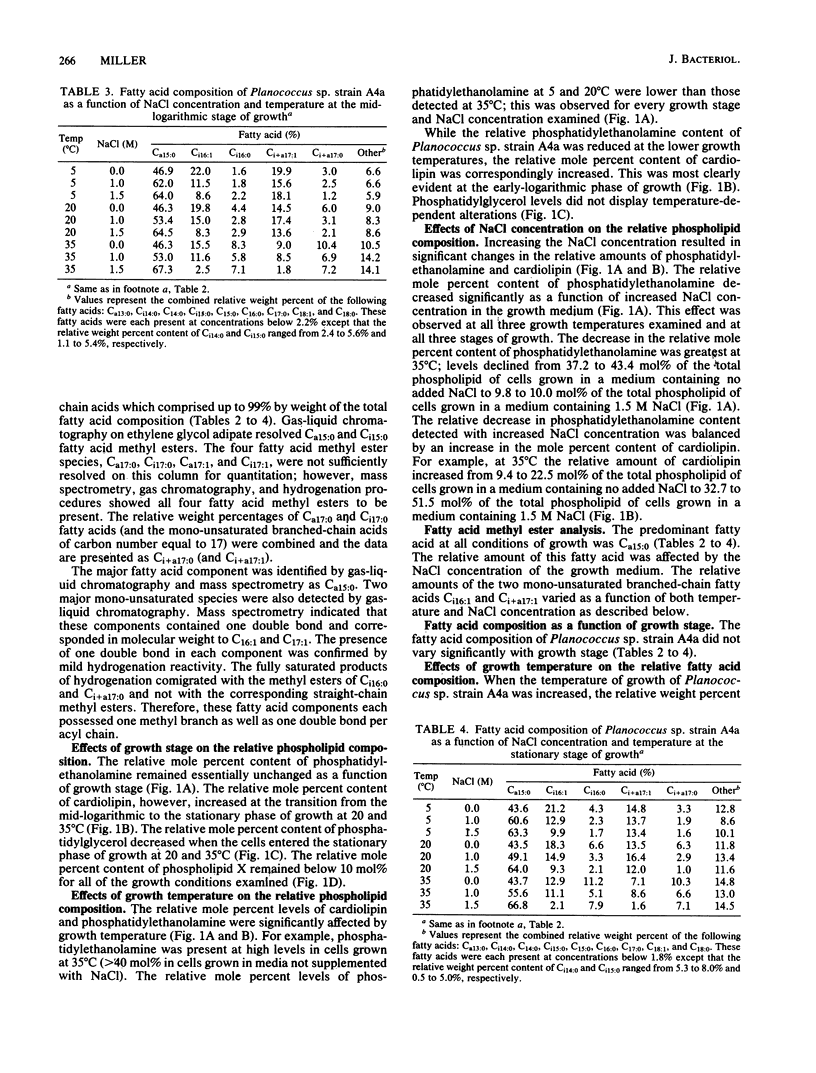
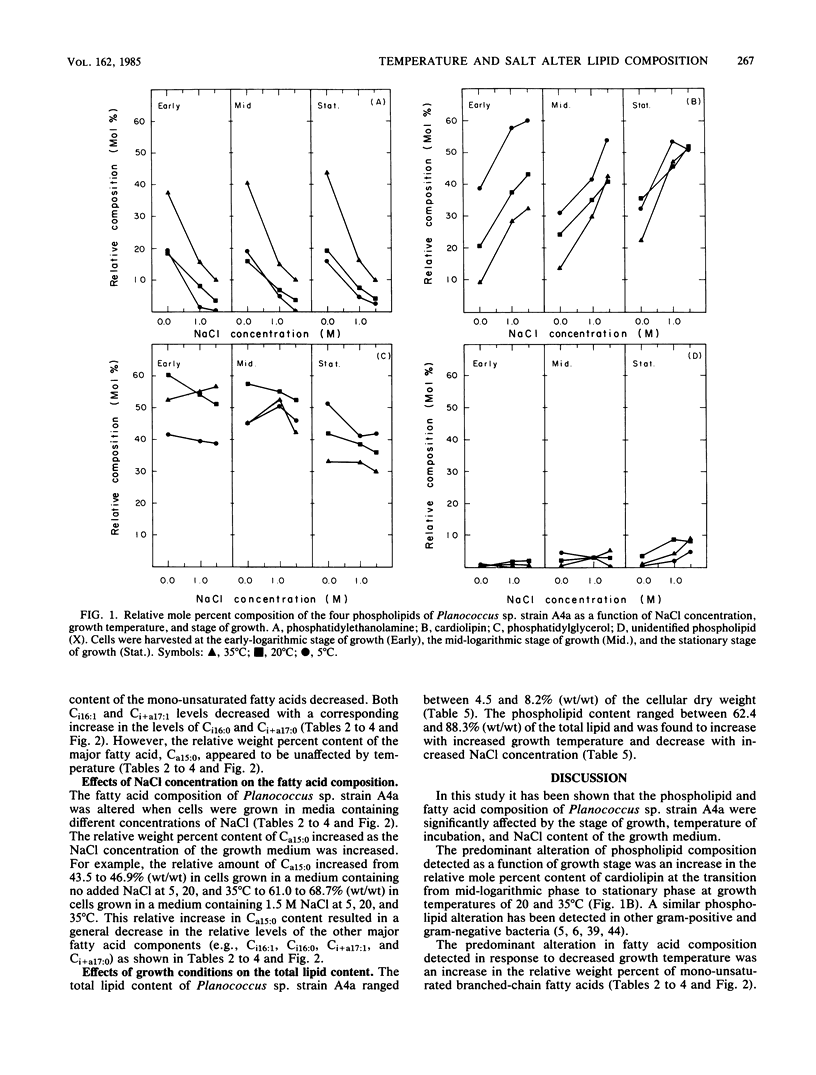
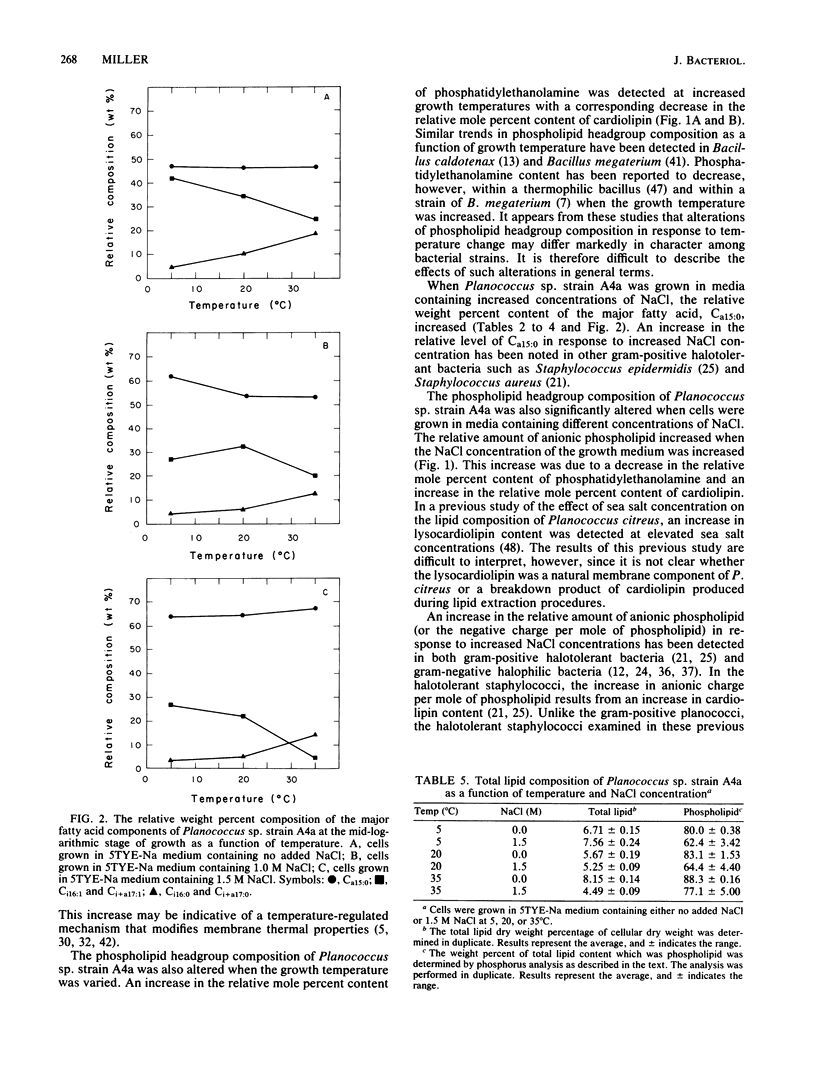
The phospholipid headgroup composition and fatty acid composition of a gram-positive halotolerant Planococcus sp. (strain A4a) were examined as a function of growth temperature (5 to 35 degrees C) and NaCl content (0 to 1.5 M) of the growth medium. When the growth temperature was decreased, the relative amount of mono-unsaturated branched-chain fatty acids increased. When Planococcus sp. strain A4a was grown in media containing high NaCl concentrations, the relative amount of the major fatty acid, Ca15:0, increased. The relative amount of anionic phospholipid also increased when the NaCl concentration of the growth medium was increased. The increase in anionic phospholipid content resulted from a decrease in the relative mole percent content of phosphatidylethanolamine and an increase in the relative mole percent content of cardiolipin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelqvist L. A. A simple and convenient procedure for the hydrogenation of lipids on the micro- and nanomole scale. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jan;13(1):146–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley S. T., Morton R. A. Recent developments in the molecular biology of extremely halophilic bacteria. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(2):151–205. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr, Gelmann E. P. Physical properties of membrane lipids: biological relevance and regulation. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):232–256. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.232-256.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Vagelos P. R. Metabolism and function of the membrane phospholipids of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):25–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg A. D., Corner T. R. Effects of growth temperature on protoplast membrane properties in Bacillus megaterium. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Apr;24(4):386–396. doi: 10.1139/m78-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The anionic polymers in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis var. niger grown in phosphorus-limiting environments supplemented with increasing concentrations of sodium chloride. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):349–351. doi: 10.1042/bj1210349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther T., Richter L., Schmalbeck J. Phospholipids of Escherichia coli in magnesium deficiency. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):191–193. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., de Gier J., den Kamp JA O. P., Bartels P., van Deenen L. L. Chages in permeability of Staphylococcus aureus and derived liposomes with varying lipid composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):720–733. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa Y., Kawada N., Nosoh Y. Change in chemical composition of membrane of Bacillus caldotenax after shifting the growth temperature. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jun;126(2):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00511214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The binding of calcium at lipid-water interfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Stow M., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Function of teichoic acids and effect of novobiocin on control of Mg2+ at the bacterial membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 13;229(2):53–55. doi: 10.1038/newbio229053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Cronan J. E., Jr An estimate of the minimum amount of fluid lipid required for the growth of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 4;512(3):472–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemasa Y., Yoshioka T., Hayashi H. Alteration of the phospholipid composition of Staphylococcus aureus cultured in medium containing NaCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 30;280(3):444–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaratat P., Kates M. The lipid composition of a halotolerant species of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 19;398(3):464–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J., Onishi H. Contribution of protein and lipid components to the salt response of envelopes of an extremely halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):653–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.653-660.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Occurrence and function of membrane teichoic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 31;472(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier M. P. Lipids in bacterial taxonomy - a taxonomist's view. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):109–210. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. R., SMITH L. M. PREPARATION OF FATTY ACID METHYL ESTERS AND DIMETHYLACETALS FROM LIPIDS WITH BORON FLUORIDE--METHANOL. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:600–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W. The influence of growth-limiting substrate and medium NaCl concentration on the synthesis of magnesium-binding sites in the walls of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):325–331. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Abdolrahimzadeh H., Baddiley J. Variation of polar lipid composition of Bacillus subtilis (Marburg) with different growth conditions. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):16–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80398-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Yano I., Hiramatsu T., Masui M. Lipids and fatty acids of a moderately halophilic bacterium, No. 101. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Yano I., Masui M. Effect of NaCl concentration and temperature on the phospholipid and fatty acid compositions of a moderately halophilic bacterium, Pseudomonas halosaccharolytica. J Biochem. 1979 Feb;85(2):413–421. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D. Na + -K + discrimination by "pure" phospholipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):254–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYHAGE R., STENHAGEN E. Mass spectrometry in lipid research. J Lipid Res. 1960 Oct;1:361–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle C. L., Albro P. W., Dittmer J. C. The phosphoglyceride composition of Gram-negative bacteria and the changes in composition during growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;187(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilfors L., Wieslander A., Ståhl S. Lipid and protein composition of membranes of Bacillus megaterium variants in the temperature range 5 to 70 degrees C. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1043-1052.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C. Metabolism of phosphatidylglycerol, lysylphosphatidylglycerol, and cardiolipin of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):219–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.219-226.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M. Homeoviscous adaptation--a homeostatic process that regulates the viscosity of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):522–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza K. A., Kostiw L. L., Tyson B. J. Alterations in normal fatty acid composition in a temperature-sensitive mutant of a thermophilic bacillus. Arch Microbiol. 1974 Apr 19;97(2):89–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00403049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkell D., Summerfield M. The membrane lipids of Planococcus citreus Migula from cells grown in the presence of three different concentrations of sea salt added to a basic medium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1977;43(1):43–54. doi: 10.1007/BF02316209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Gelpi E., Oró J. Identification of fatty acids and aliphatic hydrocarbons in Sarcina lutea by gas chromatography and combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):333–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.333-343.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



