Abstract
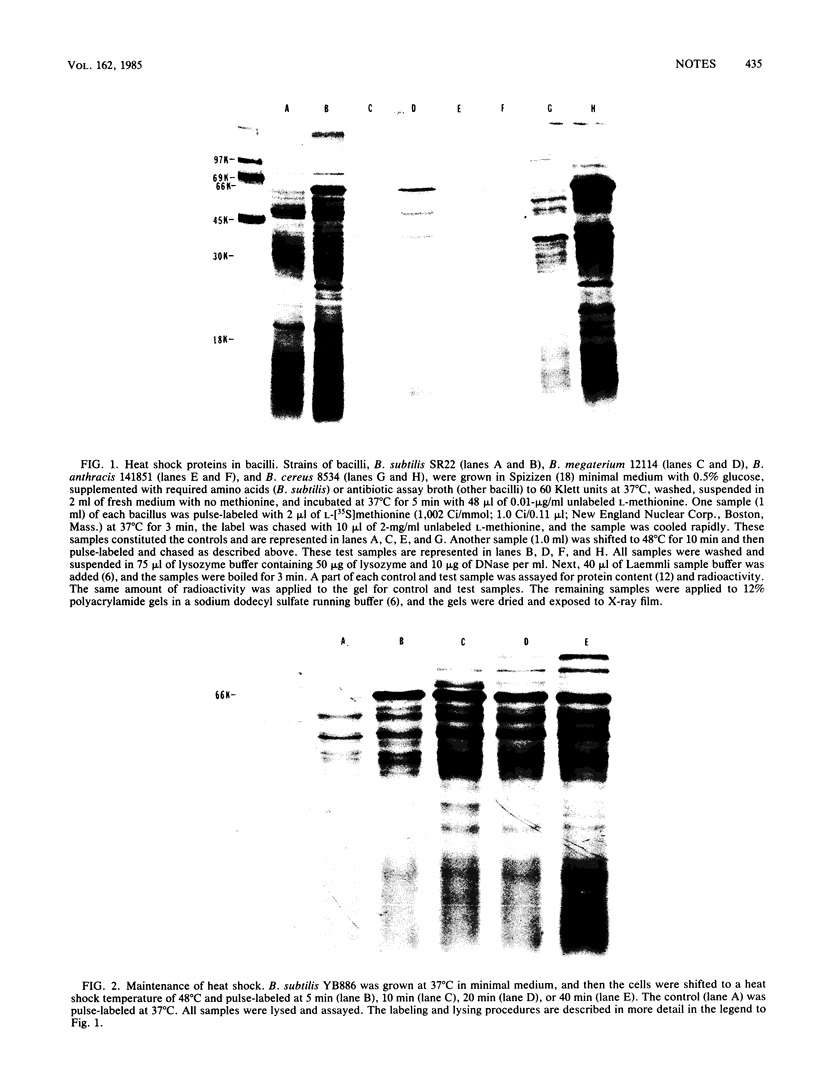
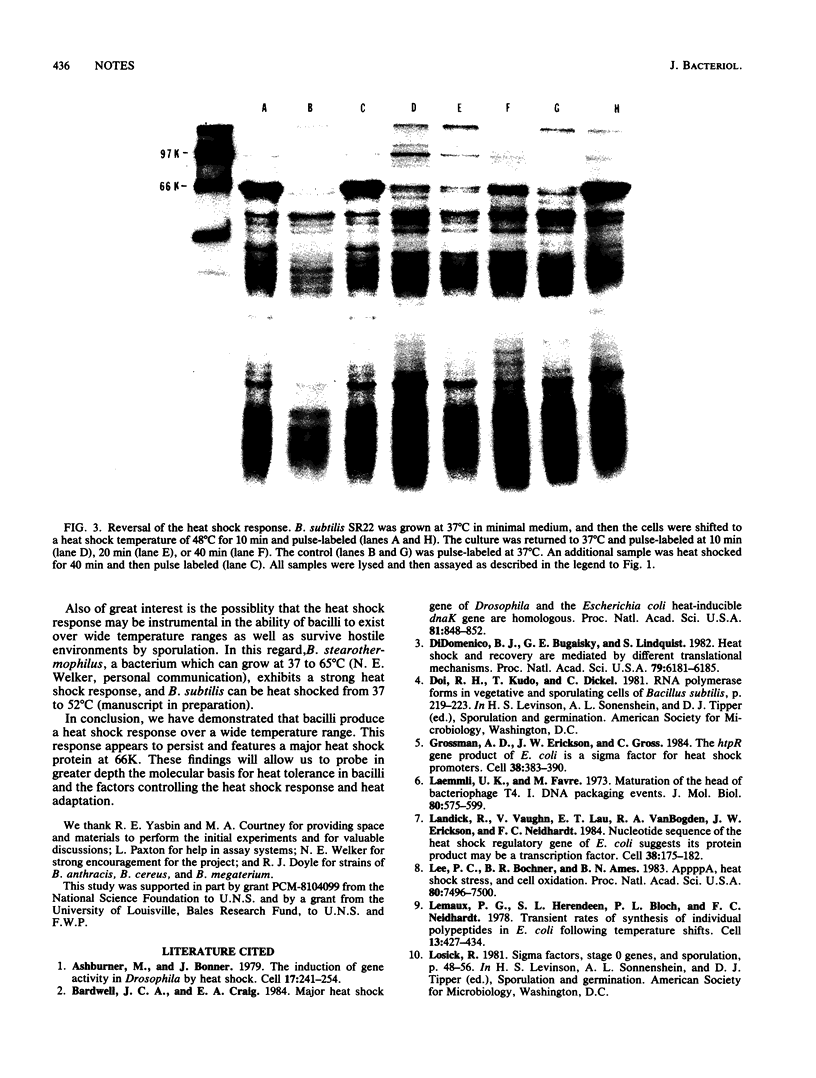
Five strains of bacilli, including a nonsporulating strain, when heat shocked, accelerated the synthesis of a specific subset of proteins. The major heat shock protein in all bacilli had a molecular weight of 66,000. The response persisted for at least 40 min and could be eliminated upon a shift down to 37 degrees C.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. Heat shock and recovery are mediated by different translational mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Vaughn V., Lau E. T., VanBogelen R. A., Erickson J. W., Neidhardt F. C. Nucleotide sequence of the heat shock regulatory gene of E. coli suggests its protein product may be a transcription factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. AppppA, heat-shock stress, and cell oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaux P. G., Herendeen S. L., Bloch P. L., Neidhardt F. C. Transient rates of synthesis of individual polypeptides in E. coli following temperature shifts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Pero J. Cascades of Sigma factors. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):582–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Lau E. T. Molecular cloning and expression of a gene that controls the high-temperature regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.597-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A. Positive regulatory gene for temperature-controlled proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):894–900. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa T., Yura T. Effects of reduced amount of RNA polymerase sigma factor on gene expression and growth of Escherichia coli: studies of the rpoD450 (amber) mutation. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):166–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00272900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciandra J. J., Subjeck J. R., Hughes C. S. Induction of glucose-regulated proteins during anaerobic exposure and of heat-shock proteins after reoxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachlin G., Hecker M. Proteinbiosynthesen nach Hitzeschock in Bacillus subtilis. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1984;24(6):397–401. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630240606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Yura T. Transient regulation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli upon shift-up of growth temperature. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1133-1140.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]