Abstract
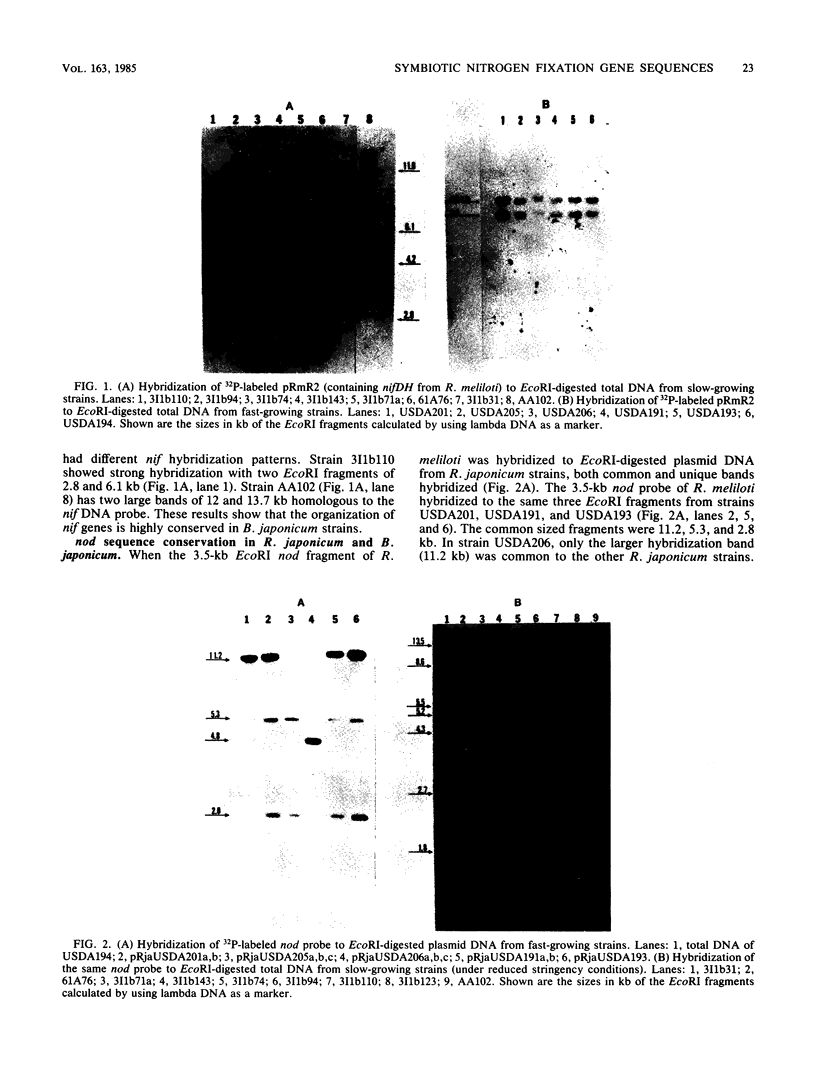
Southern hybridization with nif (nitrogen fixation) and nod (nodulation) DNA probes from Rhizobium meliloti against intact plasmid DNA of Rhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains indicated that both nif and nod sequences are on plasmid DNA in most R. japonicum strains. An exception is found with R. japonicum strain USDA194 and all B. japonicum strains where nif and nod sequences are on the chromosome. In R. japonicum strains, with the exception of strain USDA205, both nif and nod sequences are on the same plasmid. In strain USDA205, the nif genes are on a 112-megadalton plasmid, and nod genes are on a 195-megadalton plasmid. Hybridization to EcoRI digests of total DNA to nif and nod probes from R. meliloti show that the nif and nod sequences are conserved in both R. japonicum and B. japonicum strains regardless of the plasmid or chromosomal location of these genes. In addition, nif DNA hybridization patterns were identical among all R. japonicum strains and with most of the B. japonicum strains examined. Similarly, many of the bands that hybridize to the nodulation probe isolated from R. meliloti were found to be common among R. japonicum strains. Under reduced hybridization stringency conditions, strong conservation of nodulation sequences was observed in strains of B. japonicum. We have also found that the plasmid pRjaUSDA193, which possess nif and nod sequences, does not possess sequence homology with any plasmid of USDA194, but is homologous to parts of the chromosome of USDA194. Strain USDA194 is unique, since nif and nod sequences are present on the chromosome instead of on a plasmid as observed with all other strains examined.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. O., Atherly A. G. Induced plasmid-genome rearrangements in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.218-224.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantino P., Mauro M. L., Micheli G., Risuleo G., Hooykaas P. J., Schilperoort R. Fingerprinting and sequence homology of plasmids from different virulent strains of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):170–182. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Chilton M. D. Tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmids of Agrobacterium share extensive regions of DNA homology. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1178–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1178-1183.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Fuhrmann M., Hahn M., Regensburger B., Hennecke H. In Rhizobium japonicum the nitrogenase genes nifH and nifDK are separated. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):915–918. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.915-918.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Bohlool B. B., Hu T. S., Weber D. F. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1631–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4540.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Panagopoulos C. G., Nester E. W. Comparison of Ti plasmids from three different biotypes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens isolated from grapevines. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1535–1542. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1535-1542.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Russell P. R., Atherly A. G. Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes and large plasmids of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):928–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.928-931.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash R. K., Atherly A. G. Reiteration of genes involved in symbiotic nitrogen fixation by fast-growing Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):785–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.785-787.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash R. K., Schilperoort R. A., Nuti M. P. Large plasmids of fast-growing rhizobia: homology studies and location of structural nitrogen fixation (nif) genes. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1129–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1129-1136.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash R. K., Van Brussel A. A., Quint A., Mennes A. M., Schilperoort R. A. The map position of Sym-plasmid regions expressed in the bacterial and endosymbiotic form of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash R. K., van Veen R. J., Schilperoort R. A. Restriction endonuclease mapping of a Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. Interspecies homology of nitrogenase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):191–195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Relationship between the limited and wide host range octopine-type Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.484-493.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]