Abstract
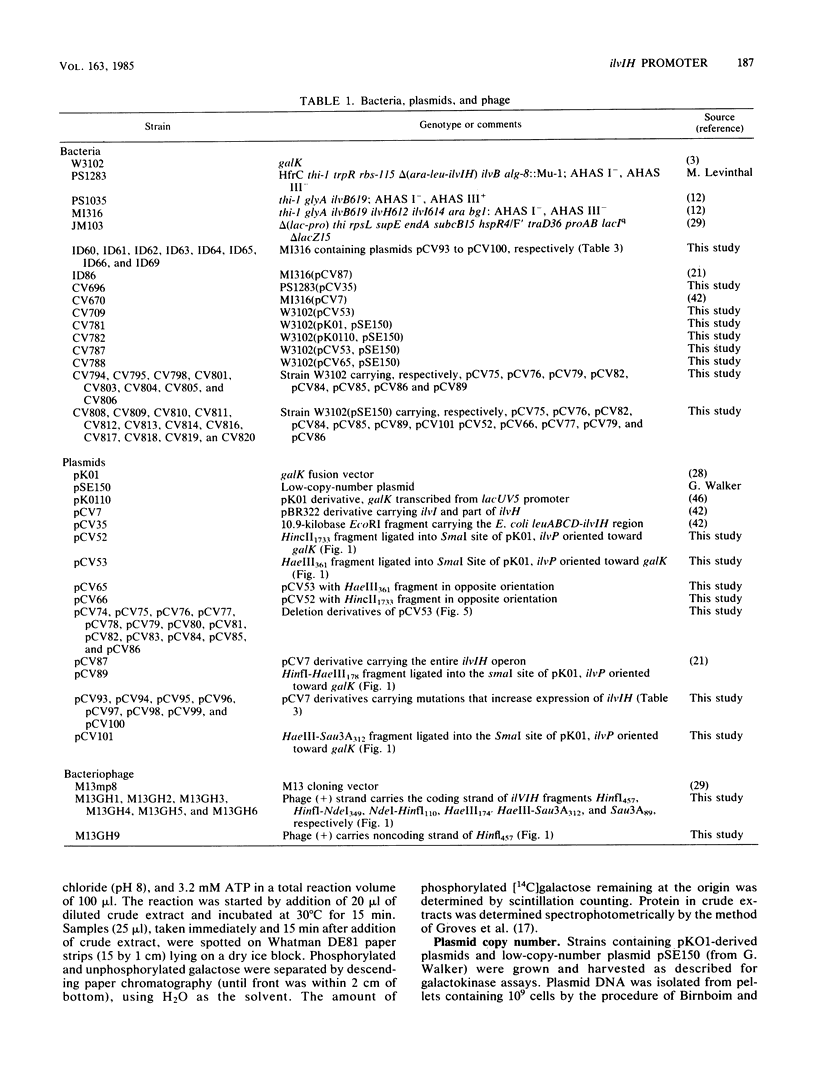
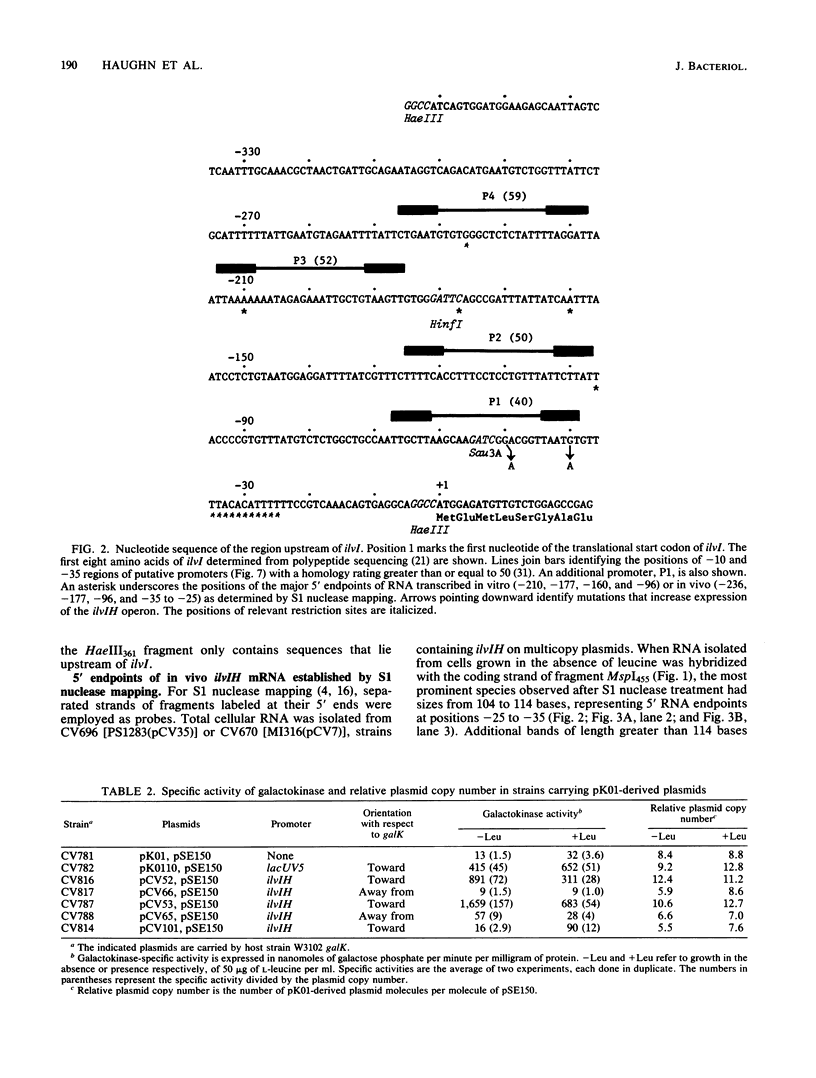
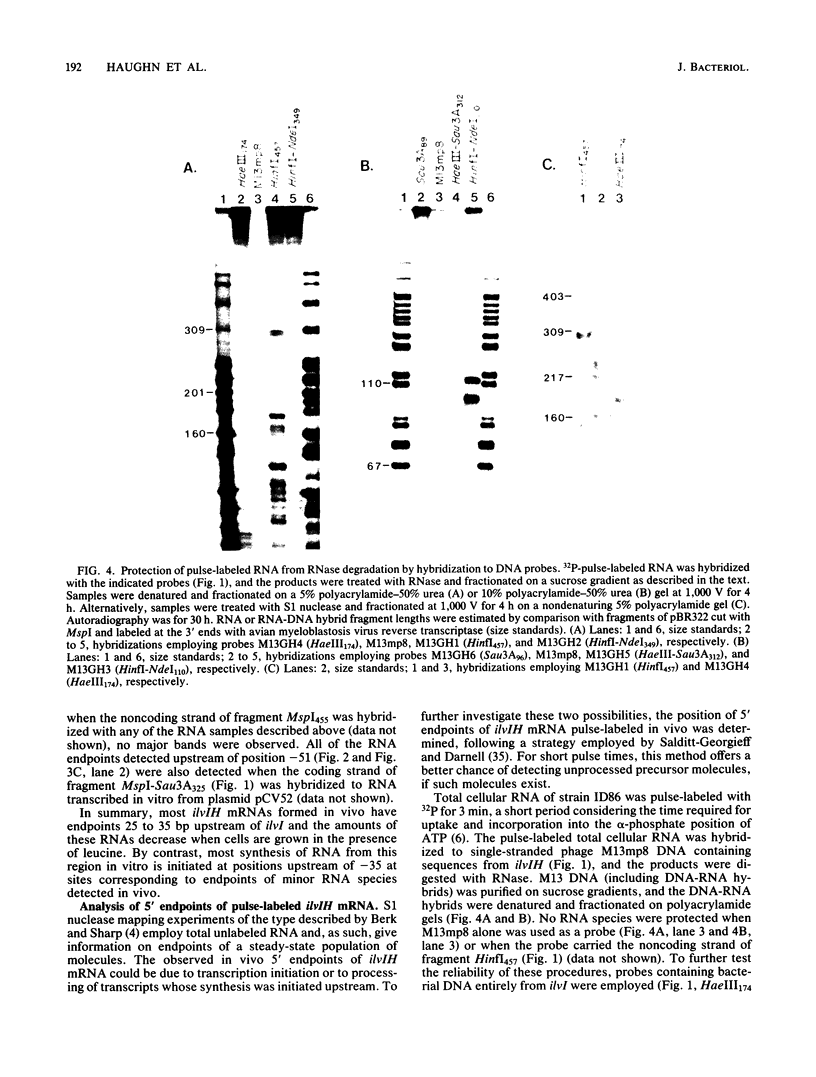
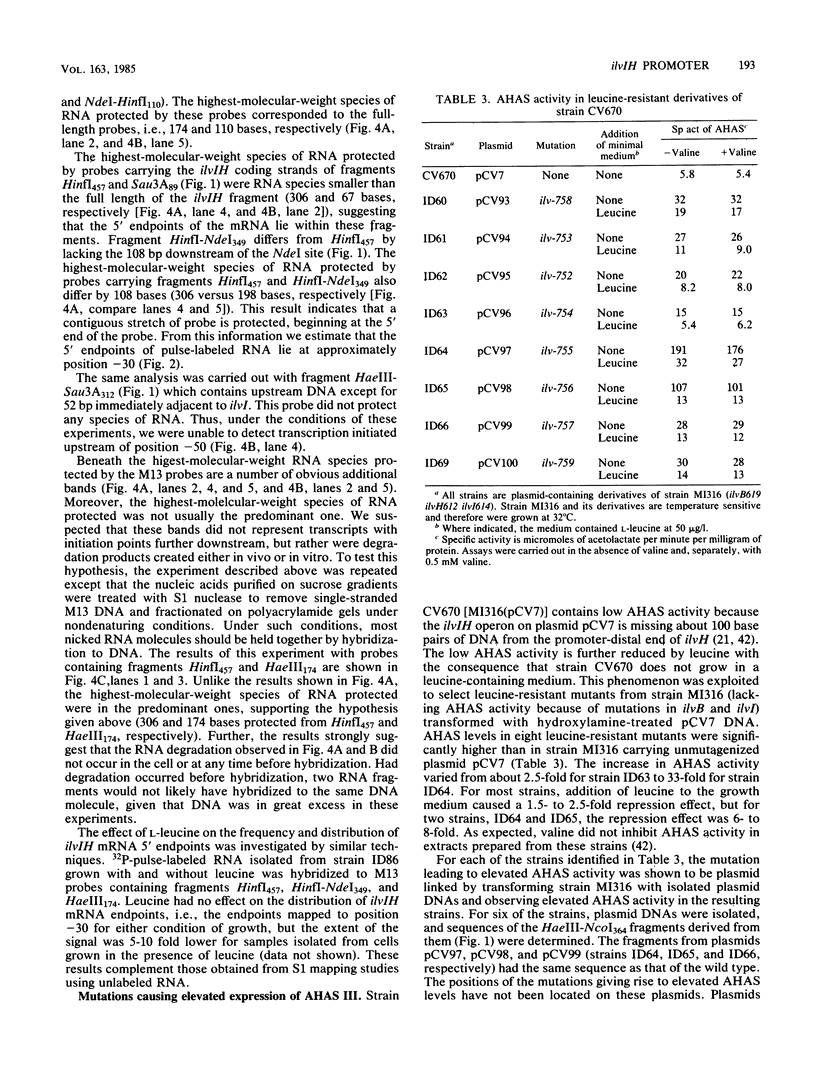
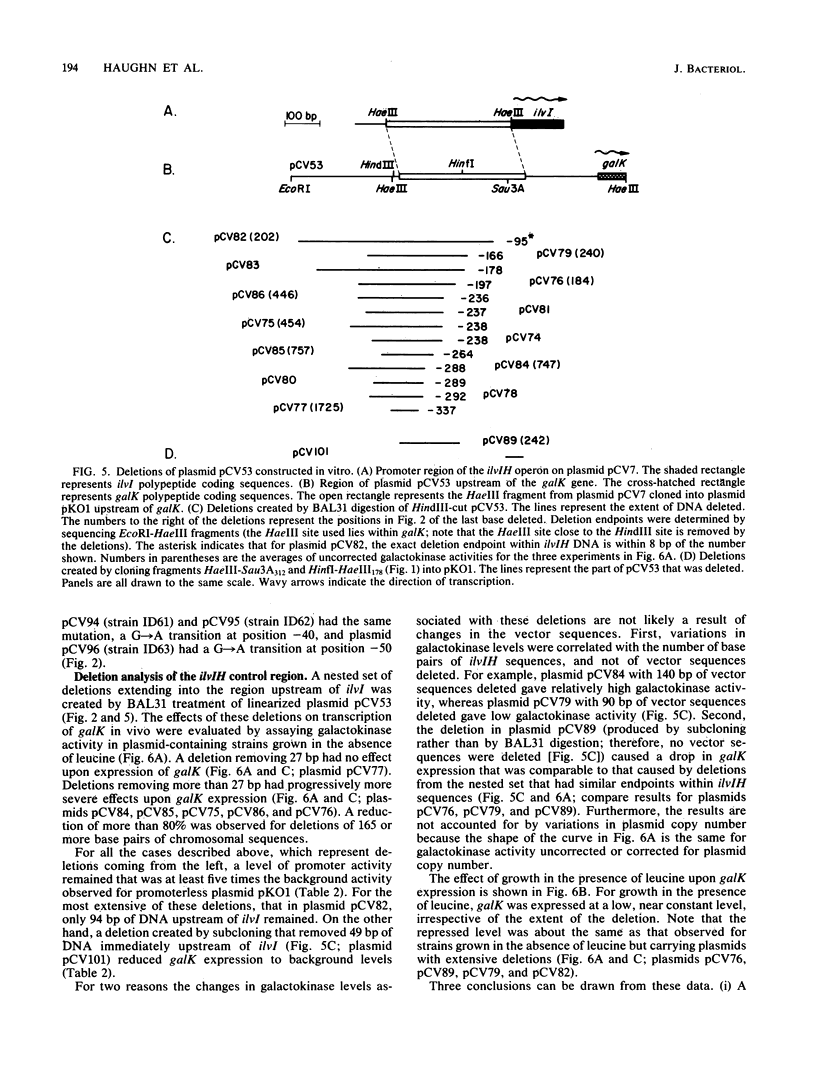
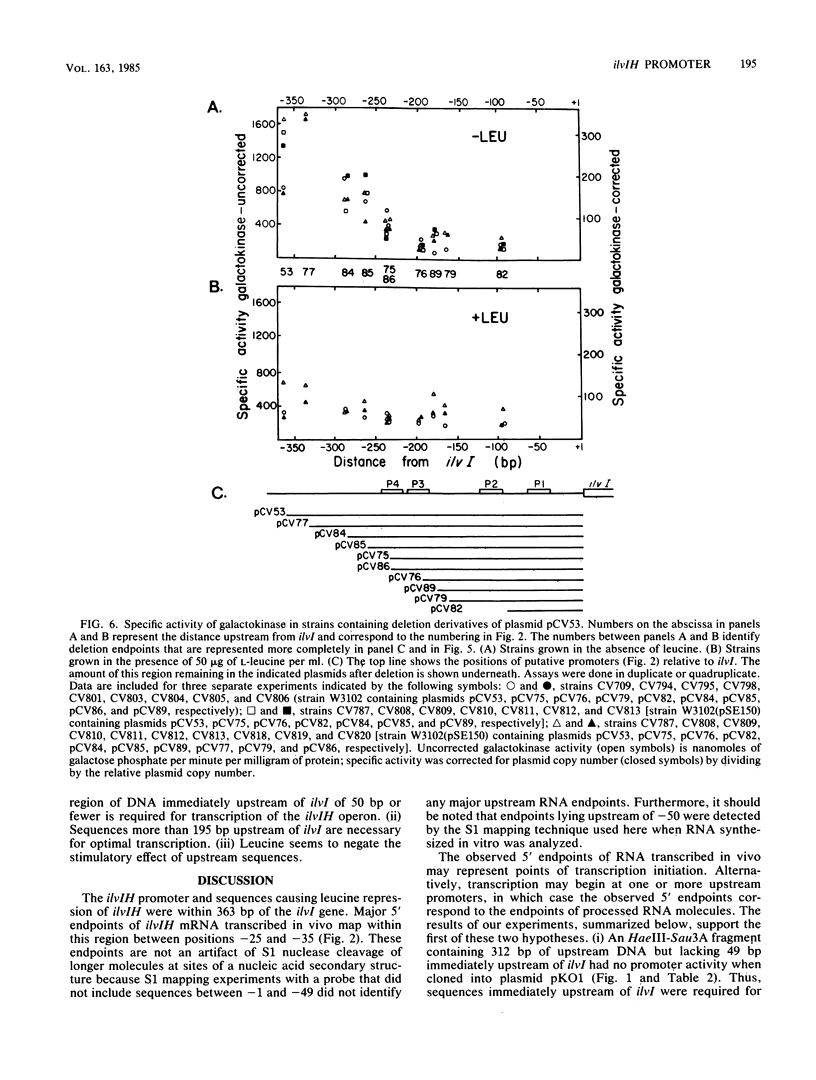
Analysis of plasmids containing ilvIH-galK fusions indicated that the Escherichia coli ilvIH promoter and sequences sufficient to cause leucine repression lie within 363 base pairs (bp) of ilvI. Experiments designed to locate the promoter and regulatory sequences more precisely gave the following results. The positions of the 5' endpoints of both unlabeled and pulse-labeled ilvIH mRNAs transcribed in vivo lie 30 bp upstream of ilvI. By contrast, the major in vitro RNA endpoints lie at positions further upstream. Several mutations which increase the expression of ilvIH lie 40 to 50 bp upstream of ilvI, within a putative promoter termed P1. Deletion of a 50-bp region immediately upstream of ilvI, which includes P1, resulted in the loss of all ilvIH promoter activity. Deletion of sequences more than 200 bp upstream of ilvI reduced ilvIH promoter activity by more than 80%. These results suggest that transcription of the ilvIH operon is initiated from promoter P1 but that sequences more than 200 bp upstream are required for optimal transcription of the operon.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Hatfield G. W. Effects of promoter strengths and growth conditions on copy number of transcription-fusion vectors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7399–7403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhya S., Miller W. Modulation of the two promoters of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):492–494. doi: 10.1038/279492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo J. M., Freundlich M., Umbarger H. E. Regulation of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of regulatory mutants. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1272–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1272-1282.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Whitney P., Magasanik B. Reaction of lac-specific ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli with lac deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6548–6555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M., Guardiola J., Esposito B., Iaccarino M. Structural genes for a newly recognized acetolactate synthase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1068–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1068-1077.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M., Levinthal M. The acetohydroxy acid synthase III isoenzyme of Escherichia coli K-12: regulation of synthesis by leucine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 7;79(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Clements J., Merrick M., Dixon R. Positive control and autogenous regulation of the nifLA promoter in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1983 Jan 27;301(5898):302–307. doi: 10.1038/301302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves W. E., Davis F. C., Jr, Sells B. H. Spectrophotometric determination of microgram quantities of protein without nucleic acid interference. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Sekiguchi M. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of R plasmid by in vitro mutagenesis with hydroxylamine. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1561–1563. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1561-1563.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Cara F., De Felice M. Chromatographic detection of the acetohydroxy acid synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K-12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lago C. T., Sannia G., Marino G., Squires C. H., Calvo J. M., De Felice M. The ilvIH operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Identification of the gene products and recognition of the translational start by polypeptide microsequencing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 29;824(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Matzura H. Binding of RNA polymerase and the catabolite gene activator protein within the cat promoter in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 5;150(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. L., Gielow W. O., Wallace R. G. Mechanism of araC autoregulation and the domains of two overlapping promoters, Pc and PBAD, in the L-arabinose regulatory region of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden S., Haggerty D., Stoner C. M., Kolodrubetz D., Schleif R. The Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon: binding sites of the regulatory proteins and a mechanism of positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Jeffrey A., Johnson A. D., Maurer R., Meyer B. J., Pabo C. O., Roberts T. M., Sauer R. T. How the lambda repressor and cro work. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr A precise termination site in the mouse beta major-globin transcription unit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4694–4698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase synthesis in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00267852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Uhlin B. E., Gustafsson P., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of a novel two-plasmid system for accomplishing temperature-regulated, amplified expression of cloned adventitious genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. H., De Felice M., Devereux J., Calvo J. M. Molecular structure of ilvIH and its evolutionary relationship to ilvG in Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5299–5313. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. H., De Felice M., Wessler S. R., Calvo J. M. Physical characterization of the ilvHI operon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):797–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.797-804.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Lamond A. I., Mace H. A., Berman M. L. RNA polymerase interactions with the upstream region of the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursini M. V., Arcari P., De Felice M. Acetohydroxy acid synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K-12: a trans-acting regulatory locus of ilvHI gene expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(4):491–496. doi: 10.1007/BF00428741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., Schaller H. Segment-specific mutagenesis: extensive mutagenesis of a lac promoter/operator element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Felice M., Lago C. T., Squires C. H., Calvo J. M. Acetohydroxy acid synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K12 and Salmonella typhimurium. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]