Abstract
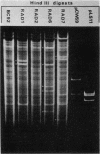
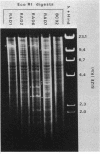
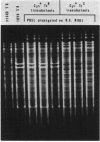
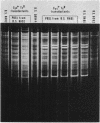
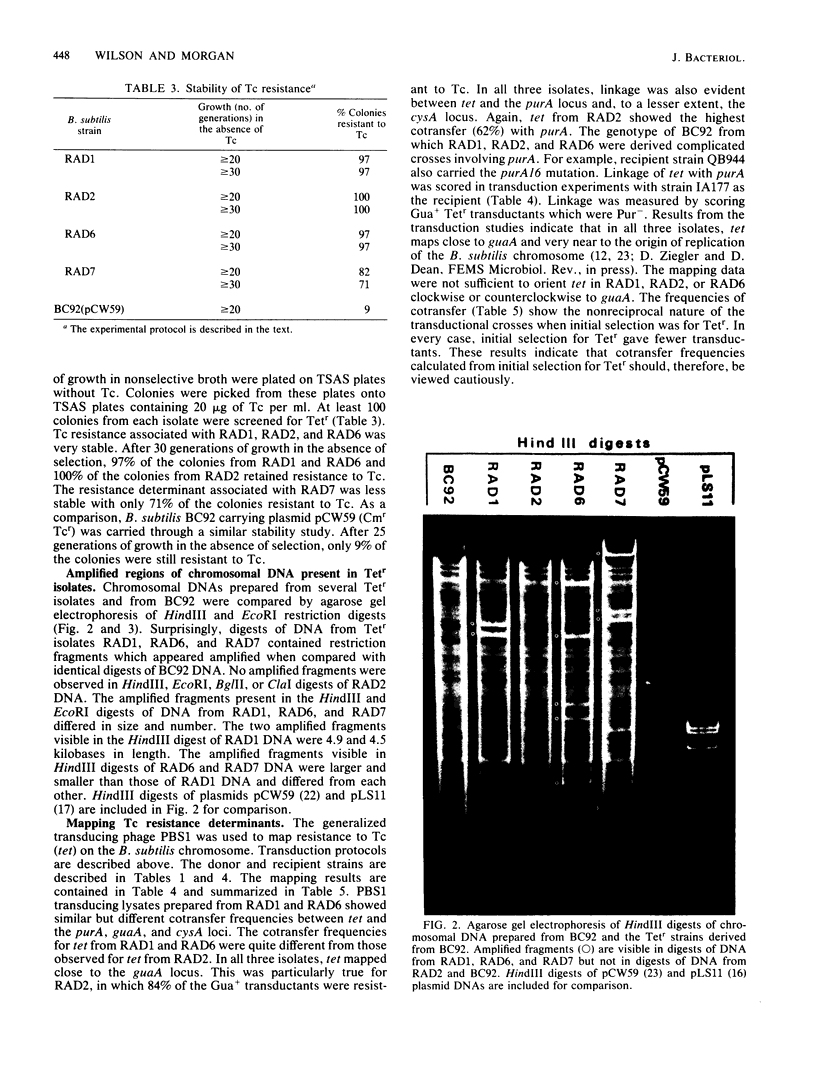
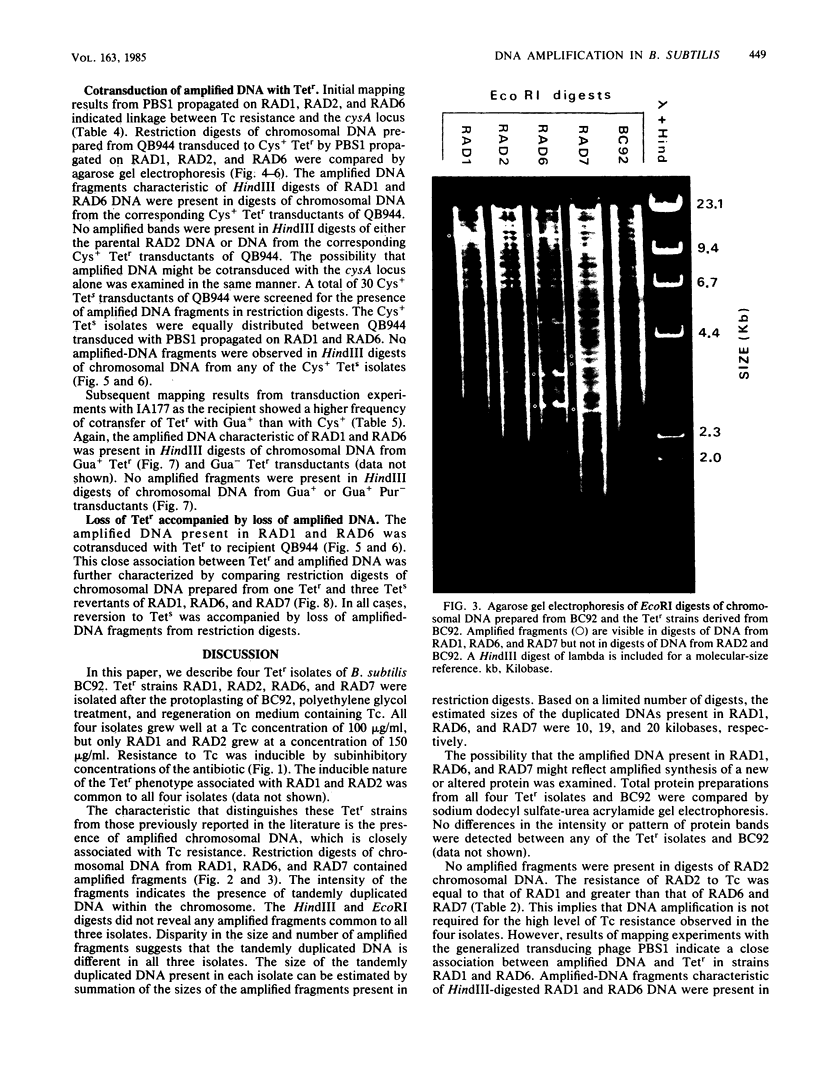
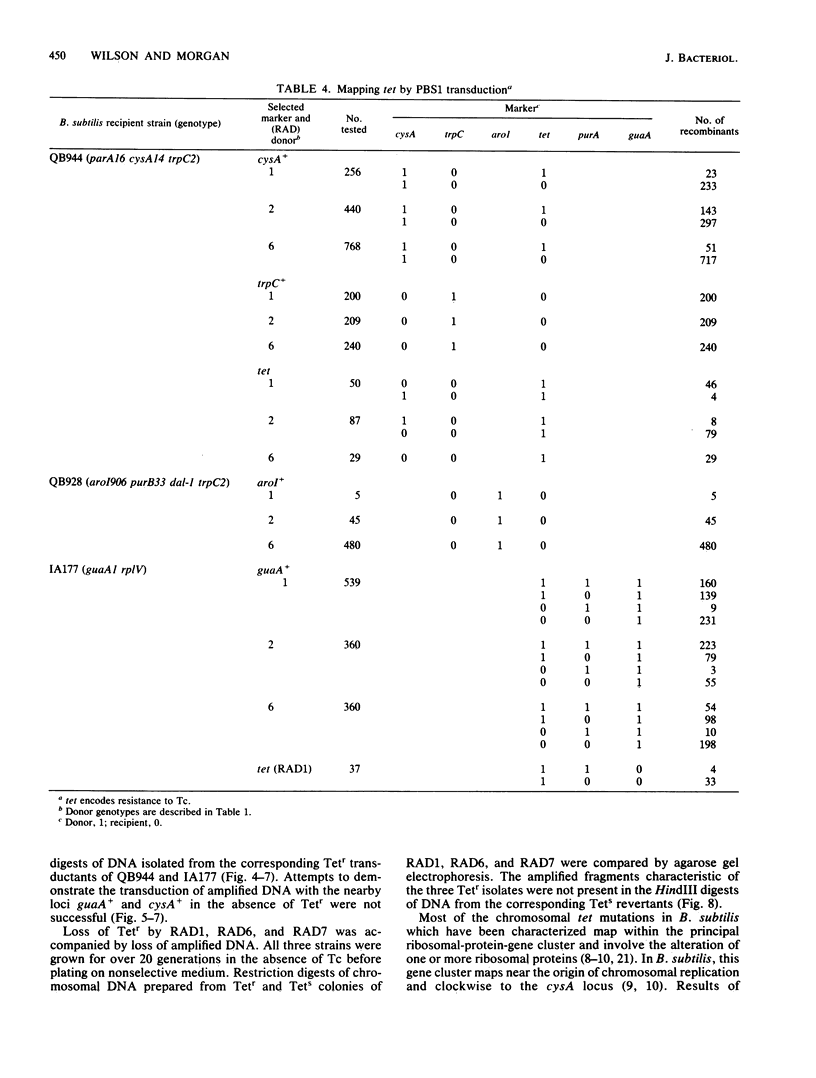
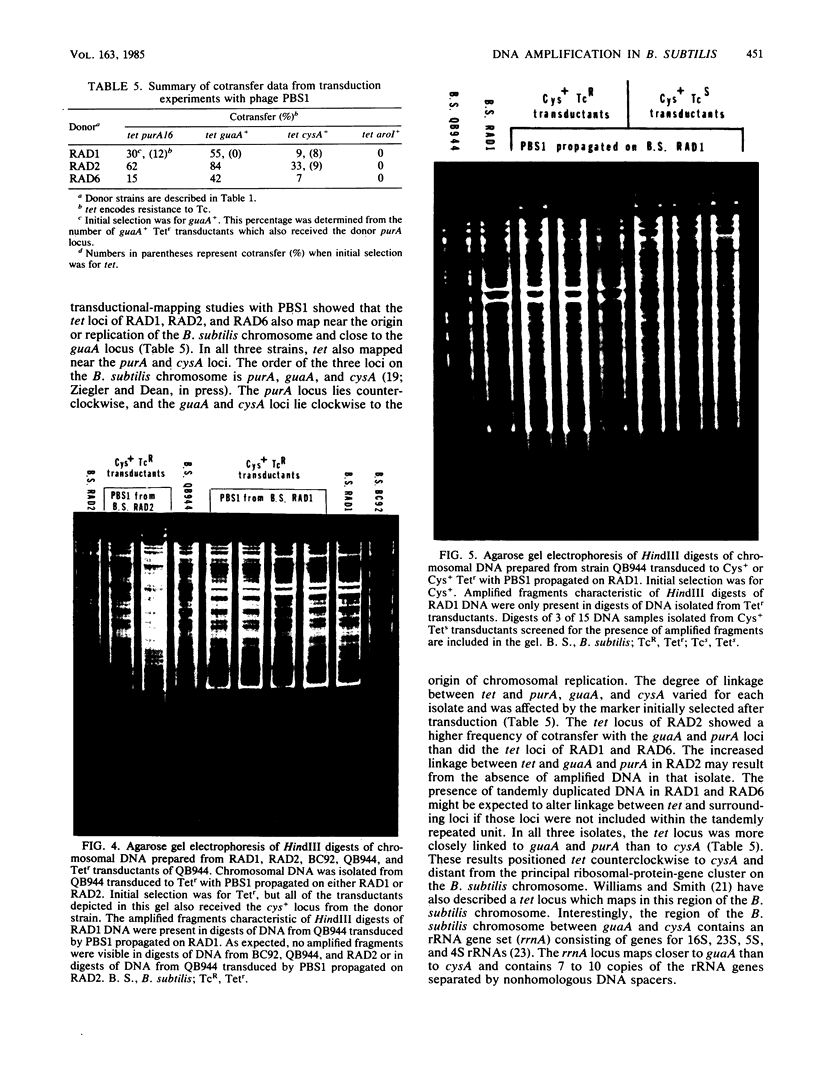
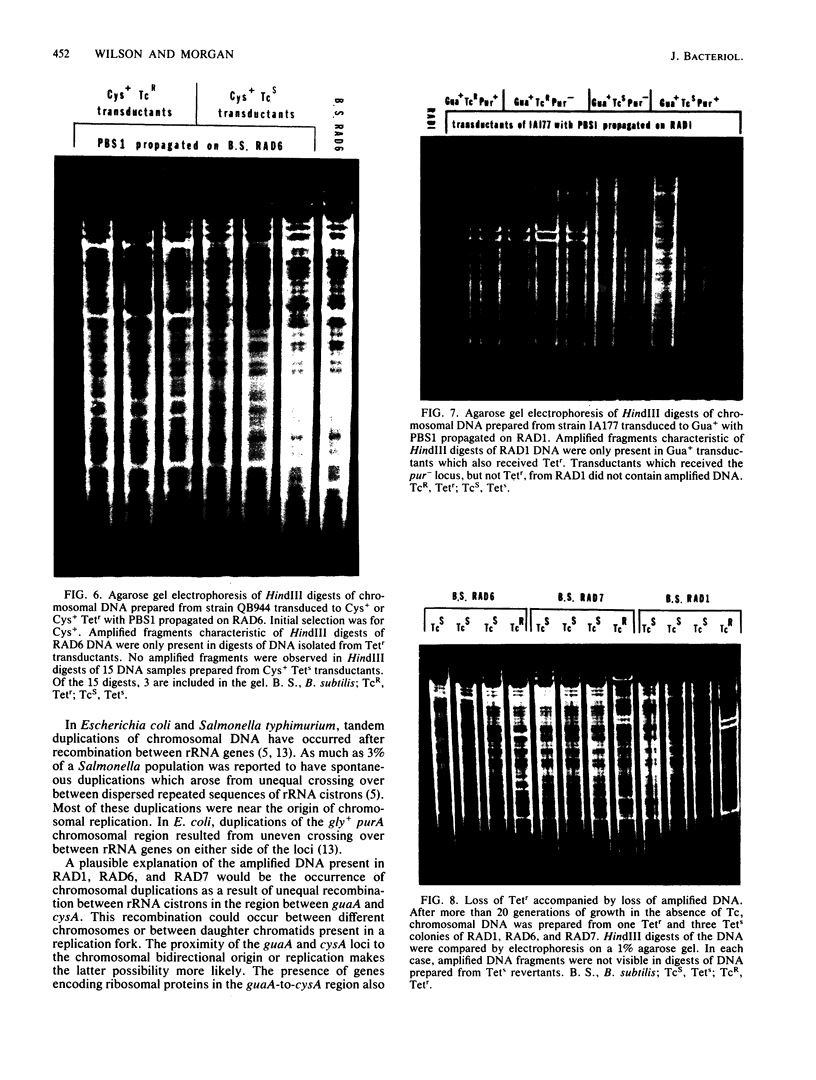
Tetracycline-resistant (Tetr) mutants RAD1, RAD2, RAD6, and RAD7 were isolated from Bacillus subtilis BC92 after protoplasting, polyethylene glycol treatment, and regeneration on a medium containing tetracycline. The Tetr phenotype in RAD1, RAD2, and RAD6 was very stable with less than 5% loss of resistance after 30 generations of growth in the absence of selection. Of the four isolates, three contained amplified chromosomal DNA closely associated with the Tetr phenotype. The intensity of restriction fragments present in HindIII and EcoRI digests of chromosomal DNA from RAD1, RAD6, and RAD7 indicated the presence of tandemly duplicated DNA. Disparity in the size and number of amplified fragments suggested that the tandemly duplicated DNA is different in all three isolates. The sizes of the duplicated DNA present in RAD1, RAD6, and RAD7 were estimated to be 10, 19, and 20 kilobases, respectively. No amplified DNA was detected in RAD2. Results of transductional-mapping studies with PBS1 showed that the tetracycline resistance (tet) loci of RAD1, RAD2, and RAD6 all mapped near the origin of chromosomal replication and close to the guaA locus. Amplified DNA characteristic of RAD1 and RAD6 was cotransduced with the tet locus. Cotransfer of amplified DNA with the guaA locus or other nearby loci in the absence of tet was not observed. In every case, loss of Tetr was accompanied by loss of amplified DNA. A possible explanation for the occurrence of the amplified DNA is presented.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Roth J. Spontaneous tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium arise by unequal recombination between rRNA (rrn) cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. P., Miller C. G., Roth J. R. Tandem duplications of the histidine operon observed following generalized transduction in Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 5;105(2):201–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem genetic duplications in phage and bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:473–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbs E. R. Arrangement of loci within the principal cluster of ribosomal protein genes of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):124–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00327657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbs E. R. Order of ribosomal protein genes in the Rif cluster of Bacillus subtilis is identical to that of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):770–772. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.770-772.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbs E. R. Selection in Bacillus subtilis giving rise to strains with mutational alterations in a variety of ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):297–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00331132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman S. E., Hershberger C. L. Amplified DNA in Streptomyces fradiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):459–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.459-466.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Banner C. D., Ollington J. F., Losick R., Hoch J. A., O'Connor M. B., Sonenshein A. L. Mapping a cloned gene under sporulation control by inserttion of a drug resistance marker into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.90-98.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Grafstrom R. H., Harnish B. W., Hillman B. S. Tandem duplications resulting from recombination between ribosomal RNA genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):407–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes are localized to a homogeneously staining region of a single chromosome in a methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5553–5556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishido K., Noguchi N., Kim C., Ando T. Isolation of a tetracycline-resistance plasmid excised from a chromosomal DNA sequence in Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):224–234. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kuroda M., Sakaguchi K. Isolation and characterization of four plasmids from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1487–1494. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1487-1494.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tlsty T. D., Albertini A. M., Miller J. H. Gene amplification in the lac region of E. coli. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Chen S. M., Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of a class of polymyxin resistant partial revertants of stage O sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: map of the chromosome region near the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasseghi H., Claverys J. P. Amplification of a chimeric plasmid carrying an erythromycin-resistance determinant introduced into the genome of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gene. 1983 Mar;21(3):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G., Smith I. Chromosomal mutations causing resistance to tetracycline in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00267249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. R., Skinner S. E., Shaw W. V. Analysis of two chloramphenicol resistance plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus: insertional inactivation of Cm resistance, mapping of restriction sites, and construction of cloning vehicles. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. E., Hoch J. A., Bott K. Genetic mapping of a linked cluster of ribosomal ribonucleic acid genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):624–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.624-628.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Gene amplification in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1613–1621. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]