Abstract
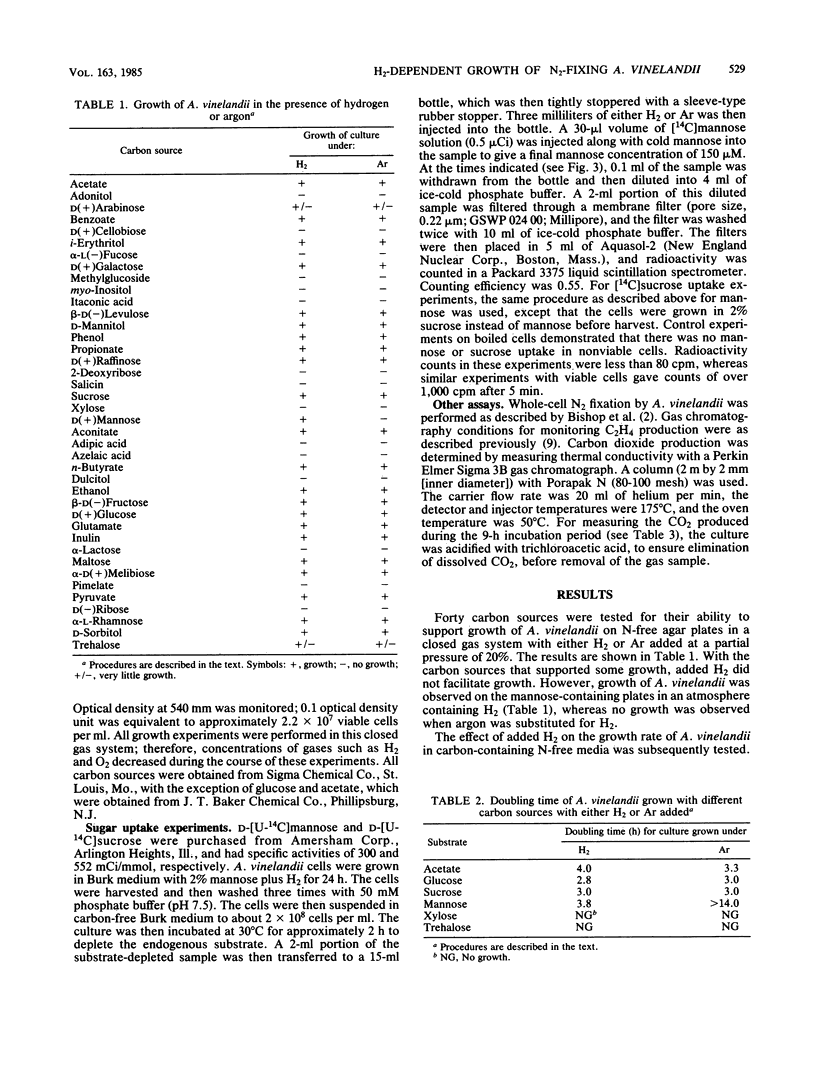
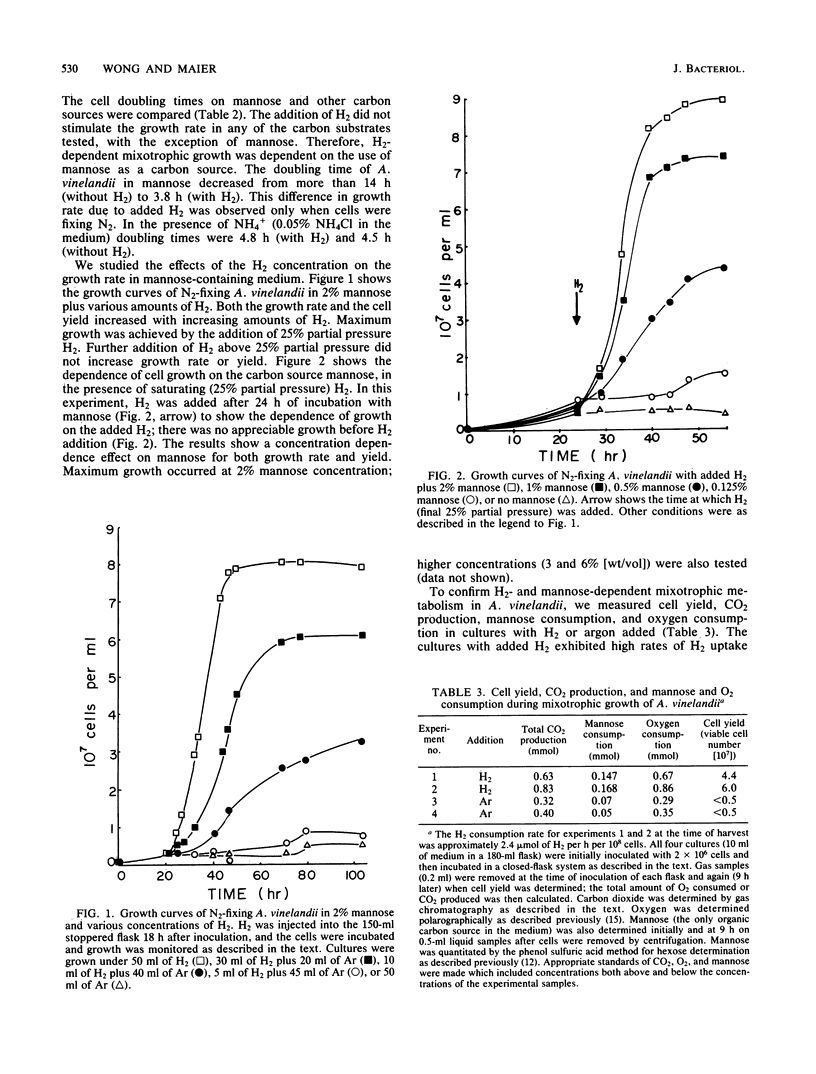
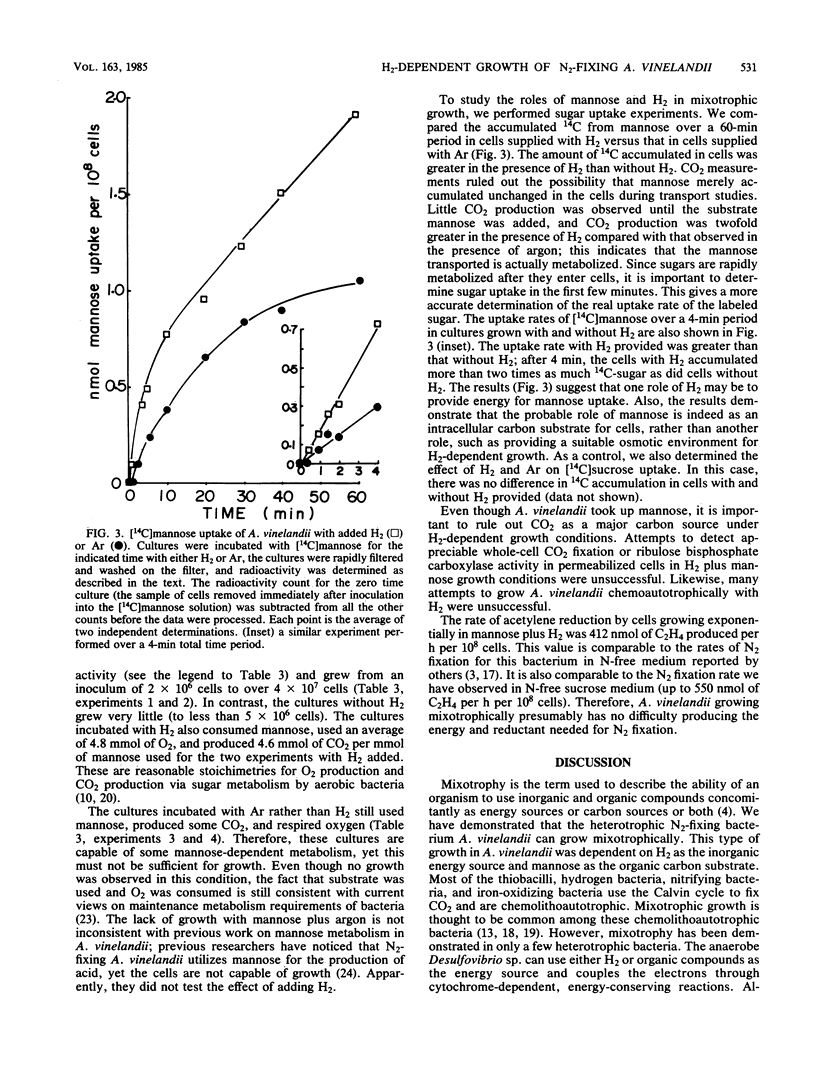
Azotobacter vinelandii can grow with a variety of organic carbon sources and fix N2 without the need for added H2. However, due to an active H2-oxidizing system, H2-dependent mixotrophic growth in an N-free medium was demonstrated when mannose was provided as the carbon source. There was no appreciable growth with either H2 or mannose alone. Both the growth rate and the cell yield were dependent on the concentrations of both substrates, H2 and mannose. Cultures growing mixotrophically with H2 and mannose consumed approximately 4.8 mmol of O2 and produced 4.6 mmol of CO2 per mmol of mannose consumed. In the absence of H2, less CO2 was produced, less O2 was consumed, and cell growth was negligible. The rate of acetylene reduction in mixotrophic cultures was comparable to the rate in cultures grown in N-free sucrose medium. The rate of [14C]mannose uptake of cultures with H2 was greater than with argon, whereas [14C]sucrose uptake was unaffected by the addition of H2; therefore, the role of H2 in mixotrophic metabolism may be to provide energy for mannose uptake. A. vinelandii is not an autotroph, as attempts to grow the organism chemoautotrophically with H2 or to detect ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity were unsuccessful.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Evidence for an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Expression of an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1244-1251.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanus F. J., Maier R. J., Evans H. J. Autotrophic growth of H2-uptake-positive strains of Rhizobium japonicum in an atmosphere supplied with hydrogen gas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Rittenberg S. C. Thiobacillus perometabolis nov. sp., a non-autotrophic thiobacillus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):218–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00406335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Merberg D. M. Rhizobium japonicum mutants that are hypersensitive to repression of H2 uptake by oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.161-167.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle G. D., Simonson J. G., Hales B. J., Braymer H. D. Nitrogen fixation system of tungsten-resistant mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):72–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.72-80.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L., Postgate J. R. Oxygen and hydrogen in biological nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Neijssel O. M. The status of YATP and maintenance energy as biologically interpretable phenomena. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:459–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. Y., Maier R. J. Hydrogen-oxidizing electron transport components in nitrogen-fixing Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):348–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.348-352.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



