Abstract
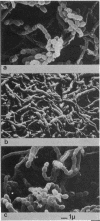
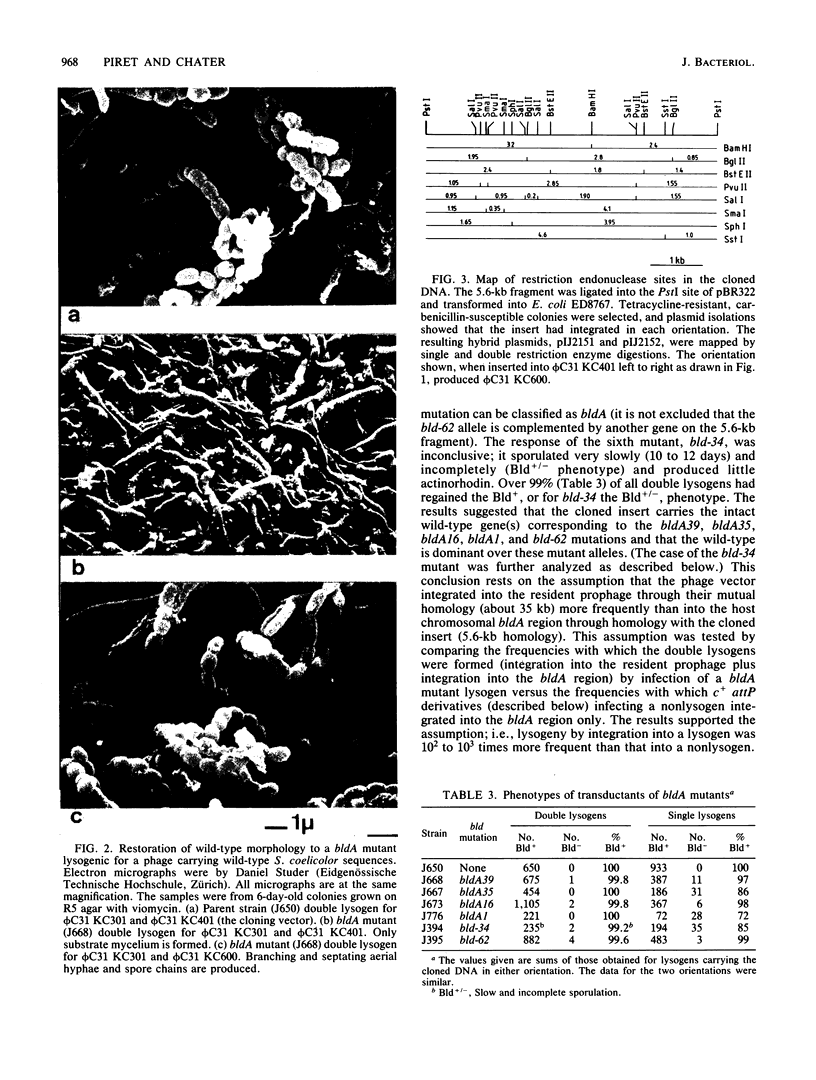
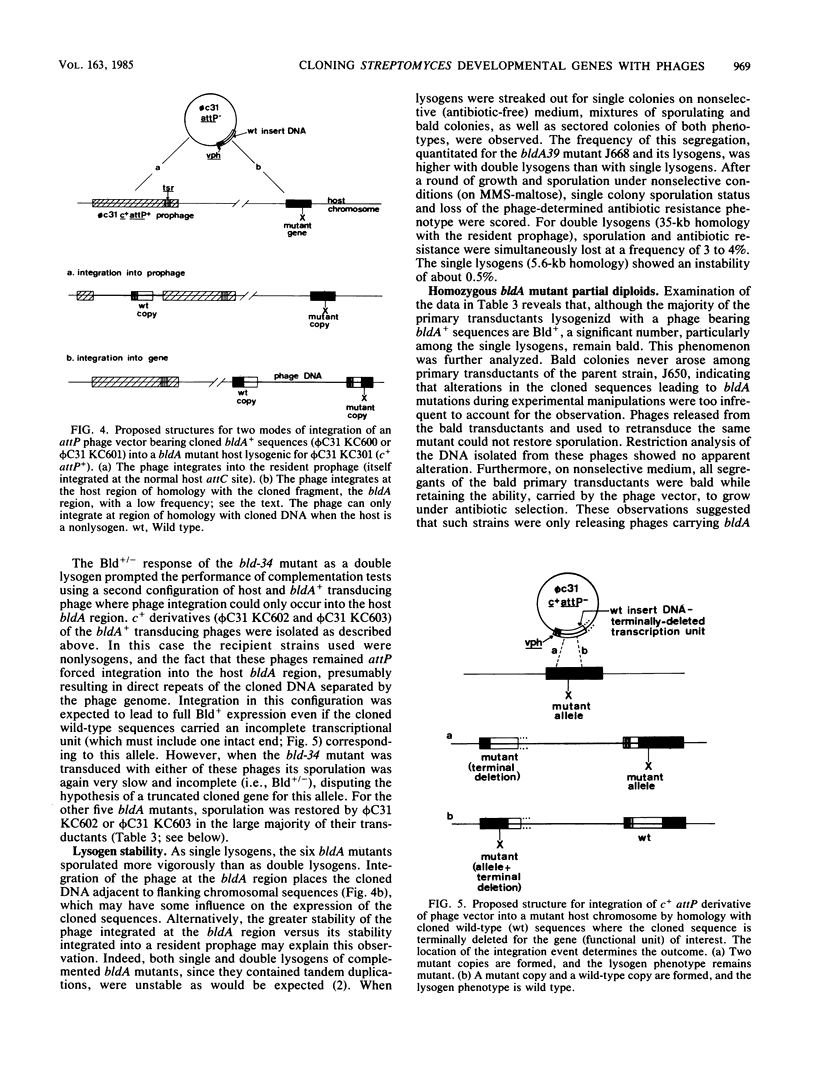
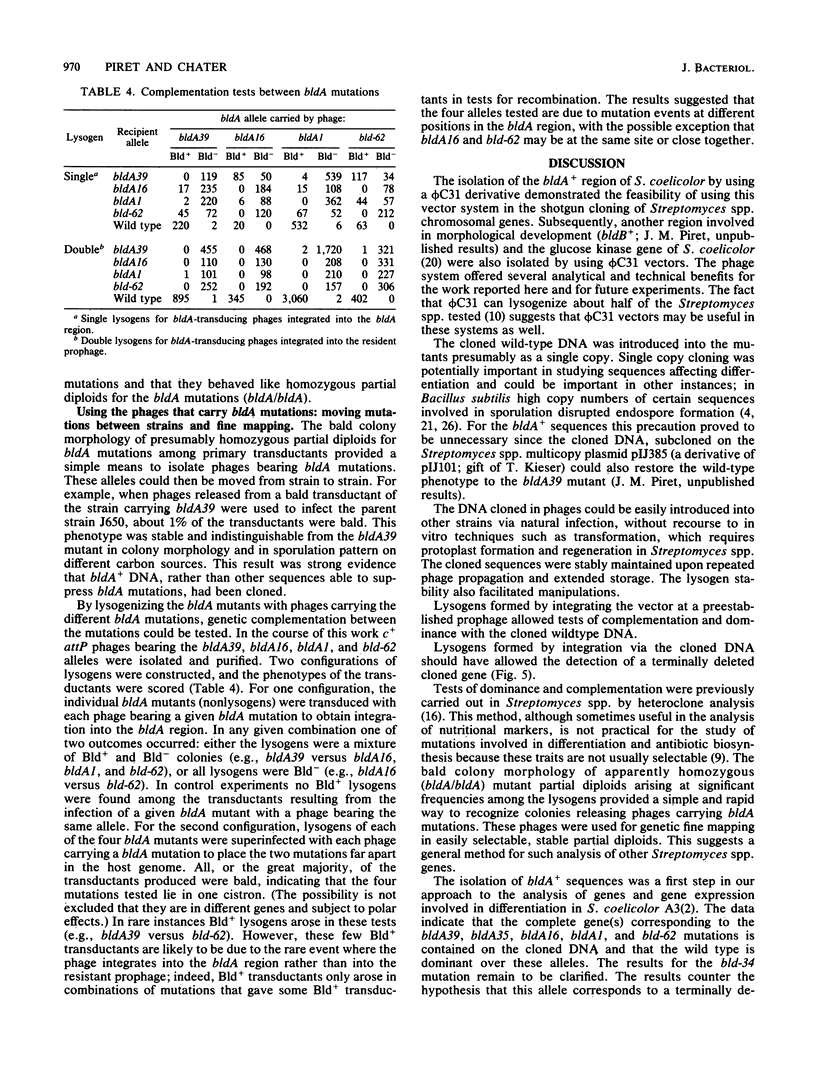
Streptomyces coelicolor bald (bld) mutants form colonies of vegetative substrate mycelium, but do not develop aerial hyphae or spore chains. The bldA strains form none of the four antibiotics known to be produced by the parent strain. With a vector derived from the temperate bacteriophage phi C31, a 5.6-kilobase fragment of wildtype DNA was cloned which restored sporulation to five independent bldA mutants when lysogenized with the recombinant phage. The cloned gene(s) was dominant over the mutant alleles. Phage integration by recombination of the cloned bldA+ DNA with the bldA region of each mutant produced mainly sporulating colonies, presumably heterozygous bldA+/bldA partial diploids for the insert DNA. However, a minority of these primary transductants were bald and were apparently homozygous bldA/bldA mutant partial diploids, formed by some homogenetization process. The phages released from the bald lysogens carried bldA mutations and were used to show that bldA+ sequences had been cloned and that fine mapping of the region could be performed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbuchner J., Cullum J. DNA amplification and an unstable arginine gene in Streptomyces lividans 66. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):134–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00332735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem genetic duplications in phage and bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:473–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner C. D., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Deletion analysis of a complex promoter for a developmentally regulated gene from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., King A. A., Suarez J. E. The expression of Streptomyces and Escherichia coli drug-resistance determinants cloned into the Streptomyces phage phi C31. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., Springer W., Suarez J. E. Dispensable sequences and packaging constraints of DNA from the Streptomyces temperate phage phi C31. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Thompson C. J. Gene cloning in Streptomyces. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:69–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowding J. E. Characterization of a bacteriophage virulent for Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):163–176. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L. Separation of very large DNA molecules by gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):653–665. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. E., Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., Piret J. M. The restriction mapping of c gene deletions in Streptomyces bacteriophage phi C31 and their use in cloning vector development. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Kumada Y., Beppu T. Unstable genetic determinant of A-factor biosynthesis in streptomycin-producing organisms: cloning and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):481–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.481-487.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Seno E. T., Bruton C. J., Chater K. F. Genetic mapping, cloning and physiological aspects of the glucose kinase gene of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):501–507. doi: 10.1007/BF00436199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T. DNAGEL: a computer program for determining DNA fragment sizes using a small computer equipped with a graphics tablet. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):679–688. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T. Factors affecting the isolation of CCC DNA from Streptomyces lividans and Escherichia coli. Plasmid. 1984 Jul;12(1):19–36. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Lea E. J., Rudd B. A., Wright H. M., Hopwood D. A. A new channel-forming antibiotic from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) which requires calcium for its activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Dec;129(12):3565–3573. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-12-3565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya N. D., Chater K. F., Mkrtumian N. M. Genetics and molecular biology of Streptomyces bacteriophages. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):206–229. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.206-229.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya N. D., Mkrtumian N. M., Gostimskaya N. L., Danilenko V. N. Characterization of temperate actinophage phi C31 isolated from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):258–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.258-262.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler I., Warburg R., Tipper D. J., Halvorson H. O. Cloning of an unstable spoIIA-tyrA fragment from Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Feb;130(2):411–421. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-2-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara-Nakano M., Kataoka Y., Ogawara H. Unstable mutation of beta-lactamase production in Streptomyces lavendulae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):124–128. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J. A morphological and genetic mapping study of bald colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):299–315. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Genetic recombination: strand transfer and mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:847–880. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redshaw P. A., McCann P. A., Pentella M. A., Pogell B. M. Simultaneous loss of multiple differentiated functions in aerial mycelium-negative isolates of streptomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):891–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.891-899.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodicio M. R., Chater K. F. Small DNA-free liposomes stimulate transfection of streptomyces protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1078–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1078-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrempf H. Deletion and amplification of DNA sequences in melanin-negative variants of Streptomyces reticuli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(3):501–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00325917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Gill R. E., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus and the spoC locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. DNA cloning in Streptomyces: resistance genes from antibiotic-producing species. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):525–527. doi: 10.1038/286525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]