Abstract
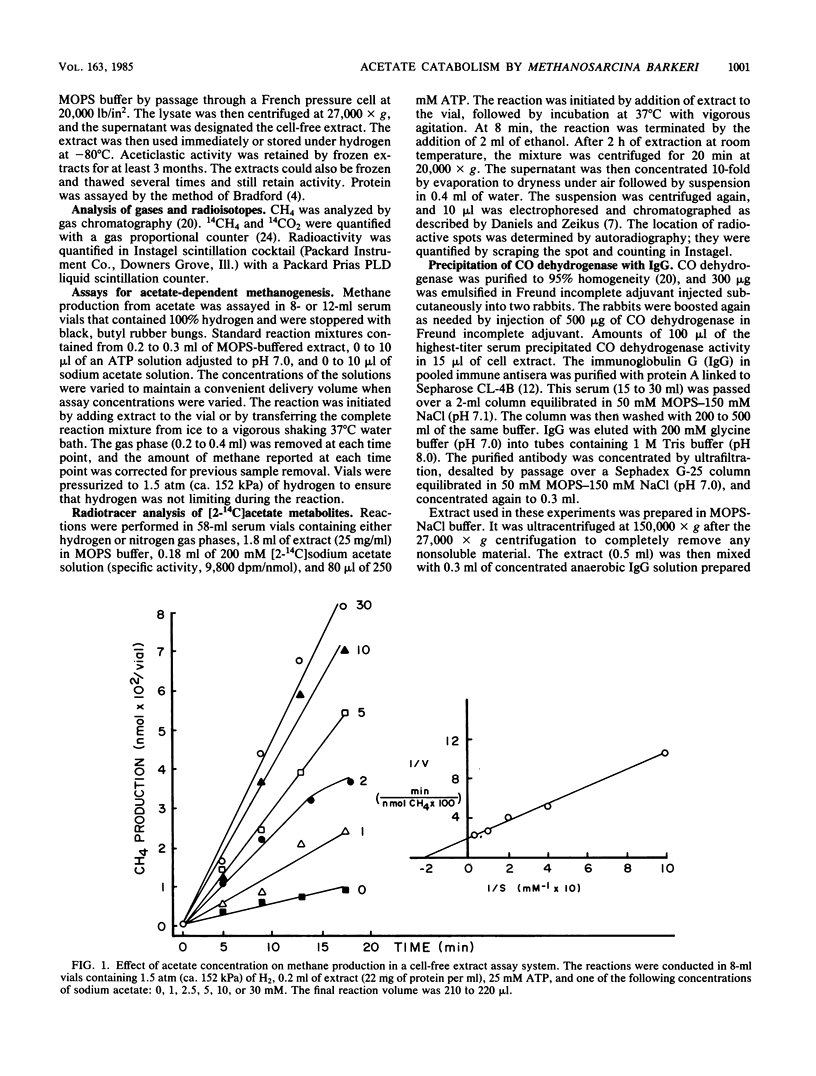
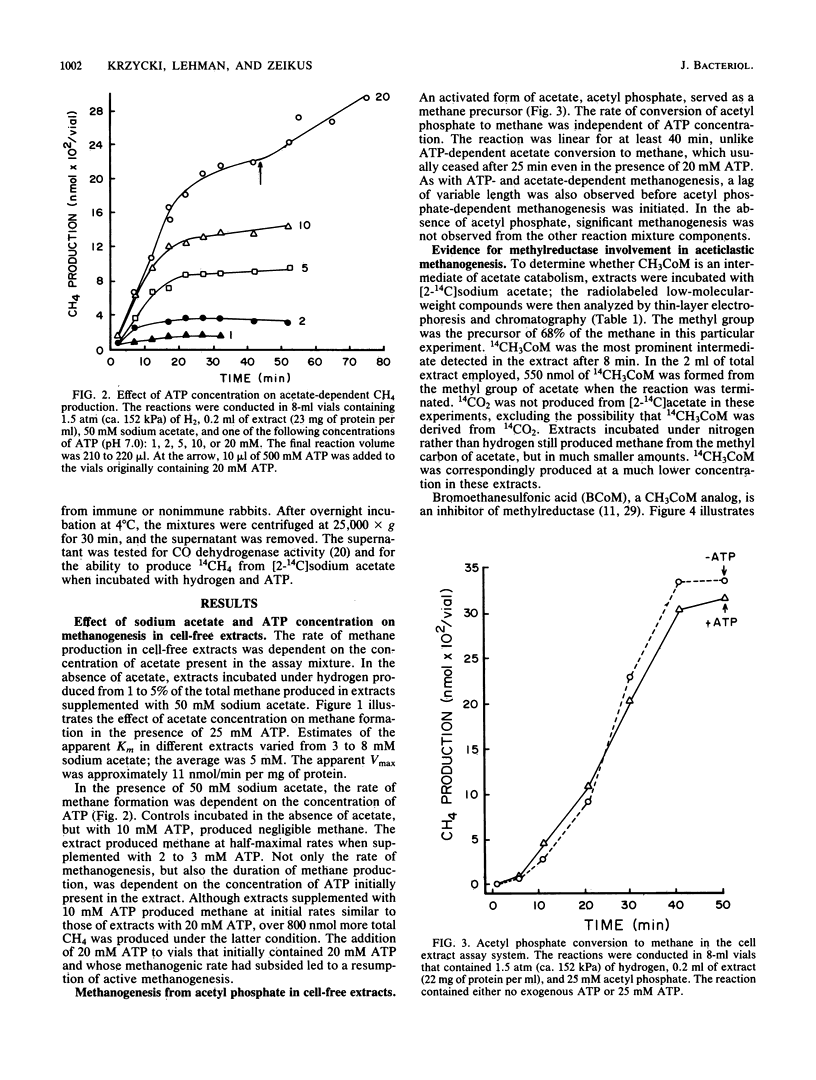
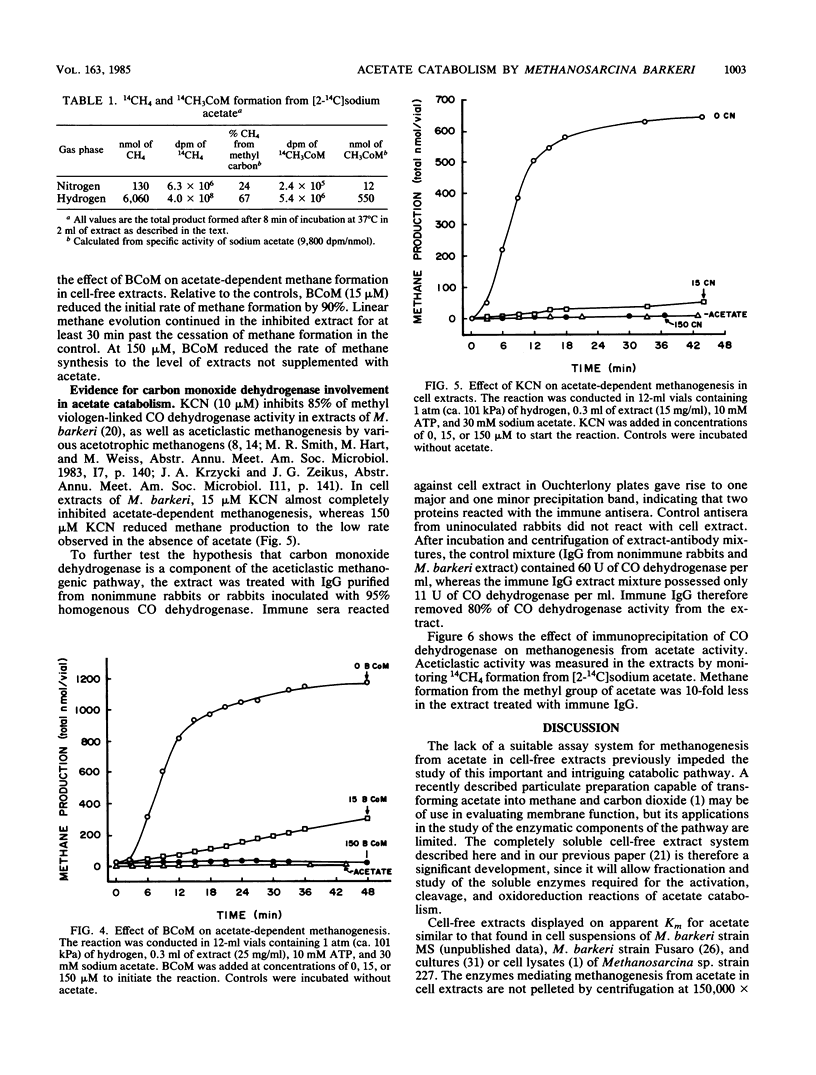
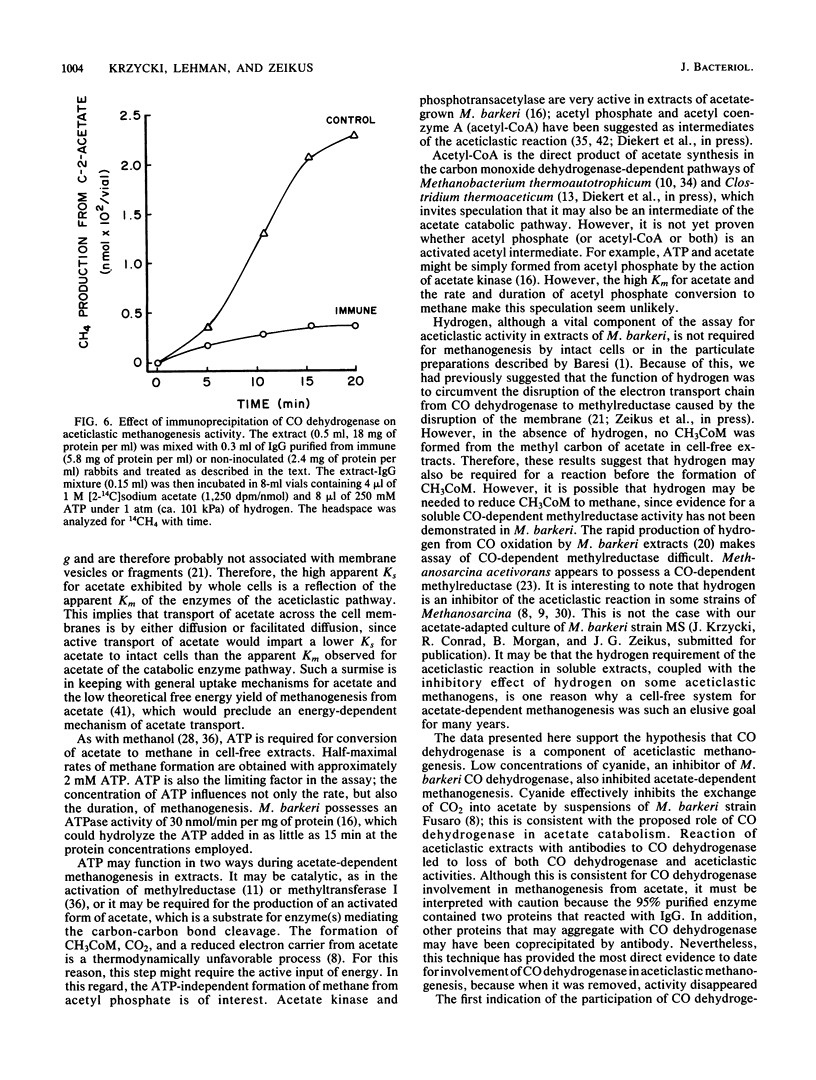
The pathway of acetate catabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri strain MS was studied by using a recently developed assay for methanogenesis from acetate by soluble enzymes in cell extracts. Extracts incubated with [2-14C]acetate, hydrogen, and ATP formed 14CH4 and [14C]methyl coenzyme M as products. The apparent Km for acetate conversion to methane was 5 mM. In the presence of excess acetate, both the rate and duration of methane production was dependent on ATP. Acetyl phosphate replaced the cell extract methanogenic requirement for both acetate and ATP (the Km for ATP was 2 mM). Low concentrations of bromoethanesulfonic acid and cyanide, inhibitors of methylreductase and carbon monoxide dehydrogenase, respectively, greatly reduced the rate of methanogenesis. Precipitation of CO dehydrogenase in cell extracts by antibodies raised to 95% purified enzyme inhibited both CO dehydrogenase and acetate-to-methane conversion activity. The data are consistent with a model of acetate catabolism in which methylreductase, methyl coenzyme M, CO dehydrogenase, and acetate-activating enzymes are components. These results are discussed in relation to acetate uptake and rate-limiting transformation mechanisms in methane formation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baresi L. Methanogenic cleavage of acetate by lysates of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):365–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.365-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baresi L., Wolfe R. S. Levels of coenzyme F420, coenzyme M, hydrogenase, and methylcoenzyme M methylreductase in acetate-grown Methanosarcina. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):388–391. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.388-391.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Zeikus J. G. One-carbon metabolism in methanogenic bacteria: analysis of short-term fixation products of 14CO2 and 14CH3OH incorporated into whole cells. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.75-84.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson T. J., Mah R. A. Effect of H(2)-CO(2) on Methanogenesis from Acetate or Methanol in Methanosarcina spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):348–355. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.348-355.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Wolfe R. S. ATP activation and properties of the methyl coenzyme M reductase system in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.851-857.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. I., Drake H. L., Wood H. G. Synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A from carbon monoxide, methyltetrahydrofolate, and coenzyme A by enzymes from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):440–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.440-448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W. R., Zeikus J. G. One-carbon metabolism in methanogens: evidence for synthesis of a two-carbon cellular intermediate and unification of catabolism and anabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):932–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.932-941.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W., Zeikus J. G. Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):133–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.133-140.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Wolkin R. H., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of unitrophic and mixotrophic substrate metabolism by acetate-adapted strain of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.247-254.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Zeikus J. G. Characterization and purification of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):231–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.231-237.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., White R. H., Ferry J. G. Identification of methyl coenzyme M as an intermediate in methanogenesis from acetate in Methanosarcina spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):521–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.521-525.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Ferry J. G. Carbon monoxide-dependent methyl coenzyme M methylreductase in acetotrophic Methosarcina spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):526–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.526-532.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE M. J., BARKER H. A. Studies on the methane fermentation. XII. The pathway of hydrogen in the acetate fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jun;71(6):644–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.6.644-648.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN T. C., BARKER H. A. Studies on the methane fermentation. IX. The origin of methane in the acetate and methanol fermentations by methanosarcina. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.1.81-86.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S., Wolfe R. S. Methyl-coenzyme M, an intermediate in methanogenic dissimilation of C1 compounds by Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):728–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.728-734.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Mah R. A. Acetate as sole carbon and energy source for growth of methanosarcina strain 227. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):993–999. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.993-999.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Mah R. A. Growth and methanogenesis by Methanosarcina strain 227 on acetate and methanol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):870–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.870-879.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R. Reversal of 2-bromoethanesulfonate inhibition of methanogenesis in Methanosarcina sp. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):516–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.516-523.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Mah R. A. Kinetics of acetate metabolism during sludge digestion. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.368-371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stupperich E., Hammel K. E., Fuchs G., Thauer R. K. Carbon monoxide fixation into the carboxyl group of acetyl coenzyme A during autotrophic growth of Methanobacterium. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 7;152(1):21–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Acetate assimilation pathway of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):332–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.332-339.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Acetate metabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Nov 13;119(2):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00964270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Brock T. D. Biological energy production in the apparent absence of electron transport and substrate level phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Kerby R., Krzycki J. A. Single-carbon chemistry of acetogenic and methanogenic bacteria. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1167–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.3919443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. Metabolism of one-carbon compounds by chemotrophic anaerobes. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:215–299. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meijden P., te Brömmelstroet B. W., Poirot C. M., van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Purification and properties of methanol:5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamide methyltransferase from Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):629–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.629-635.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



