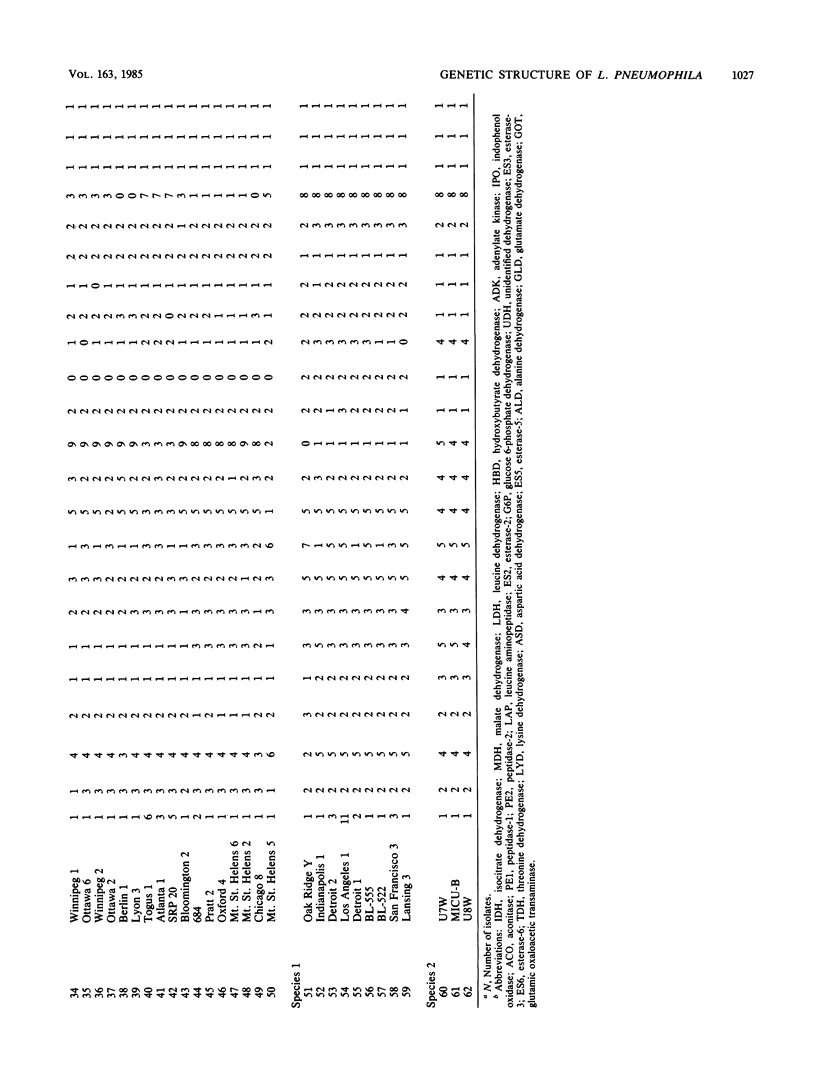
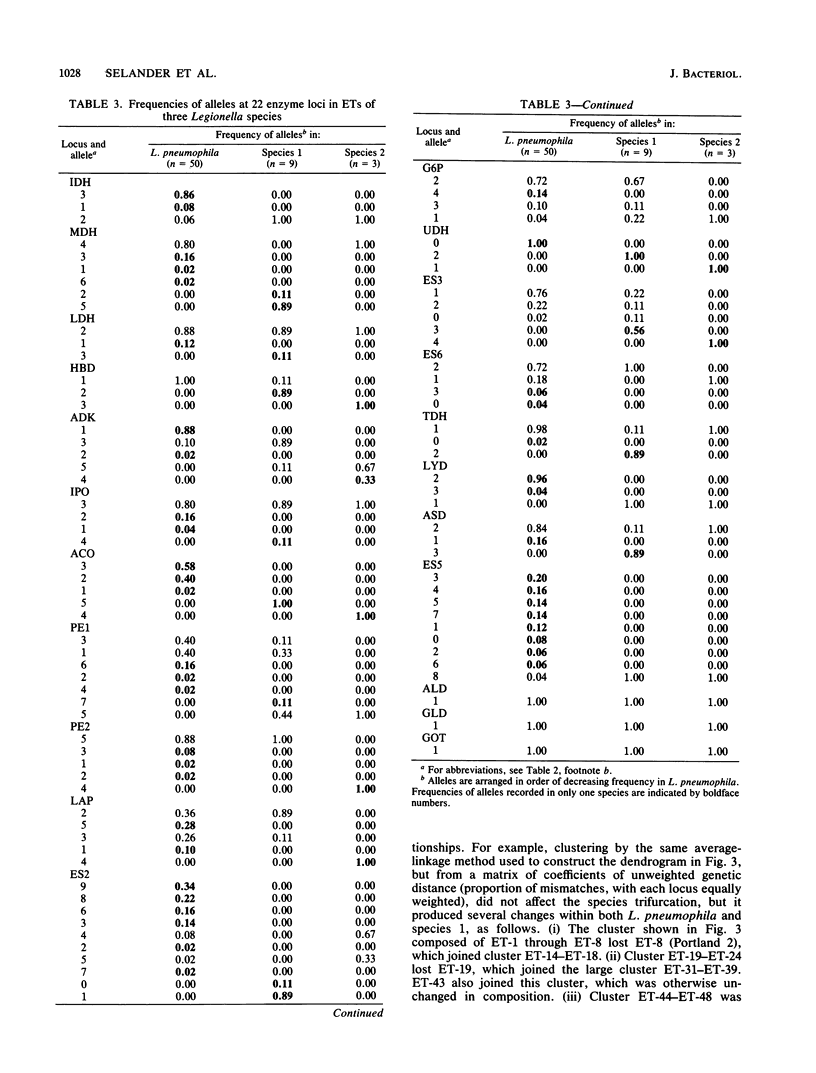
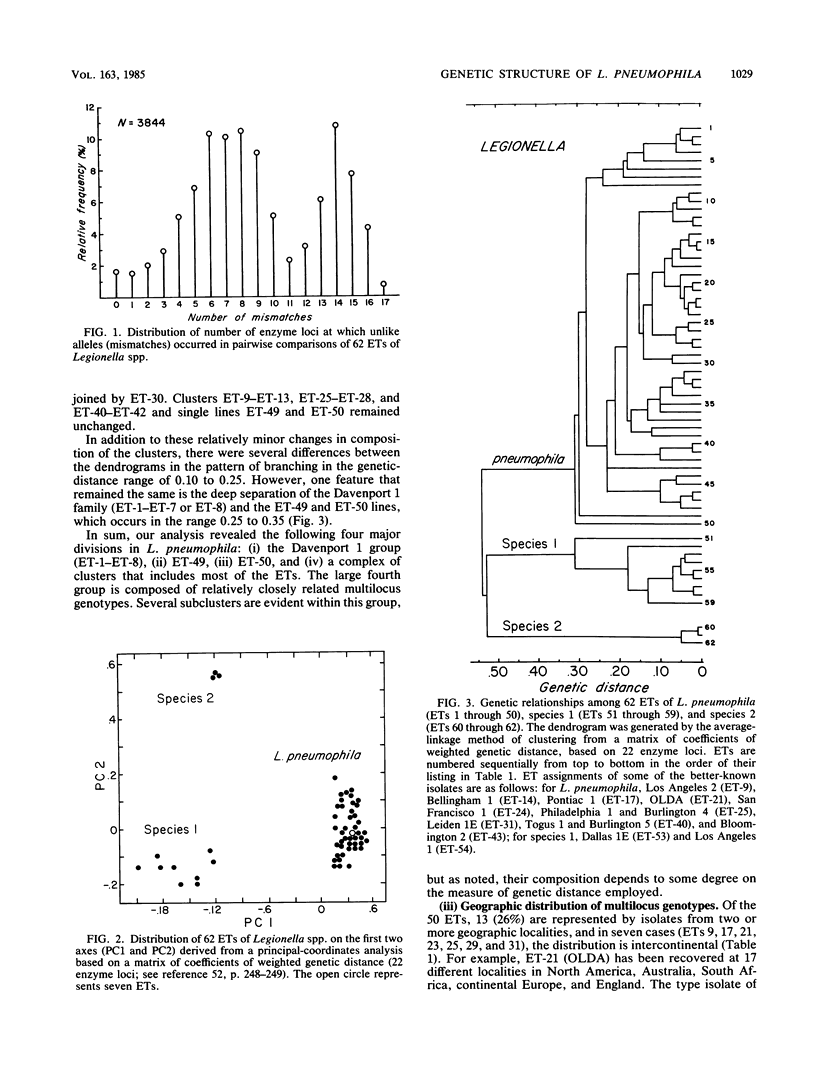
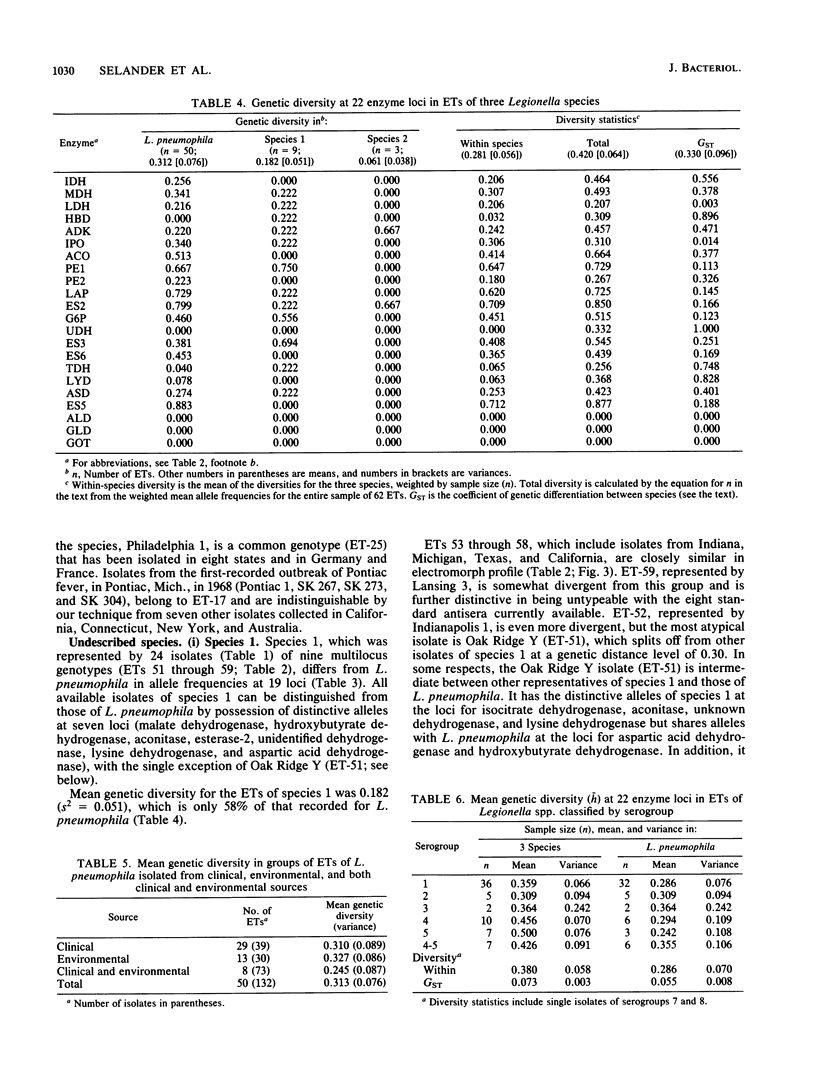
Abstract
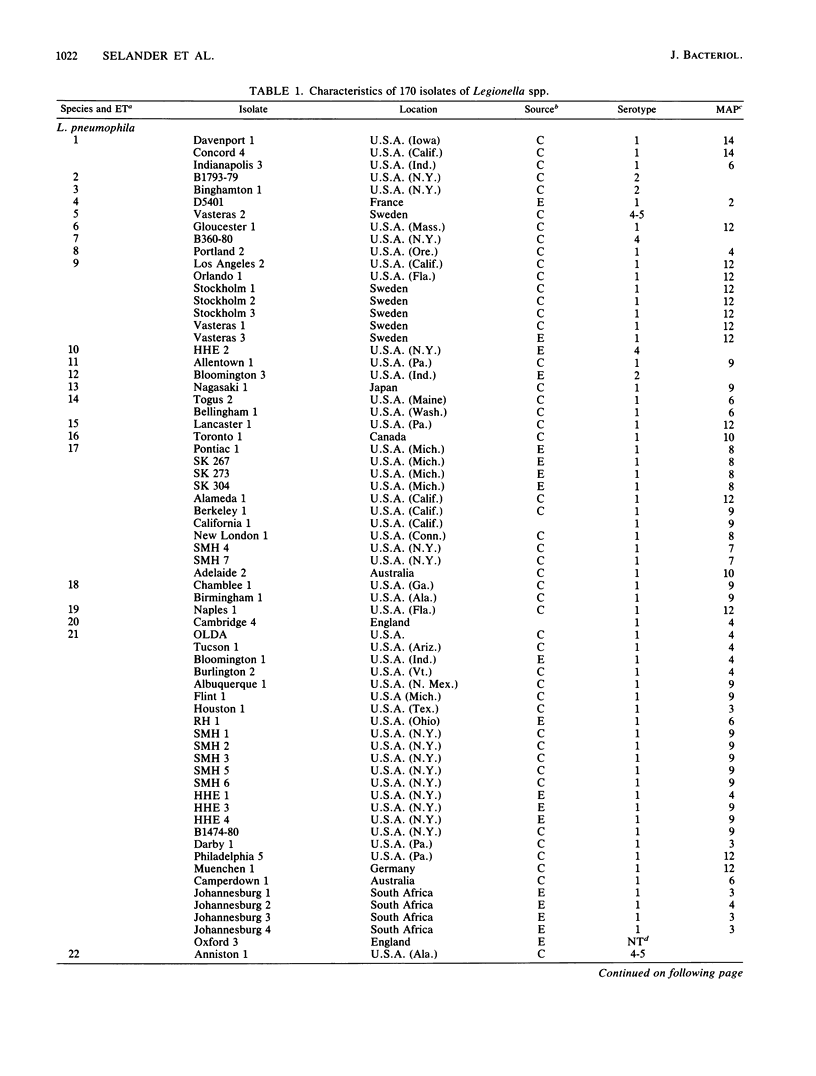
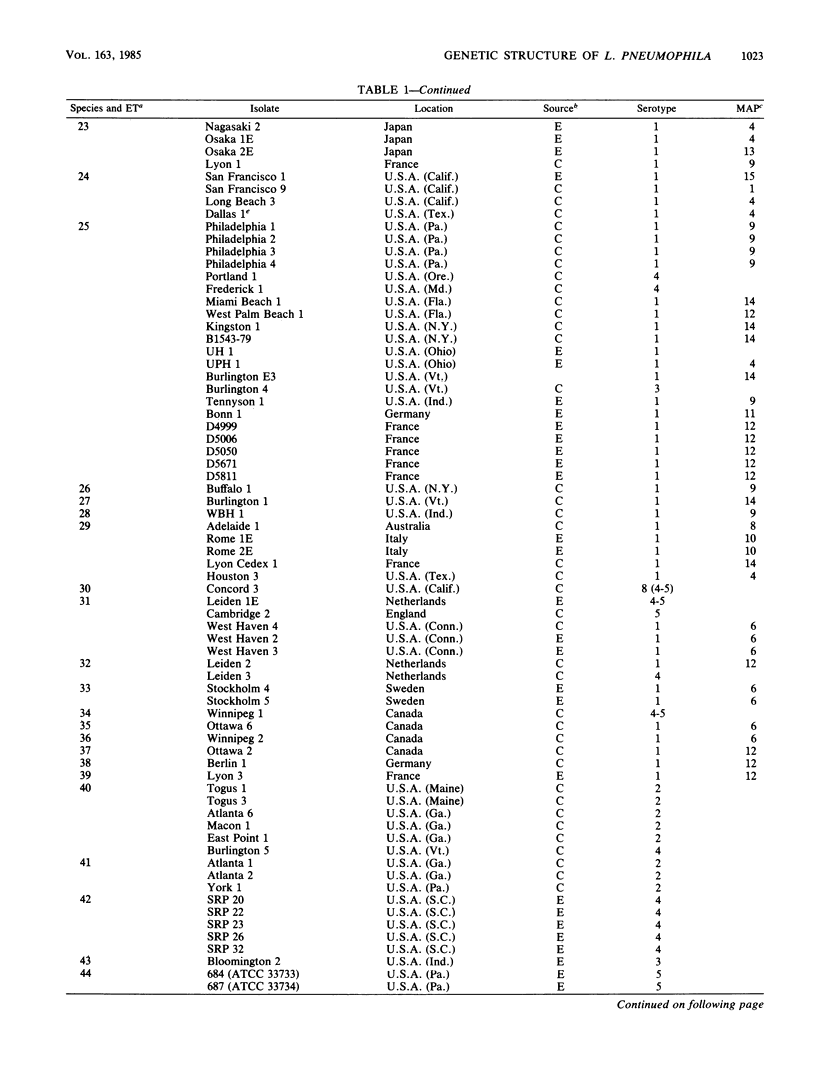
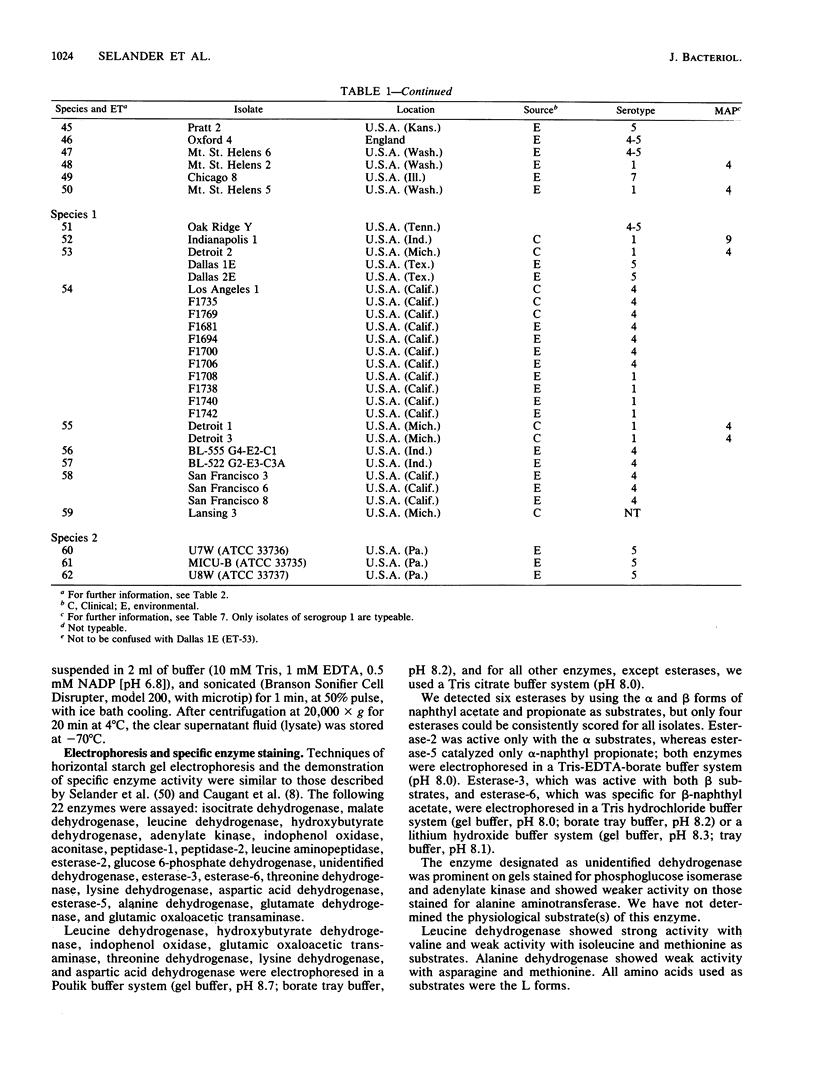
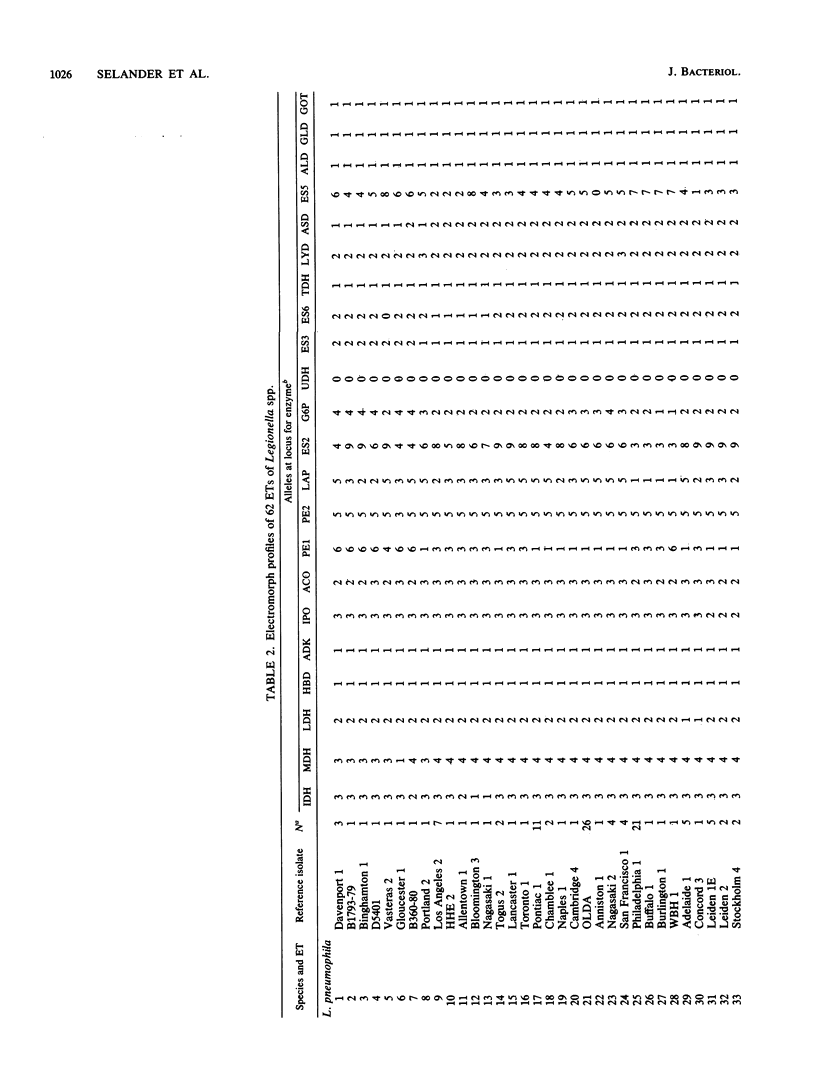
The genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila was defined by an analysis of electrophoretically demonstrable allelic variation at structural genes encoding 22 enzymes in 292 isolates from clinical and environmental sources. Nineteen of the loci were polymorphic, and 62 distinctive electrophoretic types (ETs), representing multilocus genotypes, were identified. Principal coordinates and clustering analyses demonstrated that isolates received as L. pneumophila were a heterogeneous array of genotypes that included two previously undescribed species. For 50 ETs of L. pneumophila (strict sense), mean genetic diversity per locus was 0.312, and diversity was equivalent in ETs represented by isolates recovered from clinical sources and those collected from environmental sources. Cluster analysis revealed four major groups or lineages of ETs in L. pneumophila. Genetic diversity among ETs of the same serotype was, on average, 93% of that in the total sample of ETs. Isolates marked by particular patterns of reactivity to a panel of nine monoclonal antibodies were also genetically heterogeneous, mean diversity within patterns being about 75% of the total. Both Pontiac fever and the pneumonic form of legionellosis may be caused by isolates of the same ET. The genetic structure of L. pneumophila is clonal, and many clones apparently are worldwide in distribution. The fact that L. pneumophila is only 60% as variable as Escherichia coli raises the possibility that isolates recovered from clinical cases and man-made environments are a restricted subset of all clones in the species as a whole.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Vickers R. M., Elder E. M., Lema M., Garrity G. M. Plasmid and surface antigen markers of endemic and epidemic Legionella pneumophila strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):230–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.230-235.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and temporal variation in the E. coli population of a human host. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):467–490. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Iglewski B. H. Conjugation-mediated genetic exchange in Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):80–84. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.80-84.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Francis E. M., George W. L. Legionella wadsworthii species nova: a cause of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):809–813. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, McKinney R. M., Skaliy P., Gorman G. W. A fifth serogroup of Legionella pneumophila. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):58–59. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):467–471. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Horwitz M. A. Isolation and characterization of the cytoplasmic and outer membranes of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila). J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):409–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity G. M., Elder E. M., Davis B., Vickers R. M., Brown A. Serological and genotypic diversity among serogroup 5- reacting environmental Legionella isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):646–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.646-653.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick T. H., Gregg M. B., Berman B., Mallison G., Rhodes W. W., Jr, Kassanoff I. Pontiac fever. An epidemic of unknown etiology in a health department: I. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Feb;107(2):149–160. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Hoebeke J., Tram C., Marullo S., Strosberg A. D. Characterization, serological specificity, and diagnostic possibilities of monoclonal antibodies against Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):793–797. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.793-797.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley C. E., Cohen M. L., Halter J., Meyer R. D. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease: a continuing common-source epidemic at Wadsworth Medical Center. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):583–586. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E. The population genetics of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:31–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herwaldt L. A., Gorman G. W., McGrath T., Toma S., Brake B., Hightower A. W., Jones J., Reingold A. L., Boxer P. A., Tang P. W. A new Legionella species, Legionella feeleii species nova, causes Pontiac fever in an automobile plant. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Mar;100(3):333–338. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann A. F., McDade J. E., Patton C. M., Bennett J. V., Skaliy P., Feeley J. C., Anderson D. C., Potter M. E., Newhouse V. F., Gregg M. B. Pontiac fever: isolation of the etiologic agent (Legionella pneumophilia) and demonstration of its mode of transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Sep;114(3):337–347. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. The pertinence of the periodic selection phenomenon to prokaryote evolution. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lema M., Brown A. Electrophoretic characterization of soluble protein extracts of Legionella pneumophila and other members of the family Legionellaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1132–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1132-1140.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. R. Periodic selection, infectious gene exchange and the genetic structure of E. coli populations. Genetics. 1981 Sep;99(1):1–23. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre R., Medeiros A. A., Pasculle A. W. Characterization of the beta-lactamases of six species of Legionella. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.216-221.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Brenner D. J., Bozeman F. M. Legionnaires' disease bacterium isolated in 1947. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):659–661. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thacker L., Wells D. E., Wong M. C., Jones W. J., Bibb W. F. Monoclonal antibodies to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1: possible applications in diagnostic tests and epidemiologic studies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;255(1):91–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D. Legionella infections: a review of five years of research. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):258–278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Granoff D. M., Pattison P. E., Selander R. K. A population genetic framework for the study of invasive diseases caused by serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. F-statistics and analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Ann Hum Genet. 1977 Oct;41(2):225–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1977.tb01918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Selander R. K. Evidence for clonal population structure in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):198–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Plouffe J. F. Production of monoclonal antibodies to Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 and 6. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):895–900. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.895-900.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schill W. B., Phelps S. R., Pyle S. W. Multilocus Electrophoretic Assessment of the Genetic Structure and Diversity of Yersinia ruckeri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):975–979. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.975-979.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., McEachern H. V. Survival of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium in water. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):662–663. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P. Plant-associated bacteria as human pathogens: disciplinal insularity, ambilateral harmfulness, epistemological primacy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):708–710. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J., Best M., Brown A., Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. Ubiquitousness of Legionella pneumophila in the water supply of a hospital with endemic Legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 25;306(8):466–468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202253060807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall R. L., Domingue E. L. Cocultivation of Legionella pneumophila and free-living amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):954–959. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.954-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Reingold A. L., Brake B. J., McGiboney D. L., Gorman G. W., Broome C. V. Reactivity of serum from patients with suspected legionellosis against 29 antigens of legionellaceae and Legionella-like organisms by indirect immunofluorescence assay. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


