Abstract
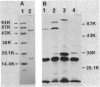
A Pseudomonas strain produced an enzyme capable of deacylating 7 beta-(4-carboxybutanamido)cephalosporanic acid to 7-aminocephalosporanic acid in response to glutaric acid. The gene for the enzyme was cloned within the PstI site of pBR325 as a 7.35-kilobase-pair DNA segment from a mutant of this strain whose enzyme is produced constitutively. The gene expression in the primary clone appeared to be low in Escherichia coli but was significantly enhanced by reducing the size of the initial segment coupled with E. coli promoters. Subsequent subcloning resulted in localization of the gene to a 2.45-kilobase-pair fragment. Three clone-specific polypeptides with molecular weights of ca. 16,000, 54,000, and 70,000 were shown by maxicell analysis. The former two corresponded to the small and large subunits of the purified enzyme from the Pseudomonas strain, and the third polypeptide was suggested to be their precursor. This was supported by DNA sequence study together with amino acid sequencing of the amino terminus of both subunits: the sequences for the small and large subunits were localized contiguously in this order on the structural gene without termination codons between them. The nucleotide sequence also disclosed the presence of a signallike sequence preceding that for the small subunit, consistent with the previous observation that the enzyme might be periplasmic in the Pseudomonas strain. Those results suggest a process for the formation of an active enzyme complex from a precursor through two steps of processing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasingham K., Warburton D., Dunnill P., Lilly M. D. The isolation and kinetics of penicillin amidase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 13;276(1):250–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckel P., Zehelein E. Expression of Pseudomonas fluorescens D-galactose dehydrogenase in E. coli. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Molecular cloning of TOL genes xylB and xylE in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1137–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1137-1143.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P., Atkinson T., Sherwood R. F. Molecular cloning of the Pseudomonas carboxypeptidase G2 gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1222–1227. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1222-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Terminal-sequence analysis of bacterial ribosomal RNA. Correlation between the 3'-terminal-polypyrimidine sequence of 16-S RNA and translational specificity of the ribosome. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
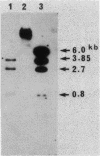
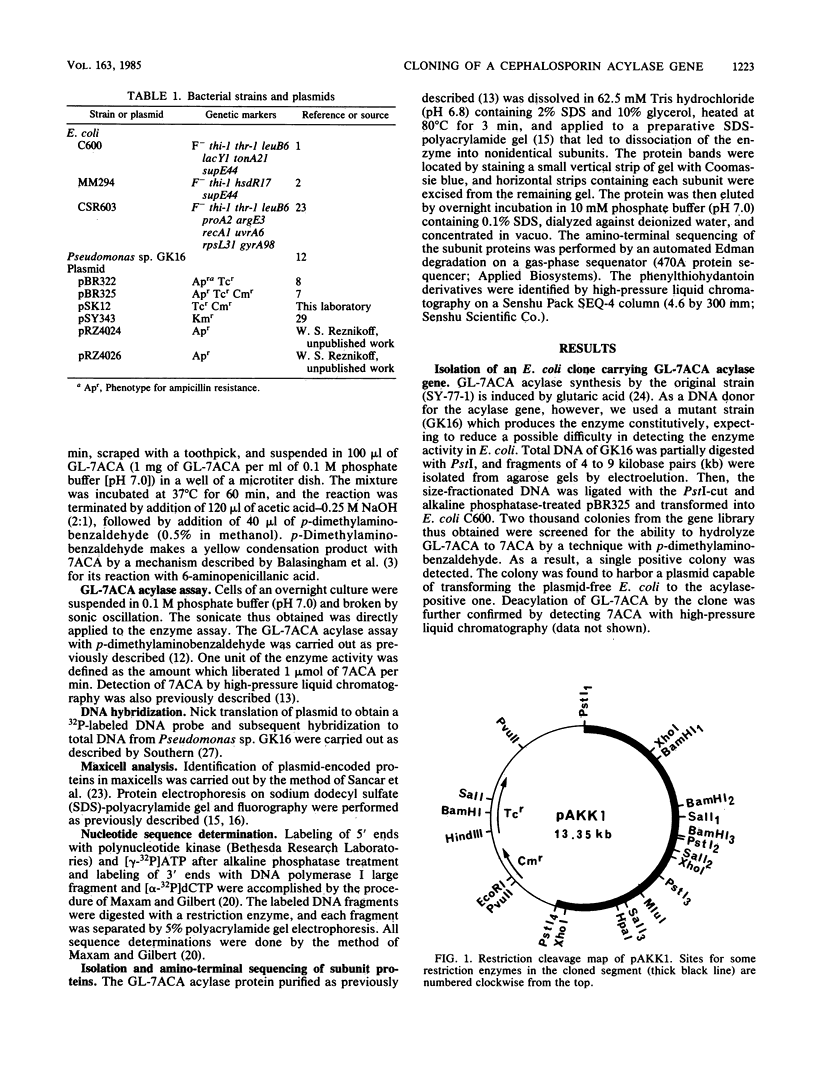
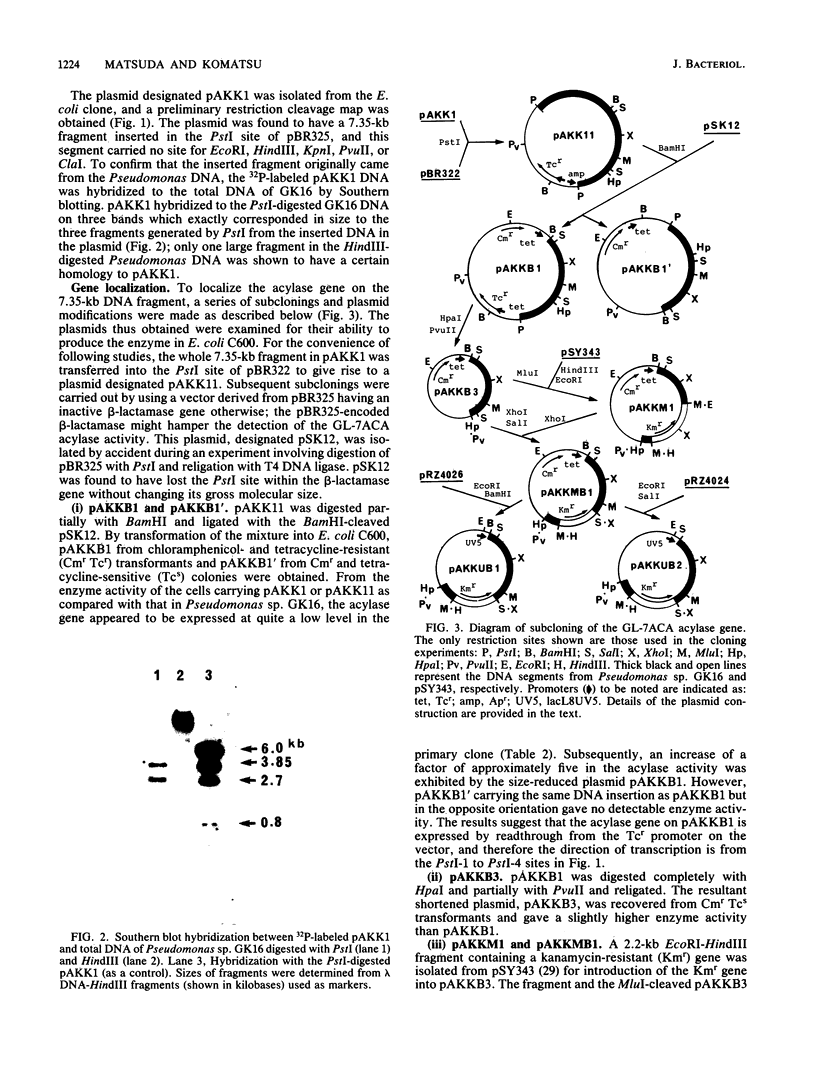
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme E. J. Enzymes involved in beta-lactam antibiotic biosynthesis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1977;21:89–123. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda S., Takagi T. Overproduction of Escherichia coli replication proteins by the use of runaway-replication plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1153–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1153-1161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]