Abstract
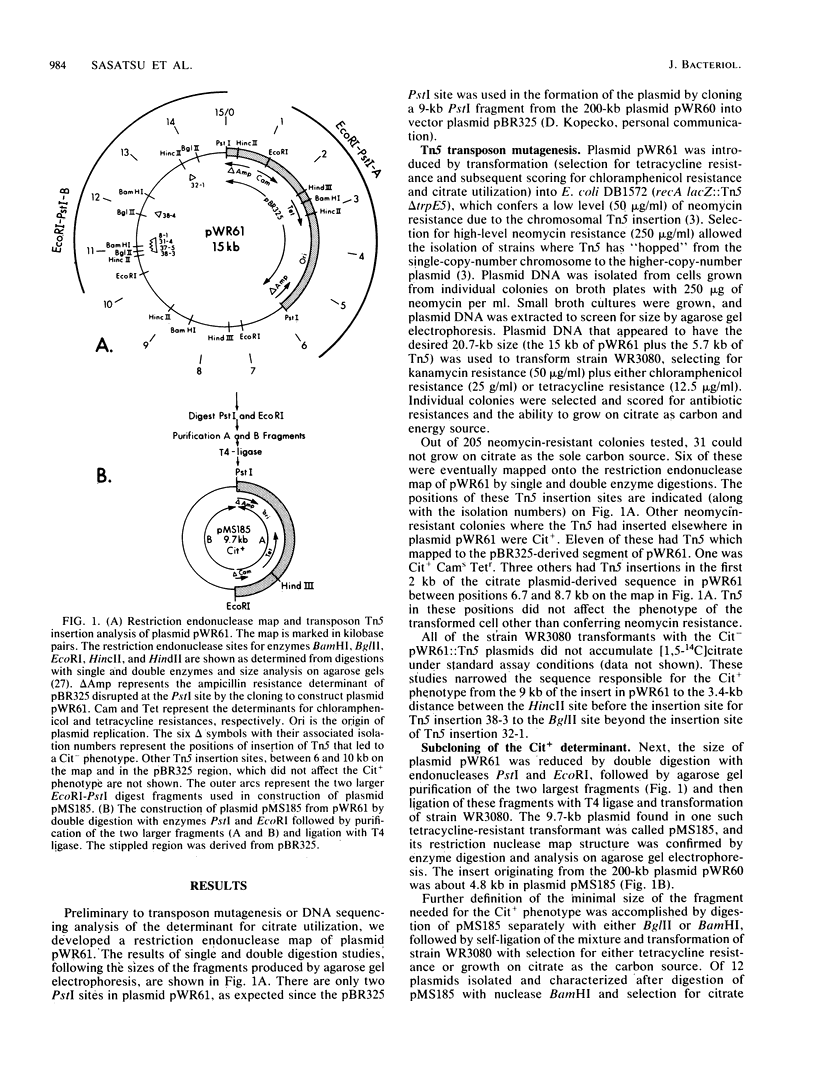
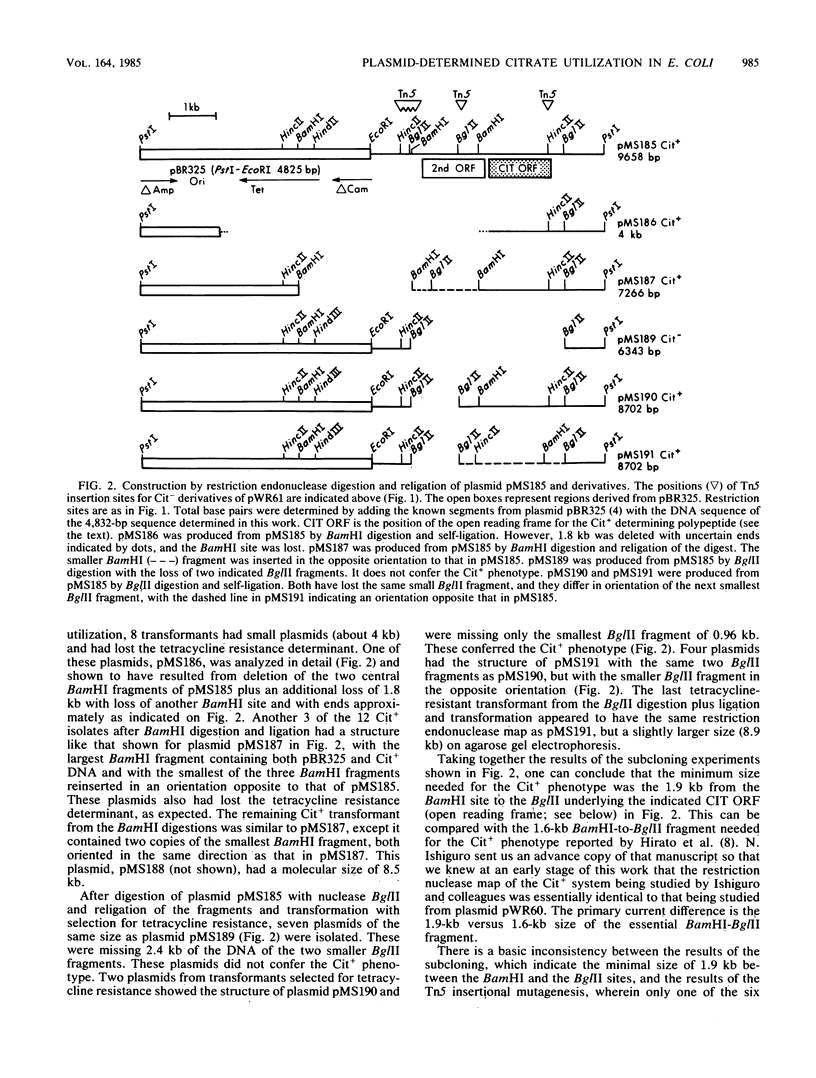
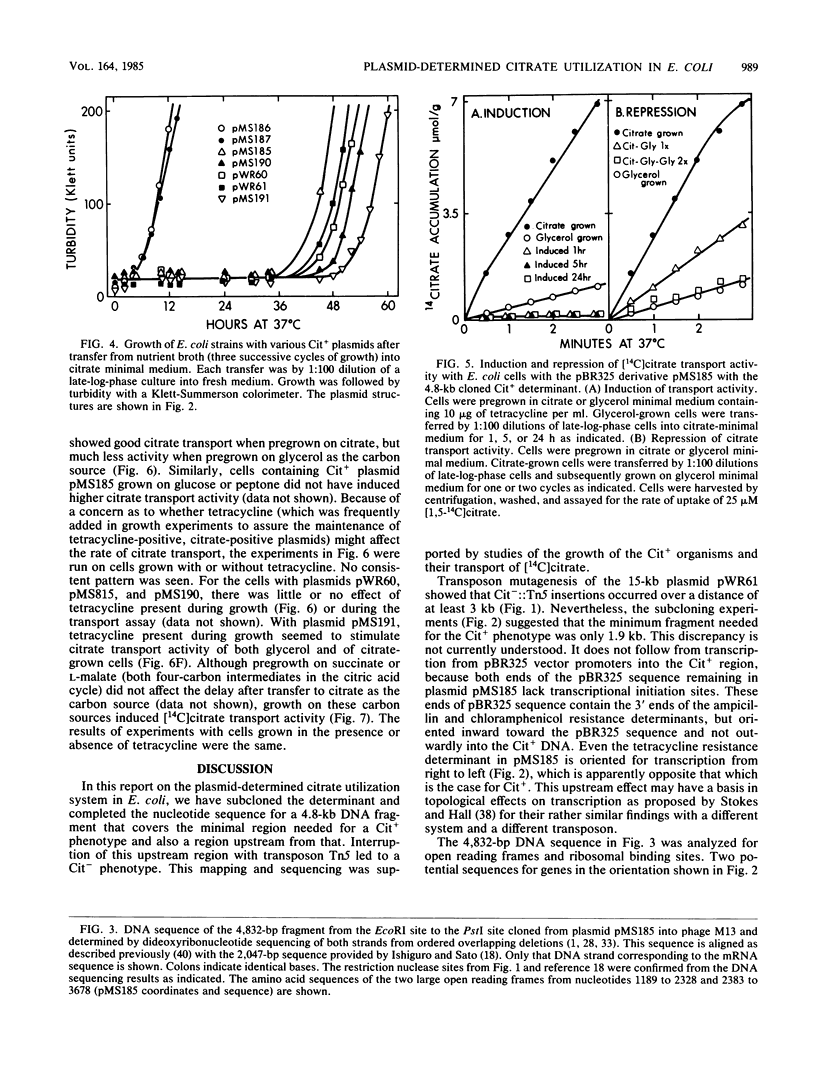
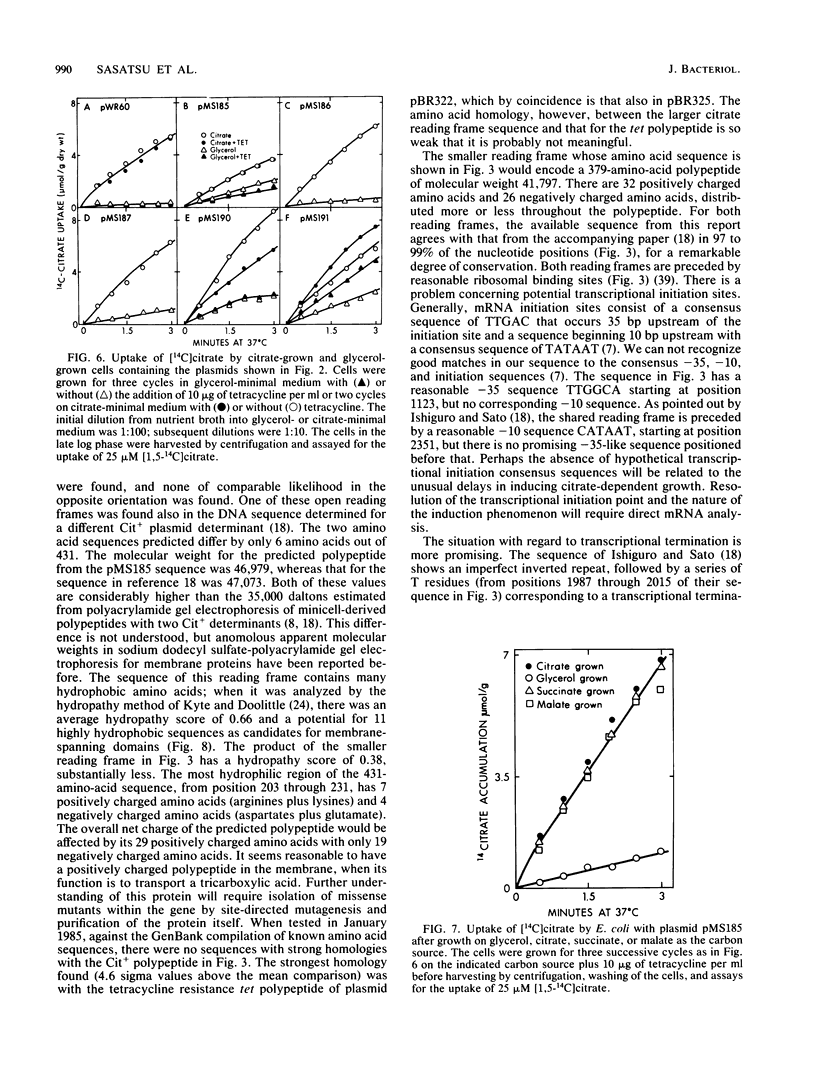
The citrate utilization determinant from a large 200-kilobase (kb) naturally occurring plasmid was previously cloned into the PstI site of plasmid vector pBR325 creating the Cit+ tetracycline resistance plasmid pWR61 (15 kb). Tn5 insertion mutagenesis analysis of plasmid pWR61 limited the segment responsible for citrate utilization to a 4.8-kb region bordered by EcoRI and PstI restriction nuclease sites. The 4.8-kb fragment was cloned into phage M13, and the DNA sequence was determined by the dideoxyribonucleotide method. Within this sequence was a 1,296-base-pair open reading frame with a preceding ribosomal binding site. The 431-amino-acid polypeptide that could be translated from this open reading frame would be highly hydrophobic. A second long open reading frame with the potential of encoding a 379-amino-acid polypeptide preceded the larger open reading frame. Portions of the 4.8-kb fragment were further subcloned with restriction endonucleases BglII and BamHI, reducing the minimum size needed for a citrate-positive phenotype to a 1.9-kb BamHI-BglII fragment (which includes the coding region for the 431-amino-acid polypeptide, but only the distal 2/3 of the reading frame for the 379-amino-acid polypeptide). Citrate utilization results from a citrate transport activity encoded by the plasmid. With the 4.8-kb fragment (as with larger fragments) the citrate transport activity was inducible by growth on citrate. On transfer from glucose, succinate, malate, or glycerol medium to citrate medium, the Cit+ Escherichia coli strains showed a delay of 36 to 48 h before growth.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M., Son P. H. Kilo-sequencing: creation of an ordered nest of asymmetric deletions across a large target sequence carried on phage M13. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:98–122. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J., McCowen S. M., Snellings N. J., Johnson E. M., Reid W. C., Life C. A. Genetic and molecular studies of the regulation of atypical citrate utilization and variable Vi antigen expression in enteric bacteria. Basic Life Sci. 1982;19:175–194. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4142-0_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Schmandt M. A., Lowe J. B. Specificity of transposon Tn5 insertion. Genetics. 1983 Dec;105(4):813–828. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnak M., Reeves H. C. Phosphorylation of Isocitrate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Science. 1979 Mar 16;203(4385):1111–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.34215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G. Chromosomal mutation for citrate utilization by Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):269–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.269-273.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirato T., Shinagawa M., Ishiguro N., Sato G. Polypeptide involved in the Escherichia coli plasmid-mediated citrate transport system. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):421–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.421-426.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Iijima T., Hasegawa T. Transport of tricarboxylic acids in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):961–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.961-965.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Hirose K., Asagi M., Sato G. Incompatibility of citrate utilization plasmids isolated from Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Mar;123(1):193–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-123-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Hirose K., Sato G. Distribution of citrate utilization plasmids in Salmonella strains of bovine origin in Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):446–451. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.446-451.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Oka C., Hanzawa Y., Sato G. Isolation of citrate utilization plasmid from a bovine Salmonella typhimurium strain. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(8):757–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Oka C., Hanzawa Y., Sato G. Plasmids in Escherichia coli controlling citrate-utilizing ability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):956–964. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.956-964.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Oka C., Sato G. Isolation of citrate-positive variants of Escherichia coli from domestic pigeons, pigs, cattle, and horses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):217–222. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.217-222.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G. Nucleotide sequence of the gene determining plasmid-mediated citrate utilization. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):977–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.977-982.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G. Properties of a transmissible plasmid conferring citrate-utilizing ability in Escherichia coli of human origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):553–556. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G., Sasakawa C., Danbara H., Yoshikawa M. Identification of citrate utilization transposon Tn3411 from a naturally occurring citrate utilization plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):961–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.961-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G. Spontaneous deletion of citrate-utilizing ability promoted by insertion sequences. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.642-650.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G. The distribution of plasmids determining citrate utilization in citrate-positive variants of Escherichia coli from humans, domestic animals, feral birds and environments. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Oct;83(2):331–344. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koser S. A. CORRELATION OF CITRATE UTILIZATION BY MEMBERS OF THE COLON-AEROGENES GROUP WITH OTHER DIFFERENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS AND WITH HABITAT. J Bacteriol. 1924 Jan;9(1):59–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.9.1.59-77.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulla H. G. Regulatory citrate lyase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):546–549. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.546-549.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein with kinase and phosphatase activities involved in regulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):458–460. doi: 10.1038/300458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütgens M., Gottschalk G. Why a co-substrate is required for anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli on citrate. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jul;119(1):63–70. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K. A new strategy to create ordered deletions for rapid nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Brown N. L., Haberstroh L., Schmidt A., Goddette D., Silver S. Mercuric reductase structural genes from plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: functional domains of the enzyme. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. H., Silver S. Citrate utilization by Escherichia coli: plasmid- and chromosome-encoded systems. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1019–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1019-1024.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa M., Makino S., Hirato T., Ishiguro N., Sato G. Comparison of DNA sequences required for the function of citrate utilization among different citrate utilization plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):1046–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.1046-1050.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z., Green P. Thermosensitive H1 plasmids determining citrate utilization. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Dec;109(2):305–311. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Measurements of the effects that coding for a protein has on a DNA sequence and their use for finding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):551–567. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes H. W., Hall B. G. Topological repression of gene activity by a transposable element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6115–6119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



