Abstract
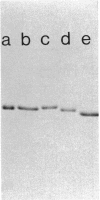
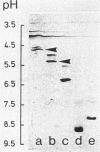
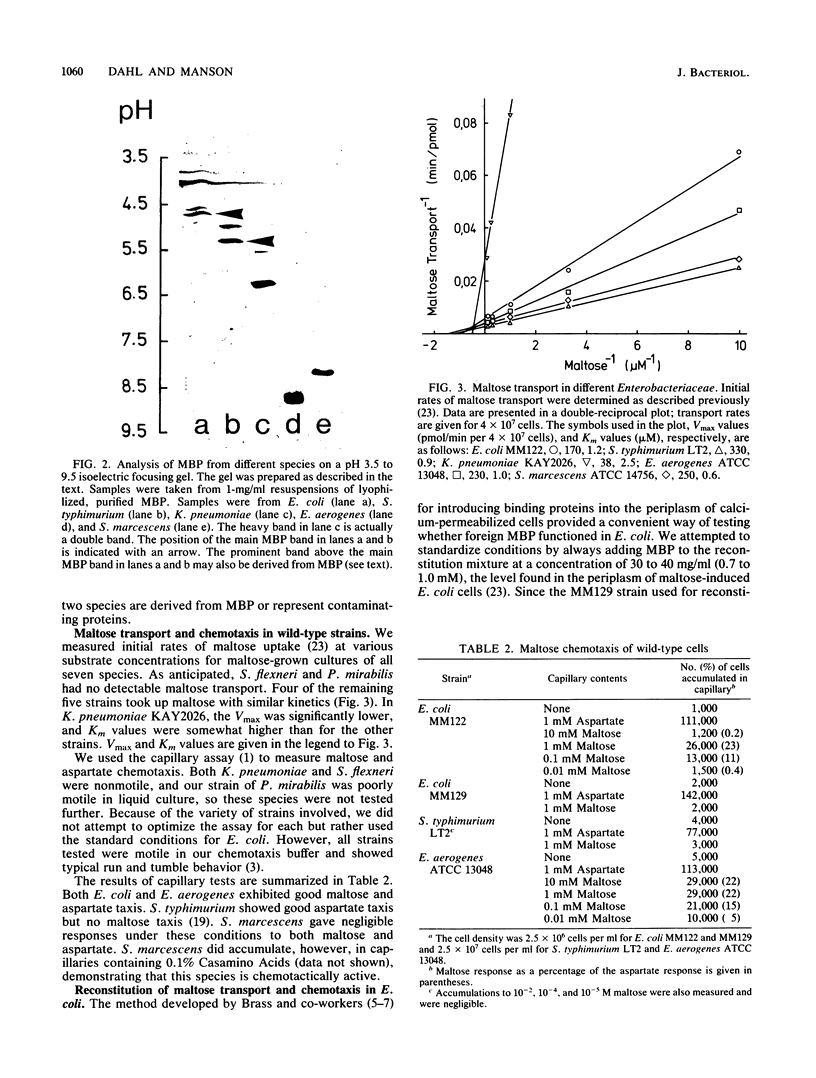
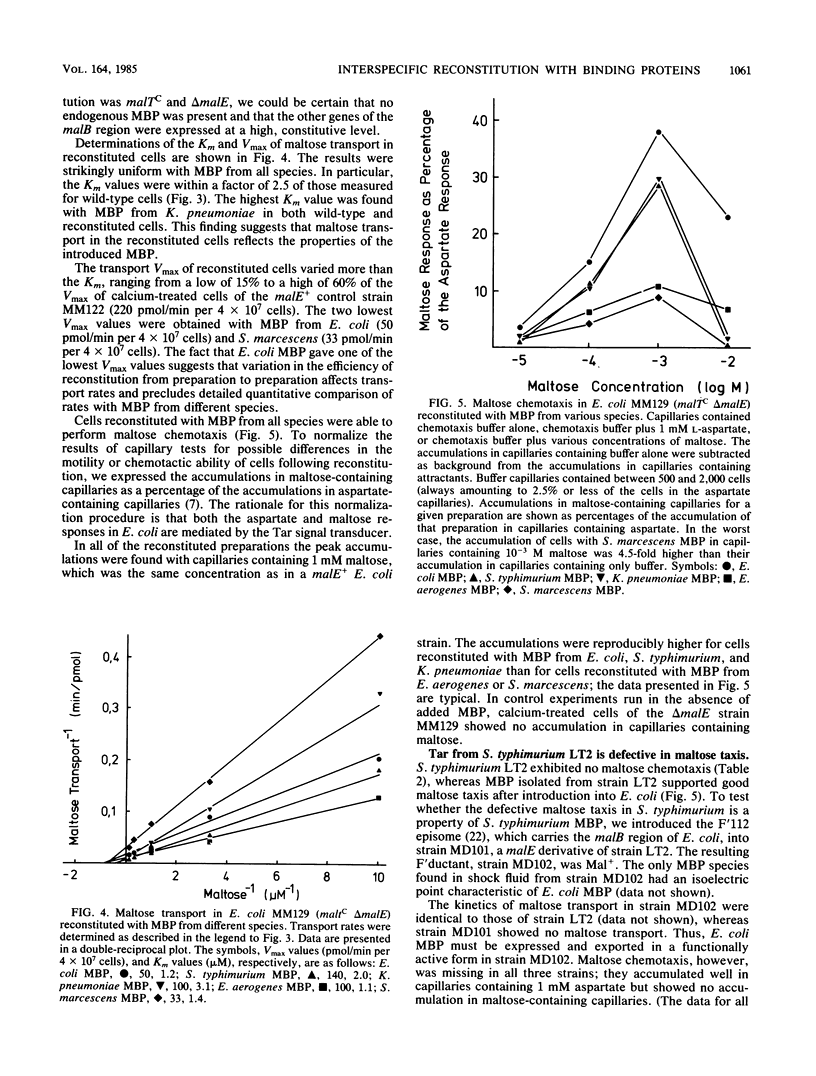
In Escherichia coli, the periplasmic maltose-binding protein (MBP), the product of the malE gene, is the primary recognition component of the transport system for maltose and maltodextrins. It is also the maltose chemoreceptor, in which capacity it interacts with the signal transducer Tar (taxis to aspartate and some repellents). In studies of the maltose system in other members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, we found that MBP is produced by Salmonella typhimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Serratia marcescens. MBP from all of these species cross-reacted with antibody against the E. coli protein and had a similar molecular weight (about 40,000). The Shigella flexneri and Proteus mirabilis strains we examined did not synthesize MBP. The isoelectric points of MBP from different species varied from the acid extreme of E. coli (4.8) to the basic extreme of E. aerogenes (8.9). All species with MBP transported maltose with high affinity, although the Vmax for K. pneumoniae was severalfold lower than that for the other species. Maltose chemotaxis was observed only in E. coli and E. aerogenes. In S. typhimurium LT2, Tar was completely inactive in maltose taxis, although it signaled normally in response to aspartate. MBP isolated from all five species could be used to reconstitute maltose transport and taxis in a delta malE strain of E. coli after permeabilization of the outer membrane with calcium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W., Steinacher I., Engelhardt-Altendorf D. Mapping of mglB, the structural gene of the galactose-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):508–518. doi: 10.1007/BF00352531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Boos W., Hengge R. Reconstitution of maltose transport in malB mutants of Escherichia coli through calcium-induced disruptions of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.10-17.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Ehmann U., Bukau B. Reconstitution of maltose transport in Escherichia coli: conditions affecting import of maltose-binding protein into the periplasm of calcium-treated cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):97–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.97-106.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Manson M. D. Reconstitution of maltose chemotaxis in Escherichia coli by addition of maltose-binding protein to calcium-treated cells of maltose regulon mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):881–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.881-890.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duplay P., Bedouelle H., Fowler A., Zabin I., Saurin W., Hofnung M. Sequences of the malE gene and of its product, the maltose-binding protein of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10606–10613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Schwartz M. Dominant constitutive mutations in malT, the positive regulator gene of the maltose regulon in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Klotz U. Affinity chromatographic isolation of the periplasmic maltose binding protein of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 15;94(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80940-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L. Maltose chemoreceptor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):206–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.206-214.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge R., Boos W. Maltose and lactose transport in Escherichia coli. Examples of two different types of concentrative transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):443–478. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M. Divergent operons and the genetic structure of the maltose B region in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):169–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Jezierska A., Braun-Breton C. lamB mutations in E. coli K12: growth of lambda host range mutants and effect of nonsense suppressors. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00269595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann O., Szmelcman S. Active transport of maltose in Escherichia coli K12. Involvement of a "periplasmic" maltose binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koiwai O., Hayashi H. Studies on bacterial chemotaxis. IV. Interaction of maltose receptor with a membrane-bound chemosensing component. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr A model regulatory system: bacterial chemotaxis. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):811–862. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low K. B. Escherichia coli K-12 F-prime factors, old and new. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):587–607. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.587-607.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Boos W., Bassford P. J., Jr, Rasmussen B. A. Dependence of maltose transport and chemotaxis on the amount of maltose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9727–9733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojica-A T., Middleton R. B. Fertility of Salmonella typhimurium crosses with Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1161–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1161-1167.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray S. L., Petsko G. A. Preliminary X-ray data for the ribose binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):545–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray S. L., Petsko G. A. The x-ray structure of the periplasmic galactose binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium at 3.0-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7991–7997. doi: 10.2210/pdb1gbp/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel D., Nikaido K., Ames G. F. A single amino acid substitution in a histidine-transport protein drastically alters its mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4159–4165. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Liljeström P., Harayama S. Cosmid cloning and transposon mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium using phage lambda vehicles. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00268420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Associative properties of the Escherichia coli galactose binding protein and maltose binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):476–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91459-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Interaction of the maltose-binding protein with membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.662-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G., Kepes A. Study of binding protein-ligand interaction by ammonium sulfate-assisted adsorption on cellulose esters filters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 12;742(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richey D. P., Lin E. C. Importance of facilitated diffusion for effective utilization of glycerol by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.784-790.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. G., Silverman M., Simon M. I. Localization of proteins controlling motility and chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):657–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.657-665.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A. F., Koshland D. E., Jr Separation of signal transduction and adaptation functions of the aspartate receptor in bacterial sensing. Science. 1983 Jun 3;220(4601):1016–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.6302843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Genetic relatedness in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:327–349. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Le Minor L. Occurrence of the bacteriophage lambda receptor in some enterobacteriaceae. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):679–685. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.679-685.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H. A. Active transport of maltose in Escherichia coli K12. Role of the periplasmic maltose-binding protein and evidence for a substrate recognition site in the cytoplasmic membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5455–5461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger G. A., Lengeler J. W. L-Sorbose metabolism in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Sor+ derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12 and chemotaxis toward sorbose. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):39–45. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.39-45.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Schwartz M., Ferenci T. Escherichia coli mutants impaired in maltodextrin transport. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.1-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor structure in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]