Abstract
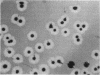
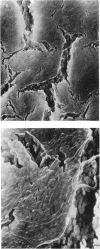
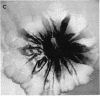
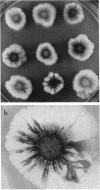
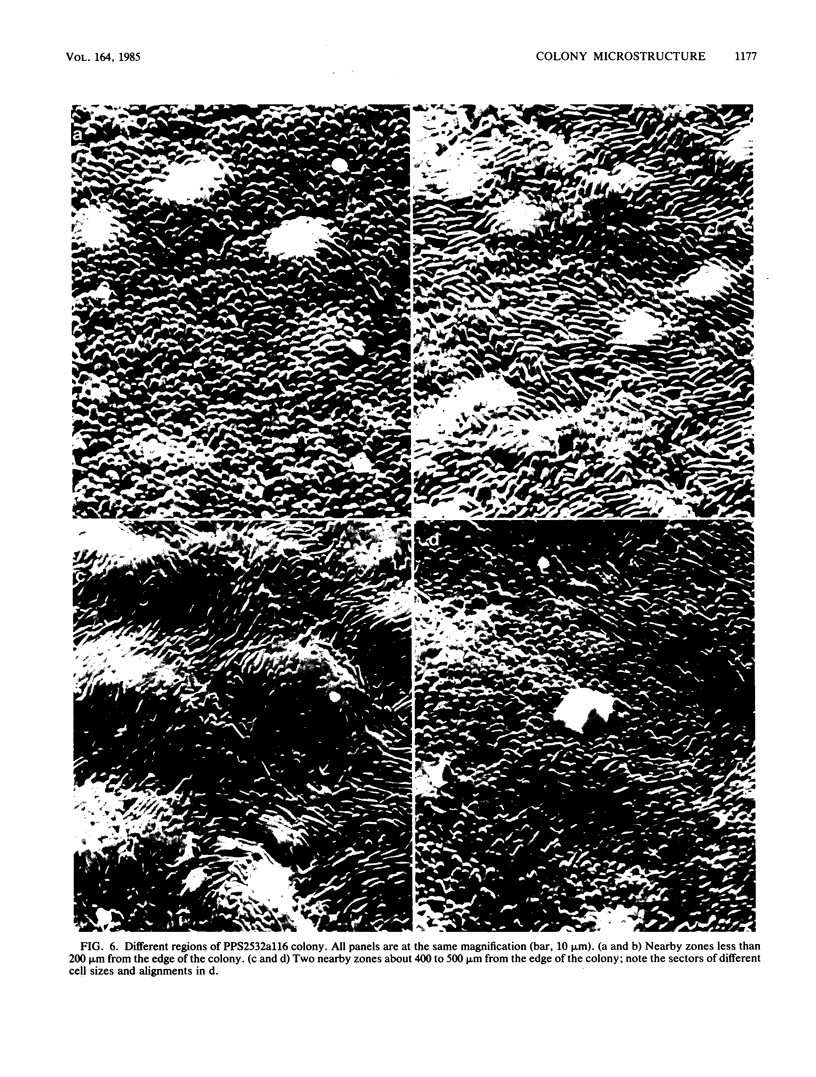
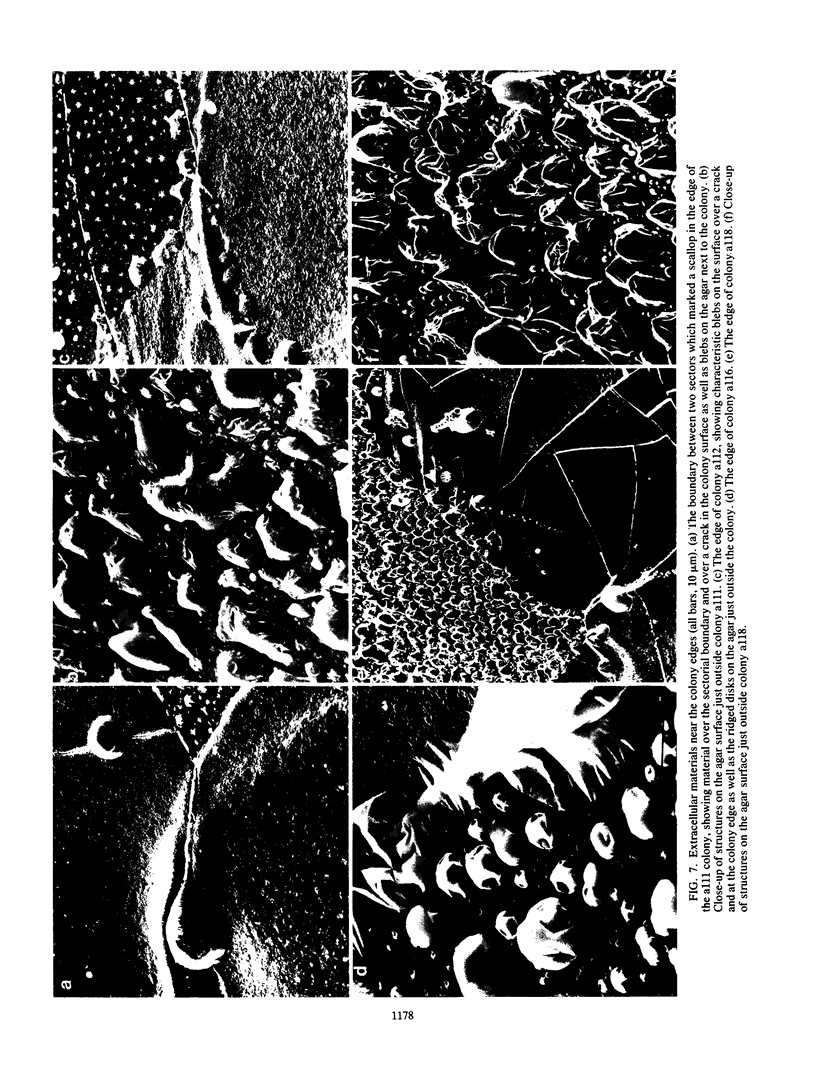
Pseudomonas putida colonies were examined by scanning electron microscope. A variety of cell morphologies, multicellular arrangements, and extracellular materials were observed in the fixed material. Different regions of a single colony showed characteristic organizations of these architectural elements. In some cases, the detailed microstructure of the fixed colony surfaces observed by scanning electron microscopy could be correlated with macroscopic patterns visualized by histochemical staining and surface relief photography of live colonies. Extracellular materials were seen to extend onto the agar surface beyond the boundaries of the cell mass, and the final structures of these materials, after fixation and desiccation, were colony specific. The significance of these features of colony microstructure for formulating hypotheses about the control of colony morphogenesis is discussed.
Full text
PDF

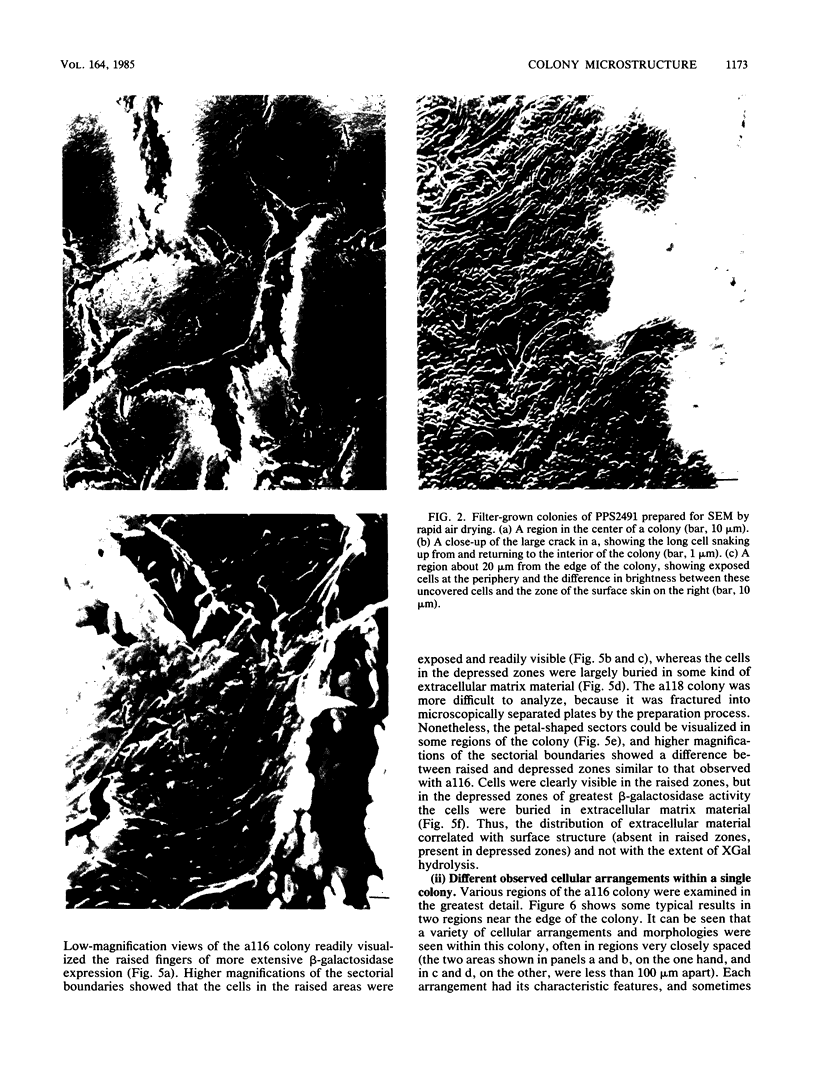
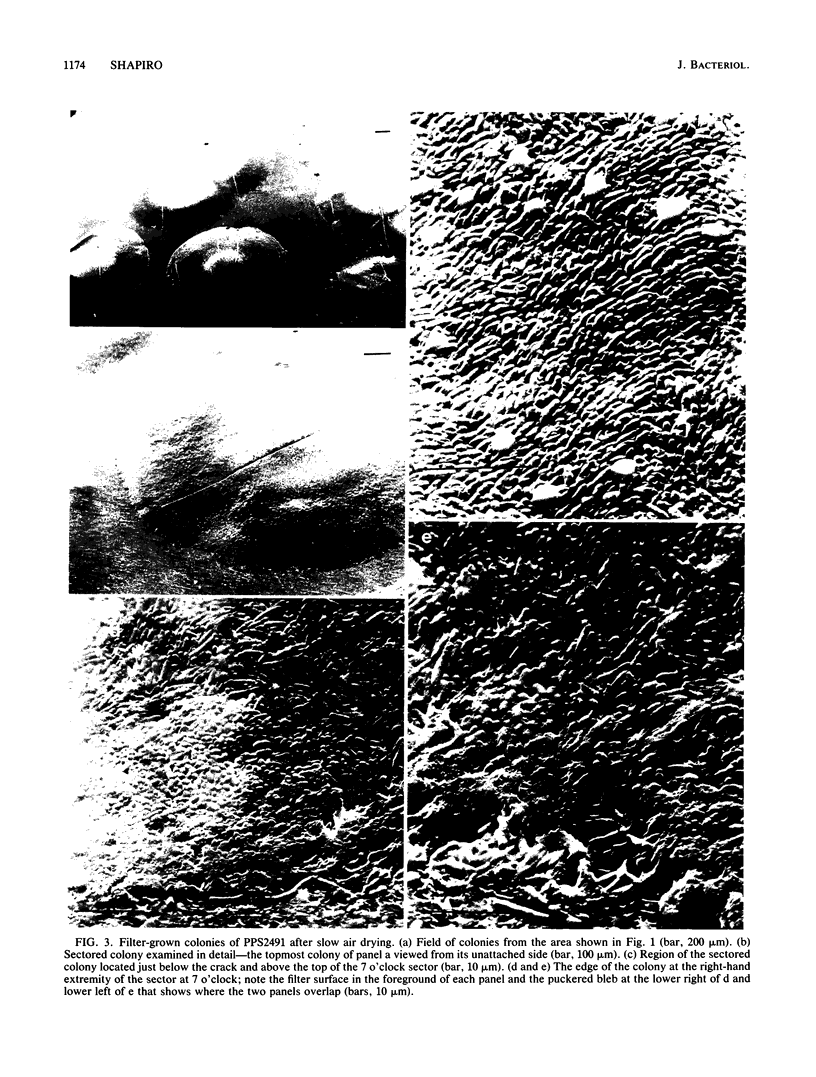

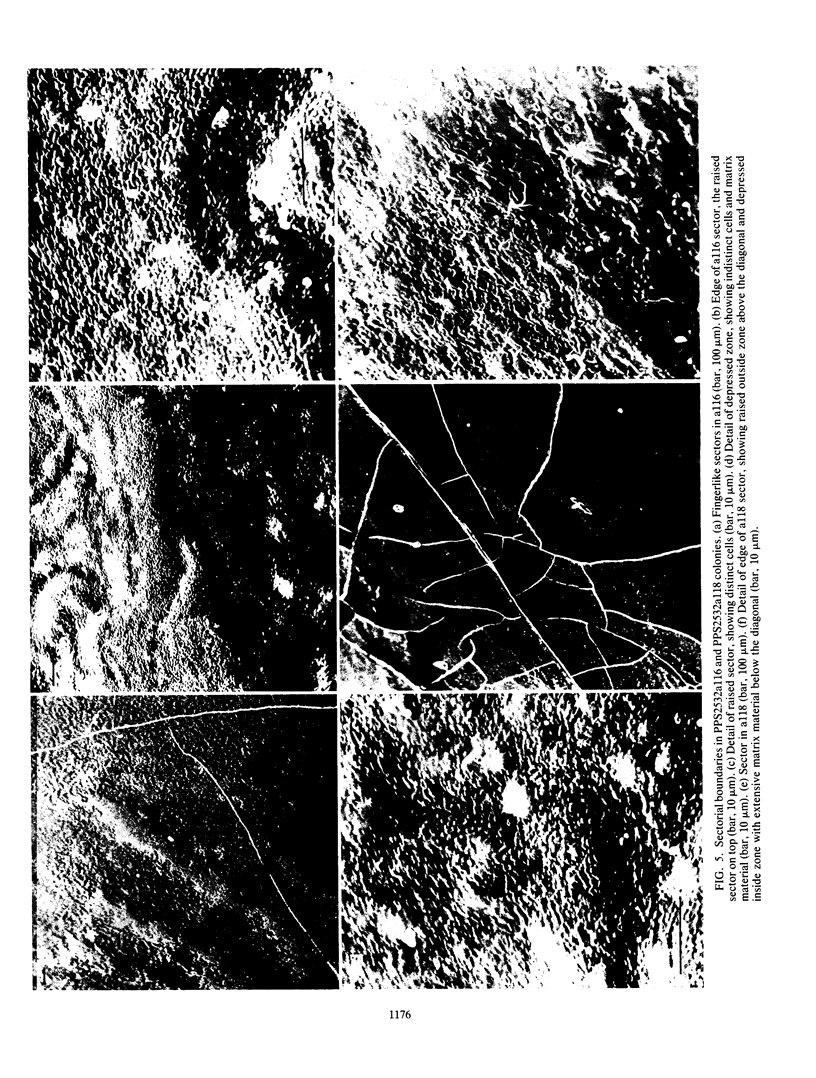



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afrikian E. G., St Julian G., Bulla L. A., Jr Scanning electron microscopy of bacterial colonies. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):934–937. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.934-937.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer H., Sigarlakie E., Faure J. C. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of three strains of Bifidobacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Sep;21(9):1305–1316. doi: 10.1139/m75-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. B., Whittaker D. K. Examination of certain bacterial colonies by scanning electron microscopy. Microbios. 1971 Sep;4(14):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. Tactic behavior of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):452–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.452-459.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. Morphology and ultrastructure of staphylococcal L colonies: light, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):1049–1053. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.1049-1053.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Nelligan J., Costerton J. W. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of an infected endocardial pacemaker lead. Circulation. 1982 Dec;66(6):1339–1341. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.6.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Short J. A., Walker P. D. An electron-microscope study of naturally occurring and cultured cells of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):413–427. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. The use of Mudlac transposons as tools for vital staining to visualize clonal and non-clonal patterns of organization in bacterial growth on agar surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1169–1181. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Stewart K. R., Williams F. D. Extracellular slime associated with Proteus mirabilis during swarming. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.930-937.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]