Abstract
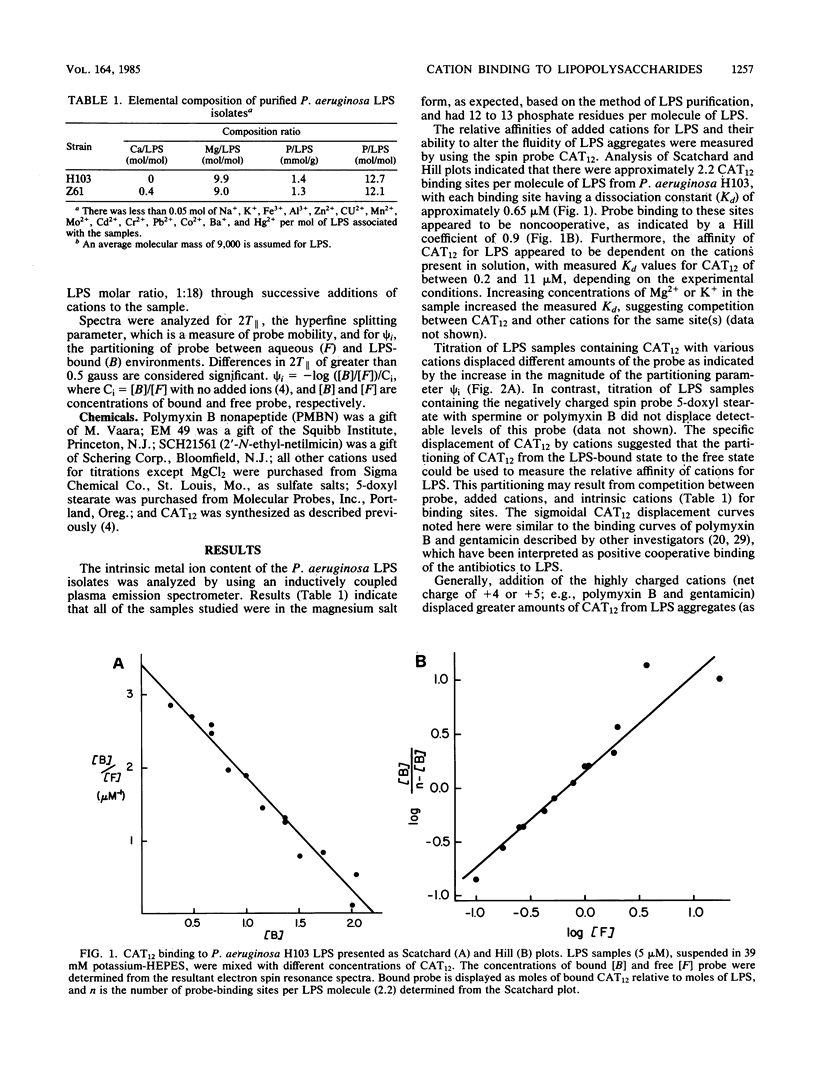
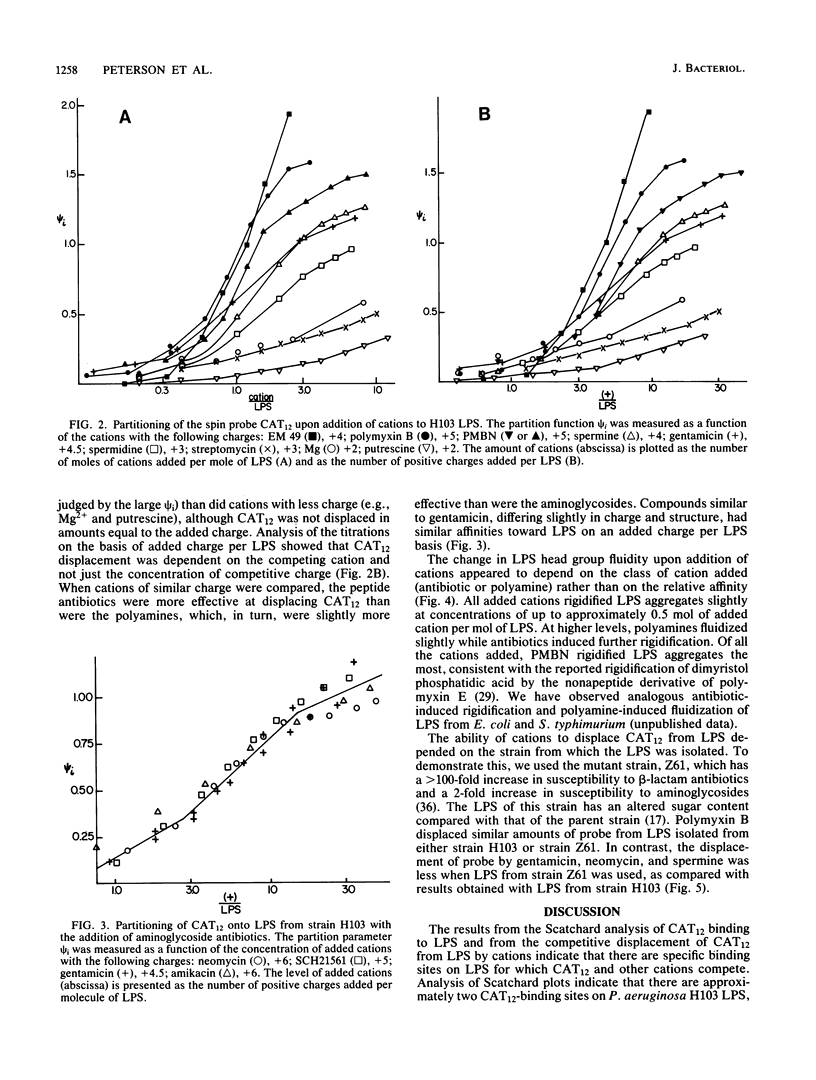
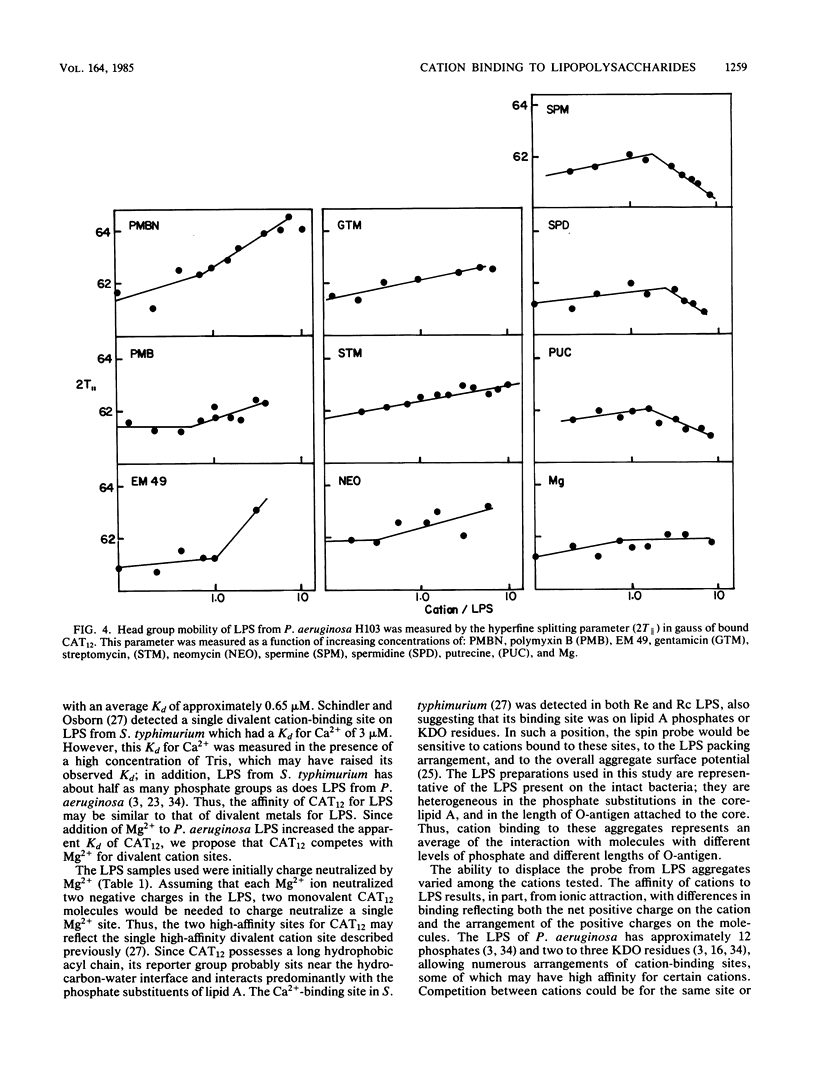
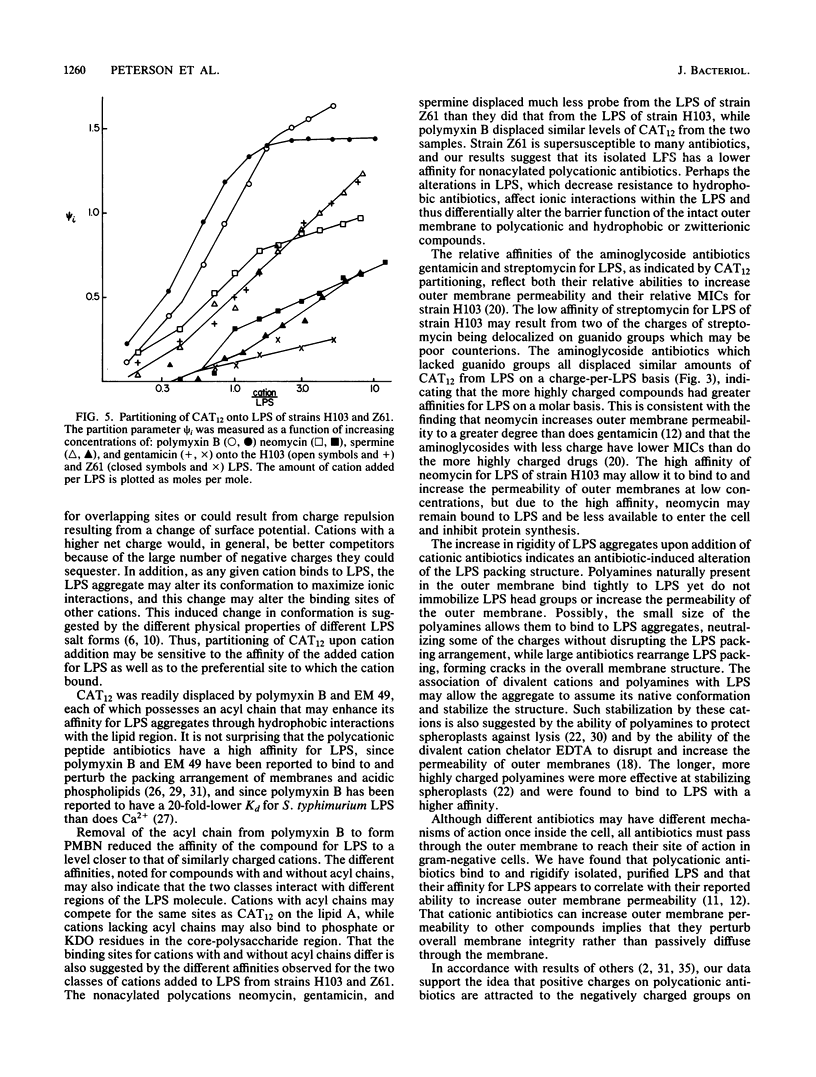
Polycations, such as aminoglycoside and peptide antibiotics, and naturally occurring polyamines were found to bind to the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alter its packing arrangement. Binding of cations was measured by the displacement of a cationic spin probe from lipopolysaccharide into the aqueous environment upon addition of competitive cations. The level of probe displacement was dependent on the concentration and charge of the competing cation, with the more highly charged cations being more effective at displacing probe. The relative affinity of several antibiotics for lipopolysaccharide correlated with their ability to increase outer membrane permeability, while the relative affinity of several polyamines correlated with their ability to stabilize the outer membrane. Probe mobility within the lipopolysaccharide head group was shown to be decreased by cationic antibiotics and unaltered or increased by polyamines. We propose that antibiotic permeability and disruption of outer membrane integrity by polycationic antibiotics results from binding of the antibiotic to anionic groups on lipopolysaccharide with a consequent change in the conformation of lipopolysaccharide aggregate structure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. Role of Multivalent Cations in the Organization, Structure, and Assembly of the Cell Wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):380–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.380-387.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Tsang J. C. Chemical and electrophoretic changes induced by polymyxin B on outer membrane components from Serratia marcescens. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Jun;31(6):603–609. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M., Pitt T. L. The relationship between the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides and serological specificity in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different O-serotypes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Caldwell C. R., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. A cationic electron spin resonance probe used to analyze cation interactions with lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1137–1142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Tonsager S., McGroarty E. J. Quantitation of metal cations bound to membranes and extracted lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEW A. V. The interaction of polymyxin E with bacterial and other lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Koike M. Cell wall alterations of gram-negative bacteria by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):95–97. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: accessibility of phospholipid head groups to phospholipase c and cyanogen bromide activated dextran in the external medium. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 15;15(12):2561–2570. doi: 10.1021/bi00657a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L. C., Milazzo F. H. The extraction and analysis of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO, and three rough mutants. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):390–398. doi: 10.1139/m79-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Kuzio J., Angus B. L., Hancock R. E. Chemical and chromatographic analysis of lipopolysaccharide from an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):310–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodhi S., Weiner N. D., Schacht J. Interactions of neomycin with monomolecular films of polyphosphoinositides and other lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh B., Grant C., Hancock R. E. Use of the fluorescent probe 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):546–551. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Inniss W. E. Electron microscopy of effect of polymyxin on Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1128–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1128-1130.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J. The stabilizing effect of spermine and related polyamines and bacterial protoplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Dec;36:529–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Wray V., Lehmann V. A 31P-nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of the phosphate groups in lipopolysaccharide and lipid A from Salmonella. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Transmembrane diffusion of some hydrophobic substances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):118–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintanilha A. T., Packer L. Surface potential changes on energization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jun 15;78(2):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E., Storm D. R. Disruption of Escherichia coli outer membranes by EM 49. A new membrane active peptide. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5783–5792. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Osborn M. J. Interaction of divalent cations and polymyxin B with lipopolysaccharide. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4425–4430. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixl F., Galla H. J. Calorimetric investigation of polymyxin binding to phosphatidic acid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 22;693(2):466–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90455-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens L. Studies on the interaction of homologues of spermine with deoxyribonucleic acid and with bacterial protoplasts. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):811–815. doi: 10.1042/bj1030811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:723–763. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Viljanen P., Vaara T., Mäkelä P. H. An outer membrane-disorganizing peptide PMBN sensitizes E. coli strains to serum bactericidal action. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2582–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G., Galbrath L. Studies of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):331–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Activity of aminoglycoside antibiotics aganst Pseudomonas aeruginosa: specificity and site of calcium and magnesium antagonism. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):663–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W. Penetration through the gram-negative cell wall: a co-determinant of the efficacy of beta-lactam antibiotics. Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1979 Mar;17(3):131–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


