Abstract
During specific stages of thymocyte development, the T cell receptor (TCR) locus is assembled from variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) gene segments. Proper TCR γ and δ V(D)J rearrangement during thymocyte development requires the presence of the E2A proteins. Here we show that E2A and a closely related protein, HEB, in the presence of recombination activating gene (RAG)1 and RAG2, each have the ability to activate TCR γ and δ rearrangement in human kidney cells. The coding joints are diverse, contain nucleotide deletions, and occasionally show the presence of P nucleotides. Interestingly, only a subset of V, D, and J segments are targeted by the E2A and HEB proteins. Thus, E2A and HEB permit localized accessibility of the TCR γ and δ loci to the recombination machinery. These data indicate that a distinct but diverse TCR repertoire can be induced in nonlymphoid cells by the mere presence of the V(D)J recombinase and the transcriptional regulators, E2A and HEB.
Keywords: E2A, HEB, recombination activating gene, T cell receptor γ and δ rearrangements, chromatin accessibility
Introduction
The ability of lymphocytes to recognize a large array of antigens is dependent on the successful rearrangement of the Ig and TCR loci 1 2. This is accomplished by the joining of V(D)J segments during specific stages of thymocyte development. Conserved sequence motifs, known as recombination signal sequences (RSSs), flank one or both sides of the coding regions. Rearrangement is mediated by the two recombination activation gene (RAG) products, RAG1 and RAG2, which recognize the RSSs and introduce double-stranded DNA breaks at the coding signal sequence boundaries 3 4 5. These cleavage products are joined and processed by the DNA repair machinery to generate loci that have the ability to encode antigen-specific B and T cell receptors 6.
V(D)J recombination is controlled by several regulatory mechanisms. Ig V(D)J rearrangement is completed only in cells committed to the B cell lineage, whereas TCR V(D)J recombination occurs exclusively in thymocytes 7 8 9. Within the lymphoid lineages, V(D)J recombination is ordered and developmentally regulated 10. In differentiating B cells, Ig heavy chain gene rearrangement generally precedes Ig light chain gene recombination 11 12. Likewise, during thymocyte development, TCR γ, δ, and β V(D)J joining is completed before the onset of TCR-α rearrangement 7. TCR-β gene rearrangement is ordered as well: D and J regions are joined before the initiation of V to DJ joining. In contrast, TCR-δ rearrangement is unordered 13.
Ig V(D)J recombination is regulated by transcriptional activators that bind to sequence elements present in the Ig enhancers. Among the Ig enhancer binding proteins are members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family, including E12 and E47 14 15. E12 and E47 are encoded by the E2A gene and arise through differential splicing. E12 binds with relatively low affinity to its optimal binding site, the E2 box, whereas E47 binds with high affinity to the same site. Both E12 and E47 belong to a subset of bHLH proteins, named E-proteins 15. The family of E-proteins also include E2-2, HEB, and the Drosophila gene product, daughterless 15. E-proteins have the ability to bind their target sites either as homo- or heterodimers 15. In B lineage cells, both E12 and E47 exist mainly as homodimers 16. In contrast, the E2A proteins form heterodimers with HEB, another member of the bHLH family in developing thymocytes 15.
The E2A proteins are required for proper B lineage development, as B lymphocyte development in E2A-deficient mice is arrested at a stage before the initiation of Ig gene rearrangement 17 18 19. E2A-deficient mice also show a block, albeit incomplete, at a similar stage during T lineage maturation 20. HEB functions during a later stage of thymocyte development, specifically during the maturation of CD4−CD8− into CD4+CD8+ T lineage cells 21.
Recent evidence has indicated that TCR γ and δ V(D)J recombination in E2A-deficient mice is severely perturbed, specifically those rearrangements used predominantly during adult thymocyte maturation 22. E2A proteins are also required during adult thymocyte development to inhibit V(D)J rearrangements that normally recombine exclusively during fetal thymocyte maturation 22. How E2A proteins both regulate TCR γ and δ rearrangement remains an open question.
Here we demonstrate that both E2A and HEB, as homo- and heterodimers, have the ability to activate TCR γ and δ V(D)J rearrangements in nonlymphoid cells. Activation of TCR γ and δ V(D)J rearrangement is restricted to a subset of V, D, and J regions. The TCR coding joints are diverse, contain P nucleotides and show nucleotide deletions. We demonstrate that the induction of TCR γ and δ rearrangements correlates with the activation of TCR Vγ and Vδ germline transcription. These data suggest that E2A and HEB have the ability to regulate TCR γ and δ recombination by promoting localized accessibility of the RSSs to the recombination machinery.
Materials and Methods
Cell Culture.
BOSC 23 cells were grown in DMEM mixed with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C as described earlier 23 24.
DNA Constructs and Transfection Protocol.
The pEBB-Rag1 and pEBB-Rag2 expression vectors expressed wild-type proteins 25. The E2A transcription factors E12 and E47 were cloned into the pHβAPneo vector, which has been described previously 26. The HEB cDNA was cloned into the pXS vector, which is a derivative of the pcDL-SRα296 vector. Calcium phosphate precipitation transfections were carried out essentially as reported previously 23 24. BOSC 23 cells were plated 12–16 h before transfection at 2 × 106 cells per 6-cm dish. The following day, 9–12 μg of total DNA, comprised of 3 μg of each expression vector or carrier DNA, was used for each transfection. The cells were harvested ∼3 d after transfection.
PCR and TCR Rearrangements.
200 ng of genomic DNA, isolated from BOSC 23 cells after transfection, was analyzed by PCR in a 25-μl reaction volume. Each of these reaction mixtures contained 10 mM Tris, pH 8.3, 50 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 100 ng of each primer, 200 μM dNTPs, and 1 unit of Amplitaq Gold (PE Biosystems). PCR reactions were performed as follows: 10 min preactivation at 94°C; 26–35 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, 1 min at 51–61°C, as indicated by the figure legends, 80 s at 72°C; followed by a 10-min extension at 72°C 24. The primers used to detect TCR γ and δ rearrangements are listed in the Table 27 28. 15 μl of each PCR product was analyzed on an 1.5% agarose gel followed by ethidium bromide staining and/or Southern blotting.
Table 1.
Nucleotide Sequences of PCR Primers
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| TCR-δ gene | |
| Vδ1 | CTCAAGCCCAGTCATCAGTATCC |
| Vδ2 | CGCGTCGACCAAACAGTGCCTGTGTCAATAGG |
| Vδ3 | CGCGTCGACCAGACGGTGGCGAAGTGGC |
| Dδ1 | CGCGTCGACTCCATGTTCAAATAGATATAGTATT |
| Dδ2 | GTAGATCTAGAAGAGGGTTTTTATACTGATGTG |
| Dδ3 | GTAGATCTAGAAATGGCACTTTTGCCCCTGCAG |
| Jδ1 | CACGGGATCCTTTTCCAAGGATGAG |
| Vδ2-rev | GGTCAGTGGTTTTTGAGCTGC |
| TCR-γ gene | |
| VγI | GAAGATCTAGACAGGCCGACTGGGTCATCTGC |
| VγII | GAAGATCTAGACAGCCCGCCTGGAATGTGTGG |
| VγIV | CCTGAAAGATCTATTTCTAGACCAGC |
| Jγ1.1/2.1 | GAAGATCTAGACTTACCAGGTGAAGTTACTATAAGC |
| Jγ1.2-3 | AAGAAAACTTACCTGTAATGATAAGC |
| Jγ1.3/2.3-3 | CTAGTCTAGACCGTATATGCACAAAGCCAGATC |
| VγI-rev | GTCACAAGGCAGATTTTCAGTGTGG |
| VγII-rev | GCACACTGGTGGTAACTGTGGCTTCC |
| β-actin | |
| huβact-for | GGATGATGATATCGCCGCG |
| huβact-rev | GGATAGCAACGTACATGGCTGGG |
| CD14 | |
| huCD14-for | CAGAGGTTCGGAAGACTTATCGAC |
| huCD14-rev | GTTATCTTTAGGTCCTCGAGCGTC |
The primer sequences are listed 5′ to 3′.
Reverse Transcription PCR and Germline Transcription.
cDNA was prepared from BOSC 23 cells as described previously 24. The efficiency of each cDNA reaction was checked by amplification of the β-actin transcripts with human specific primers: huBact-for and huBact-rev using the following conditions: 3 min at 94°C; 28 cycles of 94°C for 15 s, 58°C for 15 s, 72°C for 45 s; and 10 min at 72°C. PCR to detect Vδ2 germline transcripts was performed as described above using the primers Vδ2 and Vδ2-rev and the PCR protocol, 10 min preactivation at 94°C; 26 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, 60 s at 53°C, 80 s at 72°C; followed by a 10-min extension at 72°C. Similarly, VγI germline transcripts were detected with primers Vγ1 and Vγ1-rev using the PCR protocol 10 min preactivation at 94°C; 26 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, 60 s at 59°C, 80 s at 72°C, followed by a 10-min extension at 72°C. VγII PCR conditions were as follows: 45 s at 94°C, 60 s at 62°C, and 60 s at 72°C.
Results
Activation of TCR-γ VJ Rearrangement in Embryonic Kidney Cells by the E2A and HEB Proteins.
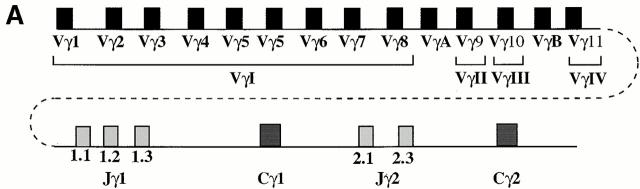
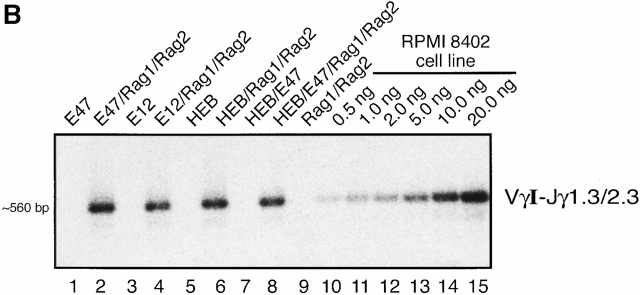
Previously we demonstrated that TCR-γ VJ rearrangements in E2A-deficient thymocytes are perturbed 22. To determine whether the E2A and its heterodimeric partner, HEB, have the ability to directly activate TCR-γ VJ rearrangement, we employed a strategy described previously 24. In brief, either E12, E47, or HEB were transfected in the absence or presence of wild-type RAG1 and RAG2, in BOSC 23 cells, a human embryonic kidney cell line. Genomic DNA from the transfected cells was harvested 3 d after transfection and amplified by PCR using the appropriate primers. The TCR-γ locus contains a limited set of V segments as well as two clusters of J segments, each located upstream of a distinct constant region (Fig. 1 A). To examine for the presence of Vγ-Jγ rearrangements, forward degenerate primers were used that recognize specific V regions, belonging to several of the Vγ gene families (Table ). The reverse primers contained degenerate sequences with specificity for the Jγ1.3 and Jγ2.3, which differ from each other by a single nucleotide. As a probe, a Vγ8-Jγ2.3 fragment was used, which has the ability to hybridize with various members of the VγI family. When DNA was analyzed from BOSC 23 cells transfected with either E12 or E47 or RAG1 and RAG2 alone, rearrangements were not detectable (Fig. 1 B). Interestingly, in the presence of RAG1 and RAG2 and either E12 or E47, VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 rearrangements were readily formed (Fig. 1 B, lanes 2 and 4).
Figure 1.
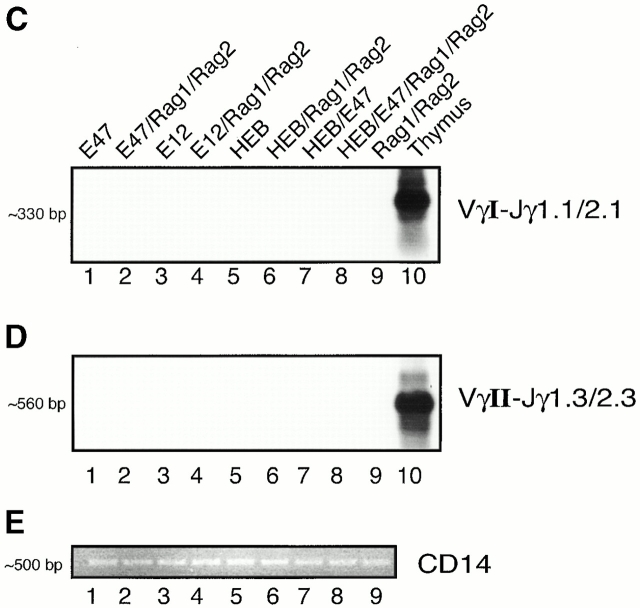
Induction of TCR-γ rearrangement in BOSC 23 cells by the bHLH transcription factors E2A and HEB. (A) Schematic representation of TCR-γ locus. (B) BOSC 23 cells were transfected with expression vectors for E12, E47, HEB, RAG1, and RAG2 and analyzed by PCR for Vγ8-Jγ1.3/2.3 recombination. DNA derived from a cell line, RPMI 8402, was included to quantitate the level of rearrangement (lanes 10–15). PCR products were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel, transferred to Nytran Plus, and hybridized with a cloned Vγ8-Jγ2.3 fragment. (C) Transfected BOSC 23 cells were analyzed by PCR for VγI-Jγ1.1/2.1 rearrangement. PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, transferred to Nytran Plus, and hybridized with a radiolabeled Vγ8 probe. (D) Transfected BOSC 23 cells were analyzed by PCR for VγII-Jγ1.3/2.3 rearrangement. PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, transferred to Nytran Plus, and hybridized with a radiolabeled VγII probe. (E) Genomic DNA was analyzed with primers to the CD14 locus to demonstrate that all samples contained comparable amounts of DNA.
VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 rearrangements were also present in cells transfected with HEB, RAG1, and RAG2 (Fig. 1 B). To determine whether heterodimers of E47 and HEB have the ability to promote VJ rearrangement, both proteins were introduced into BOSC 23 cells in conjunction with RAG1 and RAG2. Nuclear extracts were derived from the transfected cells and analyzed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) to ensure that heterodimers of E47 and HEB were formed (unpublished observations). E47/HEB heterodimers showed a significant induction of VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 rearrangements in the transfected cells at levels comparable to E47 or HEB alone (Fig. 1 B, lane 8). Thus, in the presence of the V(D)J recombinase, both E2A and HEB, both as homo- and as heterodimers, have the ability to activate TCR-γ VJ rearrangement in nonlymphoid cells.
To obtain an estimate of the frequency of TCR VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 recombination, the levels of rearrangements of the transfected cells was compared with that of DNA isolated from a lymphoid cell line, RPMI 8402, which harbors endogenous VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 joints. By comparing the hybridization signal of genomic DNA (100 ng) isolated from the transfectants to that of DNA isolated from the RPMI 8402 cell line, we estimate that up to 5–10% of the transfected cells contain VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 joints (Fig. 1 B, lanes 10–15). Thus, rearrangement involving VγI-Jγ1.3/2.3 occurs with a relatively high frequency in BOSC 23 cells that overexpress either E2A or HEB and RAG1 and RAG2.
To determine whether the E2A proteins also have the ability to activate rearrangements using the Jγ1.1 and Jγ2.1 segments, genomic DNA from the transfectants was analyzed by PCR using the appropriate primers (Table ). Interestingly, rearrangements involving Jγ1.1, Jγ1.2, and Jγ2.1 were not detectable in cells transfected with either E2A or HEB (Fig. 1 C). Additionally, VγII-Jγ1.3/2.3 rearrangements were not activated by the overexpression of E2A and HEB (Fig. 1 D). Taken together, these data indicate that E2A and HEB promote joining of a subset of V regions to a selected group of Jγ segments.
Both E2A and HEB Have the Ability to Activate TCR-δ VD Rearrangement in BOSC 23 Cells.
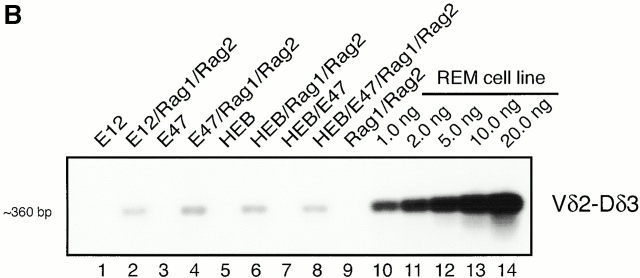
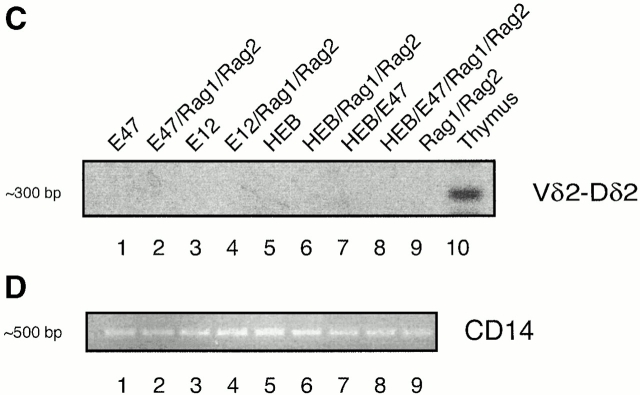
In addition to the defects in TCR-γ VJ joining, TCR-δ rearrangements in E2A-deficient thymocytes are affected as well 22. To determine whether E2A proteins have the ability to promote TCR-δ rearrangement, we employed the same strategy as described above. Interestingly, Vδ2-Dδ3, but not Vδ2-Dδ2 joints, were present in cells expressing E2A or HEB in the presence of RAG1 and RAG2 (Fig. 2). However, we note that in contrast to TCR-γ VJ rearrangement, the frequency of TCR Vδ2-Dδ3 rearrangements is relatively low (<1%) in the transfected BOSC 23 cells (Fig. 2 B). We also have examined genomic DNA derived from the various transfectants for the presence of rearrangements involving Vδ1-Dδ1, Vδ3-Dδ1, Dδ2-Dδ3, and Dδ-Jδ1 segments. None of these rearrangements were detectable in genomic DNA derived from transfected cells (data not shown). These data indicate that E2A and HEB have the ability to promote accessibility of distinct Vδ and Dδ regions to the recombination machinery.
Figure 2.
E2A and HEB promote TCR-δ rearrangement in BOSC 23 cells. (A) Schematic representation of TCR δ locus. (B) BOSC 23 cells were transfected with expression vectors for E12, E47, HEB, RAG1, and RAG2. 100 ng of DNA was amplified by PCR for Vδ2-Dδ3 recombination using the Vδ2 and Dδ3 primers. PCR products were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel, transferred to Nytran Plus, and hybridized with a Vδ2 probe. The REM cell line contains endogenous Vδ2-Dδ3 rearrangements. (C) Transfected BOSC 23 cells were analyzed by PCR for Vδ2-Dδ2 rearrangement. PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, transferred to Nytran Plus, and hybridized with a Vδ2 probe. (D) Genomic DNA was analyzed with primers to the CD14 locus to demonstrate that all samples contained comparable amounts of DNA.
Both E2A and HEB Activate Vγ and Vδ Germline Transcription.
To examine how E2A and HEB proteins promote accessibility, transfected cells were analyzed for the presence of VγI and Vδ2 germline transcripts. RNA was isolated from the transfected cells, examined by reverse transcription (RT)-PCR using the appropriate primers and analyzed by Southern blotting. RT-PCR using β-actin–specific primers was used as a control for RNA integrity and cDNA synthesis (Fig. 3 D). VγI and Vδ2 transcripts were absent in cells transfected with expression vectors encoding the RAG proteins alone (Fig. 3A and Fig. C; lane 10). In contrast, the presence of either E12, E47, or HEB, as homodimers and as heterodimers, promoted the induction of VγI- and Vδ2-specific germline transcription (Fig. 3A and Fig. C; lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8). Interestingly, VγII germline transcription was not induced upon overexpression of the E-proteins (Fig. 3 B). In summary, E2A and HEB have the ability to activate Vγ1 and Vδ2 but not VγII germline transcription. The data indicate a close relationship between the ability of E2A and HEB to activate germline transcription and to induce rearrangement.
Figure 3.
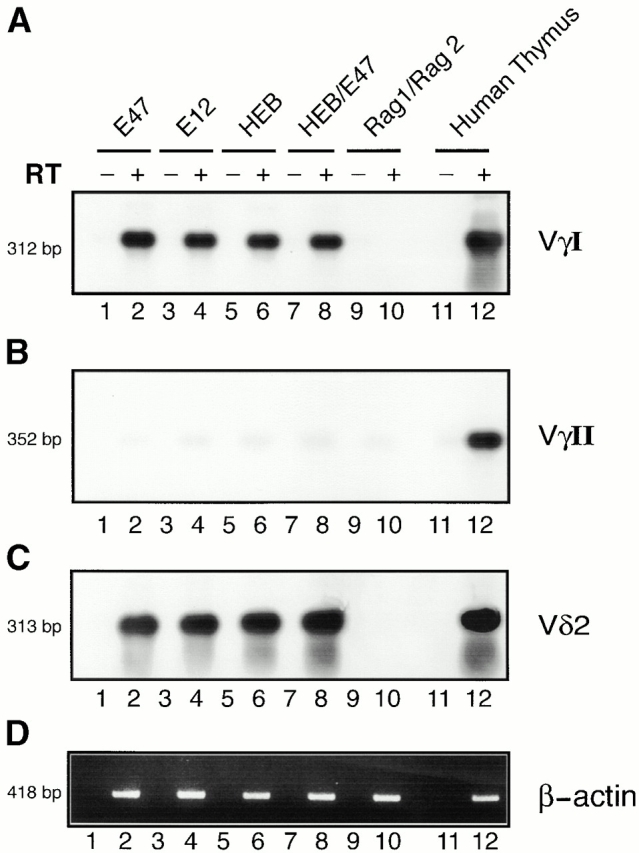
Induction of Vγ and Vδ germline transcription by E2A and HEB in BOSC 23 cells. (A) Transfected BOSC 23 cells were analyzed by RT-PCR for the presence of VγI germline transcripts. (B) Transfected BOSC 23 cells were analyzed by RT-PCR for the presence of Vγ1I germline transcripts. The blots were hybridized with a VγII-specific probe. (C) Transfected BOSC 23 cells were analyzed by RT-PCR for the presence of Vδ2 germline transcripts as indicated. The blots were hybridized with a Vδ2-specific probe. (D) RT-PCR was performed on the same cDNA samples with primers to amplify β-actin transcripts.
Analysis of the Coding Joints Isolated from Embryonic Kidney Cells Expressing the RAG Proteins and either E12 or E47 or HEB.
To examine the nature of the TCR coding joints, rearrangements were amplified by PCR and analyzed by DNA sequencing. The VγI-Jγ joints showed significant diversity. Over 20 recombinant clones were analyzed (Table ). Distinct Vγ regions, interspersed throughout the VγI locus, were used in the presence of either E2A or HEB (Table ). Interestingly, only a selected group of Vγ regions, including Vγ3, Vγ4, and Vγ8 and one pseudogene, Vγ7, were isolated (Table ). Rearrangements involving segments of other Vγ gene families were not detected. Of the Jγ regions, only the most distal J segment, Jγ2.3, was used (Table ). All coding joints showed nucleotide excisions of variable sizes (Table ). Several of the sequences showed P nucleotide additions (Table ). Interestingly, several nucleotide residues could not be matched to germline sequences and may reflect N nucleotide additions, possibly caused by the presence of DNA polymerase mu in kidney cells (29; Table ). DNA sequencing also showed considerable Vδ2-Dδ3 junctional diversity (Table ). Specifically, Vδ2-Dδ3 coding joints showed nucleotide deletions and occasionally the presence of P nucleotide additions (Table ). Thus, the expression of E2A or HEB in conjunction with the V(D)J recombinase is sufficient to generate a diverse repertoire of VγJ and VδD joints, resembling those of γδ T lineage cells.
Table 2.
Sequences of Vγ-Jγ Coding Joints in Transfected BOSC 23 Cells
| Vγ | Jγ2.3 | V segment used | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC TGG GAT AGG | G | AAT TAT TAT AAG | ||
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | C | – | ––T TAT TAT AAG | V3 |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | C | – | ––– ––T TAT AAG | V3 |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | – | –AT TAT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | C | – | ––T TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | C | – | –AT TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC T–– ––– ––– | – | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V8 | |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | – | –AT TAT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | CC | – | gAT TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC TGG GA– ––– | G | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | C | – | ––T TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | – | ––– –AT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | CC | – | gAT TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC TGG GAC ––– | – | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | – | –AT TAT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | – | ––– –AT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC T–– ––– ––– | – | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V8 | |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | CC | – | gAT TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC TGG GAT AG– | G | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V8 | |
| ACC TGG GAT GGG | C | – | ––T TAT TAT AAG | V4 |
| ACC TGG GAC AGG | – | –AT TAT TAT AAG | V7 | |
| ACC TGG GAT AG– | – | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V8 | |
| ACC T–– ––– ––– | – | AAT TAT TAT AAG | V8 |
Coding joints in BOSC 23 cells transfected with either E2A or HEB and RAG1 and RAG2, are diverse and resemble those found in T lineage cells. Genomic DNA from transfected cells was amplified with the VγI family and Jγ1.3/2.3 primers. The resulting fragments were cloned and sequenced. Dashes represent bases that have been deleted. Underlined bases indicate P nucleotide additions. Bases in lowercase lettering could not be matched to the germline DNA sequence.
Table 3.
Sequences of Vδ-Dδ Coding Joints in Transfected BOSC 23 Cells
| Vδ2 | Dδ3 | |
|---|---|---|
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC AC– | –CT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC AC– | –CT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | ––T GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | –CT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC AC– | –CT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | ––– –GG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | ––T GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | –CT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | –CT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | ACT GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | G t | ––T GGG GGA TAC G |
| GCC TGT GAC ACC | ––T GGG GGA TAC G | |
| GCC TGT GAC ––– | ––– ––– ––– –AC G |
DNA sequences of Vδ2-Dδ3 coding joints isolated from BOSC 23 cells transfected with E2A or HEB and RAG1 and RAG2 are diverse and resemble those found in T lineage cells. Genomic DNA from transfected cells was amplified with Vδ2 and Dδ3 primers. The resulting fragments were cloned and sequenced. Dashes indicate bases that have been deleted. Underlined bases represent P nucleotide additions. Bases in lowercase lettering could not be matched to the germline DNA sequence.
Discussion
The data presented here demonstrate that the bHLH transcription factors E2A and HEB act in concert with RAG1 and RAG2 to activate a subset of TCR-γ/δ rearrangements in nonlymphoid cells. The striking finding is that E2A and HEB permit only a limited repertoire of rearrangements. This raises the question how the presence of E2A and HEB allow only a subset of rearrangements. It is possible that other factors affecting recombination efficiency influence the repertoire of rearrangements. For example, coding and RSS sequences may effect the effect the efficiency of TCR rearrangements in the transfectants. Thus, E2A and HEB may modestly promote general TCR γ and δ locus accessibility allowing for detection only of those V regions that normally rearrange more efficiently. Such a scenario cannot be excluded for the rearrangements that we observe for the TCR-δ locus. However, we note that recombination at the TCR-γ locus is efficient, suggesting that in the transfectants, the accessibility of this TCR locus to the recombination machinery is localized. Further support for localized accessibility is provided by the data indicating a close relationship between the ability of E2A and HEB to activate germline transcription and to induce rearrangement.
A role for E2A in TCR γ and δ rearrangement is not unexpected. Our previous data using E2A-deficient mice showed that the E2A proteins are required for proper γδ T lineage development 22. Specifically, the number of γδ T cells found in the secondary lymphoid tissues and the intraepithelial layers of the intestine are significantly reduced in E2A-null mutant mice 22. Both TCR-γ VJ and TCR-δ VD rearrangements are perturbed. In contrast, TCR-δ DJ joining is not affected in E2A-deficient thymocytes 22. These observations are consistent with our data indicating that E2A proteins have the ability to promote Vδ-Dδ but are not involved in Dδ-Jδ rearrangement. Selective targeting of the recombinase by either E2A or HEB was also observed in the TCR-γ locus. The VJ and VD joints that were formed showed significant diversity. All of the rearrangements showed deletions of various sizes and many showed P nucleotide additions. Interestingly, a few bases could not be assigned to germline sequences (Table and Table ). TdT is not expressed in kidney cells, but a related enzyme, DNA polymerase μ, is detectable in kidney cells 29. It is conceivable that the additions of these nucleotides in the transfectants are caused by the activity of DNA polymerase μ 29.
Remarkably, rearrangement involving the most distal Jγ region (Jγ2.3) was readily detectable in cells expressing E2A or HEB, whereas the Jγ1.3 was not used. These data raise the question how E2A and HEB permit localized accessibility. Both E2A and HEB belong to a distinct group of HLH proteins, termed class I HLH or E-proteins. They contain highly conserved activation domains, designated AD1 and AD2. AD1 has been shown to recruit a group of proteins, termed the SAGA complex which contains histone acetyl transferase (HAT) activity 30. Both AD1 and AD2 have also been shown to interact with p300, which also has HAT activity 31. It is conceivable that E2A and HEB permit localized opening of chromatin surrounding the RSSs by modification of histones through the recruitment of complexes containing HAT activity. Consistent with these observations are the findings that the level of germline transcripts of Vγ and Vδ region genes in E2A-deficient mice correlates precisely with the level of rearrangements 22.
E2A and HEB may also directly recruit RAG1 and RAG2 to the RSSs. E box sites in the proximity of the V and J regions have been identified and it will be interesting to determine by mutational analysis if these sites are required for proper V(D)J rearrangement (unpublished observations). As both E2A and HEB have the ability to promote rearrangement and to activate germline transcription, the protein domains and amino acids that permit recruitment must be conserved between these two proteins. Identification of the domains and residues that promote accessibility may provide further insight as to how E-proteins regulate both Ig and TCR gene rearrangement.
In summary, the data described here demonstrate that a diverse TCR γ and δ repertoire can be induced in nonlymphoid cells by the mere presence of a transcriptional activator and the VDJ recombinase. The striking observation is that E2A and HEB do not promote accessibility throughout the TCR γ and δ loci. Rather, E2A and HEB permit chromatin opening to only a selected set of V, D, and J region genes. Recent data have demonstrated a tight correlation with regulated changes in histone H3 acetylation and VDJ recombination at the TCR-δ locus 32. It will be particularly interesting to determine if E2A-deficient thymocytes show abnormalities in histone H3 acetylation along the TCR-δ locus.
Acknowledgments
J.K. Ghosh thanks Dr. R.R. Rivera for many helpful suggestions and Dr. A.W. Langerak for genomic DNA from the RPMI 8402 and REM cell lines.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (C. Murre). W.J. Romanow is supported by a Developmental Biology National Institutes of Health Training Grant.
References
- Mombaerts P., Iacomini J., Johnson R.S., Herrup K., Tonegawa S., Papaioannou V.E. RAG-1-deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell. 1992;68:869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Rathbun G., Lam K.P., Oltz E.M., Stewart V., Mendelsohn M., Charron J., Datta M., Young F., Stall A.M., Alt F.W. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell. 1992;68:855–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D.G., Oettinger M.A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989;59:1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M.A., Schatz D.G., Gorka C., Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990;248:1517–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.2360047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D.C., McBlane J.F., Ramsden D.A., Sadofsky M.J., Hesse J.E., Gellert M. Initiation of V(D)J recombination in a cell-free system. Cell. 1995;81:925–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D., Boubnov N., Wills Z., Hall K., Staunton J. V(D)J recombinationdouble-strand break repair gene products used in the joining mechanism. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1995;764:99–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb55811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willerford D.M., Swat W., Alt F.W. Developmental regulation of V(D)J recombination and lymphocyte differentiation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1996;6:603–609. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F.W., Yancopoulos G.D., Blackwell T.K., Wood C., Thomas E., Boss M., Coffman R., Rosenberg N., Tonegawa S., Baltimore D. Ordered rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region segments. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 1984;3:1209–1219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Young F., Bottaro A., Stewart V., Smith R.K., Alt F.W. Mutations of the intronic IgH enhancer and its flanking sequences differentially affect accessibility of the JH locus. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 1993;12:4635–4645. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D.G., Oettinger M.A., Schlissel M.S. V(D)J recombinationmolecular biology and regulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1992;10:359–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleckman B.P., Gorman J.R., Alt F.W. Accessibility control of antigen-receptor variable-region gene assemblyrole of cis-acting elements. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:459–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M.S., Stanhope-Baker P. Accessibility and the developmental regulation of V(D)J recombination. Semin. Immunol. 1997;9:161–170. doi: 10.1006/smim.1997.0066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleckman B.P., Khor B., Monroe R., Alt F.W. Assembly of productive T cell receptor δ variable region genes exhibit allelic inclusion. J. Exp. Med. 1999;188:1465–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.8.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Bain G., van Dijk M.A., Engel I., Furnari B.A., Massari M.E., Matthews J.R., Quong M.W., Rivera R.R., Stuiver M.H. Structure and function of helix-loop-helix proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1994;1218:129–135. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massari M.E., Murre C. Helix-loop-helix proteinsregulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;20:429–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.2.429-440.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain G., Gruenwald S., Murre C. E2A and E2-2 are subunits of B-cell-specific E2-box DNA-binding proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993;13:3522–3529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain G., Maandag E.C., Izon D.J., Amsen D., Kruisbeek A.M., Weintraub B.C., Krop I., Schlissel M.S., Feeney A.J., van Roon M. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell. 1994;79:885–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X.-H. Constitutive expression of the Id1 gene impairs mouse B cell development. Cell. 1994;79:893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Soriano P., Weintraub H. The helix-loop-helix gene E2A is required for B cell formation. Cell. 1994;79:875–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain G., Engel I., Robanus Maandag E.C., te Riele H.P., Voland J.R., Sharp L.L., Chun J., Huey B., Pinkel D., Murre C. E2A deficiency leads to abnormalities in αβ T-cell development and to rapid development of T-cell lymphomas. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997;17:4782–4791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.8.4782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Cheng P., Weintraub H. B-lymphocyte development is regulated by the combined dosage of three basic helix-loop-helix genes, E2A, E2-2, and HEB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996;16:2898–2905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.6.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain G., Romanow W.J., Albers K., Havran W.L., Murre C. Positive and negative regulation of V(D)J recombination by the E2A proteins. J. Exp. Med. 1999;189:289–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pear W.S., Nolan G.P., Scott M.L., Baltimore D. Production of high-titer helper-free retroviruses by transient transfection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1993;90:8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanow W.J., Langerak A.W., Goebel P., Wolvers-Tettero I.L.M., van Dongen J.J.M., Feeney A.J., Murre C. E2A and EBF act in synergy with the V(D)J recombinase to generate a diverse immunoglobulin repertoire in nonlymphoid cells. Mol. Cell. 2000;5:343–353. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C.A., Cherry S.R., Baltimore D. Complementation of V(D)J recombination deficiency in RAG-1−/− B cells reveals a requirement for novel elements in the N-terminus of RAG-1. Immunity. 1997;7:13–24. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kee B.L., Murre C. Induction of early B cell factor (EBF) and multiple B lineage genes by the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor E12. J. Exp. Med. 1998;188:699–713. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breit T.M., Wolvers-Tettero I.L., Hahlen K., van Wering E.R., van Dongen J.J. Extensive junctional diversity of gamma delta T-cell receptors expressed by T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemiasimplications for the detection of minimal residual disease. Leukemia. 1991;5:1076–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneba M., Bolz I., Linke B., Hiddemann W. Analysis of rearranged T-cell receptor beta-chain genes by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) DNA sequencing and automated high resolution PCR fragment analysis. Blood. 1995;86:3930–3937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez O., Ruiz J.F., de Lera T., Garcia-Diaz M., Gonzalez M.A., Kirchoff T., Martinez-A C., Bernad A., Blanco L. DNA polymerase mu (Pol μ) homologous to TdT, could act as a DNA mutator in eucaryotic cells. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 2000;19:1731–1742. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.7.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massari M.E., Grant P.A., Pray-Grant M.G., Berger S.L., Workman J.L., Murre C. A conserved motif present in a class of helix-loop-helix proteins activates transcription by direct recruitment of the SAGA complex. Mol. Cell. 1999;4:63–73. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qui Y., Sharma A., Stein R. p300 mediates transcriptional stimulation by the basic helix-loop-helix factors of the insulin gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998;18:2957–2964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.5.2957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry M.T., Krangel M.S. A role for histone acetylation in the developmental regulation of VDJ recombination. Science. 2000;287:495–498. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5452.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]