Abstract
We investigated the mechanism by which B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS)/BAFF, a tumor necrosis factor superfamily ligand, promotes B-cell survival and resistance to atrophy. BLyS stimulation activates 2 independent signaling pathways, Akt/mTOR and Pim 2, associated with cell growth and survival. BLyS blocks the cell volume loss (atrophy) that freshly isolated B cells normally undergo when maintained in vitro while concurrently increasing glycolytic activity and overall metabolism. This atrophy resistance requires Akt/mTOR. We used a genetic approach to resolve the contributions of Akt/mTOR and Pim kinase pathways to BLyS-mediated survival. Pim 2–deficient B cells are readily protected from death by BLyS stimulation, but this protection is completely abrogated by treatment with the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. Furthermore, rapamycin treatment in vivo significantly reduces both follicular and marginal zone B cells in Pim-deficient but not healthy hosts. BLyS-dependent survival requires the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1. Mcl-1 protein levels rise and fall in response to BLyS addition and withdrawal, respectively, and conditional deletion of the Mcl-1 gene renders B cells refractory to BLyS-mediated protection. Because BlyS is required for the normal homeostasis of all B cells, these data suggest a therapeutic strategy simultaneously inhibiting mTOR and Pim 2 could target pathogenic B cells.
Introduction
The majority of naive lymphocytes are small cells in the Go stage of the cell cycle, a condition providing economy of space and efficient resource utilization. Lymphocytes at rest are not static but are actively maintained by the action of growth and survival factors necessary for nutrient uptake and suppression of apoptosis.1 Two unique survival factors for B cells have been identified: B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS; BAFF, TALL-1, THANK, TNFSF13B, and zTNF4) and APRIL, both members of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily of ligands.2 APRIL depletion has little effect on the homeostasis of naive B cells but compromises the survival of plasma cells.3,4 In contrast, BLyS is essential for the survival of peripheral B lymphocytes.5 BLyS-deficient mice have striking deficits in marginal zone and follicular B-cell populations,6,7 whereas ectopic expression of BLyS from a transgene markedly expands follicular and marginal peripheral zone B cells without affecting T cells, early (T1) transitional peripheral B cells, or developing B cells in the marrow.8 BLyS is also required for the maintenance of a variety of B cell tumors and dysregulated BLyS stimulation rescues autoantibody producing B cells from deletion.9,10 Thus, BLyS has a critical role in the homeostasis of both normal and pathogenic B cells
BLyS acts through 3 receptors: BCMA (B-cell maturation antigen), TACI (transmembrane activator and CAML interactor), and BR3 (BLyS receptor 3) or BAFF receptor.8 Targeted mutation of BCMA has no striking effect on naive B-cell survival, but BCMA is up-regulated on and required for the survival of long-lived plasma cells.4 Elimination of TACI causes a marked increase of follicular and marginal zone B cells and the production of autoantibodies suggesting a primary regulatory role for this receptor.11 BR3 is found on mature follicular and marginal zone B cells and on T2, T3 transitional B cells.12 Mice with a spontaneous mutation in the BR3 signaling motif (A/WySn) or mice in which the BR3 gene has been targeted lose these B-cell subpopulations.13,14 The phenotype of BR3-deficient mice for the most part recapitulates that of BLyS-deficient mice, suggesting that naive B-cell survival depends primarily on BLyS acting through BR3.
The molecular mechanism by which BLyS affects naive B-cell survival has not been completely elucidated. BLyS stimulation mobilizes tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors (TRAFs) promoting NF-κB activation through the induction of both canonical (p50, NF-kB1) and noncanonical (p52, NF-kB2) NF-kB pathways.15–17 NF-kB induction up-regulates genes for a variety of antiapoptotic proteins, including A1/Bfl-1, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-2 any of which could account for BLyS-dependent apoptosis inhibition.17–19 Alternatively, inhibition of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members is proposed as a mechanism of protection.20,21
We report here that BLyS attenuates atrophy and death of primary naive B lymphocytes by activating 2 independent growth and survival pathways, Akt/mTOR and Pim 2. In the absence of Pim 2, BLyS-mediated B-cell survival becomes rapamycin-sensitive in vitro and in vivo. A key effector molecule necessary for protection is Mcl-1, an antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family member; BLyS-dependent survival is not induced in B cells where Mcl-1 was conditionally deleted. The data suggest that 2 independent signaling pathways mediate BLyS-dependent survival and that Mcl-1 is a critical downstream mediator of BLyS action.
Methods
Mice
Pim-1+/+2+/+, Pim-1−/−2+/+, Pim-1+/+2−/−, and Pim-1−/−2−/− mice were generated from Pim-1+/−2+/− stock generously provided by Paul Rothman, Columbia University, New York, NY. C57BL/6 (B6) mice were obtained from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Mx-CRE transgenics were backcrossed with mice with floxed Mcl-1 to produce Mcl-1f/f, Mcl-1f/null, and Mcl-1f/wt populations.22 CBA/Ca × B6 mice expressing the human Bcl-2 transgene under the control of an Ig enhancer and promoter have been described.23,24 Animals were maintained at the University of Pennsylvania, Harvard Medical School, or the University of Massachusetts Medical School under Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines.
B-cell purification
Murine B cells were prepared by antithy1.2 and complement treatment of splenocytes followed by purification of resting B cells using a step Percoll gradient harvesting cells at the 60% to 70% interface.23 CD23+ B cells were obtained by magnetic separation of murine splenocytes using biotinylated anti-CD23 antibody (BD Biosciences-Pharmingen, San Diego, CA) and streptavidin-coated microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, Auburn CA). Splenic B cells were more than 90% B220+, whereas CD23+ B cells were more than 95% pure.
Cell cultures
Purified B cells or CD23+ B cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 2-mercaptoethanol, MEM-nonessential amino acids, glutamine, penicillin, and streptomycin (CM) at 37°C in 5% CO2 and air. For B-cell survival, enzyme and protein induction assays recombinant human (rhu) BLyS (Human Genome Sciences, Rockville, MD) was used at 50 to 100 ng/mL, the optimum dose for survival established by BlyS titrations between 1 and 500 ng/mL. Murine BLyS was purchased from Alexis Biochemicals (San Diego, CA) and interferon alpha (IFNα) from PBL Biomedical (Piscataway, NJ). Rapamycin at a final concentration of 50 nM, a concentration established in preliminary experiments to inhibit mitogen responses in vitro without affecting viability, was added to cultures from a stock dissolved in methanol; control B cells were treated with methanol only. For enzyme phosphorylation assays B cells cultured overnight at 37°C were activated with soluble antimurine IgM (5 μg/mL; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA), anti-CD40 (0.5 μg/mL; eBioscience, San Diego, CA), or 100 ng/mL of rhuBLyS added to assay buffer (Hanks balanced salt solution, 2% bovine serum albumin). To assess PI 3-kinase dependence of BLyS-induced Akt phosphorylation, B cells were treated for 60 minutes with LY294002 or the negative control LY 303511 (EMD Bioscience, La Jolla, CA) at 10 μM in DMSO before BLyS addition. Long-term Mcl-1 expression was determined using B cells from huBcl-2 tg+ donors (3 × 106 cells /well in 12-well plates) cultured for 10 days with and without 50 ng/mL of rhuBLyS.
Antibodies and Western blotting
Anti-Pim 2 (1D12), Pim 1 (19F7), and actin (1-19) anti–mouse, – rabbit, and – goat Ig coupled to HRP were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Rabbit antiphospho-Akt (S473) and phospho-Akt (T308), phospho-p70 S6 kinase (T389), phosph-Fox01/Fox03a (T24/32), phospho-Gsk-3α/β (S21/9), phospho-4E-BP1 (T37/46), PI3 kinase (p85), Gsk-3β, 4E-BP1, and Akt were purchased from Cell Signaling (Beverly, MA). Rabbit anti–mouse Mcl-1 was purchased from Rockland (Wilmington, MA) and anti-Bcl-2 and anti-Bcl-XL from eBioscience. Whole cell lysates were prepared by washing B cells in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline and lysing pellets in RIPA (150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0) supplemented with protease inhibitors (Complete Mini, Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis IN) and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails I and II (Sigma, St Louis, MO); 10 to 50 μg of protein was resolved on 4% to 12% NuPage bis-tris polyacrylamide gels (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and transferred to nitrocellulose. Blots were blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin, 0.2% Tween-20 in Tris-buffered saline and incubated with primary antibody in the same buffer overnight at 4°C. Blots were washed, incubated with secondary antibody conjugated with HRP, and developed using ECLplus (Amersham Bioscience, Piscataway, NJ). Blots were stripped for reprobing by incubation for 20 minutes at 65°C in Tris-buffered saline supplemented with 1% SDS and 100 μM β-mercaptoethanol. Quantitation of Western signals was performed with a Molecular Dynamics Densitometer (Amersham, Sunnyvale, CA) using BioRad (San Diego, CA) Multi-analyst software.
Survival and atrophy assays
B cells at 5 × 106/mL were cultured in 24-well tissue culture dishes in CM at 37°C with test stimulators and supplements. B cells were pretreated with 50 nM rapamycin or vehicle 1 hour before culture with the test stimulants with fresh rapamycin added after 48 hours. Survival was monitored daily by counting viable cells using trypan blue exclusion with each determination done in triplicate. Apoptosis and cell survival were monitored, respectively, by FACS using PI staining25 or a Live/Dead Fixable Blue Stain kit (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR). Cell size was determined with a Coulter Z2 particle size analyzer after removing dead cells by Percoll flotation.
Glucose use
Glucose use was determined for B cells cultured for 2 days with rhuBLyS, anti-Ig, or anti-CD40 as described.26 Briefly, after culture, cells were harvested, washed, and pulsed with 10 μCi (370 kBq) of 5-3H-glucose in 24-well plates for 1 to 2 hours at 37°C. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 0.2N HCL. 3H2O was separated from 5-3H-glucose by diffusion into a reservoir of H2O in an airtight scintillation vial. Diffused and undiffused 3H2O was measured using a 1450 Microbeta scintillation counter (Wallac, Turkua, Finland) to determine the rate of glycolysis.
Statistical analyses
Data were compared using a paired t test or one-way ANOVA test with Tukey posttest, InStat version 3 statistical package (Graphpad Software, San Diego, CA). P values are provided or represented as P is more than .05 (not significant), P is less than .05 (*), P is less than .01 (**), and P is less than .001 (***).
Results
BLyS promotes both growth and survival of B lymphocytes
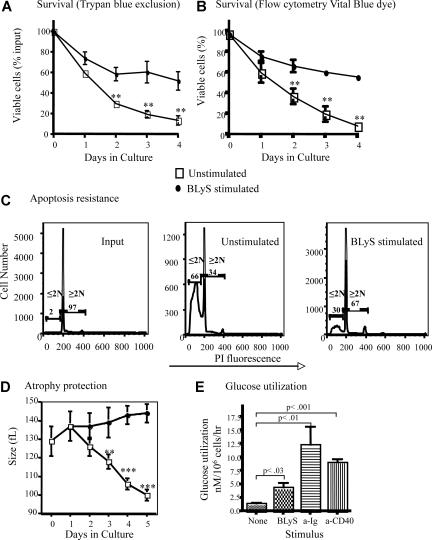
B lymphocytes removed from their normal microenvironment undergo death by neglect that can be blocked by inducers of cell growth and antiapoptotic molecules.27 Positively selected CD23+ follicular B cells cultured without stimulation die rapidly ex vivo, demonstrated by direct observation using trypan blue dye exclusion (Figure 1A) or Flow analysis using blue-fluorescent reactive vital dye (Figure 1B). These 2 methods for determining viability yielded statistically indistinguishable results (P > .05). Survival was markedly enhanced (P < .01 for days 3, 4, and 5) for B cells cultured with recombinant huBLyS compared with unstimulated controls (Figure 1A,B). Cell loss by apoptosis was significantly inhibited by BLyS stimulation (Figure 1C). Maintenance of viability is not attributable to contaminating endotoxin in the BLyS preparation because BLyS-dependent survival of TLR4−/− and wild-type CD23+ B cells in culture was equivalent and TLR4−/− B cells were not rescued by LPS (Figure S1A, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).
Figure 1.
BLyS stimulation promotes B-cell survival and growth. (A,B) BLyS sustains B cells ex vivo. Mature small resting murine splenic B cells positively selected with anti-CD23 and streptavidin magnetic beads were cultured for 4 days with or without 100 ng/mL huBLyS. The number of viable cells was determined daily by trypan blue exclusion (A) or by flow cytometry using blue fluorescent vital dye (B); data are the arithmetic mean (± SD) of 2 separate experiments. (C) B cells cultured with BLyS resist apoptosis. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry using PI on CD23+ B cells freshly prepared or cultured for 3 days with and without 100 ng/mL of huBLyS. The results are representative of 3 independent experiments. PI indicates propidium iodide. (D) B cells cultured with BLyS maintain cell size ex vivo. Percoll-purified B cells were cultured for 5 days in CM with and without 50 ng/mL of rhuBLyS and sized daily using a Coulter Z2 particle analyzer. Dead cells were excluded by sedimentation over Percoll. Data shown are the arithmetic means (±SD) for 3 independent experiments with statistical comparisons between unstimulated and BlyS-stimulated B cells indicated (**P < .01; ***P < .001). (E) BLyS promotes increased glucose metabolism. Glucose use by cultured CD23+ B cells left unstimulated or stimulated with 100 ng/mL rhuBLyS, 5 μg/mL anti-Ig or 0.5 μg/mL of anti-CD40 for 2 days. Results are the arithmetic means (± SD) for 2 independent experiments.
T lymphocytes cultured without growth factors lose cell volume as a consequence of nutrient deprivation.28 This cell atrophy subsequent to growth factor withdrawal is seen in B lymphocytes. Freshly isolated B cells, averaging 129 plus or minus 8 fL in volume shrank to 100 plus or minus 3 fL, for viable cells recovered after 5 days in culture, whereas B cells cultured with BLyS increased in volume to 144 plus or minus 8 fL over the same period (Figure 1D). Contaminating endotoxin could not explain BLyS-dependent atrophy resistance, which was comparable in TLR4−/− and wild-type CD23+ B cells, although TLR4−/− B cells failed to enlarge when stimulated with LPS (Figure S1B). Maintenance of cell size reflects the preservation of essential metabolic pathways; B cells cultured with BLyS have significantly increased glucose metabolism (4.3 ± 1.9 nM/106 B cells/hr) compared with B cells cultured without BLyS (1.4 ± 0.4 nM/106B cells/h; Figure 1E). Stimulation with anti-Ig or anti-CD40 induced blastogenesis and a markedly increased glucose use relative to BLyS-treated B cells, which did not undergo blastogenesis (Figure 1E). For example, B cells stimulated through CD40 exhibited a greater cell volume (198 ± 3 fL), after 3 days of culture than BLyS-stimulated cells (140 ± 4 fL). BLyS stimulation induces a generalized metabolic enhancement; RNA (3H-uridine uptake) and amino acid (3H-leucine uptake) metabolism are increased, but 3H-thymidine incorporation remains at background levels (data not shown), and progression to the S phase of the cell cycle did not occur (Figure 1C). These data suggest that BLyS functions as both a growth and survival factor because BLyS-stimulated B cells retain viability, size, and metabolic activity ex vivo, whereas unstimulated B cells do not.
BLyS stimulation activates the AKT/mTOR pathway in B cells
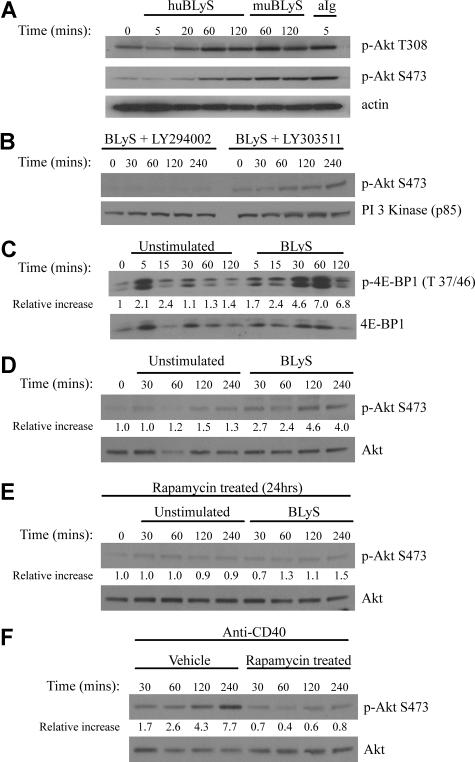
Maintenance of growth and survival are known functions of the Akt/mTOR pathway. To determine whether BLyS activated Akt, we stimulated primary murine B cells with recombinant human or murine BLyS or with anti-Ig, a known inducer of this pathway. Phosphorylation of the 2 target sites necessary for full Akt activity, T308 and S473, was readily apparent in B cells stimulated with either soluble human or murine rBLyS (Figure 2A). BlyS-induced Akt phosphorylation peaked at 60 minutes and was still detectable at 120 minutes (Figure 2A), whereas anti-Ig induced phosphorylation was more rapid. Akt phosphorylation was dependent on PI3-kinase as it was inhibited by LY294002 but not by the inactive analog LY303511 (Figure 2B). The activation of mTOR, a major Akt downstream effector associated with cell growth, was demonstrated by the phosphorylation of its substrate the translation inhibitor 4E-BP1 (Figure 2C). We found incubation of B cells without activator sometimes led to phosphorylation of 4E-BP1, but this was always more transient and less intense than activation with BLyS. Akt phosphorylation on S473 was not seen in extracts from cells cultured for 4 hours in the absence of BLyS (Figure 2D). We also found p70 S6 kinase, Gsk-3β, FOXO1, and FOXO3a were phosphorylated by BLyS stimulation with kinetics similar to the phosphorylation of Akt (Figure S2).
Figure 2.
BLyS stimulates Akt and mTOR activation. (A) Phosphorylation of Akt. Purified B cells were stimulated for the indicated times with 100 ng/mL recombinant human or murine rBLyS or 5 μg/mL of anti-Ig at 37°C in pregassed medium. Lysates were prepared from iced samples and analyzed by Western Blot, using antibodies specific for the phosphoserine (S473) and phosphothreonine (T308) residues associated with Akt activation. (B) Inhibition of BLyS induced Akt phosphorylation by the PI 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002. Akt phosphorylation on Ser 473 was followed in purified B cells treated with LY294002 or the inactive analog LY303511 for 1 hour before BLyS stimulation. (C) BLyS induced phosphorylation of the mTOR substrate 4E-BP1. Phosphorylation of E4-BP1 on Thr 37/46 was followed by unstimulated or BLyS-stimulated purified B cells. Quantitation of Western signals represent fold increases of phosphorylated 4E-BP1 relative to that found in unstimulated B cells at time zero with a correction for sample loading performed on the same Western blot stripped and reprobed for total 4E-BP1 protein. Quantitation was performed with a Molecular Dynamics Densitometer as described in “Antibodies and Western blotting.” (D) BLyS induces Akt phosphorylation, whereas incubation of B cells in media only does not. Purified B cells were analyzed over 4 hours for Akt phosphorylation on S473 in the absence and presence of 100 ng/mL of rhuBLyS. Quantitation was as described in panel C. (E) Akt phosphorylation on S473 is inhibited in purified B cells precultured with rapamycin. B cells were cultured for 24 hours with 50 nM of rapamycin and then cultured for the indicated times with media only or media with 100 ng/mL of rhuBLyS. Panel D shows the response to BLyS of B cells incubated without rapamycin. (F) Akt phosphorylation on S473 is impaired in B cells precultured in rapamycin and activated with anti-CD40 antibody. Purified B cells were cultured for 24 hours in vehicle or 50 nM of rapamycin and then stimulated with 0.5 μg/mL of anti-CD40 antibody.
Akt phosphorylation at S473 has recently been attributed to the normally rapamycin-insensitive rictor containing mTORC2 complex.29 This complex can be disassembled, however, in some mammalian cell lines after prolonged rapamycin treatment making Akt phosphorylation at S473 rapamycin sensitive.30 To assess the action of mTORC2 on Akt activation in primary B cells, B cells were cultured for 24 hours with 50 nM rapamycin before BLyS (Figure 2E) or anti-CD40 (Figure 2F) stimulation. We found Akt phosphorylation at S473 was significantly impaired for both activators in rapamycin-treated B cells.
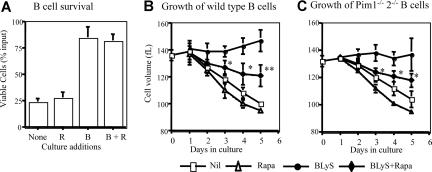
Rapamycin inhibits BLyS-dependent B-cell growth but not survival
Rapamycin inhibits growth-factor dependent maintenance of cell survival and size.28,31–33 To assess the effect of rapamycin on BLyS-mediated survival and growth, total B or CD23+ selected B cells were cultured with rapamycin or vehicle. Treatments with rapamycin neither exacerbated significantly spontaneous B-cell loss nor impeded BLyS-dependent survival (Figure 3A). In contrast, BLyS-dependent maintenance of cell size was inhibited by rapamycin with significant differences found for days 3 through 5 of culture (Figure 3B). This rapamycin-induced effect was not complete; B cells stimulated with both BLyS and rapamycin were still significantly larger than untreated or rapamycin only treated controls.
Figure 3.
Rapamycin inhibits B-cell growth but not survival. (A) BLyS-dependent ex vivo B-cell survival is resistant to rapamycin. Small resting B cells from normal donors were cultured for 4 days with and without 100 ng/mL rhuBLyS, vehicle, or 50 nM rapamycin, which was used to pretreat B cells before culture, added directly to cultures on initiation and readded every 2 days. Viable cells were determined at day 4. Data are the arithmetic mean (±SD) and the results of 3 independent experiments. (B,C) Rapamycin inhibits BLyS-dependent maintenance of B cell size. CD23+ B cells from (B) normal or (C) Pim 1−/− 2−/− double-deficient donors were cultured with and without BLyS and with vehicle or rapamycin for 5 days. Cell size was determined for viable cells daily by a Coulter Z2 size analyzer. Results are the arithmetic mean (±SD) from 3 independent experiments. Statistical comparisons are between BLyS and BLyS plus rapamycin cell populations (* P < .05; ** P < .01).
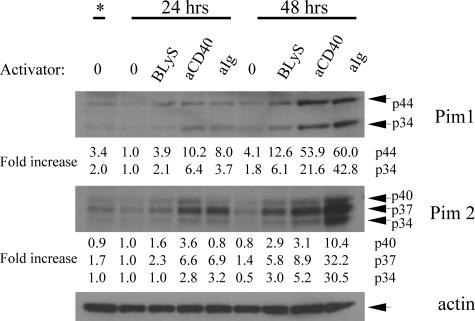
BLyS induces Pim 1 and Pim 2 and promotes Pim 2–dependent survival
The failure of rapamycin to suppress BLyS-mediated survival in normal B cells suggested a BLyS-induced signaling pathway independent of Akt/mTOR. Pims are a family of 3 serine/threonine kinases induced in hematopoietic cells by numerous activators that can provide rapamycin-resistant protection against apoptosis and atrophy.34,35 To assess Pim induction by BLyS, we analyzed extracts from purified B cells left unstimulated or stimulated with BLyS, anti-CD40, or anti-IgM antibody for 24 or 48 hours. Figure 4 shows that both isoforms of Pim 1 are induced by BLyS (2- to 4-fold over unstimulated controls) with similar kinetics but at a lower intensity than with the other activators. Likewise, all isoforms of Pim 2 were induced by BLyS (2- to 6-fold over unstimulated controls), with similar kinetics but a lower intensity than the other activators.
Figure 4.
BLyS induces both Pim 1 and Pim 2. Purified small resting B cells were cultured for 2 days unstimulated or with 100 ng/mL rhuBLyS, 5 μg/mL anti-Ig or 0.5 μg/mL anti-CD40. Lysates from the freshly isolated input population (*) and after 24 and 48 hours of culture were prepared and analyzed by Western blot. Results are representative of 4 independent experiments and show the 2 isoforms of Pim1 at 33 and 44 kDa, and the 3 isoforms of Pim 2 at 34, 37, and 40 kDa. Relative protein levels of each Pim isoform were determined by densitometry and normalized to the unstimulated B-cell population cultured for 24 hours as described in Figure 2C.
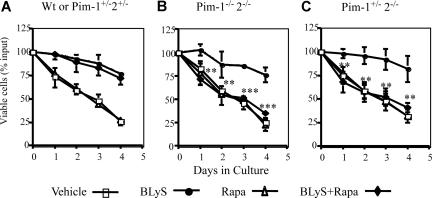
Can Pims account partially or fully for BLyS-dependent survival? Multiple signal pathways promote apoptosis resistance in hematopoietic cell lines and T cells.21,36 To assess the potential contribution of simultaneously active protective pathways using Pims and/or Akt/mTOR, we determined the survival of normal (wild-type or Pim1+/−2+/− heterozygotes) and Pim 1−/− 2−/− doubly deficient CD23+ B cells treated with BLyS, and/or rapamycin or vehicle. BLyS-dependent survival of wild-type B cells was fully resistant to rapamycin (Figure 5A). Pim 1 and 2 doubly deficient B cells were also fully protected by culture with BLyS, showing that Pims were not obligatory for BLyS-mediated protection. Protection was completely abolished, however, in Pim 1– and 2–deficient B cells by rapamycin treatment (Figure 5B), showing that Akt/mTOR and Pims fully account for BLyS-dependent protection. Pim 1 and 2 mediate growth factor–induced apoptosis protection in B and T cells, respectively.21,37 To determine whether one or both Pims were necessary to protect B cells in which mTOR was inhibited, we assessed the effect of rapamycin on B cells from mice deficient only in Pim 2. BLyS failed to rescue rapamycin–treated Pim 1+/−2−/− B cells (Figure 5C), showing that Pim 1 does not confer rapamycin resistance. These data, in toto, suggest that the Akt/mTOR– and Pim 2–dependent pathways independently mediate BLyS–dependent survival.
Figure 5.
BLyS-dependent survival is rapamycin sensitive in Pim 2–deficient B cells. CD23+ B cells from: (A) wild-type or Pim 1−/+2−/+ heterozygotes, (B) Pim 1−/− 2−/− double-deficient, or (C) Pim 2 only− deficient (Pim 1+/− 2−/−) donors were cultured in CM for 4 days with vehicle, 100 ng/mL rhuBLyS, with or without 50 nM rapamycin (Rapa). Viability was determined daily by trypan blue exclusion. Results are the arithmetic means (±SD) from 3 independent experiments. Statistical comparisons are between BLyS-treated and BLyS and rapamycin-treated B cells (**P < .01; ***P < .001).
Because rapamycin induced only a partial inhibition of BLyS-dependent B-cell growth and Pims mediate both growth and survival in hematopoietic cells,34,38 we asked if rapamycin-dependent growth inhibition was more effective in Pim 1 and 2 doubly deficient B cells. BLyS-dependent maintenance of cell size was unimpaired in Pim-deficient B cells and the magnitude of rapamycin–induced inhibition of BLyS-dependent atrophy protection was comparable in Pim-deficient and normal B cells (Figure 3B,C).
Mcl-1 is required for BLyS-dependent survival
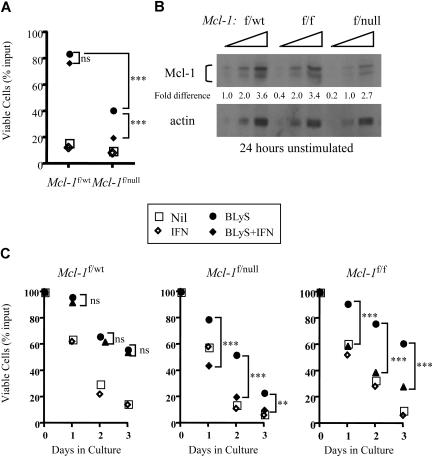
Mcl-1 plays a critical role in peripheral B- and T- cell homeostasis. Excision of Mcl-1 causes the loss of mature T and B cells in situ or of adoptively transferred lymphocytes in vivo.22 Given these results, combined with our finding that neither wild-type nor Pim 1−/−2−/−–deficient B cells stimulated with BLyS consistently up-regulated Bcl-2 or Bcl-XL proteins (Figure S3), we used B cells in which Mcl-1 could be conditionally deleted to test the hypothesis that BLyS-mediated survival required Mcl-1.B cells bearing a CRE transgene under the control of the interferon responsive MX promoter, and heterozygous for floxed and wild-type Mcl-1 alleles (Mcl-1f/wt) or floxed and null Mcl-1 alleles (Mcl-1f/null) were examined for in vitro viability when cultured with and without BLyS in the presence or absence of recombinant IFNα. BLyS-treated B cells from Mcl-1f/wt mice were fully protected from death in culture and this BLyS-dependent protection was unaffected by IFNα in the cultures (P > .05; Figure 6A). In contrast, although B cells from Mcl-1f/null mice were also protected from death by BLyS, protection was completely lost when Mcl-1 was excised on addition of IFNα to the cultures (P < .001; Figure 6A).
Figure 6.
Cre-dependent excision of Mcl-1 blocks BLyS-dependent in vitro B-cell survival. (A) Excision of the Mcl-1 gene in Mcl-1 f/null B cells renders the targeted B cells refractory to BLyS-mediated survival protection. Small resting B cells from donors expressing an Mx-cre transgene and heterozygous for floxed and wild-type Mcl-1 alleles (Mcl-1f/wt) or for floxed and null Mcl-1 alleles (Mcl-1f/null) were cultured for 3 days with and without 100 ng/mL rhuBLyS in the presence of 200 units of IFNα to induce Mcl-1 excision. Viability was assessed by trypan blue dye exclusion. Each point is the average of 3 determinations with statistical comparisons included: P > .05 (not significant); ***P < .001. (B) Gene dose affects the amount of Mcl-1 protein in Percoll purified resting B cells. Mcl-1 protein was determined by Western blot of serially diluted (2-fold) cell lysates prepared from B cells taken from donors heterozygous for floxed and wild-type (Mcl-1f/wt) or floxed and null (Mcl-1f/null) alleles or homozygous for floxed Mcl-1 alleles. Proteins were quantified by densitometry as described Figure 2C. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments. (C) Mcl-1 gene dose modulates the effectiveness of BLyS-dependent B-cell protection. Small resting B cells from Mcl-1f/wt, Mcl-1f/null, or Mcl-1f/f donors expressing an Mx-cre transgene were cultured for 3 days with or without 100 ng/mL rhuBLyS in the presence or absence of 200 units of IFNα. Viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion. Statistical comparisons between B cells cultured with BLyS and B cells cultured with BLyS and interferon (P > .05, not significant; **P < .01; ***P < .001). Each point is the average of 3 determinations in this representative experiment done 3 times. Nil indicates cells cultured without BLyS or IFNα.
We also found that Mcl-1f/wt B cells cocultured with BLyS in the absence of IFNα were better protected form death in vitro than B cells expressing Mcl-1f/null alleles (P < .001, Figure 6A). We speculated that gene dose could diminish the amount of Mcl-1 protein found in the absence of interferon and account for the difference in BLyS-mediated protection. Indeed, the amount of Mcl-1 protein in untreated Mcl-1f/null B cells was approximately half that found in either Mcl-1f/f or Mcl-1f/wt B cells (Figure 6B). To determine whether the amount of Mcl-1 protein influenced BLyS-dependent protection, we assessed B-cell viability of Mcl-1f/wt, Mcl-1f/f, and Mcl-1f/null populations cultured with and without BLyS in the presence or absence of IFN. In the absence of IFN, BLyS-dependent survival was comparable for Mcl-1f/wt and Mcl-1f/f B cells (P, not significant) throughout the culture period, whereas Mcl-1f/null B cells were protected significantly less well (P < .01-.001) compared with Mcl-1f/wt and Mcl-1f/f populations (Figure 6C). When Mcl-1 was excised after IFN-induced Cre expression, the protective effect of BLyS was lost in both Mcl-1f/f and Mcl-1f/null cells but unaffected in Mcl-1f/wt B cells (comparing BLyS to BLyS plus IFNα, Figure 6C). These data suggest that Mcl-1 expression is required for BLyS-dependent survival, and the amount of available Mcl-1 protein dictates the efficiency of BLyS protection.
Modulation of Mcl-1 protein by rapamycin and Pim and B-cell depletion in vivo in Pim-deficient mice treated with rapamycin
Mcl-1 is a short-lived protein needing constant translational replenishment.39 Both mTOR and Pim 2 inactivate the translation inhibitor 4E-BP1,34,40 suggesting in the absence of BLyS that both of these pathways would be dormant and the production of Mcl-1 protein reduced. To model this condition, we assayed Mcl-1 protein in cultured apoptosis–resistant Bcl-2-tg+ B cells. Consistent with the hypothesis, we found Mcl-1 is reduced in B cells cultured unstimulated for 1 to 10 days, whereas Mcl-1 was induced/maintained in cultures supplemented with BLyS (Figure S4).
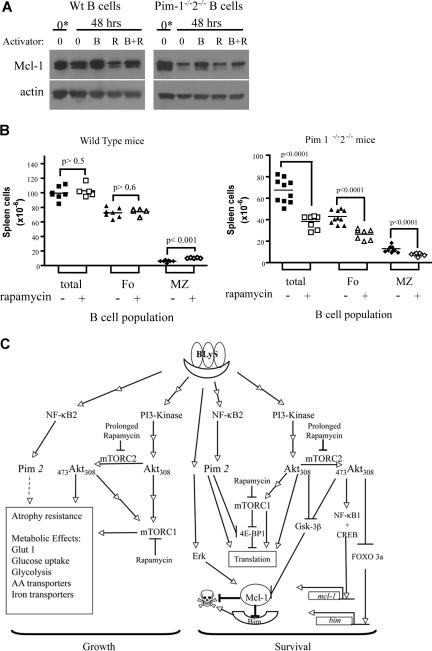
We showed previously that Pim-deficient B cells become refractory to BLyS-mediated protection when cultured with rapamycin (Figure 5B). To determine if Mcl-1 expression were sensitive to combined rapamycin treatment and Pim deficiency, we assessed Mcl-1 protein in cell extracts from wild-type or Pim 1– and 2–deficient B cells cultured with and without BLyS and/or rapamycin. There was a decline in Mcl-1 protein in unstimulated normal B cells over 2 days in culture exacerbated somewhat by rapamycin (Figure 7A). Normal B cells cultured with BLyS, however, maintained a higher amount of Mcl-1 than vehicle or rapamycin-treated B cells, which was not significantly diminished by culture with BLyS and rapamycin combined (Figure 7A). BLyS stimulation also maintained Mcl-1 expression in Pim 1– and 2–deficient B cells, but rapamycin had a stronger inhibitory effect; Mcl-1 protein in B cells cocultured with BLyS and rapamycin was comparable with that seen in vehicle or rapamycin-treated populations (Figure 7A). Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL proteins were unaffected by Pim deficiency, BLyS, or rapamycin treatment (Figure S3).
Figure 7.
Modulation of Mcl-1 by BLyS, rapamycin and Pim; reduction of peripheral B-cell populations in Pim 1 and 2 doubly deficient mice receiving rapamycin in vivo; and a minimal molecular model of BLyS-dependent growth and survival. (A) Modulation of Mcl-1 protein by BLyS, rapamycin, and Pim. Extracts of small resting wild-type or Pim 1−/−2−/− B cells either freshly isolated (*) or cultured for 2 days in CM with or without rhuBLyS (50 ng/mL) and with vehicle or rapamycin (50 nM) were electrophoretically separated and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were probed with anti–Mcl-1 antibody, stripped, and reprobed with anti-actin antibody. (B) Peripheral B-cell survival in rapamycin-treated mice; 5- to 8-week-old Pim 1−/−2−/− doubly deficient or normal littermates were injected intraperitoneally with 2.5 mg/kg of rapamycin or diluent every other day for 6 days and killed on day 7. The number of viable spleen cells from individual mice was determined by counting and trypan blue exclusion. Peripheral B-cell subpopulations were identified by flow cytometry of viable lymphocytes stained for B220, CD 21/35 and CD23. Total B lymphocytes (B220+; □ represents rapamycin-treated donors; ■, diluent-treated donors) were subdivided into marginal zone (MZ: B220+, CD21/35hi, and CD23lo; ◇ represents rapamycin-treated donors; ♦, diluent-treated donors) or follicular (Fo: B220+, CD21/35int, CD23hi; △ represents rapamycin-treated donors; ▲, diluent-treated donors) B-cell subpopulations, and their number in each donor spleen was determined by reference to the splenocyte counts. Data pooled from 2 independent experiments are shown. (C) BLyS-mediated signaling pathways regulating B-cell growth and survival. Stimulation of B cells by BLyS leads to the activation of PI3-kinase, which phosphorylates Akt on T30842 (current study) and by a separate pathway, the processing and nuclear localization of NF-κB2 with the subsequent induction of pim 2 mRNA and production of constitutively active Pim 2 protein.15,17,34 (current study). Akt is fully activated by phosphorylation on S473 mediated by the rictor containing TOR complex mTORC230 (current study). Akt and the raptor containing TOR complex mTORC1 converge to promote rapamycin-sensitive cell growth31,32 (current study) by inducing glucose uptake and use and up-regulating amino acid and iron transporters, which maintain cell size and promote atrophy resistance28,31,47 (current study). Pim 2 also increases glycolysis and promotes maintenance of cell size by a rapamycin-independent, glucose-dependent mechanism34,35 (current study). BLyS-induced survival requires the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family member Mcl-122 (current study). Akt induces the activation of CREB and NF-κB1,44 which promote mcl-1 transcription.73,74 Akt also inactivates FOXO3a,48,56 (current study), suppressing the transcription of the proapoptotic protein Bim, a major regulator of B-cell homeostasis.55,57 Mcl-1 protein levels are controlled at the level of translation by mTORC1 and Pim 2, which inactivate the translational repressor 4E-BP1 by rapamycin-dependent and -independent processes; Mcl-1 protein is stabilized by Erk,76 reported to be induced by BLyS stimulation,20 whereas Mcl-1 turnover is enhanced by the action of Gsk-3b,75 which is inhibited by active Akt48 (current study). Mcl-1 protein is reduced by rapamycin treatment54 (current study). Reference citations in this legend for activities induced by BLyS stimulation are in bold. AA indicates amino acid.
Because either Akt/mTOR or Pim 2 signaling can promote BLyS-dependent B-cell survival in vitro, then the administration of rapamycin in vivo should reduce mature peripheral B cell populations in Pim-deficient but not wild-type mice. To test this prediction, age-matched Pim 1 and 2 doubly deficient mice and wild-type littermates were injected intraperitoneally with rapamycin or diluent every other day for a week before death. Spleen cell populations were quantified and B-cell subpopulations identified by flow cytometry. There was no significant change in the total or follicular B-cell populations in normal mice treated with rapamycin and an increase in marginal zone B cells (7 ± 2 × 10−6 vs 11 ± 1 × 10−6, P < .01; Figure 7B). In marked contrast total, follicular and marginal zone B cells in Pim-deficient mice were all significantly reduced (P < .001), by more than 45%, after a single week of rapamycin treatment (Figure 7B).
Discussion
We demonstrate in these studies that the growth and survival of B lymphocytes are processes regulated directly by BLyS stimulation acting through 2 pathways, Akt/mTOR and Pim 2. B cells, like T cells, removed from the protective niches of the in vivo microenvironment undergo atrophy. Although nutrients are abundant in culture, their entry and use is restricted by the lack of transporters and enzymes regulated by growth factors.1,41 BLyS functions as a growth factor; it increases amino acid and nucleic acid uptake and the glycolytic rate, and it raises basal metabolic activity and blocks B-cell shrinkage. In so doing, BLyS confers a coincident heightened functional responsiveness marked by faster kinetics of proliferation induced with lower doses of activator than is seen in freshly isolated B cells or B cells undergoing atrophy (R.T.W., M.R.S., laboratory observations, December 2006).
The signaling pathways that connect BLyS stimulation to Akt activation and Pim 2 production are an active area of investigation. Akt activation requires PI3-kinase producing phosphoinositides that facilitate membrane localization of Akt and PDK1 with subsequent phosphorylation of Akt at T308; full activation of Akt requires phosphorylation at S473 by a second kinase recently suggested to be PKCβ,42 or the rictor containing mTOR complex mTORC2.29 We find that BLyS-induced Akt phosphorylation at S473 is fully inhibited in primary B cells cultured for 24 hours with rapamycin, revealing a major role for mTORC2 in Akt activation. BLyS stimulation also activates the noncanonical NF-κB2 pathway,15,43 required for the production of Pim 2.17 Akt and Pim 2 can synergize to amplify the canonical NF-κB pathway by activating the serine/threonine kinase Cot promoting the survival of transformed lymphocytes.44 This is consistent with the finding that the selective activation of the canonical NF-kB pathway, by expressing constitutively active IKKβ, replaces BR3-dependent survival signals for peripheral B cells.45
B cells stimulated with BLyS in vitro are rescued from atrophy, a process by which lymphocytes shrink in size when cultured in the absence of growth factors necessary to facilitate nutrient uptake. BLyS-induced atrophy protection was fully active in normal as well as Pim 1– and 2–deficient B cells and was partially dependent on mTOR, as it could be significantly inhibited by rapamycin. It has been shown previously that atrophy resistance induced by growth factors results from increased glucose uptake and use and the up-regulation of nutrient transporters, and is Akt dependent and rapamycin sensitive.28,46,47 In our studies, we found a rapamycin-insensitive component of BLyS-induced atrophy protection that cannot be explained by the action of Pim1 or 2; BLyS-stimulated Pim-deficient B cells were no more sensitive to atrophy when cultured with rapamycin than wild-type B cells. Pathways upstream of mTORC1 could provide this atrophy protection. Although we found that prolonged rapamycin treatment can block Akt S473 phosphorylation, many of the normal effectors of Akt, Gsk-3, and TSC2, and the mTORC1 effectors, S6 kinase and 4E-BP1, are activated even when mTORC2 is inactive.48 It may be noteworthy that mitogen-induced B-cell growth during blastogenesis requires Akt and NF-κB but is rapamycin-insensitive.49 Our findings with B cells support the notion that growth factor–dependent regulation of metabolism is a common attribute of the homeostasis of resting lymphocytes.
The action of Akt/mTOR and Pim 2 fully accounts for ex vivo B cell viability mediated by BLyS stimulation. This is shown by our finding that rapamycin, an acute inhibitor of mTORC1, and chronic regulator of Akt completely suppresses BLyS-dependent survival in Pim 2–deficient B cells but has no effect on Pim 2–sufficient wild-type B cells. Akt has been shown to act in parallel with other signaling pathways to effect growth factor–dependent survival in lymphocytes.21,36 In these instances, inhibition of the overlapping pathway by mutation or drugs renders the cells susceptible to rapamycin-induced death. The survival and growth promoting properties of Akt are well known,27,50–52 and inhibitors of PI3 kinase provoke apoptosis in B cells.42,53 The rapamycin sensitivity of BLyS-induced protection in the absence of Pim 2 is probably because of the translational enhancement necessary to maintain the short-lived protein Mcl-154 in primary B cells, and it is noteworthy that Pim 2 modulation of translation is rapamycin resistant.21,33 Alternatively, Akt phosphorylates and inactivates FOXO3a, a transcription factor necessary for Bim expression.55,56 Because Bim is a major regulator of B cells,57 suppression of this key proapoptotic protein could also occur through BLyS stimulation. Furthermore, FOXO3a phosphorylation is dependent on the action of Akt 308/47348 and would be sensitive to the destabilization of the mTORC2 complex by chronic rapamycin treatment of B cells. Of the 3 members of the Pim kinase family, only Pim 2 appears to be required for BLyS-dependent survival. BLyS did not protect B cells deficient in Pim 2 when mTOR was inhibited, although Pim 1 was readily induced by BLyS stimulation of Pim 2–deficient B cells. These results also suggest that Pim 3, if induced, is unnecessary for rapamycin resistant apoptosis protection.
The molecular basis for BLyS-dependent apoptosis attenuation has been controversial. It has been reported that BLyS stimulation: (1) up-regulates the Bcl-2 family of antiapoptotic proteins including, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, or Bfl-1/A1,17–19,58 (2) inhibits the induction or function of the proapoptotic proteins Bak, Bim, or Bad17,20,59,60 and/or (3) blocks the translocation of catalytically active PKCδ to the nucleus preventing histone phosphorylation leading to apoptosis.61,62 Recent studies using murine and human B cells and our own data have failed to show consistent up-regulation of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, or Bfl-1/A1,16,63–65 and B cells deficient in PKCβ were not rescued by BLyS, although PKCδ translocation to the nucleus was blocked.42
Mcl-1 is an antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family member necessary for mature B and T cell survival.22 Mcl-1 is known to interact preferentially with and sequester the proapoptotic proteins Bak,66 Bax,67 and Bim,22,68 the major negative regulators of B-cell homeostasis.69 Our studies show that BLyS modulates Mcl-1 protein and that BLyS could not induce apoptosis protection in B cells when the Mcl-1 gene was deleted. Unlike other Bcl-2 family members Mcl-1 has a relatively short half-life and is dynamically regulated39; suppression of the Akt pathway70,71 or mTOR,54 results in a decline of Mcl-1 protein and the induction of apoptosis in hematopoietic cells. As for Pim 2, it is known that Pims and Akt/mTOR can mediate overlapping functions,72 and both can activate the canonical NF-κB pathway through the serine/threonine kinase Cot producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein (CREB) and NF-kB, transcription factors critical for Mcl-1 expression.73,74 Pim 2 and mTOR both inactivate the translation inhibitor 4E-BP1, enhancing translation efficiency.34,40 Akt and Pim 2 both inhibit Gsk-3β, which, when active, phosphorylates Mcl-1, leading to its ubiquitinylation and accelerated decay.75 BLyS induces the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk),20 which can phosphorylate Mcl-1 at T163 slowing turnover76 and also reduces the formation of enzymatically active PKCδ, which phosphorylates and accelerates the catabolism of Mcl-1.77 Accordingly, BLyS stimulation of Akt/mTOR and Pim 2 can regulate the expression and/or maintenance of Mcl-1 at the transcriptional, translational, and posttranslational levels.
BLyS supports the survival of malignant, autoreactive B cells and normal B cells. Multiple myelomas, lymphomas, and non-Hodgkin leukemias use BLyS for survival,78–82 and a subset of transformed B cells can produce BLyS, establishing a pathologic autocrine loop associated with poor disease prognosis.80 Dysregulated BLyS expression is also seen in rheumatic diseases, such as arthritis, lupus erythematosis, and Sjogren.83–86 In autoimmune responses, BLyS stimulation overcomes tolerance rescuing autoreactive B cells normally targeted for elimination.60,87 These considerations have fostered a clinical approach for treating both autoimmune B cells and B-cell cancers, which consists of inactivating BLyS with monoclonal antibodies or recombinant decoy receptors.88–90 We suggest that pharmacologic inhibition of B-cell survival signaling may be a useful adjunct to this current approach. BLyS is expressed as a biologically active membrane bound or soluble ligand,91,92 and inhibition of membrane-bound ligand may require higher concentrations of BLyS competitor than are feasible.
The identification of 2 and only 2 pathways, Akt/mTOR and Pim 2 mediating BLyS-induced survival, reduces the array of pharmacologic targets for clinical intervention. Indeed, we find that simultaneously targeting these pathways using a brief course of rapamycin treatment in Pim 1– and 2–deficient mice significantly reduced both marginal zone and follicular B cell populations without affecting Pim-sufficient littermate controls. Rapamycin is a well-tolerated and highly efficient inhibitor of mTOR, and genetically induced Pim 2 deficiencies are relatively benign,93 as most biologic processes mediated by Pim 2, other than B-cell survival, can be effected by other members of the Pim family. A combination therapy targeting mTOR and Pim 2 may have clinical efficacy for the treatment pathogenic B cells.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sarah Kenward for expert technical assistance, the members of the Thompson and Woodland laboratories for helpful comments and support, and Dr Randolph Noelle (Dartmouth Medical School) for special reagents. The contents of this publication are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
This work was supported by NIH grants AI041054 and AI057463 (C.B.T., R.T.W.), an institutional Diabetes Endocrinology Research Center grant DK32520, and a Special Fellowship from the Leukemia Society (3277-05; C.J.F.).
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: R.T.W. conceived and designed the research plan, performed experiments, and wrote the manuscript; C.J.F. and P.S.H. contributed to the research plan and provided critical reagents; J.T.O., S.J.K., and D.M.H. provided critical reagents; M.R.S. performed experiments and contributed to the research plan; and C.B.T. contributed to the experimental design and interpretation.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: D.M.H. owns stock in Human Genome Sciences. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Stanley J. Korsmeyer died on March 31, 2005.
Correspondence: Robert T. Woodland, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology, 55 Lake Ave N, Worcester, MA 01655; e-mail: Robert.Woodland@umassmed.edu.
References
- 1.Plas DR, Rathmell JC, Thompson CB. Homeostatic control of lymphocyte survival: potential origins and implications. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:515–521. doi: 10.1038/ni0602-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Tschopp J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002;27:19–26. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(01)01995-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Varfolomeev E, Kischkel F, Martin F, et al. APRIL–deficient mice have normal immune system development. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:997–1006. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.3.997-1006.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O'Connor BP, Raman VS, Erickson LD, et al. BCMA is essential for the survival of long-lived bone marrow plasma cells. J Exp Med. 2004;199:91–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rolink AG, Melchers F. BAFFled B cells survive and thrive: roles of BAFF in B-cell development. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:266–275. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(02)00332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schiemann B, Gommerman JL, Vora K, et al. An essential role for BAFF in the normal development of B cells through a BCMA-independent pathway. Science. 2001;293:2111–2114. doi: 10.1126/science.1061964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gross JA, Dillon SR, Mudri S, et al. TACI-Ig neutralizes molecules critical for B cell development and autoimmune disease: impaired B cell maturation in mice lacking BLyS. Immunity. 2001;15:289–302. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mackay F, Schneider P, Rennert P, Browning J. BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B-cell survival. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:231–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Groom JR, Fletcher CA, Walters SN, et al. BAFF and MyD88 signals promote a lupuslike disease independent of T cells. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1959–1971. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kalled SL. The role of BAFF in immune function and implications for autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 2005;204:43–54. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Seshasayee D, Valdez P, Yan M, Dixit VM, Tumas D, Grewal IS. Loss of TACI causes fatal lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity, establishing TACI as an inhibitory BLyS receptor. Immunity. 2003;18:279–288. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thompson JS, Bixler SA, Qian F, et al. BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically interacts with BAFF. Science. 2001;293:2108–2111. doi: 10.1126/science.1061965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Smith SH, Cancro MP. Cutting edge: B cell receptor signals regulate BLyS receptor levels in mature B cells and their immediate progenitors. J Immunol. 2003;170:5820–5823. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.12.5820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shulga-Morskaya S, Dobles M, Walsh ME, et al. B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family acts through separate receptors to support B-cell survival and T cell-independent antibody formation. J Immunol. 2004;173:2331–2341. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.4.2331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Claudio E, Brown K, Park S, Wang H, Siebenlist U. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-kappa B2 in maturing B cells. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:958–965. doi: 10.1038/ni842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zarnegar B, He JQ, Oganesyan G, Hoffmann A, Baltimore D, Cheng G. Unique CD40–mediated biological program in B cell activation requires both type 1 and type 2 NF-kappaB activation pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:8108–8113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402629101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Enzler T, Bonizzi G, Silverman GJ, et al. Alternative and classical NF-kappaB signaling retain autoreactive B cells in the splenic marginal zone and result in lupus-like disease. Immunity. 2006;25:403–415. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Do RK, Hatada E, Lee H, Tourigny MR, Hilbert D, Chen-Kiang S. Attenuation of apoptosis underlies B lymphocyte stimulator enhancement of humoral immune response. J Exp Med. 2000;192:953–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hatada EN, Do RK, Orlofsky A, et al. NF-kappa B1 p50 is required for BLyS attenuation of apoptosis but dispensable for processing of NF-kappa B2 p100 to p52 in quiescent mature B cells. J Immunol. 2003;171:761–768. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.2.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Craxton A, Draves KE, Gruppi A, Clark EA. BAFF regulates B-cell survival by downregulating the BH3-only family member Bim via the ERK pathway. J Exp Med. 2005;202:1363–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fox CJ, Hammerman PS, Thompson CB. The Pim kinases control rapamycin-resistant T cell survival and activation. J Exp Med. 2005;201:259–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.20042020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Opferman JT, Letai A, Beard C, Sorcinelli MD, Ong CC, Korsmeyer SJ. Development and maintenance of B and T lymphocytes requires antiapoptotic MCL-1. Nature. 2003;426:671–676. doi: 10.1038/nature02067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Woodland RT, Schmidt MR, Korsmeyer SJ, Gravel KA. Regulation of B-cell survival in xid mice by the proto-oncogene bcl-2. J Immunol. 1996;156:2143–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.McDonnell TJ, Deane N, Platt FM, et al. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B-cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989;57:79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Woodland RT, Schmidt MR, Riggs JE, Korsmeyer SJ, Lussier AM, Gravel KA. Radiation-induced apoptosis is differentially regulated in primary B cells from normal mice and mice with the CBA/N X-linked immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 1995;155:3453–3463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bauer DE, Harris MH, Plas DR, et al. Cytokine stimulation of aerobic glycolysis in hematopoietic cells exceeds proliferative demand. FASEB J. 2004;18:1303–1305. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1001fje. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tumang JR, Owyang A, Andjelic S, et al. c-Rel is essential for B lymphocyte survival and cell cycle progression. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:4299–4312. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199812)28:12<4299::AID-IMMU4299>3.0.CO;2-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rathmell JC, Farkash EA, Gao W, Thompson CB. IL-7 enhances the survival and maintains the size of naive T cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:6869–6876. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.12.6869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005;307:1098–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.1106148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, et al. Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell. 2006;22:159–168. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Edinger AL. Controlling cell growth and survival through regulated nutrient transporter expression. Biochem J. 2007;406:1–12. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Edinger AL, Thompson CB. Akt maintains cell size and survival by increasing mTOR–dependent nutrient uptake. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13:2276–2288. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-12-0584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fox CJ, Hammerman PS, Thompson CB. Fuel feeds function: energy metabolism and the T-cell response. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:844–852. doi: 10.1038/nri1710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fox CJ, Hammerman PS, Cinalli RM, Master SR, Chodosh LA, Thompson CB. The serine/threonine kinase Pim-2 is a transcriptionally regulated apoptotic inhibitor. Genes Dev. 2003;17:1841–1854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1105003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hammerman PS, Fox CJ, Birnbaum MJ, Thompson CB. Pim and Akt oncogenes are independent regulators of hematopoietic cell growth and survival. Blood. 2005;105:4477–4483. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shinjyo T, Kuribara R, Inukai T, et al. Downregulation of Bim, a proapoptotic relative of Bcl-2, is a pivotal step in cytokine-initiated survival signaling in murine hematopoietic progenitors. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:854–864. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.3.854-864.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhu N, Ramirez LM, Lee RL, Magnuson NS, Bishop GA, Gold MR. CD40 signaling in B cells regulates the expression of the Pim-1 kinase via the NF-kappa B pathway. J Immunol. 2002;168:744–754. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.2.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Domen J, van der Lugt NM, Laird PW, et al. Impaired interleukin-3 response in Pim-1–deficient bone marrow-derived mast cells. Blood. 1993;82:1445–1452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Craig RW. MCL1 provides a window on the role of the BCL2 family in cell proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. Leukemia. 2002;16:444–454. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chen WW, Chan DC, Donald C, Lilly MB, Kraft AS. Pim family kinases enhance tumor growth of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2005;3:443–451. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vander Heiden MG, Plas DR, Rathmell JC, Fox CJ, Harris MH, Thompson CB. Growth factors can influence cell growth and survival through effects on glucose metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:5899–5912. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.17.5899-5912.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Patke A, Mecklenbrauker I, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Tarakhovsky A. BAFF controls B cell metabolic fitness through a PKC beta- and Akt–dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2551–2562. doi: 10.1084/jem.20060990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kayagaki N, Yan M, Seshasayee D, et al. BAFF/BLyS receptor 3 binds the B-cell survival factor BAFF ligand through a discrete surface loop and promotes processing of NF-kappaB2. Immunity. 2002;17:515–524. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hammerman PS, Fox CJ, Cinalli RM, et al. Lymphocyte transformation by Pim-2 is dependent on nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8341–8348. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sasaki Y, Casola S, Kutok JL, Rajewsky K, Schmidt-Supprian M. TNF family member B cell-activating factor (BAFF) receptor–dependent and -independent roles for BAFF in B cell physiology. J Immunol. 2004;173:2245–2252. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.4.2245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zeng Z, Sarbassov dos D, Samudio IJ, et al. Rapamycin derivatives reduce mTORC2 signaling and inhibit AKT activation in AML. Blood. 2007;109:3509–3512. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-030833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wieman HL, Wofford JA, Rathmell JC. Cytokine stimulation promotes glucose uptake via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt regulation of Glut1 activity and trafficking. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:1437–1446. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-07-0593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, et al. SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell. 2006;127:125–137. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Grumont RJ, Strasser A, Gerondakis S. B cell growth is controlled by phosphatidylinosotol 3-kinase–dependent induction of Rel/NF-kappaB regulated c-myc transcription. Mol Cell. 2002;10:1283–1294. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00779-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Andjelic S, Hsia C, Suzuki H, Kadowaki T, Koyasu S, Liou HC. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and NF-kappa B/Rel are at the divergence of CD40–mediated proliferation and survival pathways. J Immunol. 2000;165:3860–3867. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.7.3860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vivarelli MS, McDonald D, Miller M, Cusson N, Kelliher M, Geha RS. RIP links TLR4 to Akt and is essential for cell survival in response to LPS stimulation. J Exp Med. 2004;200:399–404. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Otero DC, Omori SA, Rickert RC. Cd19–dependent activation of Akt kinase in B-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:1474–1478. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003918200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Plate JM. PI3-kinase regulates survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells by preventing caspase 8 activation. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004;45:1519–1529. doi: 10.1080/10428190410001683642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Woltman AM, van der Kooij SW, Coffer PJ, Offringa R, Daha MR, van Kooten C. Rapamycin specifically interferes with GM-CSF signaling in human dendritic cells, leading to apoptosis via increased p27KIP1 expression. Blood. 2003;101:1439–1445. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, et al. The forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J Immunol. 2002;168:5024–5031. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.10.5024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cappellini A, Tabellini G, Zweyer M, et al. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway regulates cell cycle progression of HL60 human leukemia cells through cytoplasmic relocalization of the cyclin–dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) and control of cyclin D1 expression. Leukemia. 2003;17:2157–2167. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DC, et al. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science. 1999;286:1735–1738. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5445.1735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hsu BL, Harless SM, Lindsley RC, Hilbert DM, Cancro MP. Cutting edge: BLyS enables survival of transitional and mature B cells through distinct mediators. J Immunol. 2002;168:5993–5996. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.5993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Do RK, Chen-Kiang S. Mechanism of BLyS action in B cell immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:19–25. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lesley R, Xu Y, Kalled SL, et al. Reduced competitiveness of autoantigen-engaged B cells due to increased dependence on BAFF. Immunity. 2004;20:441–453. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(04)00079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mecklenbräuker I, Kalled SL, Leitges M, Mackay F, Tarakhovsky A. Regulation of B-cell survival by BAFF–dependent PKCdelta–mediated nuclear signalling. Nature. 2004;431:456–461. doi: 10.1038/nature02955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sasaki Y, Derudder E, Hobeika E, et al. Canonical NF-kappaB activity, dispensable for B cell development, replaces BAFF-receptor signals and promotes B cell proliferation upon activation. Immunity. 2006;24:729–739. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Thomas MD, Kremer CS, Ravichandran KS, Rajewsky K, Bender TP. c-Myb is critical for B cell development and maintenance of follicular B cells. Immunity. 2005;23:275–286. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Qian Y, Qin J, Cui G, et al. Act1, a negative regulator in CD40- and BAFF–mediated B-cell survival. Immunity. 2004;21:575–587. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Trescol-Biémont MC, Verschelde C, Cottalorda A, Bonnefoy-Berard N. Regulation of A1/Bfl-1 expression in peripheral splenic B cells. Biochimie. 2004;86:287–294. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G, et al. Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1294–1305. doi: 10.1101/gad.1304105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhou P, Qian L, Kozopas KM, Craig RW. Mcl-1, a Bcl-2 family member, delays the death of hematopoietic cells under a variety of apoptosis-inducing conditions. Blood. 1997;89:630–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Han J, Goldstein LA, Gastman BR, Froelich CJ, Yin XM, Rabinowich H. Degradation of Mcl-1 by granzyme B: implications for Bim–mediated mitochondrial apoptotic events. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:22020–22029. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313234200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Takeuchi O, Fisher J, Suh H, Harada H, Malynn BA, Korsmeyer SJ. Essential role of BAX,BAK in B cell homeostasis and prevention of autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:11272–11277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504783102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Liu H, Perlman H, Pagliari LJ, Pope RM. Constitutively activated Akt-1 is vital for the survival of human monocyte-differentiated macrophages: role of Mcl-1, independent of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB, Bad, or caspase activation. J Exp Med. 2001;194:113–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yu C, Rahmani M, Dai Y, et al. The lethal effects of pharmacological cyclin–dependent kinase inhibitors in human leukemia cells proceed through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt–dependent process. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1822–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Amaravadi R, Thompson CB. The survival kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2618–2624. doi: 10.1172/JCI26273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Akgul C, Turner PC, White MR, Edwards SW. Functional analysis of the human MCL-1 gene. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000;57:684–691. doi: 10.1007/PL00000728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wang JM, Chao JR, Chen W, Kuo ML, Yen JJ, Yang-Yen HF. The antiapoptotic gene mcl-1 is up-regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway through a transcription factor complex containing CREB. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:6195–6206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.9.6195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Maurer U, Charvet C, Wagman AS, Dejardin E, Green DR. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis by destabilization of MCL-1. Mol Cell. 2006;21:749–760. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kobayashi S, Lee SH, Meng XW, et al. Serine 64 phosphorylation enhances the antiapoptotic function of Mcl-1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:18407–18417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610010200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sitailo LA, Tibudan SS, Denning MF. The protein kinase C Δ catalytic fragment targets Mcl-1 for degradation to trigger apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:29703–29710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607351200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.He B, Chadburn A, Jou E, Schattner EJ, Knowles DM, Cerutti A. Lymphoma B cells evade apoptosis through the TNF family members BAFF/BLyS and APRIL. J Immunol. 2004;172:3268–3279. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.5.3268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mackay F, Tangye SG. The role of the BAFF/APRIL system in B cell homeostasis and lymphoid cancers. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:347–354. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2004.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Novak AJ, Grote DM, Stenson M, et al. Expression of BLyS and its receptors in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: correlation with disease activity and patient outcome. Blood. 2004;104:2247–2253. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Moreaux J, Legouffe E, Jourdan E, et al. BAFF and APRIL protect myeloma cells from apoptosis induced by interleukin 6 deprivation and dexamethasone. Blood. 2004;103:3148–3157. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-06-1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Jelinek DF, Darce JR. Human B lymphocyte malignancies: exploitation of BLyS and APRIL and their receptors. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2005;8:266–288. doi: 10.1159/000082107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Mackay F, Sierro F, Grey ST, Gordon TP. The BAFF/APRIL system: an important player in systemic rheumatic diseases. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2005;8:243–265. doi: 10.1159/000082106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zhang J, Roschke V, Baker KP, et al. Cutting edge: a role for B lymphocyte stimulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2001;166:6–10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Zhang M, Ko KH, Lam QL, et al. Expression and function of TNF family member B cell-activating factor in the development of autoimmune arthritis. Int Immunol. 2005;17:1081–1092. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Groom J, Kalled SL, Cutler AH, et al. Association of BAFF/BLyS overexpression and altered B cell differentiation with Sjogren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:59–68. doi: 10.1172/JCI14121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Thien M, Phan TG, Gardam S, et al. Excess BAFF rescues self-reactive B cells from peripheral deletion and allows them to enter forbidden follicular and marginal zone niches. Immunity. 2004;20:785–798. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Liu W, Szalai A, Zhao L, et al. Control of spontaneous B lymphocyte autoimmunity with adenovirus-encoded soluble TACI. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1884–1896. doi: 10.1002/art.20290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Riccobene TA, Miceli RC, Lincoln C, et al. Rapid and specific targeting of 125I-labeled B lymphocyte stimulator to lymphoid tissues and B cell tumors in mice. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:422–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Baker KP, Edwards BM, Main SH, et al. Generation and characterization of LymphoStat-B, a human monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the bioactivities of B lymphocyte stimulator. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:3253–3265. doi: 10.1002/art.11299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Schneider P, MacKay F, Steiner V, et al. BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J Exp Med. 1999;189:1747–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nardelli B, Belvedere O, Roschke V, et al. Synthesis and release of B-lymphocyte stimulator from myeloid cells. Blood. 2001;97:198–204. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.1.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Berns A, van der Lugt N, Alkema M, et al. Mouse model systems to study multistep tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1994;59:435–447. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1994.059.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.