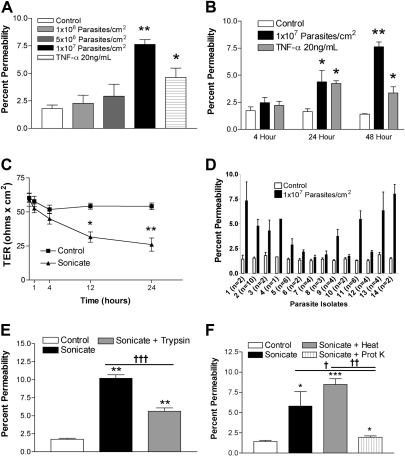
Figure 1.
Changes in endothelial permeability induced by P falciparumsonicates in HDMECs. HDMECs (105/cm2) were seeded in transwells and cultured until 3 days after confluence. (A) Increasing concentrations of parasite sonicates were added for 24 hours. An increase in the flux of FITC-albumin was observed at a threshold of 107 parasite equivalents/cm2. (B) Time course of changes in FITC-albumin flux of HDMEC monolayers incubated with 107 parasite equivalents/cm2. A significant increase in permeability was detected at 24 hours and maintained for at least 48 hours. No response was observed at 4 hours. (C) Time course of changes in transendothelial resistance (TER) of endothelial monolayers incubated with 1 107 parasite equivalents/cm2. A significant decrease in TER was observed at 12 and 24 hours. Experiments in panels A to C were performed with 4 parasite isolates. (D) Variable permeability as determined by FITC-albumin flux of 14 clinical parasite isolates at 107 parasite equivalents/cm2 for 24 hours. Parasite sonicate activity was significantly reduced after overnight (16 h) treatment with (E) trypsin (10 μg/mL) or (F) proteinase K (10 U/mL; n = 3). *P < .05; **P < .01 compared with control values by Student paired t test. For multiple comparisons †P < .05, ††P < .01, and †††P < .001 by ANOVA with post hoc analysis by Tukey test. (A-F) Results are expressed as mean (± SD).