Abstract
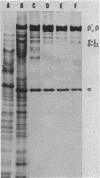
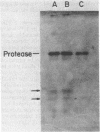
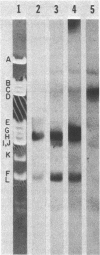
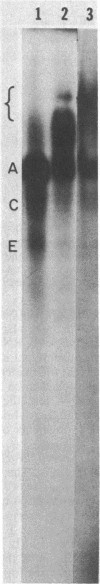
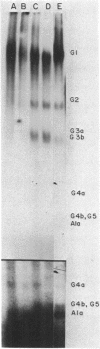
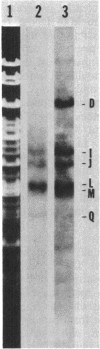
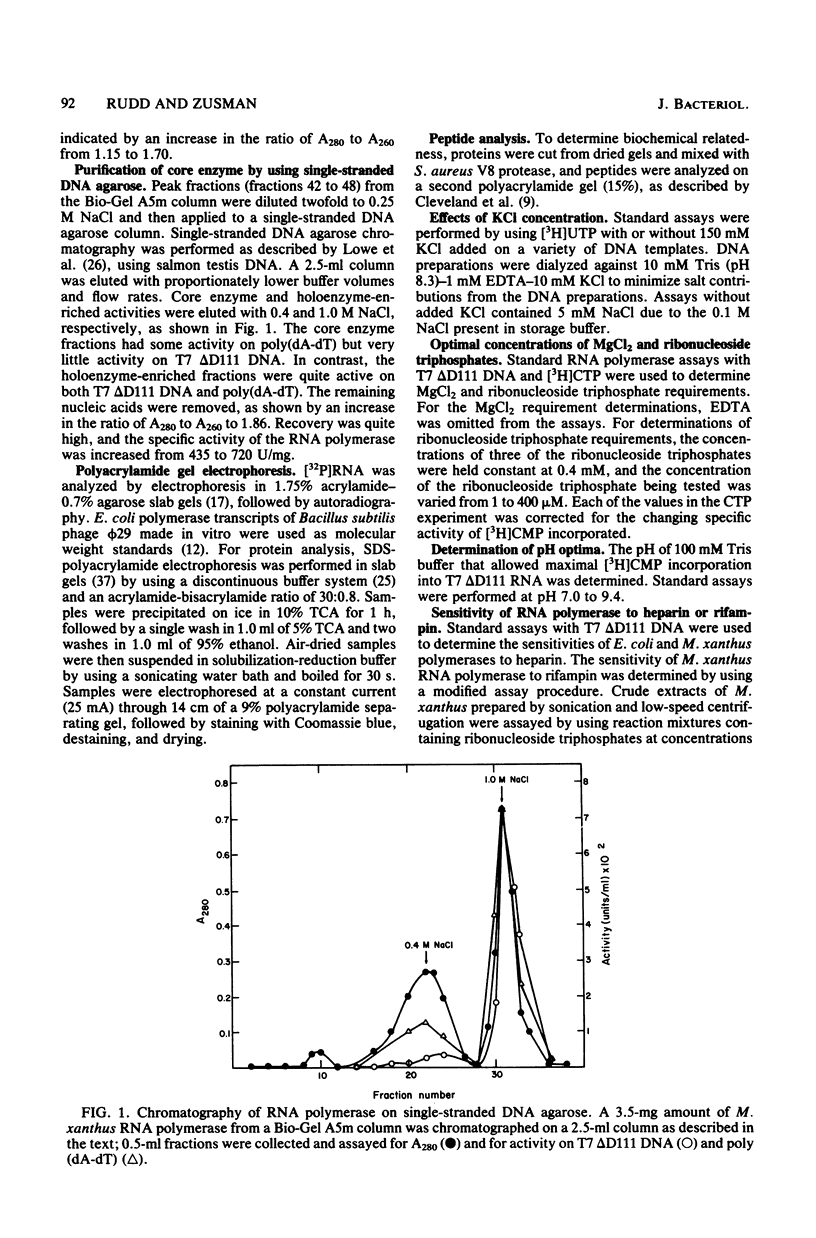
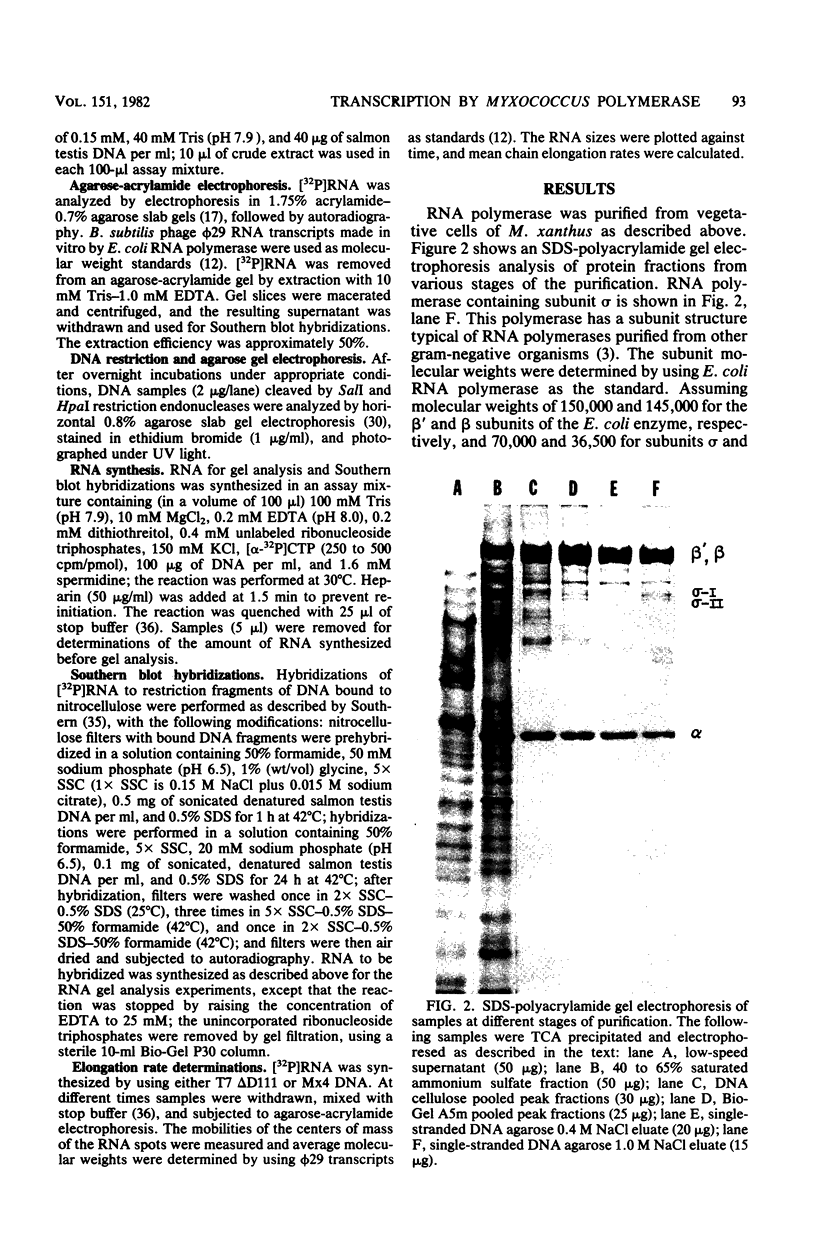
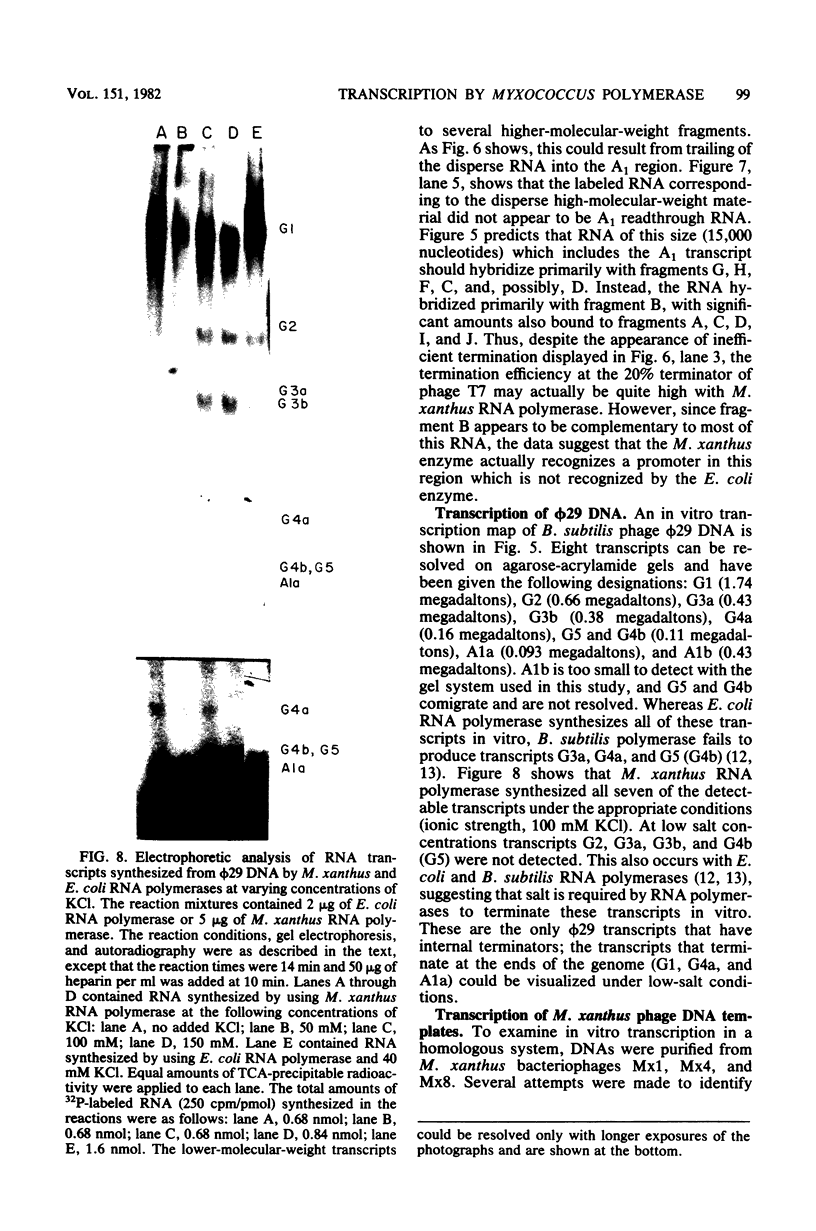
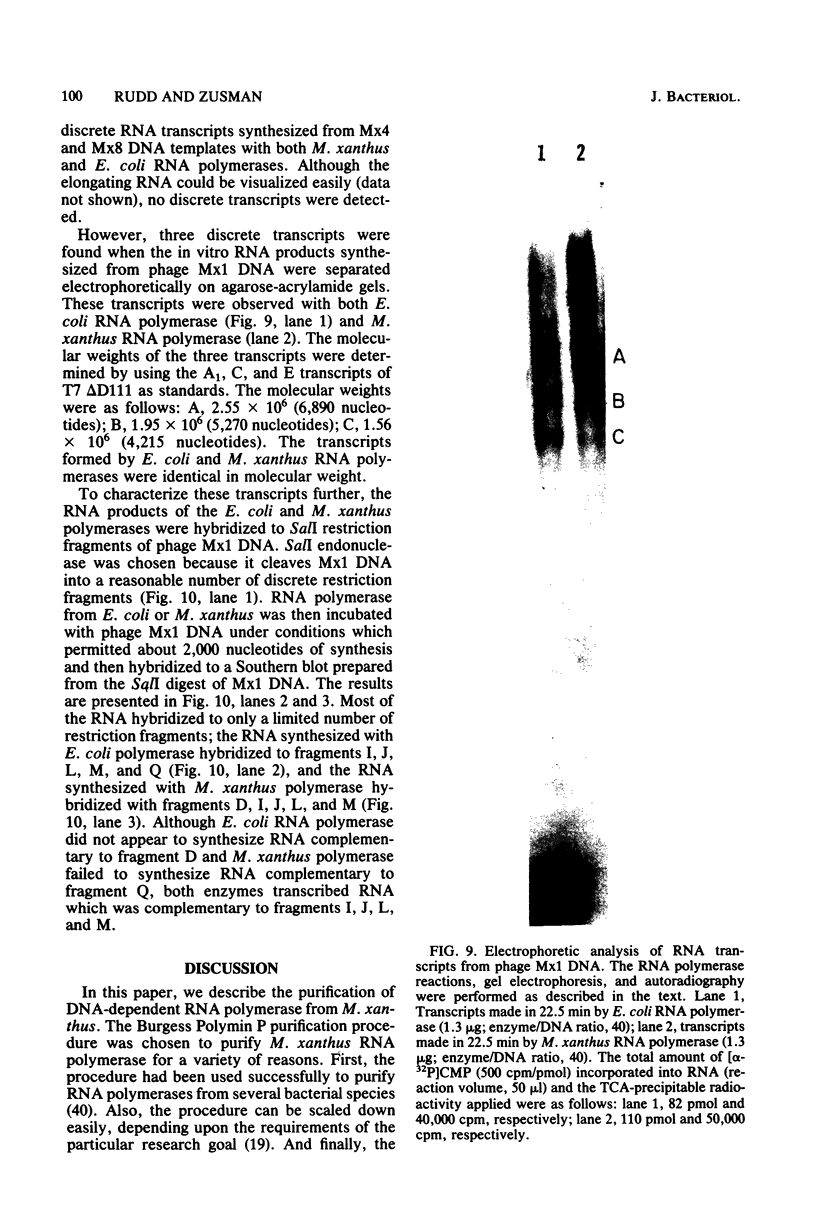
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from vegetative cells of the gram-negative, fruiting bacterium Myxococcus xanthus was purified more than 300-fold by a modified Burgess procedure (Lowe et al., Biochemistry 18:1344-1352, 1979), using Polymin P precipitation, 40 to 65% saturated ammonium sulfate fractional precipitation, double-stranded DNA cellulose chromatography, A5m gel filtration chromatography, and single-stranded DNA agarose chromatography. The last step separated the RNA polymerase into a core fraction and an enriched holoenzyme fraction. The core enzyme showed a subunit structure similar to that of the Escherichia coli polymerase, as follows: beta' and beta (145,000 and 140,000 daltons, respectively) and alpha (38,000 daltons). A comparison of the core enzyme and the holoenzyme implicated two polypeptides as possible sigma subunits. These polypeptides were closely related, as indicated by peptide analysis. M. xanthus RNA polymerase was capable of transcribing DNAs from E. coli phages T7, T4, and lambda, Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29, and M. xanthus phages Mx1, Mx4, and Mx8. Transcription of T7 and phi 29 DNAs was stimulated by KCl, whereas transcription of Mx1, Mx4, and Mx8 DNAs was inhibited by KCl. Magnesium ion dependence, rifampin and heparin sensitivities, and spermidine stimulation of M. xanthus RNA polymerase activity were similar to those found with E. coli RNA polymerase. The pH optimum of M. xanthus RNA polymerase activity was more basic than that of E. coli polymerase. M. xanthus RNA polymerase was capable of selective transcription in vitro when DNAs from phages T7 delta 111, phi 29, and Mx1 were used. The molecular weights of the resulting phage RNA transcripts made by M. xanthus RNA polymerase (as determined by agarose-acrylamide slab gel electrophoresis) were the same as the molecular weights of the transcripts synthesized by E. coli RNA polymerase. No discrete transcripts were detected as the in vitro RNA products of M. xanthus phage Mx4 and Mx8 DNA transcription. Southern transcript synthesized by M. xanthus RNA polymerase. Three transcripts (transcripts A, B, and C; molecular weights, 2.55 X 10(6), 1.95 X 10(6), and 1.56 X 10(6), respectively) were identified as in vitro RNA products of M. xanthus phage Mx1 DNA transcription when either E. coli or M. xanthus RNA polymerase was used. A Southern blot hybridization analysis indicated that the E. coli RNA polymerase and the M. xanthus RNA polymerase transcribe common SalI restriction fragments of Mx1 DNA.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown N. L., Burchard R. P., Morris D. W., Parish J. H., Stow N. D., Tsopanakis C. Phage and defective phage of strains of Myxococcus. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Jul;108(3):271–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00454852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Dworkin M. A bacteriophage for Myxococcus xanthus: isolation, characterization and relation of infectivity to host morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1305–1313. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1305-1313.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J., Nierman W. C., Wiggs J., Neff N. A quantitative assay for bacterial RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10061–10069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Purification and characterization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin, a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12581–12588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Specificity of promoter site utilization in vitro by bacterial RNA polymerases on Bacillus phage phi 29 DNA. Transcription mapping with exonuclease III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8819–8830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. T7 early RNAs are generated by site-specific cleavages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisselsoder J., Campos J. M., Zusman D. R. Physical characterization of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90432-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golomb M., Chamberlin M. A preliminary map of the major transcription units read by T7 RNA polymerase on the T7 and T3 bacteriophage chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Novel RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. D., Martinez I. I., Calendar R. A gene from Escherichia coli affecting the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1836–1840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus: pattern of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Harada W., Zusman D., Inouye M. Development-specific protein S of Myxococcus xanthus: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):678–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.678-683.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Williams R. C., Chamberlin M. J. Electron microscopic studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. II. Formation of multiple promoter-like complexes at non-promoter sites. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 5;136(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel W. F., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of ribonucleic acid chain initiation by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase bound to T7 deoxyribonucleic acid. I. An assay for the rate and extent of ribonucleic acid chain initiation. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):2995–3001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Sodergren E., Masuda T., Kaiser D. Systematic isolation of transducing phages for Myxococcus xanthus. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):44–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Localization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin in the periplasmic space and on the cell surface of Myxococcus xanthus during developmental aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12589–12595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K., Zusman D. R. Rifampin-resistant mutants of Myxococcus xanthus defective in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):295–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.295-300.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Chamberlin M. J. An expanded transcriptional map of T7 bacteriophage. Reading of minor T7 promoter sites in vitro by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 5;112(4):577–601. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti S., Zusman D. R. Genetic characterization of aggregation-defective developmental mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):768–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.768-775.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, McConnell D., Rodriguez R. L. Isolation of E.coli promoters from the late region of bacteriophage T7 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):439–447. doi: 10.1007/BF00425860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Bush J. W., Chamberlin M. J. Utilization of promoter and terminator sites on bacteriophage T7 DNA by RNA polymerases from a variety of bacterial orders. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Heterogeneity of RNA polymerase in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for an additional sigma factor in vegetative cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R., Krotoski D. M., Cumsky M. Chromosome replication in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):122–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.122-129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]