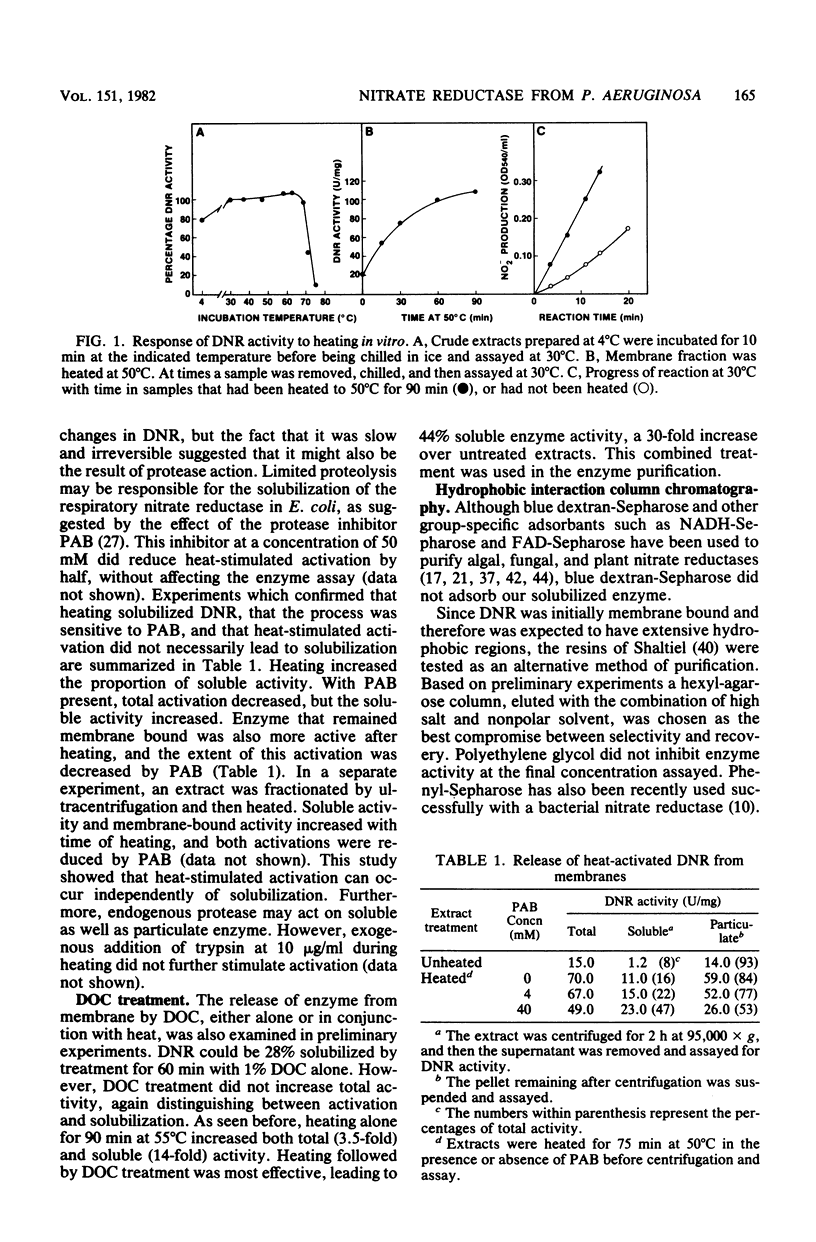
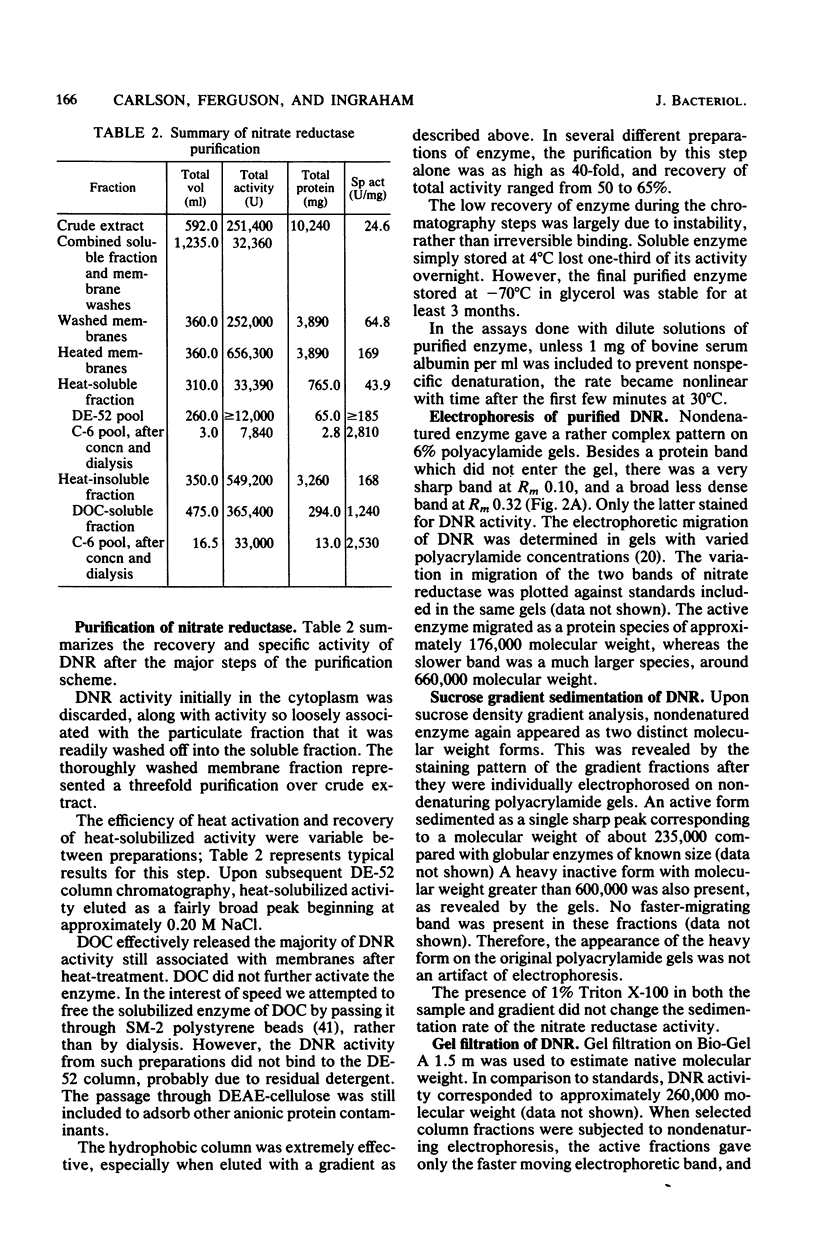
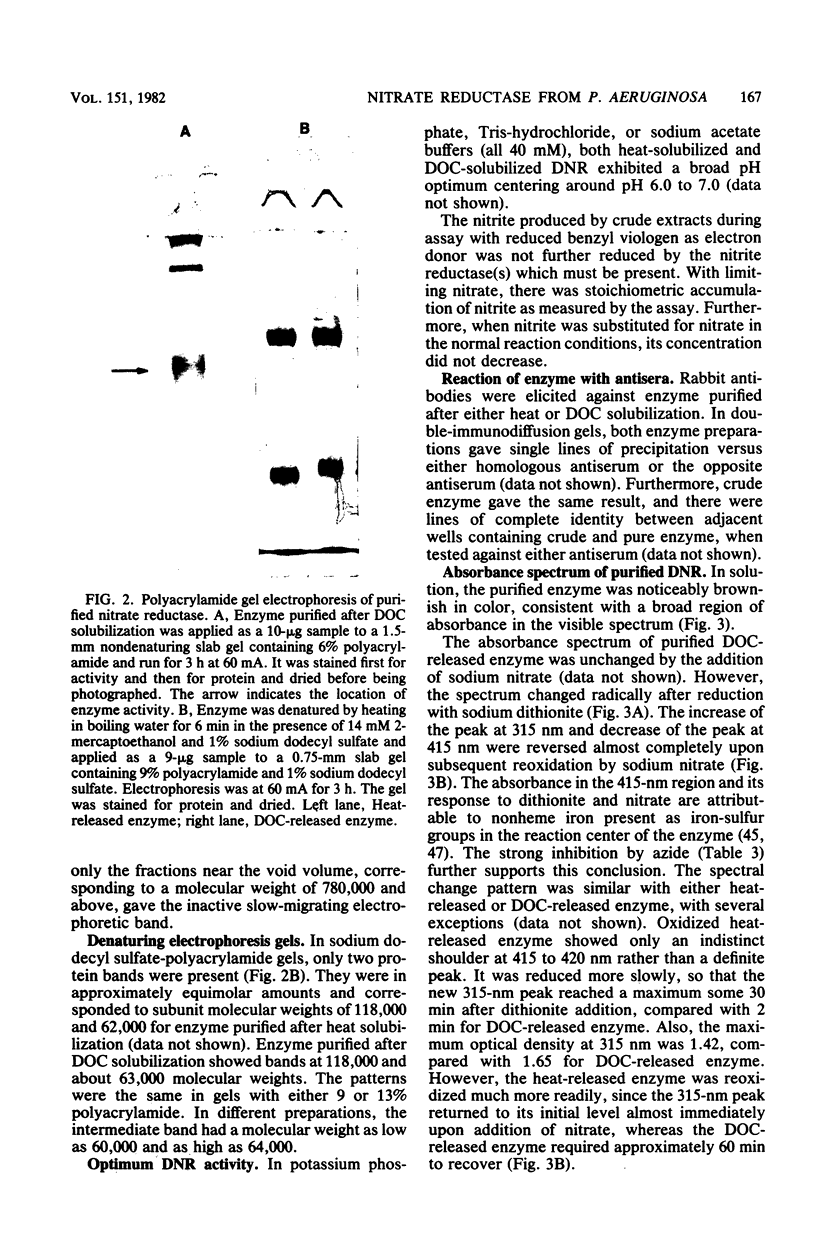
Abstract
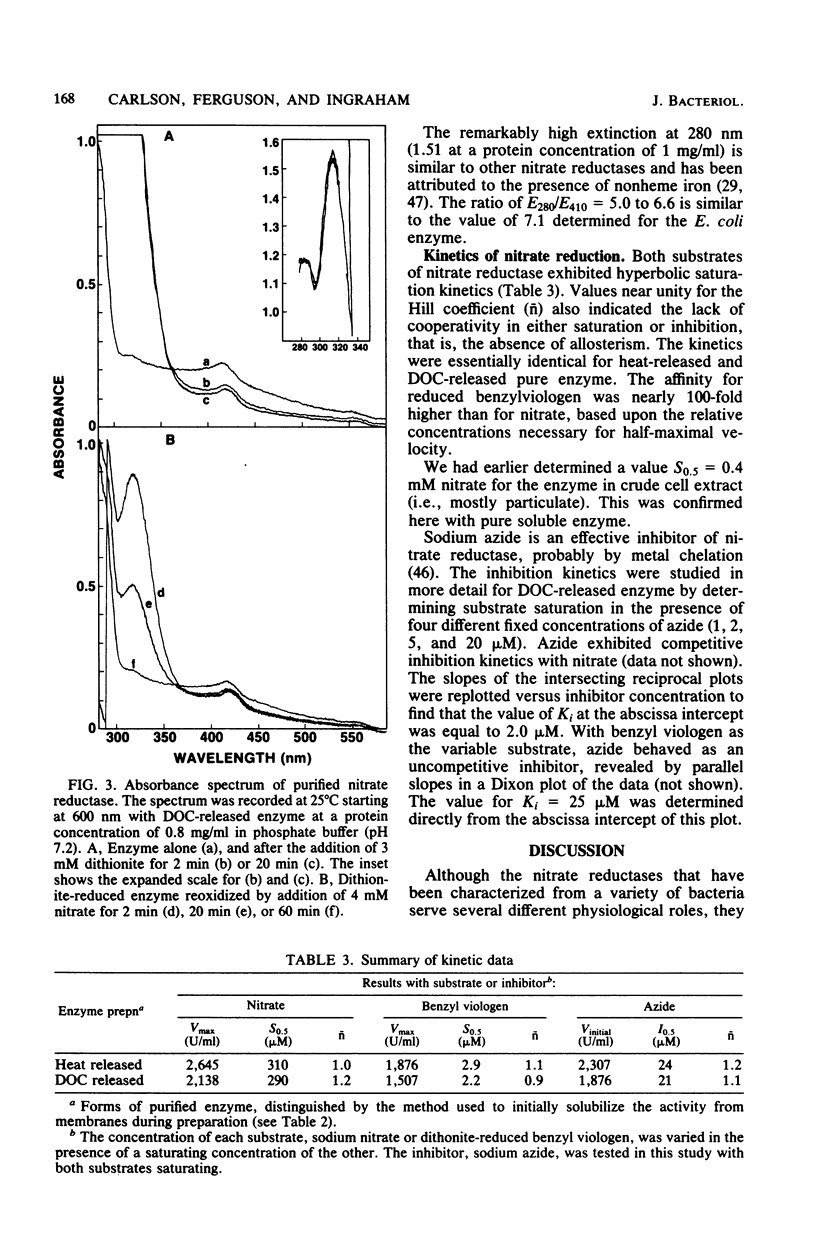
Dissimilatory nitrate reductase was purified to homogeneity from anaerobic cultures of the denitrifying bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The following procedures were used in the rapid isolation of this unstable enzyme: induction by nitrate in semianaerobic cell suspension, heat-stimulated activation and solubilization from the membrane fraction, and purification by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. The molecular weight of the purified enzyme was estimated by nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, sucrose density gradient sedimentation, and gel filtration chromatography. Subunit molecular weights were estimated by electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. The active enzyme monomer, with a molecular weight of 176,000 to 260,000 (depending upon the method of determination), was composed of subunits with molecular weights of approximately 64,000 and 118,000. The monomer aggregated to form an inactive tetramer of about 800,000 molecular weight. Purified enzyme exhibited a broad pH optimum, between 6.5 and 7.5. Kinetic studies showed that the apparent Km was 0.30 mM for nitrate, and 2.2 to 2.9 microM for dithionite-reduced benzyl viologen. Azide was an effective inhibitor: the concentration required for half-maximal inhibition was 21 to 24 microM. Azide inhibition was competitive with nitrate (Ki = 2.0 microM) but uncompetitive with reduced benzyl viologen (Ki = 25 microM). Based upon spectral evidence, the purified molybdo-enzyme had no associated cytochromes but did contain nonhaem iron that responded to dithionite reduction and nitrate oxidation. The enzyme that was purified after being heat solubilized from membranes had properties essentially identical to those of the enzyme that was purified after deoxycholate solubilization.
Full text
PDF





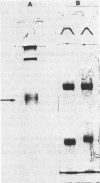
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON D. E., HATHAWAY J. A., SMITH E. C. KINETICS OF REGULATORY ENZYMES. KINETIC ORDER OF THE YEAST DIPHOSPHOPYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE ISOCITRATE DEHYDROGENASE REACTION AND A MODEL FOR THE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2682–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke K. A., Lascelles J. Partial purification and some properties of the Staphylococcus aureus cytoplasmic nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):120–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.120-125.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder K., Burke K. A., Lascelles J. Induction of nitrate reductase and membrane cytochromes in wild type and chlorate-resistant Paracoccus denitrificans. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jun;126(2):149–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00511220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. A. Purification and some properties of nitrate reductase (EC 1.7.99.4) from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1530533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMoss J. A. Limited proteolysis of nitrate reductase purified from membranes of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1696–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMoss J. A. Role of the chlC gene in formation of the formate-nitrate reductase pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):626–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.626-630.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwiche C. C. The nitrogen cycle. Sci Am. 1970 Sep;223(3):137–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demoss J. A., Fan T. Y., Scott R. H. Characterization of subunit structural alterations which occur during purification of nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jan;206(1):54–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEWSON C. A., NICHOLAS D. J. Nitrate reductase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 May 13;49:335–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget P. Les nitrate-réductases bactériennes. Solubilisation, purification et propriétés de l'enzyme A de Micrococcus denitrificans. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb 1;18(3):442–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget P. The bacterial nitrate reductases. Solubilization, purification and properties of the enzyme A of Escherichia coli K 12. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. V., Zabin I. The amino acid sequence of beta-galactosidase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1507–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano G., Grillet L., Pommier J., Terriere C., Haddock B. A., Azoulay E. Precursor forms of the subunits of nitrate reductase in chlA and chlB mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri L., Ramadoss C. S. Physical studies on assimilatory nitrate reductase from Chlorella vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11703–11712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Boxer D. H. Arrangement of respiratory nitrate reductase in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Location of beta subunit. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett C. S., MacGregor C. H. Synthesis and degradation of nitrate reductase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):352–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.352-359.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer Y. M., Krashin S., Riklis E. The use of affinity chromatography for the purification of nitrate reductase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 1;62(1):30–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE R. H., EVANS H. J. PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF A SOLUBLE NITRATE REDUCTASE FROM RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 1;85:377–389. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K., DeMoss J. A. Association-dissociation behavior and subunit structure of heat-released nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2207–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., CHANGEUX J. P., JACOB F. Allosteric proteins and cellular control systems. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:306–329. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H., Schnaitman C. A., Normansell D. E. Purification and properties of nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5321–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Solubilization of Escherichia coli nitrate reductase by a membrane-bound protease. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1102–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1102-1110.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):409–452. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.409-452.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe B. C., Nicholas D. J. Some properties of a nitrate reductase from Pseudomonas denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;205(2):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renosto F., Ornitz D. M., Peterson D., Segel I. H. Nitrate reductase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Purification and kinetic mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8616–8625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Sperl G. T., DeMoss J. A. In vitro incorporation of molybdate into demolybdoproteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.719-726.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S. Hydrophobic chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:126–140. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter I., Bloch K. Solubilization and purification of trans-farnesyl pyrophosphate-squalene synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7690–7696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomonson L. P. Purification of NADH-Nitrate Reductase by Affinity Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1975 Dec;56(6):853–855. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. Biochemistry and genetics of nitrate reductase in bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):315–375. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. T., Cass K. H., Stellwagen E. Blue dextran-sepharose: an affinity column for the dinucleotide fold in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):669–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van 't Riet J., Planta R. J. Purification, structure and properties of the respiratory nitrate reductase of Klebsiella aerogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Smith R. L. Lowry determination of protein in the presence of Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van 't Riet J., Wientjes F. B., van Doorn J., Planta R. J. Purification and characterization of the respiratory nitrate reductase of Bacillus licheniformis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 26;576(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Riet J., van Ed J. H., Wever R., van Gelder B. F., Planta R. J. Characterization of the respiratory nitrate reductase of Klebsiella aerogenes as a molybdenum-containing iron-sulfur enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]