Abstract
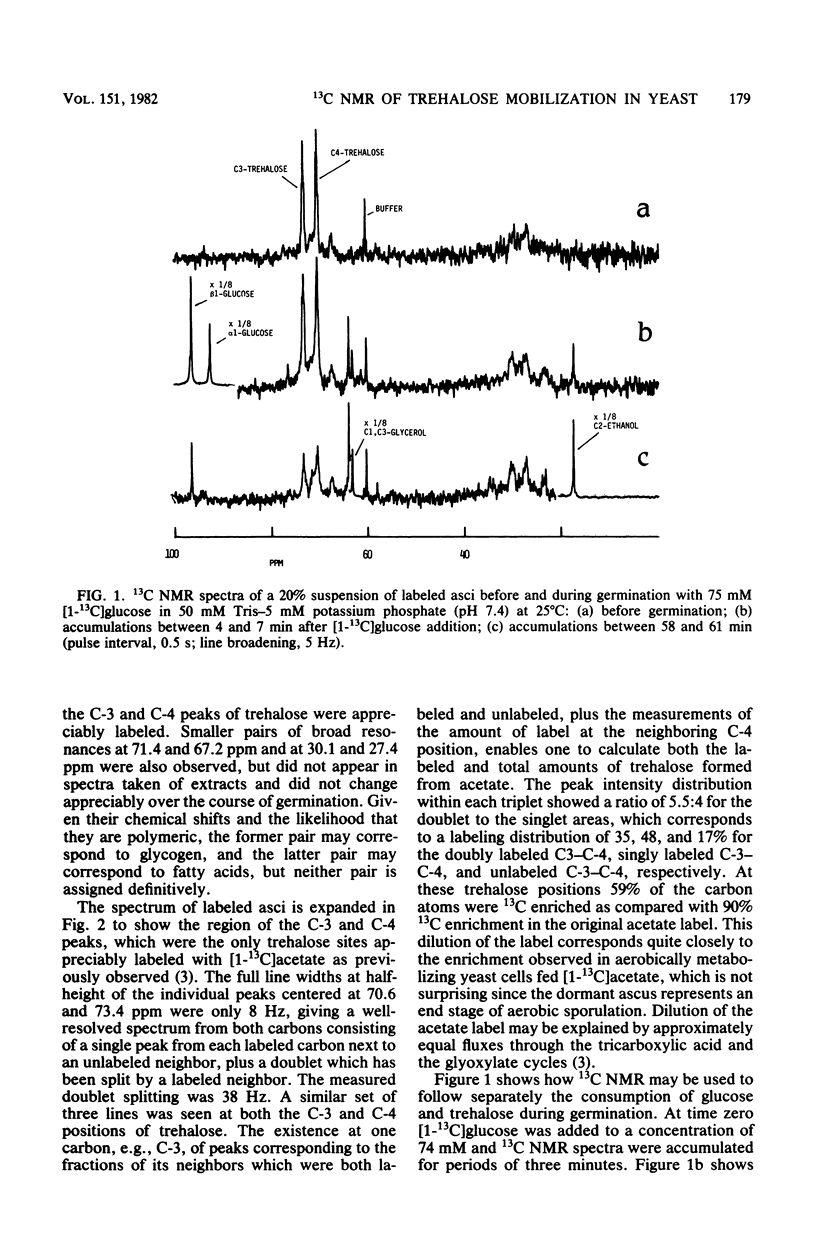
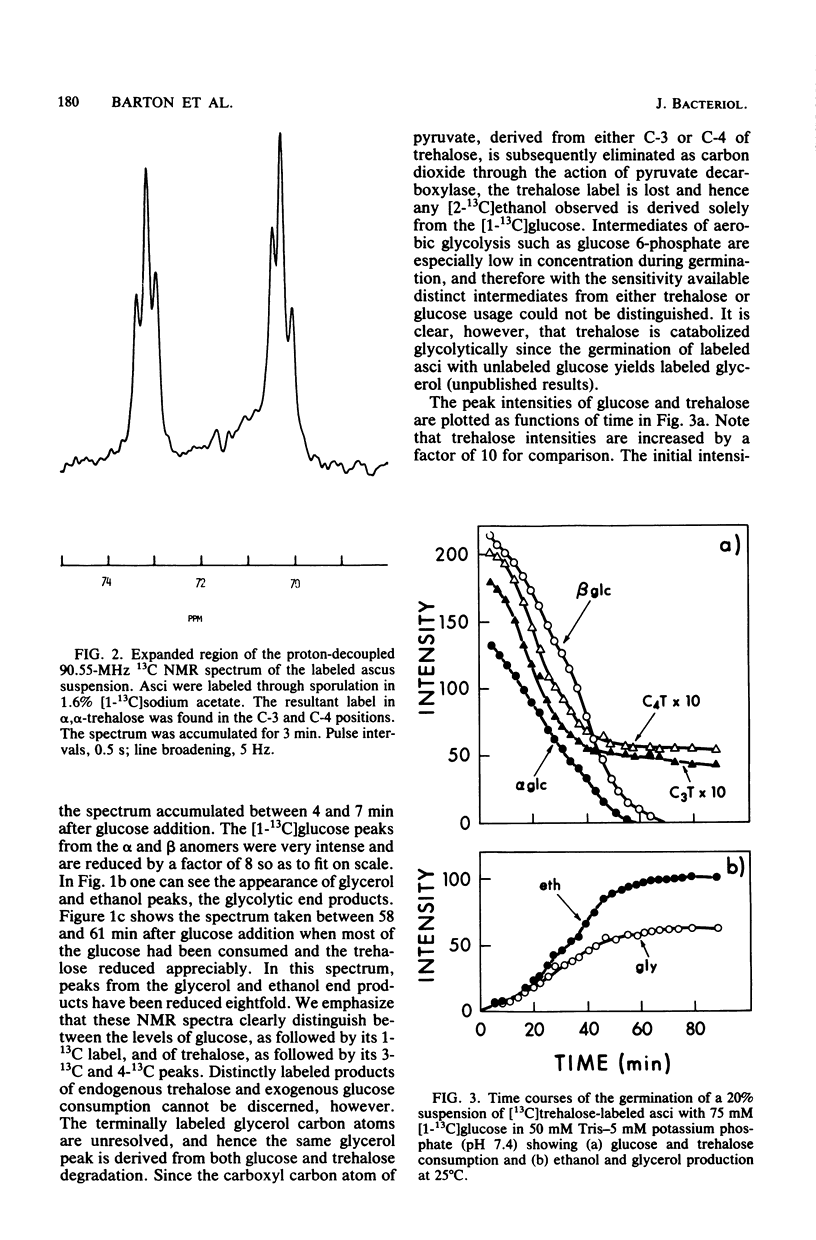
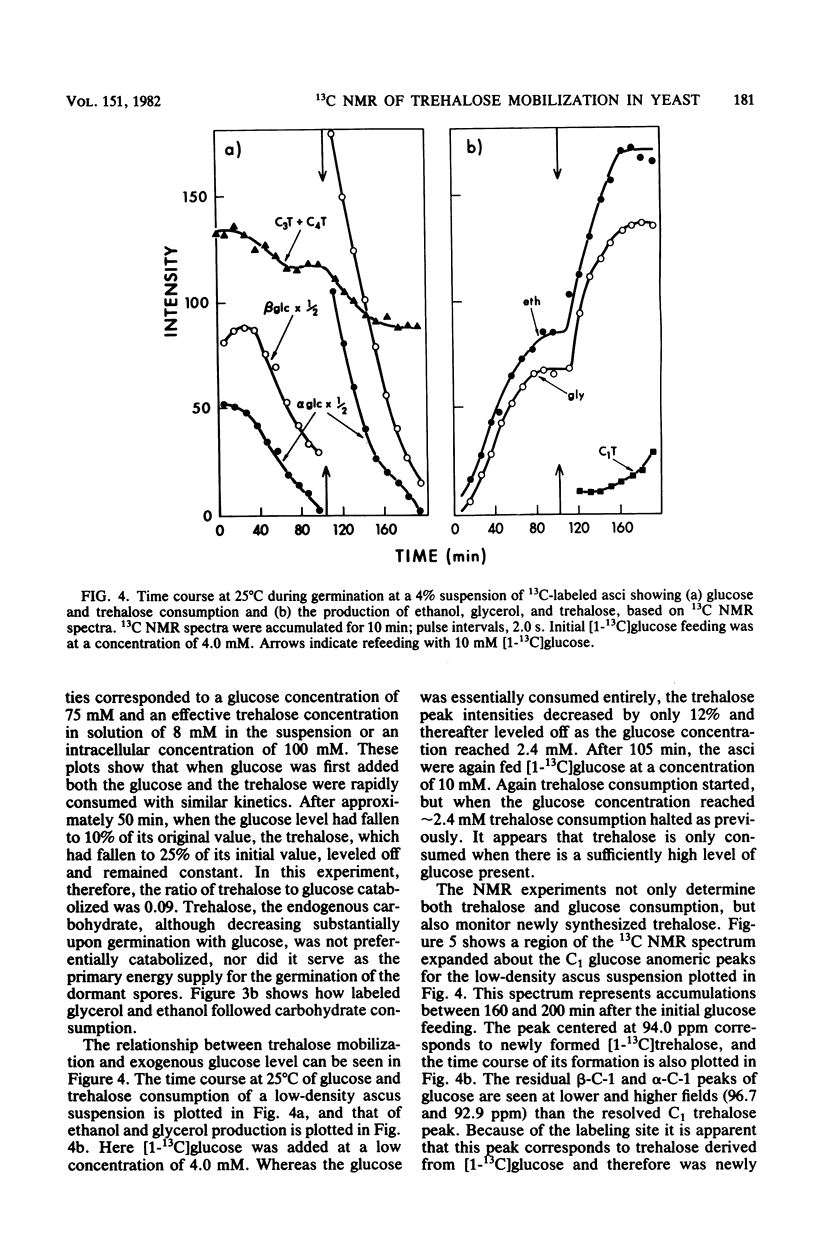
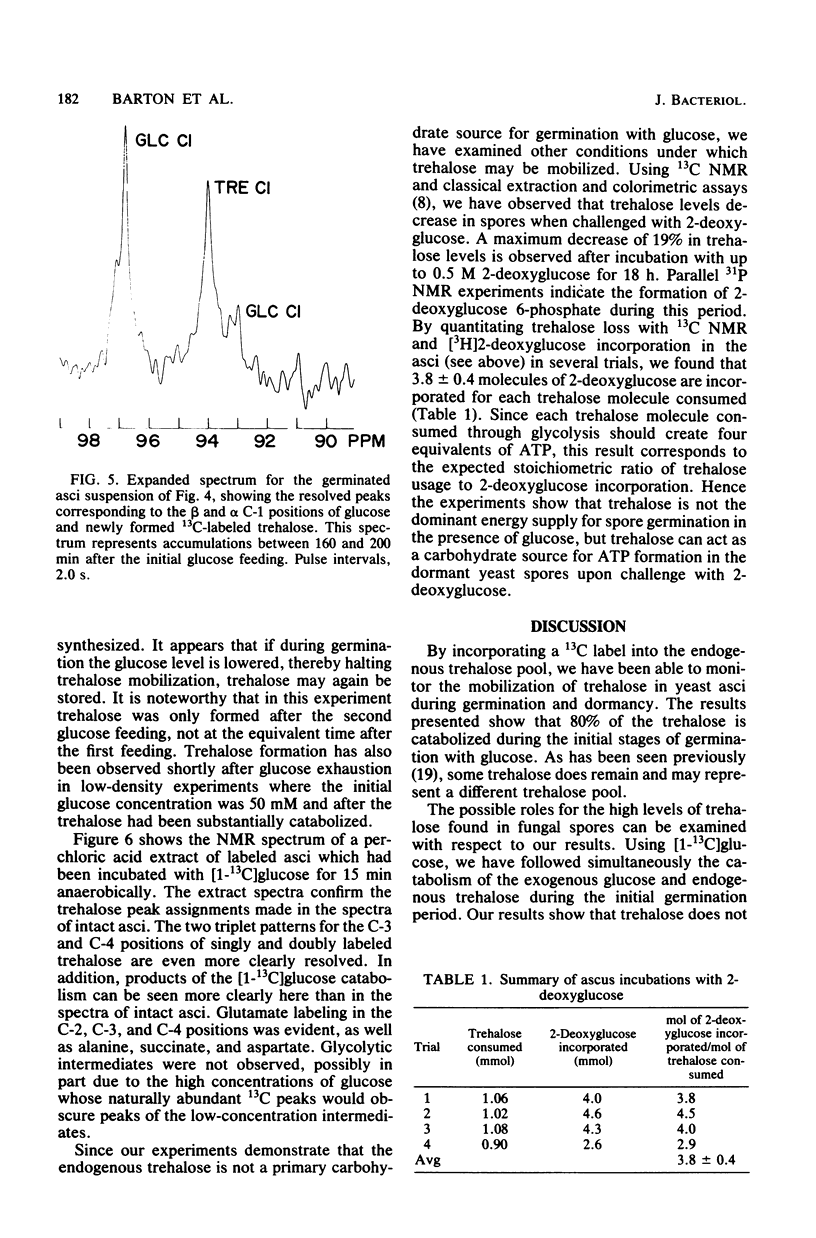
Using high-resolution 13C nuclear magnetic resonance, we examined the mobilization of endogenous trehalose in suspensions of yeast asci. Sporulation of yeast cells in [1-13C]acetate resulted in incorporation of label into the C-3 and C-4 positions of trehalose within the asci. During germination of these asci with [1-13C]glucose, the consumption of both endogenous trehalose and exogenous glucose were followed simultaneously by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance, as was the formation of glycerol and ethanol, their glycolytic and products. Time courses for carbohydrate consumption indicated that trehalose, although it decreased to 25% of its initial value upon germination, was not preferentially catabolized and did not provide the primary energy supply for germination with glucose. The ratio of trehalose to glucose catabolized was 0.09. Exogenous glucose levels appeared to regulate trehalose mobilization since trehalose was only consumed when sufficiently high levels (more than 2 mM) of glucose were present. Upon glucose depletion newly synthesized [1-13C]trehalose was observed. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of extracts confirmed the trehalose peak assignments and showed products of [1-13C]glucose catabolism. In addition by quantitating trehalose consumption and 2-deoxyglucose incorporation in dormant yeast asci, we found that 3.8 +/- 0.l4 molecules of 2-deoxyglucose were incorporated for each trehalose molecule consumed. Trehalose can therefore function as a carbohydrate source for ATP formation during dormancy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton J. K., den Hollander J. A., Lee T. M., MacLaughlin A., Shulman R. G. Measurement of the internal pH of yeast spores by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2470–2473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd K., Sussman A. S., Eilers F. I. Glucose-C14 metabolism of dormant and activated ascospores of Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):551–561. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.551-561.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deslauriers R., Jarrell H. C., Byrd R. A., Smith I. C. Observation by 13C NMR of metabolites in differentiating amoeba. Trehalose storage in encysted Acanthamoeba castellanii. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 8;118(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emyanitoff R. G., Wright B. E. Effect of intracellular carbohydrates on heat resistance of Dictyostelium discoideum spores. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1008–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1008-1012.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. M., Roth R. Carbohydrate metabolism during ascospore development in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.8-14.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie S. H., Pringle J. R. Reserve carbohydrate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: responses to nutrient limitation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1384–1394. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1384-1394.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa B. T., Sussman A. S. Endogenous Substrates of Dormant, Activated and Germinating Ascospores of Neurospora Tetrasperma. Plant Physiol. 1959 Jul;34(4):466–472. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Lin C. C. Exogenous adenosine 3': 5'-monophosphate can release yeast from catabolite repression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91500-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XIX. Phosphate metabolism during sporulation. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1137–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek A. D., Mattoon J. R. Regulation of energy metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Relationships between catabolite repression, trehalose synthesis, and mitochondrial development. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Sep;183(1):306–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau P., Halvorson H. O., Bulla L. A., Jr, St Julian G. Germination and outgrowth of single spores of Saccharomyces cerevisiae viewed by scanning electron and phase-contrast microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1232-1238.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau P., Halvorson H. O. Physiological changes following the breaking of dormancy of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospores. Can J Microbiol. 1973 May;19(5):547–555. doi: 10.1139/m73-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN A. S. The role of trehalose in the activation of dormant ascospores of neurospora. Q Rev Biol. 1961 Jun;36:109–116. doi: 10.1086/403332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XXII. Energy metabolism in early stages of germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3637–3644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza N. O., Panek A. D. Location of trehalase and trehalose in yeast cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):22–28. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90633-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander J. A., Behar K. L., Shulman R. G. 13C NMR study of transamination during acetate utilization by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander J. A., Brown T. R., Ugurbil K., Shulman R. G. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of anaerobic glycolysis in suspensions of yeast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6096–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Solingen P., van der Plaat J. B. Partial purification of the protein system controlling the breakdown of trehalose in baker's yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plaat J. B. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate stimulates trehalose degradation in baker's yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):580–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90643-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



