Abstract
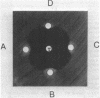
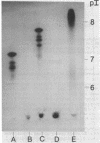
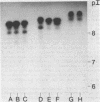
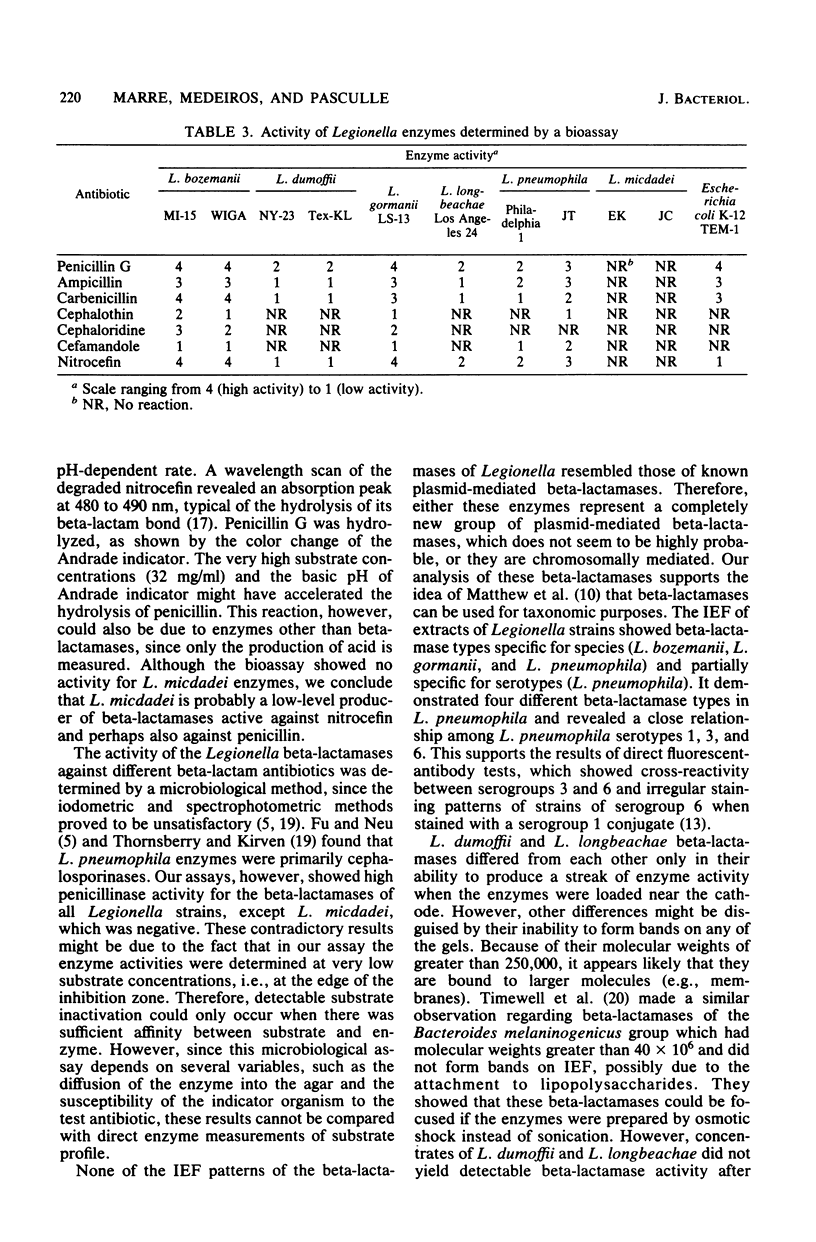
The beta-lactamases of six Legionella species were characterized by isoelectric focusing, gel filtration, and substrate profiles. Fifteen strains of L. bozemanii, L. dumoffii, L. gormanii, L. longbeachae, and L. pneumophila produced beta-lactamases active against nitrocefin. L. micdadei enzymes previously reported to be beta-lactamase negative caused a very slow pH-dependent breakdown of nitrocefin and degraded penicillin G at high substrate concentrations. The bioassay revealed predominantly penicillinase activity for all species except L. micdadei, which had no activity in this assay. The apparent molecular weights of enzymes of L. bozemanii, L. gormanii, and L. pneumophila were in the range of 15,000 to 32,000, and those of L. micdadei and L. longbeachae were greater than 250,000. The isoelectric focusing of extracts of Legionella strains in polyacrylamide gels showed beta-lactamase types specific for species (L. bozemanii, L. gormanii, and L. pneumophila) and serotype (L. pneumophila). It demonstrated four different beta-lactamase types in L. pneumophila and revealed close relationships among L. pneumophila serotypes 1, 3, and 6. L. pneumophila enzymes formed band patterns only in polyacrylamide gels containing 6 M urea, whereas L. dumoffii and L. longbeachae enzymes did not form bands in any of the gels. None of the band patterns resembled those of known plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases. These experiments suggest that isoelectric focusing of chromosomal beta-lactamases may be a valuable tool for taxonomic studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibb W. F., Sorg R. J., Thomason B. M., Hicklin M. D., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J., Wulf M. R. Recognition of a second serogroup of Legionella longbeachae. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):674–677. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.674-677.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. L., Reeves D. S. Isoelectric focusing of beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Nov;6(6):793–793. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Inactivation of beta-lactam antibiotics by Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):561–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewallen K. R., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Dail D. H., Thomason B. M., Bright R. A. A newly identified bacterium phenotypically resembling, but genetically distinct from, Legionella pneumophila: an isolate in a case of pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Dec;91(6):831–834. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-6-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda G., Tomioka S., Hasegawa M. Detection of beta-lactamase production by gram-negative bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jun;29(6):662–664. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Cornelis G., Wauters G. Correlation of serological and biochemical groupings of Yersinia enterocolitica with the beta-lactamases of the strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):55–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Porschen R. K., Edelstein P. H., Bissett M. L., Harris P. P., Bondell S. P., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Ein M. E., Lindquist D. S. Legionella longbeachae species nova, another etiologic agent of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):739–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Association of cephalosporinase activity, cephalothin resistance, and episome-mediated drug resistance in Klebsiella strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:321–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A., Feeley J. C., Wong E. S., Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella gormanii sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.718-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes by osmotic shock from Escherichia coli in exponential phase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3055–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N., Weyant R. S., Sniffen J. M., Cordes L. G., Gorman G. M., Feeley J. C. Susceptibility of Pittsburgh pneumonia agent (Legionella micdadei) and other newly recognized members of the genus Legionella to nineteen antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):793–799. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timewell R. M., Phillips I., Söderholm J., Nord C. E. Isoelectric focusing of Bacteroides melaninogenicus group beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):700–704. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]