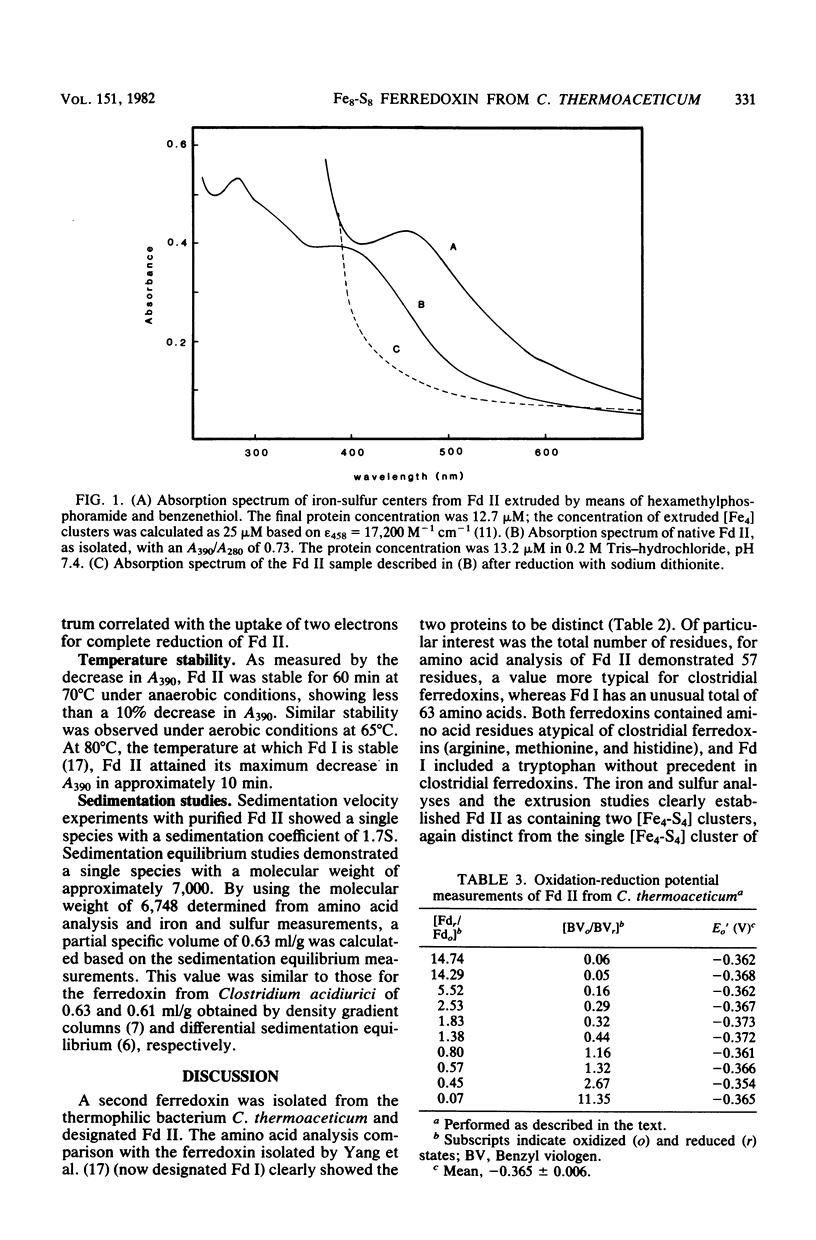
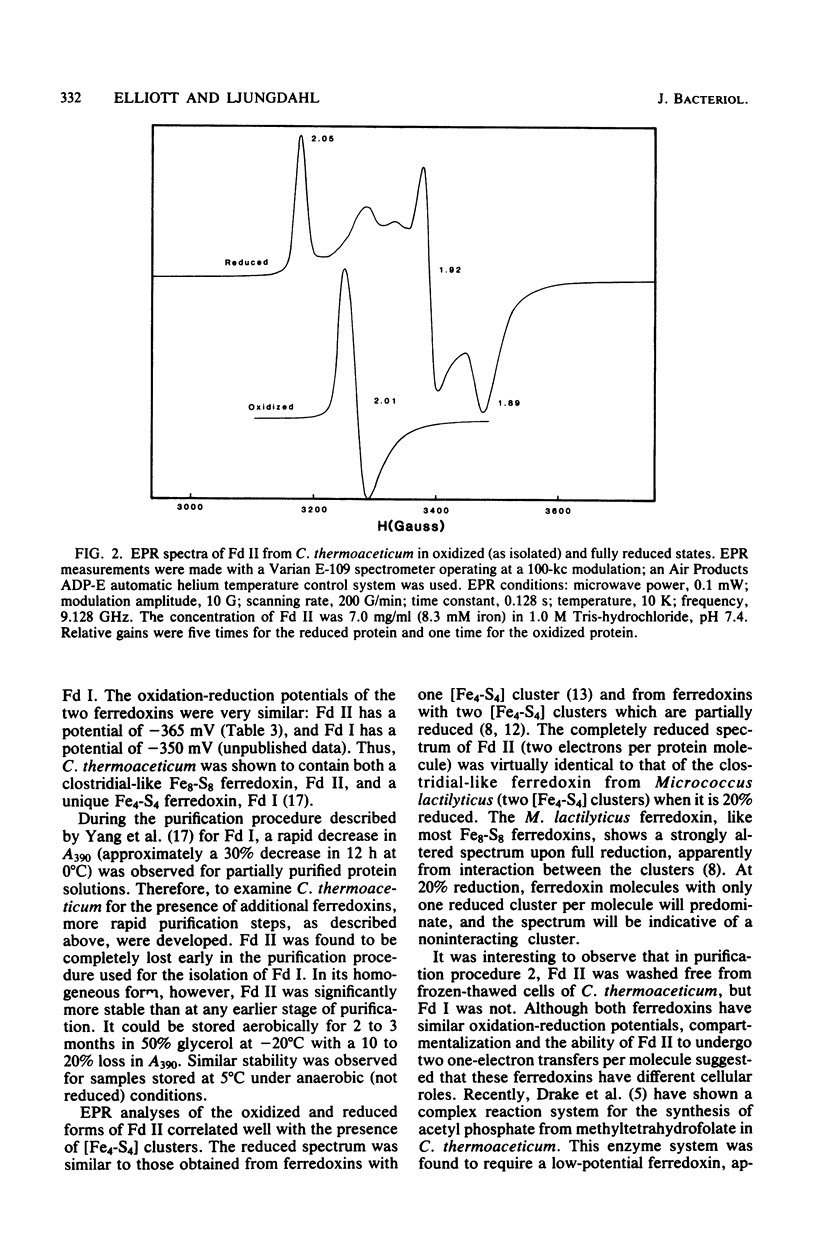
Abstract
A second ferredoxin protein was isolated from the thermophilic anaerobic bacterium Clostridium thermoaceticum and termed ferredoxin II. This ferredoxin was found to contain 7.9 +/- 0.3 iron atoms and 7.4 +/- 0.4 acid-labile sulfur atoms per mol of protein. Extrusion studies of the iron-sulfur centers showed the presence of two [Fe4-S4] centers per mol of protein and accounted for all of the iron present. The absorption spectrum was characterized by maxima at 390 nm (epsilon 390 = 30,400 M-1cm-1) and 280 nm (epsilon 280 = 41.400 M-1 cm-1) and by a shoulder at 300 nm. The ration of the absorbance of the pure protein at 390 nm to the absorbance at 280 nm was 0.74. Electron paramagnetic resonance data showed a weak signal in the oxidized state, and the reduced ferredoxin exhibited a spectrum typical of [Fe4-S4] clusters. Double integration of the reduced spectra showed that two electrons were necessary for the complete reduction of ferredoxin II. Amino histidine, and 1 arginine, and a molecular weight of 6,748 for the native protein. The ferredoxin is stable under anaerobic conditions for 60 min at 70 degrees C. The average oxidation-reduction potential for the two [Fe4-S4] centers was measured as -365 mV.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewer J. M., Ashworth R. B. Disc electrophoresis. J Chem Educ. 1969 Jan;46(1):41–45. doi: 10.1021/ed046p41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Mortenson L. E. Inhibition of methylene blue formation during determination of the acid-labile sulfide of iron-sulfur protein samples containing dithionite. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOEG K. A., ZIEGLER D. M. Simplified methods for the estimation of iron in mitochondria and submitochondrial fractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Apr;97:37–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake H. L., Hu S. I., Wood H. G. Purification of five components from Clostridium thermoaceticum which catalyze synthesis of acetate from pyruvate and methyltetrahydrofolate. Properties of phosphotransacetylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11137–11144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., BUCHANAN B. B., RABINOWITZ J. C. STUDIES ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF CLOSTRIDIAL FERREDOXIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3899–3913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews R., Charlton S., Sands R. H., Palmer G. On the nature of the spin coupling between the iron-sulfur clusters in the eight-iron ferredoxins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4326–4328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R. M. High recovery of tryptophan from acid hydrolysates of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson W. H., Beinert H. Heterogeneity of paramagnetic species in two iron-sulfur proteins: Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin and milk xanthine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Sands R. H., Mortenson L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on the ferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90733-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Ljungdahl L. G., LeGall J. A four-iron, four-sulfide ferredoxin with high thermostability from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1084–1090. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1084-1090.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Two biologically active ferredoxins from the aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteriu, Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4514–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



