Abstract
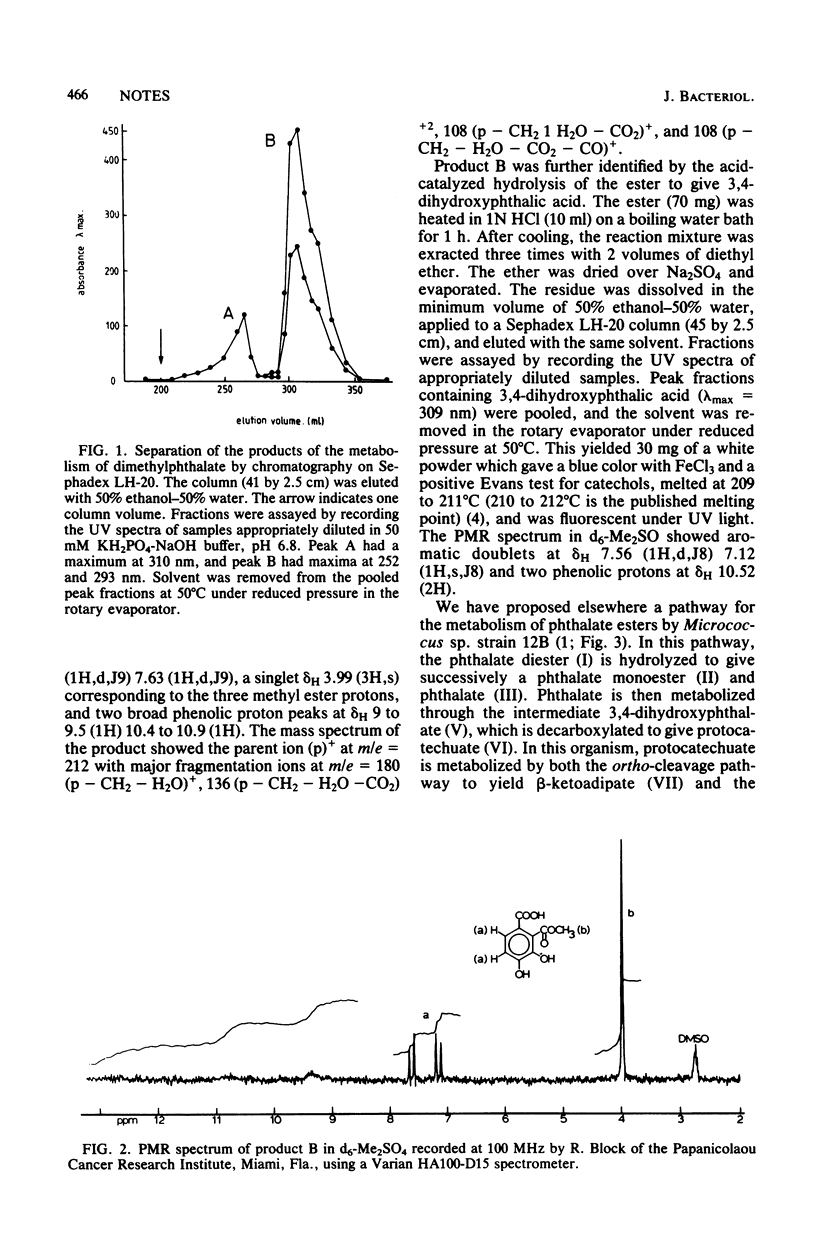
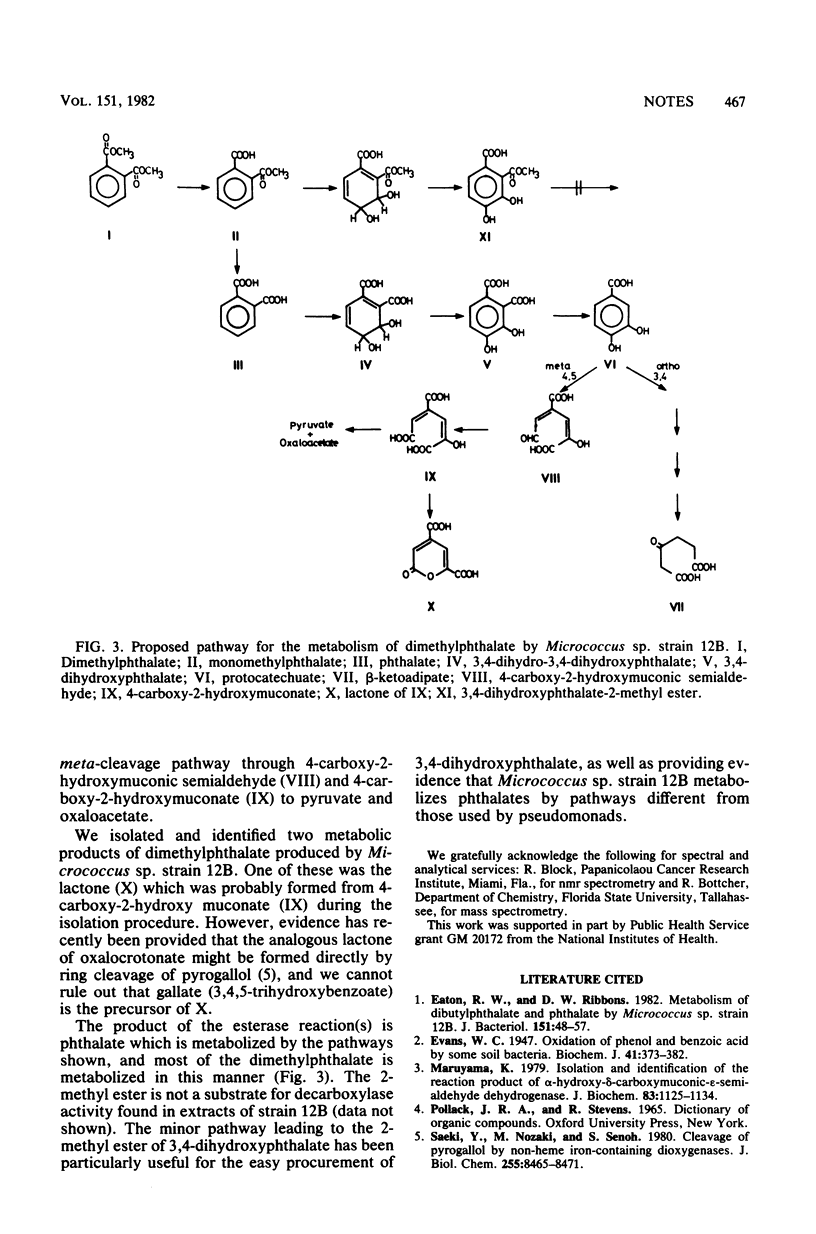
During growth of Micrococcus sp. strain 12B with dimethylphthalate, 4-carboxy-2-hydroxymuconate lactone (CHML, X) and 3,4-dihydroxyphthalate-2-methyl ester (XI) were isolated from culture filtrates. CHML is the lactone of intermediate 4-carboxy-2-hydroxymuconate (IX). Accumulation of XI which is not a substrate for 3,4-dihydroxyphthalate-2-decarboxylase in strain 12B afforded an easy access to the preparation of 3,4-dihydroxyphthalate.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eaton R. W., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of dibutylphthalate and phthalate by Micrococcus sp. strain 12B. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):48–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.48-57.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Oxidation of phenol and benzoic acid by some soil bacteria. Biochem J. 1947;41(3):373–382. doi: 10.1042/bj0410373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Ariga N., Tsuda M., Deguchi K. Purification and properties of alpha-hydroxy-gamma-carboxymuconic epsilon-semialdehyde dehydrogenase. J Biochem. 1978 Apr;83(4):1125–1134. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki Y., Nozaki M., Senoh S. Cleavage of pyrogallol by non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8465–8471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



