Abstract
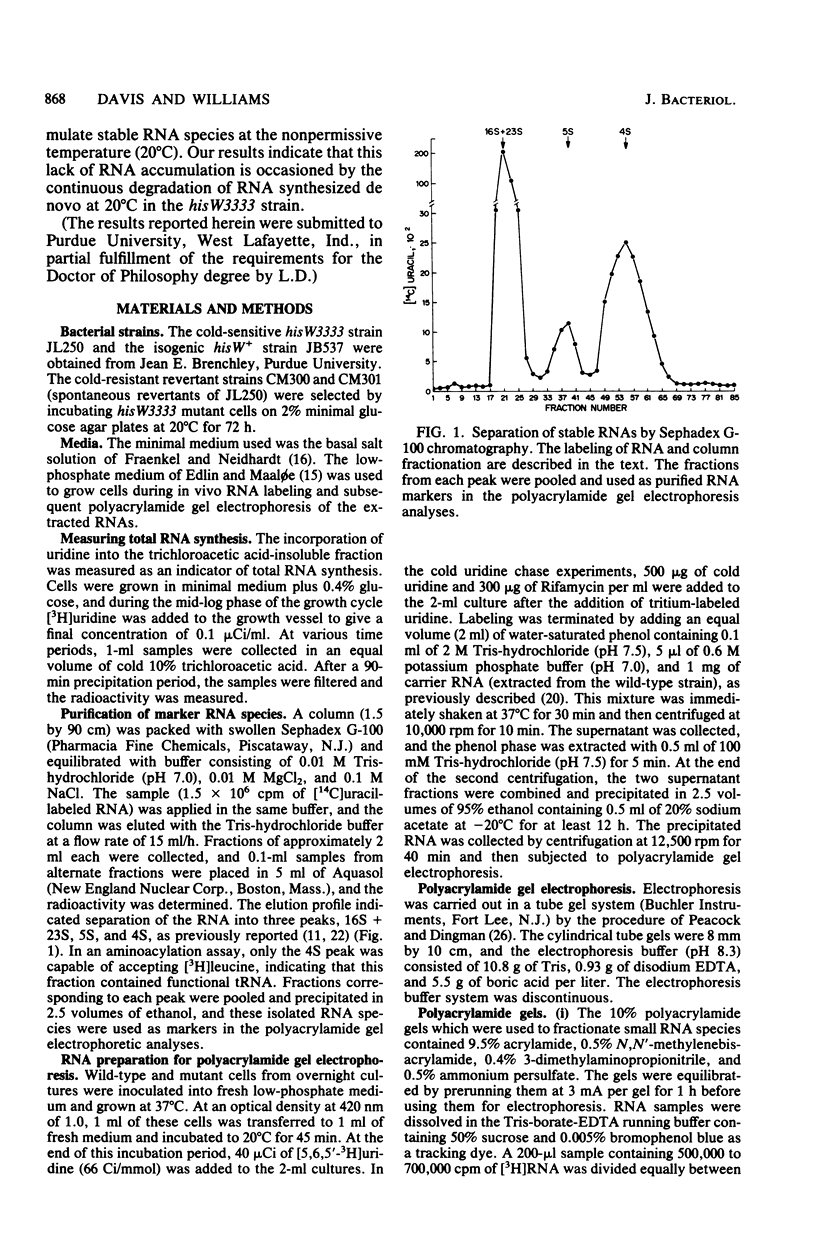
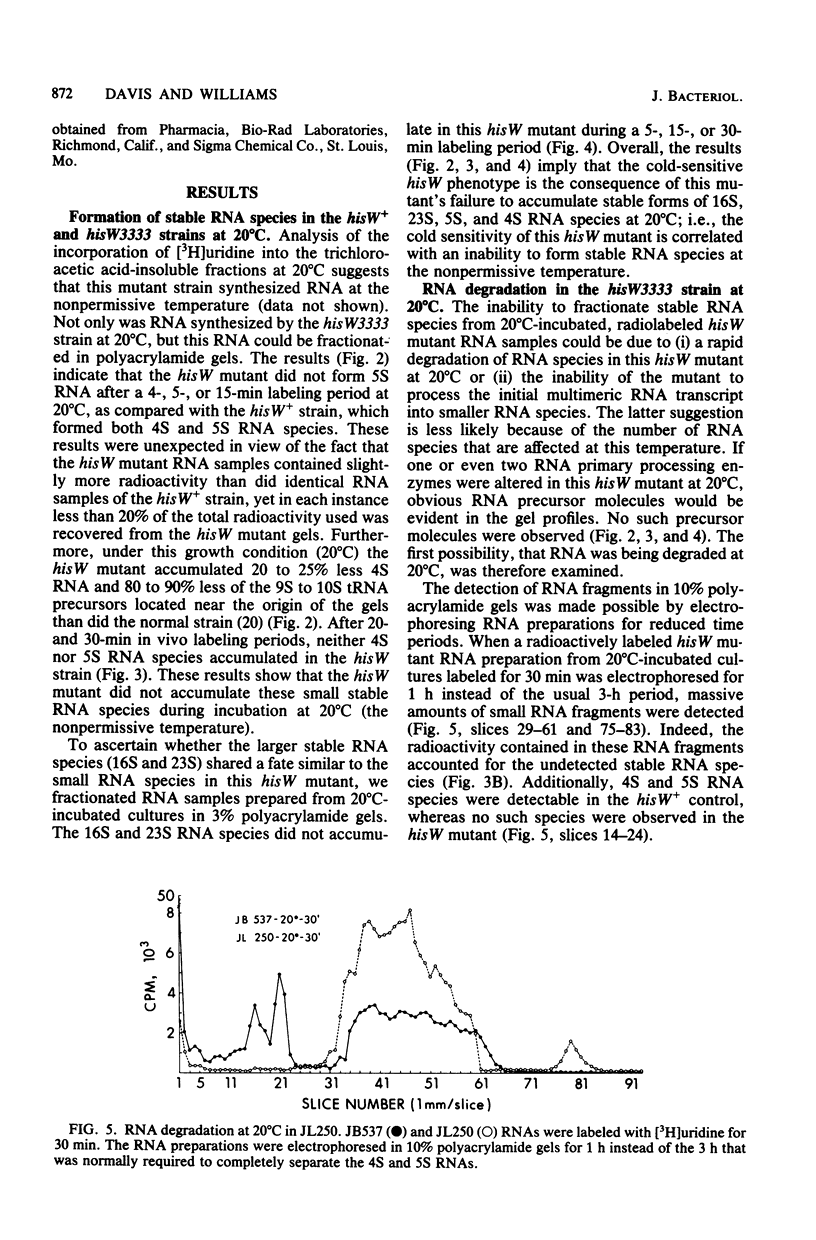
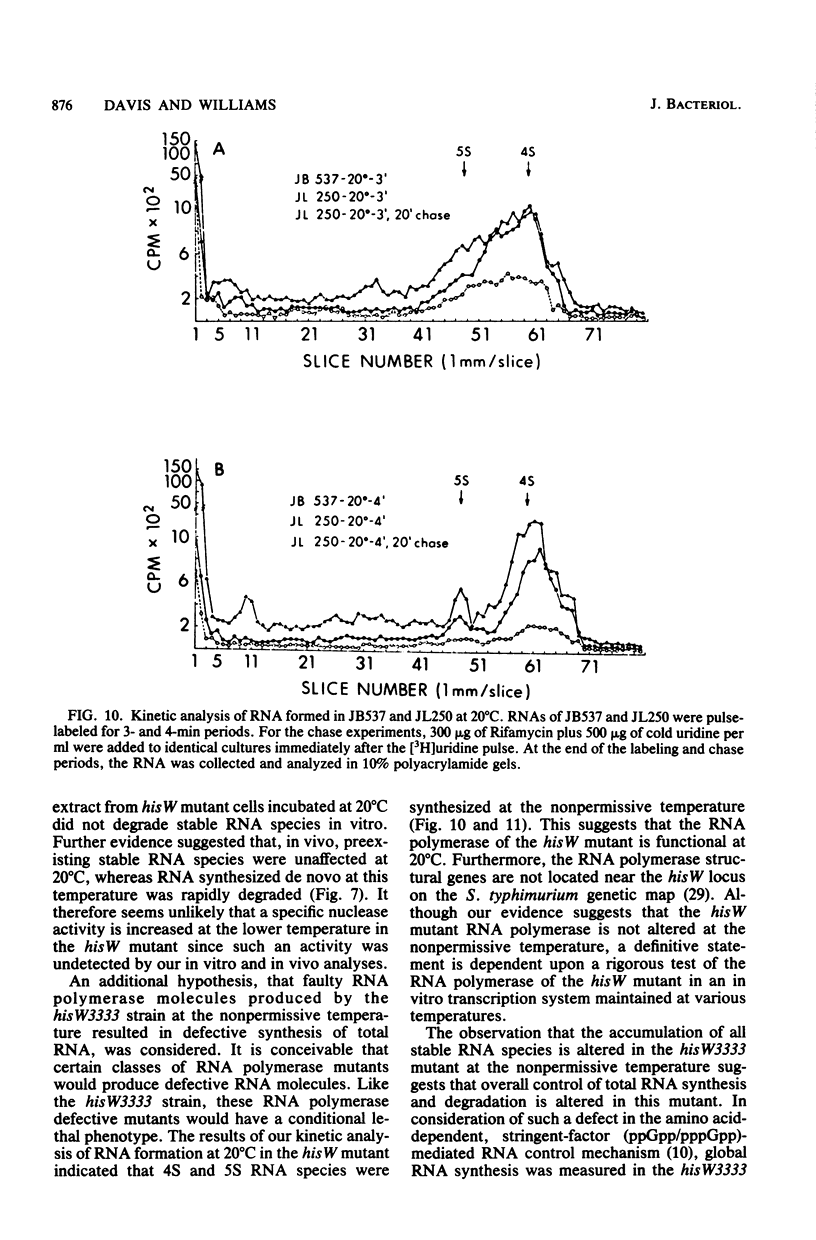
Previous studies of hisW mutants of Salmonella typhimurium have led to the suggestion that such strains are defective in tRNA maturation. (J. E. Brenchley and J. Ingraham, J. Bacteriol. 114:528-536, 1973). In this study, we report that one hisW strain is defective in the accumulation of all stable RNA species. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of radiolabeled RNA indicated tha at the nonpermissive temperature (20 degrees C) all stable RNa species in the cold-sensitive hisW3333 mutant were synthesized and rapidly degraded. We propose that the cold sensitivity of this strain is caused by such a restriction in stable RNA accumulation at low temperature. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that the RNA degraded in this strain was synthesized de novo and was not preexisting RNA. Furthermore, physiological and genetic recovery from the cold-sensitive hisW phenotype resulted in relatively normal RNA synthesis and accumulation. Thus, the RNA alterations observed in this strain were not explained by defects in a tRNA modification enzyme. Rather, these findings suggest the existence of defective RNA processing and that a control mechanism for the overall synthesis or accumulation of stable RNA species is altered in the hisW3333 mutant.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apirion D., Neil J., Watson N. Consequences of losing ribonuclease III on the Escherichia coli cell. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 22;144(2):185–190. doi: 10.1007/BF02428107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. DNA sequence from the histidine operon control region: seven histidine codons in a row. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazey D. L., Kim R., Burns R. O. Molecular cloning and expression of the ilvGEDAY genes from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):452–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.452-462.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Ciampi M. S., Cortese R. Characterization of a Salmonella typhimurium hisU mutant defective in tRNA precursor processing. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):612–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.612-620.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Cortese R. Biosynthesis of tRNA in histidine regulatory mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1945–1956. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley J. E., Ingraham J. L. Characterization of a cold-sensitive hisW mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):528–536. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.528-536.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Ames B. N. Histidine regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. IX. Histidine transfer ribonucleic acid of the regulatory mutants. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1080–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M. Regulation of bacterial ppGpp and pppGpp. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:301–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Kammen H. O., Spengler S. J., Ames B. N. Biosynthesis of pseudouridine in transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. P., Williams L. S. Regulation of isoleucine and valine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium: the effect of hisU on repression control. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 15;127(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. P., Williams L. S. Relaxed control of RNA synthesis during nutritional shiftdowns of hisU mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):682–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Williams L. S. Altered regulation of isoleucine-valine biosynthesis in a hisW mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):860–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.860-866.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Maaloe O. Synthesis and breakdown of messenger RNA without protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):428–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL D. G., NEIDHARDT F. C. Use of chloramphenicol to study control of RNA synthesis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:96–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Watson N., Apirion D. Multiple pathways for primary processing of ribosomal RNA in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3064–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghora B. K., Apirion D. Structural analysis and in vitro processing to p5 rRNA of a 9S RNA molecule isolated from an rne mutant of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S., Miller O. L., Jr Visualization of ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis in a ribonuclease III-Deficient strain of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):718–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.718-722.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Dahlberg J. E. Small ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. I. Characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5024–5032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilgen C., Kirk L. L., Carbon J. Isolation and characterization of large transfer ribonucleic acid precursors from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):922–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Feuteun J., Monier R. Identification of a 5 s RNA precursor in exponentially growing Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):605–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawther R. P., Hatfield G. W. Multivalent translational control of transcription termination at attenuator of ilvGEDA operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1862–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Ames B. N. Histidine regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. XI. The percentage of transfer RNA His charged in vivo and its relation to the repression of the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nargang F. E., Subrahmanyam C. S., Umbarger H. E. Nucleotide sequence of ilvGEDA operon attenuator region of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1823–1827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiness G., Yang H. L., Zubay G., Cashel M. Effects of guanosine tetraphosphate on cell-free synthesis of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA and other gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2881–2885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Antón D. N., Hartman P. E. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Isolation and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):305–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



