Abstract
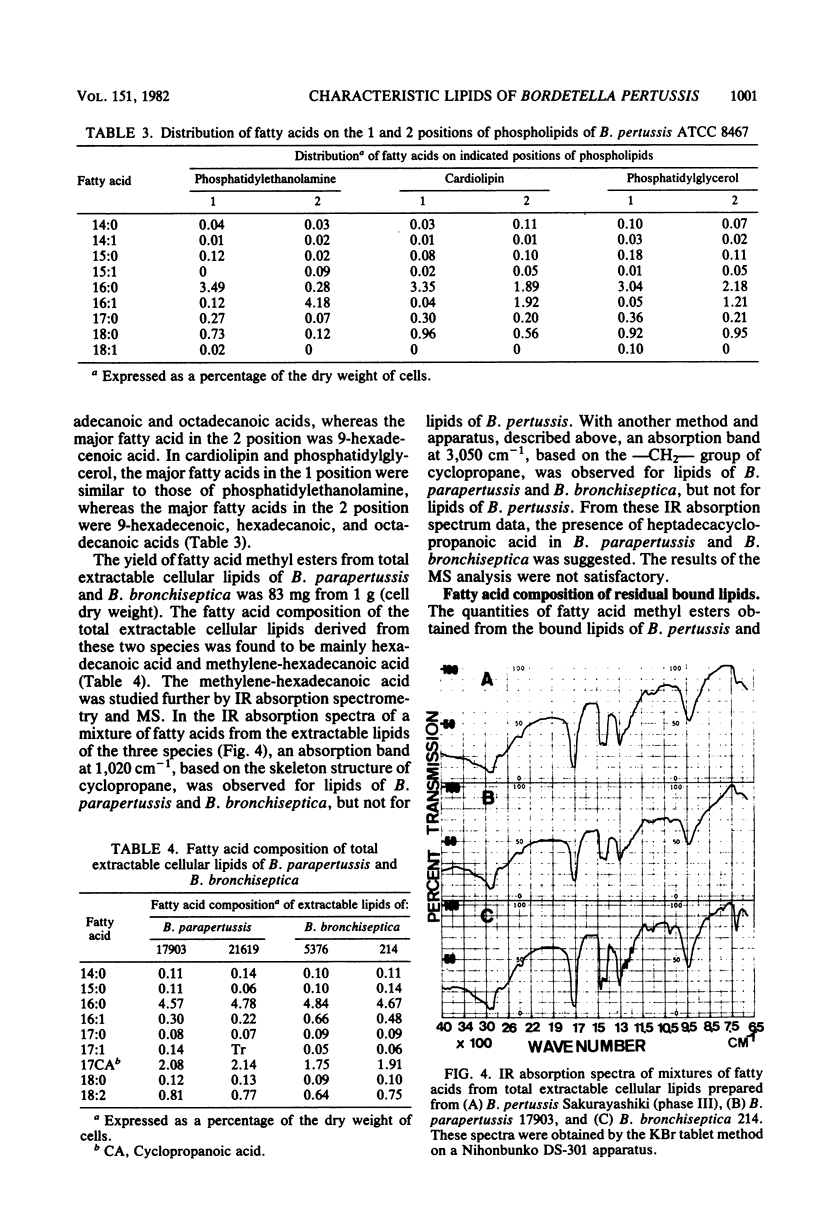
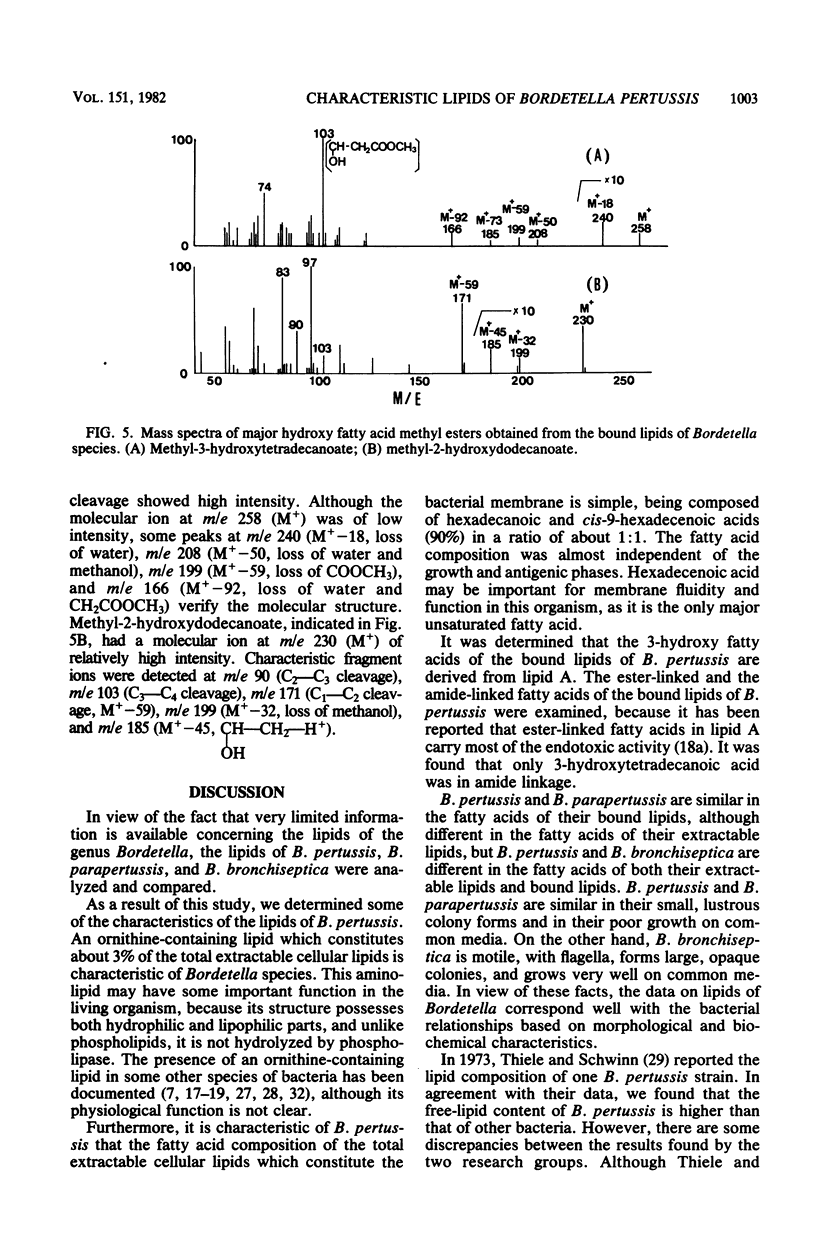
The lipids and fatty acids of Bordetella pertussis (phases I to IV) were analyzed by thin-layer chromatography, gas-liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry and compared with those of B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica. The major lipid components of the three species were phosphatidylethanolamine, cardiolipin, phosphatidylglycerol, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and an ornithine-containing lipid. The ornithine-containing lipid was characteristic of the genus Bordetella. The fatty acid composition of the total extractable cellular lipids of B. pertussis was mostly hexadecanoic and hexadecenoic acids (90%) in a ratio of about 1:1. The hexadecenoic acid of B. pertussis was in the cis-9 form. The fatty acid composition of the residual bound lipids was distinctly different from that of the extractable lipids, and residual bound lipids being mainly 3-hydroxytetradecanoic, tetradecanoic, and 3-hydroxydecanoic acids, with 3-hydroxydodecanoic acid occurring in some strains. It was determined that the 3-hydroxy fatty acids were derived from lipid A. The fatty acid composition of the total extractable cellular lipids of B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica, mainly composed of hexadecanoic and heptadecacyclopropanoic acid, differed from that of B. pertussis. Although the fatty acid composition of the residual bound lipids of B. parapertussis was similar to that of the residual bound lipids of B. pertussis, 2-hydroxydodecanoic acid was detected only in the bound lipids of B. bronchiseptica.
Full text
PDF




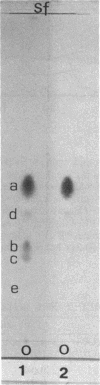
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Wheeler M. W. Pertussis Vaccine Prepared with Phase-I Cultures Grown in Fluid Medium. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1946 Apr;36(4):371–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees S., Thanabalasundrum S., Moss C. W., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of group IVe, a nonsaccharolytic organism from clinical sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):664–668. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.664-668.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fautz E., Rosenfelder G., Grotjahn L. Iso-branched 2- and 3-hydroxy fatty acids as characteristic lipid constituents of some gliding bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):852–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.852-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Gray G. W. The chemical composition of the lipopolyacarideof Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):185–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1140185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNING E. C., AHRENS E. H., Jr, LIPSKY S. R., MATTSON F. H., MEAD J. F., TURNER D. A., GOLDWATER W. H. QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF FATTY ACIDS BY GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner N., Chaby R., Szabó L. Identification of 2-methyl-3-hydroxydecanoic and 2-methyl-3-hydroxytetradecanoic acids in the 'lipid X' fraction of the Bordetella pertussis endotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):535–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANESHIRO T., MARR A. G. Hydroxy fatty acids of Azotobacter agilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 18;70:271–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90751-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N. Chemical studies on the lipid component of endotoxin, with special emphasis on its relation to biological activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):486–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Uchida K., Aida K. Direct hydroxylation in the biosynthesis of hydroxy fatty acid in lipid a of Pseudomonas ovalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 29;572(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y. Purification and characterization of pertucin produced by Pseudomonas pertucinogena. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):347–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoche H. W., Shively J. M. The structure of an ornithine-containing lipid from Thiobacillus thiooxidans. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):170–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Lehmann V., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Rosenfelder G., Simon M., Westphal O. Lipid A: chemical structure and biological activity. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):17–29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R. A., Finnerty W. R. Isolation and characterization of an ornithine-containing lipid from Desulfovibrio gigas. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):523–529. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.523-529.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Plackett P. Identification of the amide-linked fatty acids of Acholeplasma axanthum S743 as D(-)3-hydroxyhexadecanoate and its homologues. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1091-1095.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I., Bray K. K. The occurrence and properties of leukocytosis and lymphocytosis-stimulating material in the supernatant fluids of Bordetella pertussis cultures. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):523–550. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Yano I., Hiramatsu T., Masui M. Lipids and fatty acids of a moderately halophilic bacterium, No. 101. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Gottert H., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in the lipid-A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEURBRANDT G., BLOCH K. Unsaturated fatty acids in microorganisms. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2064–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND I. W., WILKINSON J. F. A new growth medium for virulent Bordetella pertussis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:431–438. doi: 10.1002/path.1700820220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara Y., Kameda M., Yamada Y., Kondo K. An ornithine-containing lipid isolated from Gluconobacter cerinus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 19;450(2):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele O. W., Biswas C. J., Hunneman D. H. Isolation and characterization of an ornithine-containing lipid from Paracoccus denitrificans. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele O. W., Schwinn G. The free lipids of Brucella melitensis and Bordetella pertussis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr;34(2):333–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells M. A., Hanahan D. J. Studies on phospholipase A. I. Isolation and characterization of two enzymes from Crotalus adamanteus venom. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):414–424. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Composition and structure of the ornithine-containing lipid from Pseudomonas rubescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 23;270(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano I., Ohno Y., Masui M., Kato K., Yabuuchi E. Occurrence of 2- and 3-hydroxy fatty acids in high concentrations in the extractable and bound lipids of Flavobacterium meningosepticum and Flavobacterium IIb. Lipids. 1976 Sep;11(9):685–688. doi: 10.1007/BF02532887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deenen L. L., de Haas G. H. The synthesis of phosphoglycerides and some biochemical applications. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:167–234. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9938-2.50011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]